Short communication: 2021 Vol: 13 Issue: 4
An Investigation On Usage Of Iot In Digital Banking To Enhance The Customer Experience
Dillip Kumar Parida, K. L. U. Business School, K. L. University
Abstract
The internet of things is the next digital revolution, and it symbolises the next phase technological transformation that will alter the lives of banking consumers and bank. While the Internet is typically limited to the electronic realm, connected objects indicate the Internet's expansion to include things and places. The influence of digital trends and IoT on a traditional bank's operational procedural is taking into shape. New edge digital technologies have started influencing bank and its processes. Bank and financial institutions started using IOT to increase the efficiency of banking process and to enhance the customer experience. The objective of this article is to illustrate the smart contract applications of IoT in banking can be leveraged to optimise the customer service and risk management. How the IOT can influence the digital trends over bank’s traditional process. We'll focus on approach of these new initiative and developments for digital transformations of banks with these new technologies like Internet of Things.
Keywords
Iot, Internet Of Things Banking Industry, Financial Industry, Customer Experience.
Introduction
The Internet of Things based applications for banks is in the evolutionary stage. Adoption of Internet of Things is still limited to a few application areas (Mital et al., 2018). Banking sector is always reserved towards the new technology due to security limitations. Financial data and customer information are extremely sensitive and cannot be exposed to outside world. There has been tremendous investment on new edge technologies now and recent developments seen due to adoption of IOT in banks. As per a joint report by IAMAI (The Internet and Mobile Association of India) and Deloitte, Industrial IoT is expected to surpass the consumer IoT space in India by 2020. It also predicts a 12 USD billion IoT opportunity. Ashton introduced the term internet of things (IoT) in 1999 (Gubbi et al., 2013). The IoT aims at extending benefits of the internet, data sharing, remote control ability, constant connectivity and so on, to goods and services in the physical world (Peoples et al., 2013). Traditional banking operations such as KYC, lending records management, collateral management, trade finance, payments, PFM, and insurance might be impacted by IoT. IoT can generate new P2P business models that have the potential to disrupt banking in a few sectors when combined with other upcoming technologies like digital identification and smart contacts. However, the bank's information at this point is limited and does not offer a complete picture of the customer's financial activity. In a future where all of a customer's devices are tied to their digital identity and customer devices, having access to the customer's unique digital footprint might aid in uncovering device usage trends.
Customer Experience
Banking industry is more focused on customer experience and services are customer centric services to retain customer. The lifetime profitability of an existing satisfied client is more profitable than acquiring new clients. Banks are actively promoting IOT to proactively monitoring activities of customer. This will help to track and provides measurements proactively and fix the issues.
The essential journeys of a customer's banking relationship span from onboarding and transacting through maintenance and problem resolution. Effective transformations must not only acknowledge the complexities of these linkages, but also prioritise the elements of the experience that matter most—in order to manage the cross-functional, end-to-end nature of customer requirements rather than deferring them.
Use of IOT for smart contracts in Bank
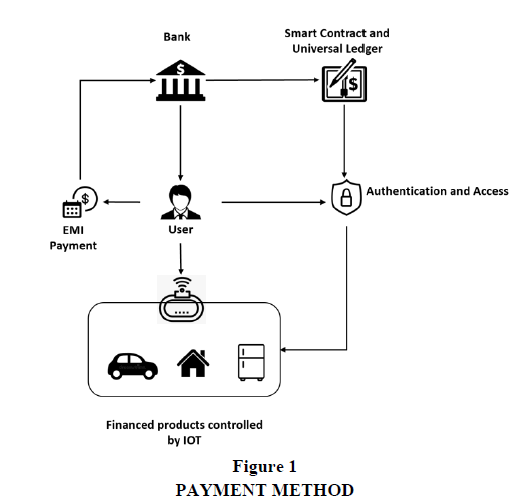
Smart contracts are computer programmes that help in contract negotiation, verification, and enforcement. Payments can be partially or entirely self-executing and self-enforcing thanks to the Internet of Things, smart contracts, and digital identities. For example, the product can be financed by bank and the contact can be linked to product. If customer does not pay regular monthly payments, then product usage can be stopped. The product can reminder customer to make payment on time to keep usage intact. This IoT-assisted smart contract approach has a lot of potential in terms of process automation and operational risk mitigation. More significantly, it's possible that this may result in new product alternatives that provide a better consumer experience in Figure 1.
The product linked with IOT device would be beneficial for bank and customer a well. IOT device linked with product can be used to monitor finance devices. Any issue or incident can be raised to service department and also provides evidence of faulty devices or product. It will help the bank and user to have automated request to claim procedure. If customer does not make payment regularly then Bank can control and prevents from usage of device. This will help bank to keep non-performing assets in control. The IOT connected device will also reminds the customer to make payment regularly. Based on continuous feedback from device will help to manage the asset values and its insurance amount.
Conclusion
The present study focused on usage of IOT for smart contracts to manage customer experience. The Internet of Things is still in its early stage, but it promises a brighter future. Some claim that technology advancements and new digital trends will supplant existing banks, while others argue that they will improve the traditional financial infrastructure. There huge change n paradigm and banks has been more advanced. Customer experience is more priority and also it should also safeguard the bank’s interest as well. Usage of IOT and smart contract will definitely help banks to enhance the customer experience. User will have less operational activity in case of insurance claim or day to day transaction. The process will be automated and there would be huge impact on customer experience in comparison to traditional banking experience. Smart contract could be future of banking and certainly a game changer in recent era.
References
- Mital, M., Chang, V., Choudhary, P., Papa, A., & Pani, A. K. (2018). Adoption of internet of things in India: A test of competing models using a structured equation modelling approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 136(1), 339–346. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.techfore.2017.03.001
- Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., & Palaniswami, M. (2013). Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Generation Computer Systems, 29(7), 1645–1660. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.future.2013.01.010
- Peoples, C., Parr, G., McClean, S., Scotney, B., & Morrow, P. (2013). Performance evaluation of green data centre management supporting sustainable growth of the internet of things. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 34, 221–242. India. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. simpat.2012.12.008