Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 6
Applying the stakeholder theory to analyze the state-owned enterprise management in Vietnam: From enterprise law to company charter and beyond
Vu Ngoc Bao, University of Economics HCMC
Tran Van Long, University of Economics HCMC
Citation Information: Bao NV., & Long TV. (2021). Applying the stakeholder theory to analyze the state-owned enterprise management in Vietnam: from enterprise law to company charter and beyond. International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 25(6), 1-17.
Abstract
The model of Soviet organization was founding base on the popular belief of collective ownership. It was the only "planned" model of the Vietnamese economy before the "Doi m oi" (The definition from Stanford Research Institute, 1963). Government send input materials and buy output products. However, this model quickly revealed many defects, and were soon to lead Vietnam's economy to crisis. Therefore, the "Doi moi" movement was born. The State eliminated the subsidized economy, began to recognize a multi-sector economy, various forms of business organizations were born, and required specific laws to nurture each type of economy. Inter alia, the s tate-owned enterprise (SOE) has been set up as a mechanism for resources exploration such as land, minerals, or capital. SOE use state budget or borrow under government guarantee. State-owned enterprises step by step definition in regulation issue by Prime minister and then upgrade laws issue by Congress.
Keywords
Stakeholder Theory, Enterprise Law to Company, Vietnam
Introduction
Since “Doi moi”, there were different definitions for State-owned enterprises (SOE). Follow that, new human resource system were setting up, new organizing operations, and new managed model. Clause to Clause 8, Article 4 of the Law on Enterprises 2014, "State-owned enterprises are enterprises with 100% of charter capital owned by the State." The conflict between Soviet states models with market economy lead m any leaders and related organizations took many interventions to the SOE especially in governance system.
Stakeholders have not been officially regulated clearly by the law in Vietnam. Nonetheless, Clause 17, Article 4 Law on Enterprise 2014 mentions the concept of “related person” are “individuals and organizations that have direct or indirect relationship with enterprises, acquiring holding company, associations, persons and group of people, manager and manager's Spouse, natural father, adoptive father, natural mother, adoptive mother, biological children, adopted children, biological siblings, younger siblings, brother-in-law, brother-in-law, sister-in-law, sister-in-law. By listing this, does 2014 corporate law omit Stakeholders? We try to digest it by using Stakeholder theory.
Stanford Research Institute defended Stakeholder is a "group without whose support the organization would cease to exist" (The definition from Stanford Research Institute, 1963) this definition was the first usage of the word in a 1963 at the internal memorandum. The theory was later developed and championed by R. Edward Freeman in the 1980s and then m any authors have studied the stakeholder; the concept has also been revised, supplemented, and improved. Stakeholder formed in the process of enterprise planning, systems theory, organization theory, and corporate social responsibility (SRI, 1963). Stakeholder was first mentioned in the 1950s by the authors: (Russell Ackoff & Charles, 1957) and was supplemented by (Ian I. Merroff & Richard O. Mason, 1983) forming the concept of "The interesting parties are those who depend on the organization / agency to realize some of their goals, and vice versa, the organization also depends in part on them to fully accomplish their goals”.
Using the theory of Stakeholders compared with SOE Stakeholder disclosure, it can be shown that: There exists an existence of Stakeholders who can directly intervene in the SOE personnel management system that is not prescribed by law. Specified, the enterprise does not publish. This leads to Investors, especially foreign investors, who do not have enough information to make investment decisions. Investments may not optimize profits or losses. Government invested in SOE, but result did not meet expectations. Many large projects were ineffective (Such as Ninh Binh fertilizer factory, Dinh Vu fiber factory, Dung Quat shipyard). Many business leaders were to face court. (Such as Ninh Binh fertilizer factory, Dinh Vu fiber factory, Dung Quat shipyard). Vietnam has just lost money and human resource, but more important has lost its confidence in the Party's policies and state's laws.
In fact, once the government regulates the law will make the number of Stakeholders change. But, Clause 17, Article 4 of the Enterprise Law 2014 on related persons, Party organizations are mentioned. Then of course many Stakeholders will be missing. Party organizations are an example
However, in the provisions of Clause 17, Article 4 of the Enterprise Law 2014 on related persons, Party organizations, or the Politburo are not mentioned. Therefore, in corporate governance announcement, SOE also does not announce the role of party organizations
These results ask us to study about affected of the role of Stakeholders in the success or failure of corporate governance especially in human resource management.
Are there any hidden Stakeholders? How are they affected to human resource in SOEs? What are the reforms that help Stakeholders interfere to SOEs to make things better?
So, apply Stakeholder theory to identify any missing Stakeholders that may affect your business, analyzing the role of key Stakeholders. Then conduct interviews with experts and SOE leaders to confirm finding. Using some case that stakeholders interfere to human resource system as example.
The expectations analysis points to the relationships between different Stakeholders with SOE that are not yet specified in the legal documents. Somehow these connections are hidden to make decisions that the rest of the party can hardly predict. This may cause remaining unnecessary.
Analyze practical situations to manifest the influence of Stakeholders. From the research results, recommendations are made for the management of Stakeholders to help SOEs work more effectively.
Stakeholder Theory and Business Management
Stakeholders Theory
Stakeholders formed in “the business planning process, theory of systems, theory of organization, and social responsibility of enterprises” (SRI, 1963). The stakeholder was first mentioned in the 1950s (Russell Ackoff & Charles, 1957). After that it was supplemented by (Ian I. Merroff & Richard O. Mason, 1983) “The Stakeholders are Stakeholders. Depends on the organization / agency to realize some of their goals, and on the contrary, the organization also depends in part on them to fulfill its goals.” (Mendelow, 1981) built a model of stakeholder analysis based on power and entitlement, thereby allocating responsibilities for appropriate monitoring and supervision of each different Stakeholders.
(Freeman, 1984) expands stakeholder under the influence of many fields. He defines stakeholder "as a person or group of people who are directly or indirectly influenced by the actions of an organization". This interest can also be described as those who are affected by or who can affect a decision or actions (Freeman et al., 2017; Ronald et al., 1997). There are also studies by (Donaldson & Preston, 1995) “the stakeholder theory has been advanced and justified in the management literature. One on the basis of its descriptive accuracy, instrumental power, and normative validity. These three aspects of the theory, although interrelated, are quite distinct; they involve different types of evidence and argument and have different implications”. Moreover (Ronald et al., 1997) has developed and “contribute to a theory of stakeholder identification and salience based on stakeholders possessing one or more of three relationship attributes: power, legitimacy, and urgency. By combining these attributes, we generate a typology of stakeholders, propositions concerning their salience to managers of the firm, and research and management implications”.
Then “employ stakeholder theory to propose how perceptions of fairness result in reciprocity and extending to all stakeholders of the firm and affecting firm performance”. The group (Edward Freeman & Robert Phillips, 1984-2010), found that there were many contradictions among the stakeholders, the authors argued that the tensions were more obvious than reality, representing the various stories of stakeholder theory, SM, especially especially profitability needs in business and ethics. The authors tried to understand the differences in these two theoretical positions because they sought to solve different problems. However, the authors have distinguished the overlapping areas and instead, we think that some of the tensions may, instead, provide interesting ways to place two areas of scholarship and realism. Opinion together.
But group of authors (Margit Huber & Martina Pallas, 2006) point out that “Nowadays, the concept of stakeholder management is no longer limited to the specific focusing of all corporate activity on interest groups, such as customers, employees, shareholders or suppliers, but has become an integral part of a company’s daily action. Measuring the quality of relationships between companies/institutions and the relevant interest groups, developing actions aimed at improving these relationships (managing) and the continuous monitoring of the effects in line with the TRI*M (TRI*M is the name of the customer retention system introduced to the market in the early 1990s) The TRI*M-Systems has been developed to measure, manage, and monitor customer relationships approach, is gaining momentum in all areas and at all levels of companies and ins- tuitions. Today, human resources departments usually measure the comment of employees in all organizational units on an annual basis, and senior managers develop strategies with their employees to the level of commitment, the success of which will ultimately be reviewed through subsequent measuring. This greater focus on employee commitment has only recently been given priority. For a long time, companies have failed to appreciate that the motivation and engagement of employees is the most important basis for excellent customer experiences and, consequently, profitability. Only engaged and motivated employees will use all their skills and energies for the benefit of the company.” So this theory is mentioned about the human resource, manager need to engage and motivated them.
(Macdonald, 2008) this investigation of the impact stake holder such as hierarchy of five crisis communication accounts and four crisis causes on multiple stakeholder reactions elicited several key findings. Although “confession” was the most preferred crisis account, “no comment” was almost as successful in mitigating negative reactions. Counter intuitively, confession reduced responsibility judgments. No comment was second to confession in mitigating negative, and promoting positive, reactions. Further, company control of a crisis was found to be the single most powerful predictor of stakeholder reactions. Involvement elicited multiple positive and negative crisis emotions, while different emotion categories elicited different behavioral intentions. Attitude to the company also impacted behavioral intentions.
(Farrokh Suntook & John Murphy, 2009) investigation in how “stakeholder reactions to company crisis communication and causes”. This paper has pointed out that the company's control over a crisis is considered the most powerful predictor of stakeholder reactions. Participation has evoked many positive and negative crisis emotions, while different types of emotions evoke different behavioral intentions. Attitudes toward the company also influence intent to behavior; Source: Kaufmann onion stakeholder, 2014 Figure 1.
In general, stakeholders can be grouped in several ways, such as “who is concerned, who finally makes decisions, who works and benefits, and who is actively collaborating”.
(Edward Freeman et al., 2017) advice to find out every stakeholder, to prevent the conflict between stakeholder we have to find out the overlap and how there are large areas of overlap, and so some of the tensions could, instead, provide interesting special ways to put the both side and two areas with each other and then maintain stakeholder theory could help benefit to each of company or group organization from a more pragmatist philosophy the theory is increasingly being improved and supplement.
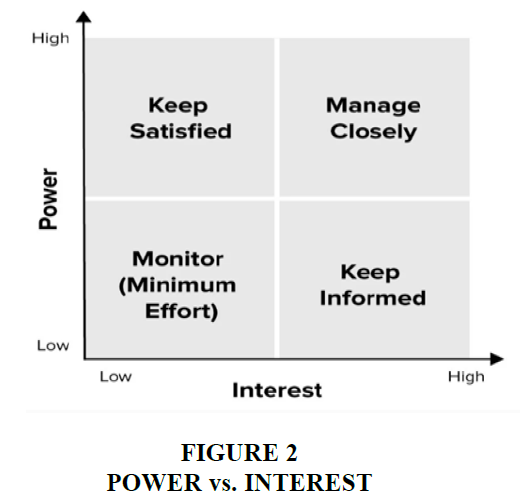
In theory, stakeholders have been developed and fostered over time. Most studies have shown that organizations or business companies need to invest in getting to know the stakeholders, the drivers of that organization's success or failure. From the research results, it will help the organization to have appropriate measures to limit the negative impacts of related parties and promote weaknesses, positive impacts to promote the success of the company or organization. If understand clear about the stakeholder will be help an organization have suitable strategy to increase benefit and reduce risk. Mendelow (1981) using model apply in Environmental Scanning - The Impact of the Stakeholder Concept. This analyst helps to have suitable plan with stakeholder.
He separates and allocates to a stakeholder on the grid corner shows the actions need to take to maintenance with them:
In the corner which has high power and highly interested people should manage and closely: Must fully engage with these group people and make the best efforts to satisfy them.
In the corners which have high power, less interested people must keep Satisfied: should put enough work with these people and then keep them satisfied, if not so much can make them become bored with your message.
In the corner which has low power and highly interested people should keep informed: with group of these people, should inform and talk to them make sure that everything keep in order and no major issues are arising. These group in this category can often useful and can helpful with the detail issue of your project.
In the corner of low power, less interested people should monitor: These group of people, should be maintenance and monitor but should not have bored them with excessive communication; Source: R. Edward Freeman. (1984): Environmental Scanning - The Impact of the Stakeholder Concept Figure 2.
Stakeholders in Business Management
According to organizational theory, an organization cannot function effectively without understanding its environment and its Stakeholders. That is the economic, political, social, legal environment, the relationship between the parties involved in it, and especially the interaction between related parties with each other and with the organization.
In strategic planning, the most important thing an organization / organization need to do is to analyze Stakeholders. A key factor in the success of public or nonprofit organizations is the ability to meet and satisfy key Stakeholders.
If the organization / project do not understand who the stakeholder is, what criteria they use to evaluate their organization, and how the organization meets those criteria, it is difficult to know how to meet the criteria.
An important objective of Stakeholder analysis is to see the overall and accurate picture of actors in the operating environment.
“Good governance will ensure the sustainability of a developed country, and good governance needs a transparent, predictable institution of stakeholder on private and public businesses. In the open and policymakers, a machine with professional ethics, professional work, a civil society participate in governance dramatically, and then detrainment experience religious law " (WB, 1994). So, if we would like to have good result of managed, we need to managed the stakeholder.
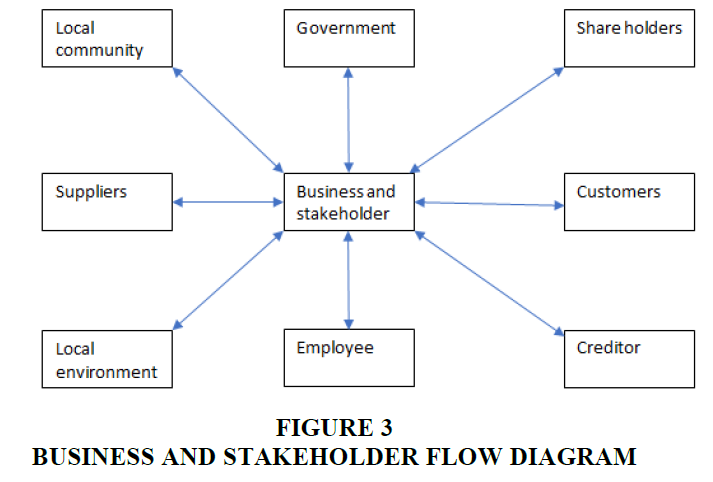
We offer the stake holder as following diagram, but not limited this Figure 3.
Freeman (1984) introduced strategic management stakeholders to address the legal social roles and obligations of businesses, and he opposed the monopoly's focus on atomic companies. Profit in orthodox theories. Stakeholder theory provides an alternative normative basis, paying attention to the interactions of businesses with all stakeholders influenced or influenced by an organization (Freeman, 1994). The standard SHT clarifies the neglected impact of external factors on a solid environment and broadly debates the role of stakeholders.
(Freeman, 1994). However, it lacks stakeholder consideration. The obligation of the related party or potential contributors to be able to convey the value created by a company. While the normative SHT provides little management involvement, its tool partner (Donaldson & Preston, 1995) tries to create a business case to invest in management. Stake holders by investigating its influence on firm performance. Although in combination, they include the relevant old people and the company's perspective, but the stakeholder according to rules and tools is still 'unidirectional'
However, Stakeholder scholars recognize the need to converge on both points of view, so new publications try to illustrate the right way of doing the stakeholder contribution to the advantage. Competition the newer document on stakeholder management has moved the basis for its arguments from stakeholder rights to the potential value of managing stakeholder sustainability and avoiding a conflict of interest. Defensive discussion regarding rights and obligations. A more fundamental contribution in this respect is the introduction of a system- focused stakeholder management (Ronald et al., 1997): Managers may want to have an exhaustive list of all both stakeholders. Unlike the stakeholder view of management, the approach focuses on this system to manage stakeholders, paying attention to the tradeoffs between stakeholder and organizational goals and do not consider them essentially when trying to mediate them. Instead, the system-centered approach says that the goals of the company and its stakeholders should be aligned, that they can work towards a common goal, like a system.
However, studies show that stakeholders are not limited to the above list, but because they mobilize and change, they can add or remove stakeholders.
Stakeholders in State Owned Enterprise
Corporate entity led to a split in 'control' and 'ownership'
• Limited liability for shareholders led to protection for third parties - Company Law - Governance requirements
• Evolved from autocratic institutions to more participative
• Importance of Stakeholders recognized
• Latest thinking encapsulated in notion of sustainability or the triple bottom line
There are no provisions on related parties in the 2014 enterprise law but there are regulations on related parties in Clause 17, Article 4 as follows:
“Related persons are organizations and individuals that have direct or indirect relationship with enterprises in the following cases:
• The parent company, the managers of the parent company and the person competent to appoint such managers for subsidiaries of the corporate group.
• Subsidiary regarding the parent company in the corporate group.
• The person or group of people capable of dominating the decision making or operation of that enterprise through the enterprise management agency.
• Enterprise managers.
• dd) Spouse, natural father, adoptive father, natural mother, adoptive mother, biological children, adopted children, siblings, siblings, brother-in-law, brother-in-law, sister-in-law, sister-in-law of the company's manager or of members or shareholders owning contributed capital or controlling shares;
• Individuals authorized to represent persons and companies defined at Points a, b, c, d and dd of this Clause.
• Enterprises in which the persons and companies defined at Points a, b, c, d, dd, e and h of this Clause possess ownership so much that govern the decision-making of the management agencies at the enterprise. that karma.
• Group of people who agree to work together to acquire capital contributions, shares or interests in the company or to dominate the decision making of the company”.
State Owned Enterprise Management in Vietnam: the Law, the Charter and Regulations
State Owned Enterprise in the Law: The Role of the State in Management
In Clause 1, Article 51 of the 2013 constitution, “Vietnam's economy is a socialist-oriented market economy with many forms of ownership and many economic sectors; State economy plays a key role". So, the water Vietnam remain state-oriented economy is driven, this is also the basis for many policies developed state sector was born. Agencies from central to local levels form and develop state-owned enterprises.
Clause 8, Article 4 of the 2014 Enterprise Law states that “a State enterprise is an enterprise with 100% of charter capital owned by the State” stipulating the percentage of this capital contribution varies through other changes to the law on other enterprises. Together however, many enterprises are joint-stock companies listed on the state stock market holding less than 100% of the capital but still capable of controlling the operation of these enterprises through the ownership ratio of over 51% or voting rules on business strategy or business development goals.
The 2014 Enterprise Law provides for SOEs in chapter IV from Article 88 to Article 109.
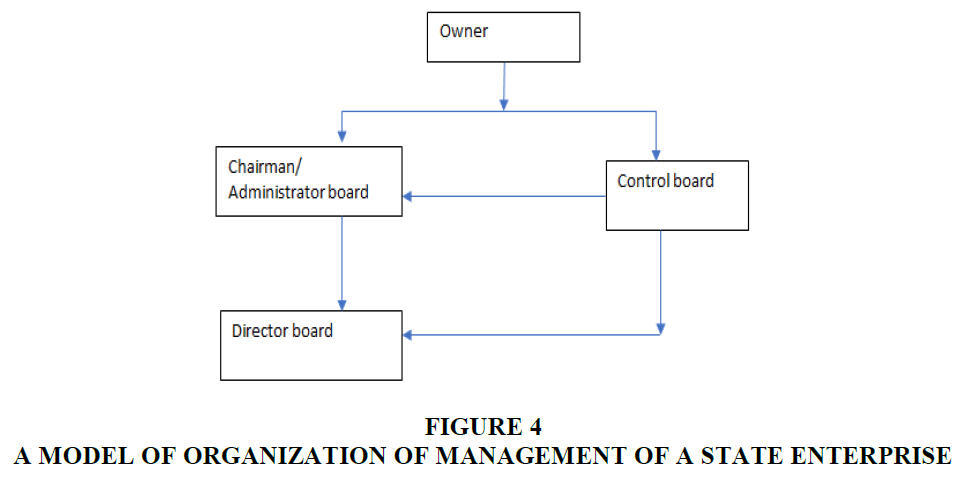
Pursuant to Article 89 of the 2014 Enterprise Law stipulating the organizational structure of state-owned enterprises and Article 78 of 2014 corporate law 2014 The organizational structure of a one-member limited liability company due to The organization as the owner of the author shall formulate a model of organization of management of a State enterprise as follows Figure 4:
T swine articles 90 and 91 corporate law 2014, council members represent the unit's management of Hurricane capital contribution by the State and the managing agency appointed. Under chapter 4 of the SOE law, the owner will manage the state enterprise through the board of members or chairman of the company. It is the Board of members or the company's president who is responsible for the maintenance of state capital. Assisting the board of members is the board of directors. The Supervisory Board will help the owner to supervise the activities of the board of directors and the board of directors.
The Myth of State Intervention in Company Charter
D glorious states economic institutions most affected by each process, each stage with the economic policy of the country. This is reflected in the percentage of shares held by the state to be considered as state-owned enterprises. Or change in the way of managing the managing unit. A common feature that has not changed throughout history is the leadership of Party organizations in businesses.
Although only a single point in Article 6 of the Enterprise Law 2014 is stated in the “Political organization, socio-political organization in enterprises operating according to the constitution, laws and regulations of the enterprise. Organization" Meanwhile, in Clause 2 of this Article stipulates, "Enterprises have the duty to respect and not to obstruct and create difficulties for the establishment of political organizations and political organizations. Society at the enterprise; must not hinder or cause difficulties for laborers to participate in activities in these organizations ". This reflects the fact that political organizations are not clearly defined on its position and role in enterprises in general and state enterprises.
From this regulation, SOEs are affected by many other Stakeholders such as: The Fatherland Front, the media, social networks, the authorities at all levels, the elected bodies, the judiciary. Trade unions, press agencies ... But all these parties are united under the leadership of the Party (Article 2, 3 4, Constitution, 2013).
Therefore, Stakeholders can mobilize and interact with each other internally or be influenced by outside parties in the process of performing tasks and policies of enterprises (Analysis of economic development policies) but all were united under the overall leadership of the Party.
T established in paragraph 17 of Article 4 that the law now in 2014 stipulated towards listed. Meanwhile, Stakeholders often campaign for changes, so they are overlooked. Among those Stakeholders, one party has a decisive impact on the vital effect on the efficiency, success or failure of enterprises, especially state-owned enterprises but not yet named. The provisions on disclosure of related information also have not mentioned these parties. This is not in line with international standards and is also a cause for interested parties to undermine the effectiveness of SOEs without joint responsibility.
Party organizations are typical. This is evidenced by Resolution No. 69-QD / TW stipulating “on the functions, tasks and powers of the Party Committee's apparatus organizations because of state-owned enterprises and state-owned enterprises. Dominates "stipulates the relationship" with the board of directors (the members' council, the president of the company), the general director and the socio-political organizations ":
Clause 1, Article 16 of Resolution No. 69-QD / TW stipulates: “The Party Committee directs all aspects of the enterprise's activities, ensuring that businesses and socio-political organizations operate according to the policy., the Party's policies, the State's policies, laws, and regulations of each organization” The Party's leadership through political-social organizations in enterprises. According to the Vietnamese constitution in 2013, the socio-political organizations organized in enterprises can be trade unions, youth unions, war veterans' associations, women's associations, etc. all members of state-owned enterprises.
Clause 1, Article 16 of Resolution No. 69-QD / TW continue to stipulate: "lead the coordination between the board of directors (the members' council, the president of the company) and the general director in carrying out their duties, authorized authority”. This shows that the new party committee is the direct leader of the entire corporate governance system. However, the 2014 Enterprise Law does not provide for the position and leadership of a Party organization.
Clause 2, Article 16 of Resolution No. 69-QD / TW stipulates: “The Party Committee discusses to issue resolutions and conclusions to lead the Board of Directors (Board of members, the president of the company) and General Director for implementation. Tasks of developing production and business, developing enterprises. Board of Directors (Board of Members, Chairman of the company), General Director report and propose the Party Committee to issue resolutions or conclusions on leadership for implementation of annual plans, medium-term and long-term plans; undertakings on investment, equalization and divestment of State investment in enterprises; important business development policy. Quarterly or irregularly upon request, representatives of the Board of Directors (the Board of members, the company's President), the General Director report to the Party Committee on the implementation situation and the guidelines and direction next service of the business”. These rules obscure the role of the board. It is stipulated that after the Party Committee discusses and issues resolutions, the General Director shall perform his duties and the Members' Council and the General Director must report periodically to the Party Committee periodically.
Clause 3, Article 16 of Resolution No. 69-QD / TW stipulates: “ Quarterly or irregularly upon request, the Standing Committee of the Party Committee works with leaders of socio-political organizations in the enterprise to grasp the operational status of each organization and adopt guidelines and measures for leadership and timely direction. " This is the supervisory work of the state enterprise control board.
This shows the leadership in the whole process of planning, implementing, and monitoring is the Party Committee rather than the role of the board of directors or the board of directors, the control board but the related party. This is not regulated in the Enterprise Law.
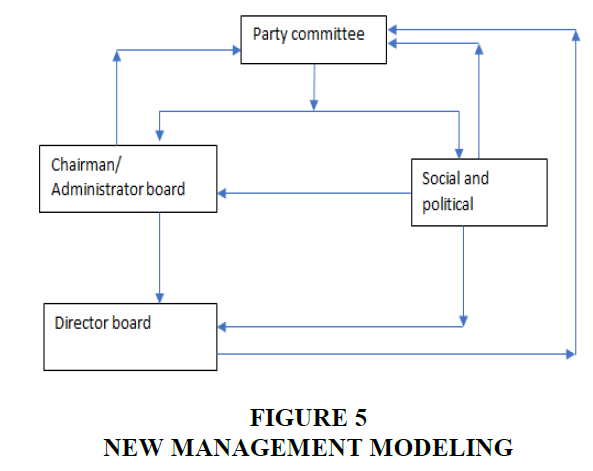
From this, the author built a new management model Figure 5:
In addition, Party organizations also perform the task of planning cadres for each managerial position in the enterprise. Party organizations also periodically evaluate the fulfillment of the annual tasks of the management staff. These assessments are the basis for making recommendations and promotions. Party organizations are also responsible for taking the vote of confidence and promoting them to the head of the enterprise or the chairman of the capital management committee, the governing body, in some cases being the Prime Minister. Human resources this increases the power of Party organizations, while associating the political lives of business leaders with political tasks, thereby forcing them to comply with the resolutions of Party organizations. Or at least they prioritize the implementation of the resolution over other laws.
However, in the provisions of Clause 17, Article 4 of the Law on Enterprises in 2014 was provided towards listed. Then the Stakeholders listed no mention of Party organizations as the Politburo, or personal Prime Minister. The management announcements of state-owned enterprises in accordance with the provisions of Article 108 of the 2014 Enterprise Law do not mention the positions and roles of these organizations.
In fact, the cases brought to trial recently proved this point. There have been wrongly issued resolutions of the Party, which are the basis for causing other violations, causing law violations and significant economic losses.
Typically, Resolution 233/NQ-ĐU, dated March 17, 2009 of the Party Committee of Petroleum Group was concluded "with content that does not conform to the law to the Board of Directors, the Board of Management of the Group and member corporations decided to appoint many illegal bidding packages ".
Besides Stakeholder can take advantage of businesses, businesses also use their resources to fund different forces to gain certain effects and advantages. This is evidenced through the recent cases when businesses spend large sums of money to congratulate the father of a business leader. Because this leader has absolute power over the enterprise at that time.
Testimony of Mr. Dinh La Thang of the appointment of contractors thermal plants Pacific 2 He is accused on trial recently on charges of "intentionally acting against the provisions of the state causing serious consequences" has repeatedly answer before the court that they comply with the regulations of the Party. He also cited the Politburo's conclusions No. 41-KL / TW of January 19, 2006, on the Vietnam Oil and Gas Industry Development Strategy to 2015 and orientation to 2025. This proves otherwise specified in the normative law, the text of the Party organization, or the organizations itself the Party can be exploited to an individual govern the activities of enterprises agricultural towards on personal interests. Without trouble they are willing to blame the resolutions of the Party organization.
Sub-conclusion: Thus, the regulations in the enumeration direction, while the stakeholder regularly campaigning changes will lead to misjudging the role of each party or omitting the new stakeholder and promoting the role of the former Stakeholders. One of the most key Stakeholders not regulated is Party organizations.
Interview Results
The author summarizes the perils of the stakeholder into SOEs in many different forms.
With the basic question asking experts to identify the Stakeholders in their activities, most leaders cannot list all their Stakeholders. One of the reasons is that SOEs have never assessed the role of Stakeholders. Nor has it been concerned about associating or splitting with any Stakeholder. However, with the question of which is the most important Stakeholder in corporate governance; all experts affirm that the same answer is the Party organizations. Some experts, such as Mr. Ho Si Thoang, former chairman of the board of directors of the Vietnam National Oil and Gas Group, also suggested that the board of directors be dismissed because the day-to-day management practice is the Board of Directors., while the business plan is a Party organization, the appearance of a board of members is redundant and contradictory. He affirmed that the management experience requires the meeting of three units of the board of directors, the party committee, and the board of directors at the same time to make decisions to avoid conflicts in executive direction.
Assessing the influence of related parties is agreed by experts as follows:
SOEs belong to many different governing units; however, they have recently been agreed under the management of the state capital management committee. However, there was a problem when the approval of projects and constructions was slower, did not receive the necessary support from Stakeholder, reducing the management efficiency of SOE.
The salary mechanism is approved hard, in that warehouse due to market fluctuations, there is a time when revenue increases do not have the opportunity to require workers to work overtime, and vice versa, not reducing the salary of workers is causing difficulties for SOE.
SOEs are required to make profits, while following the principles of operation and market cycles; it makes it difficult for SOEs. SOEs often set low targets to ensure that they cause waste of capacity.
Internal defense staff does not support mobilizing each other's strength; there is no policy to support the use of internal services.
In particular, the Stakeholder overlaps the governance of SOEs: The Government and administrative agencies, the Communist Party system of organizations all manage the people, and the line ministry is also responsible for human resource management. At the same time, these organizations are also responsible for setting up the apparatus, building the investment scale, the capital management plan, the Ministry of Finance's regulations on capital management, the Ministry of Planning and Investment, the management of investment projects and the Ministry of Finance. Rebuilding management of construction standards ... generates many clues, many conflicts arise during the implementation process. K hips like private businesses and state agencies are not the same.
Stakeholder is the Government that does not directly direct or manage SOEs, but this CBL often intervenes directly in organizing the management and handling of problems in enterprises. This is reflected in the establishment of various steering committees by the politburo and government to directly address issues that arise in 12 malfunctioning projects.
Stakeholder policy is not uniform. When the government resolution developed Ethanol, Stakeholder invested, but did not coordinate the planning of material resources. When factories go into operation, the price of low-quality input products has high prices, which increases the price of output products. While biofuel prices are considered environmentally friendly, they are subject to a royalty like the fossil fuels.
Stakeholder negotiates duty free import of crude oil for investors in Nghi Son refinery is a preferential commitment. The commitment also confirms the maintenance of import tax on gasoline elsewhere. However other Stakeholder to negotiate with Korea to reduce tariffs to 0%. This is considered a violation of commitments and the SOEs, such as PVN must compensate this tax difference.
Members' Council is the agency that administers the work of SOEs but does not have the legal status, but the General Director is the legal representative. This can lead to coercive directives that are difficult for the CEO to carry out.
Stakeholder asset transfer is N galaxies machine a mouthpiece Dung Quat from one to a different corporate SOE to shirk her main responsibilities.
Especially, Mr. Ho Sy Thoang said that “should not set up a Board of Members as an intermediary agency to reduce the management efficiency of SOEs, I do not agree with this policy. I think that, the Board of Directors operating properly functions and duties is enough; If necessary, expand the composition of the Board of General Directors, because our principle is "leadership collective, individual in charge", Enterprises whose Members' Council is a model of private enterprise, applied to SOEs are not suitable, because we have no stake in it. "According to his experience of being chairman of the Board of Directors, he must conduct meetings with the participation of all three parties, including: Members of the Board of Directors, Members of the Board of General Directors, and members of the Party's Executive Committee. SOEs, when unanimous ideas are implemented. There are not often conflicts; the party not responsible for the law often forces the party responsible for the law to perform many different tasks without thinking about the consequences of execution.
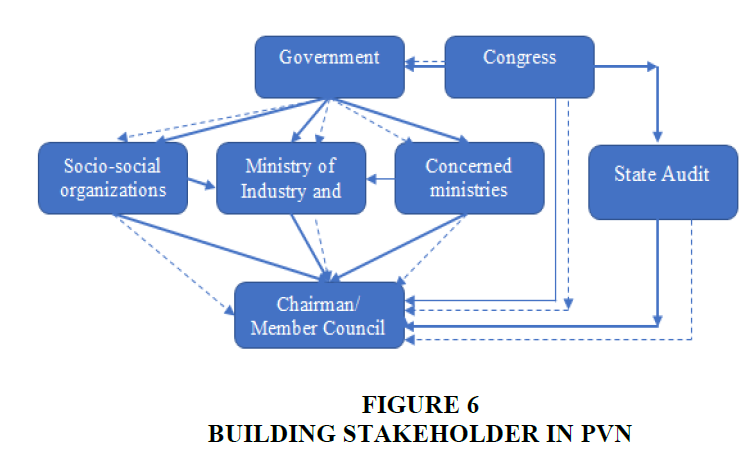
After interviewing the former experts of the Vietnam National Oil and Gas Group, the author built the influence model of the state management agencies as follows Figure 6:
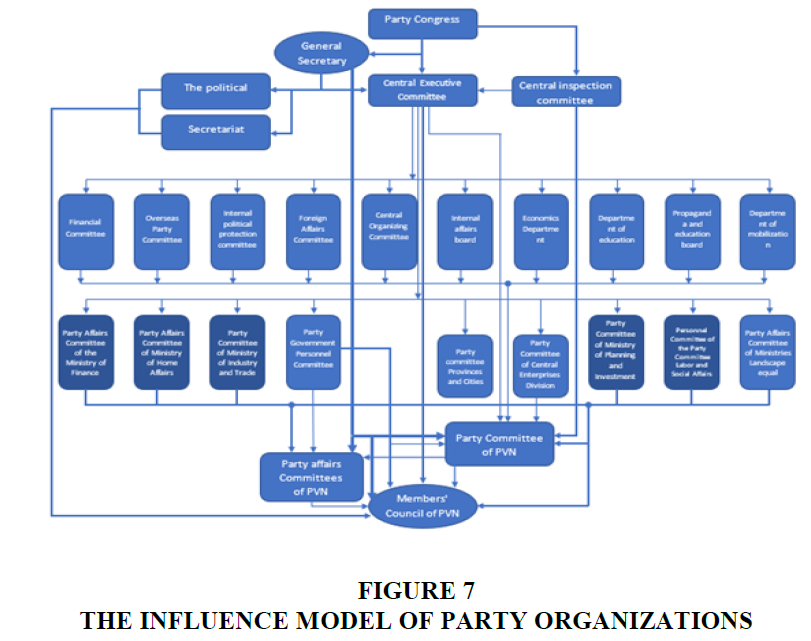
Meanwhile, the influence model of Party organizations is as follows Figure 7:
Political and State Intervention in Practice of State-Owned Enterprise Decision Making Mechanism
Direct Intervention Strategy of Political Force
The Chairman Council's regulations are stipulated in Article 41 of Decree No. 07/2018 / ND-CP appointed by the Prime Minister "at the request of the Ministry of Industry and Trade and the" Ministry of Home Affairs "appraisal and" business " at least 3 years of experience in managing and operating enterprises in the main business lines of PVN ”.
PVN has conducted the procedures and proposed the Ministry of Industry and Trade to submit to the Government, to appoint the Chairman of the Board of Directors. “On April 18, PVN Vietnam submitted a report 740 / TTr-DKVN to the Ministry of Industry and Trade for consideration and submission to the Prime Minister to appoint the Chairman of PVN Vietnam Members' Council to Mr. Nguyen Hung Dung., Deputy General Director of PVN Vietnam ”. (Tam An, 2017)
However, on December 24, 2017 the Politburo issued “Decision No. 642-QD / TW, the Politburo assigned Mr. Tran Sy Thanh, Member of the Party Central Committee, Secretary of the Provincial Party Committee, and Head of the National Delegation. The XIV Association in Lang Son province stopped joining the Executive Committee, Standing Committee and Secretary of Lang Son Provincial Party Committee for the term of 2015-2020 to hold the position of Deputy Head of the Central Economic Committee and Chairman of PVN's Member Council. " (Hoang Nam, 2017)
Then on December 27, 2017 the Prime Minister issued "Decision No. 2111 / QD-TTg, the Prime Minister appointed Mr. Tran Sy Thanh, Member of the Party Central Committee, Deputy Head of the Central Economic Committee - Former Secretary Lang Son Provincial Party Committee holds the position of Chairman of the Board of Members of Vietnam Oil and Gas Group ” (Hoang Nam, 2017).
Sub-conclusion: The Prime Minister did not issue a decision at the request of the Ministry of Industry and Trade but a decision after a decision of the Politburo.
The Key Character: The Chairman of Members 'Council
Clause 1, Article 46 of PVN's operation regulations attached to Decree 07/2018 / ND-CP on the appointment of PVN's General Director, "General Director of PVN is a member of the Board members PVN. In special cases, to be submitted to the Prime Minister for consideration and decision after obtaining the unanimous opinion of the Government Party Committee's collective staff." Working regulations of the Government issued on February 16, 2012 together with Decree No. 08/2012 / ND-CP stipulating “All activities of the Government and Government members must ensure the Party's leadership: this is reflected once again by Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung "It is said that the Prime Minister approves but it is a joint decision of the Government Party Committee. The Prime Minister has never decided a case of cadres" (Le Nhung, 2011)
Speaking at the handover ceremony of the appointment of Mr. Tran Sy Thanh, (TĐKK, 2018), after emphasizing the position and role of PVN T, Prime Minister Nguyen Xuan Phuc also indirectly asserted this by saying " The Politburo, the Central Executive Committee, the Collective Committee of the Government Party decided to appoint Mr. Tran Sy Thanh to take up duties at PVN Vietnam”.
Sub-conclusion: The Government Party Personnel Committee plays a decisive role in selecting PVN management personnel.
The Role of Party Cell in State Owned Enterprise: The Loophole of the Law
From April 24, 2017 to April 26, 2017, the Central Examination Committee met and proposed, May 7, 2017 at the 5th Conference of the 12th Party Central Committee Mr. Dinh La Thang Discipline Warning, dismissing the Politburo member one of the reasons is “ According to the Central Economic Commission, the Standing Committee of the Party Committee of PVN 2009-2015 term irresponsible, relax leadership, directing in management., using capital and assets, executing investment projects leading to the Board of Directors of the Group and some member units which have committed serious violations, losing the investment capital of nearly VND 900 billion, including VND 800 billion. Contribute capital to Ocean Bank (Ocean Bank)”.
The role of the Party Secretary of PVN “Mr. Dinh La Thang signed the Resolution No. 233 / NQ-ĐU dated March 17, 2009 of the Party Committee of PVN with content not in compliance with the law, so that the Board of Members and the board of General Directors PVN director and member corporations decided to appoint many illegal packages”.
Sub-conclusion: As such, the Party organization and its head are disciplined for directing and indulgent resolutions.
The SOE Became a Political Tool
On August 4, 2010, Mr. Pham Thanh Binh (Vinashin President) was arrested for "intentionally violating the state regulations on economic management, causing serious consequences". On August 30, 2012, the court sentenced Mr. Binh to 20 years in prison, and claimed over VND 540 billion (Dung, 2012). However, the Government is forced to pay Government- guaranteed amounts, or the Government lends it to Vinashin. The issue was pushed up when deputies Duong China took responsibility and mentioned the possibility of resignation of the Prime Minister, Mr. Nguyen Tan Dung, in the National Assembly's direct reporting session (Quoc Thanh, 2012). Vinashin is in trouble, unable to pay debts, according to the rules of the free market, this group should go bankrupt, and the loss of state assets will put enormous political pressure on the Prime Minister.
N anhydrous June 18, 2010, the Prime Minister issued Decision No. 926 / QD-TTg to restructure Vinashin. Based on this decision, Vinashin has handed over to PVN and vinalines 7 subsidiaries, 23 subsidiaries and 5 projects with 5137 employees, total assets handed over VND 21427 billion, with a total liability of 24112 billion dong. Dung Quat Shipbuilding Industry Corporation is one of the enterprises handed over to PVN. The total value of assets and net assets of this Company is VND 7,039,429 million and (VND 23,449) million (The consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ended on December 31, 2010 of PVN).
However, the handover value is determined at cost and in the report; there has been "no official written opinion of the competent authorities on the value of assets and liabilities of Dung Quat Shipyard and the amount the Group has to pay Vinashin. This value may change when there is an official approval from the competent authority on the value of the handover companies. (The consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ended on December 31, 2010 of PVN)
From the decision 926, PVN has paid Vinashin VND 3,425,065 billion, this payment of principal and interest to Natixis (French investment bank Natixis). B Shirt financial statements of PVN to 31 /1 2 / 2017 has not yet agreed price handover so that PVN construction plan or bankruptcy processing factory ship Dung Quat.
Sub-conclusion: This case shows that PVN has become a tool to pay debts on behalf of Vinashin, reducing political pressure on the Prime Minister on the loss of assets in the failure of Vinashin. Violating the principles of integrity in good QT of OECD, 2015.
Conclusion Remarks
The SOE has not actively analyzed and assessed the position and role of Stakeholders so that they can formulate appropriate strategies and passively implement related Stakeholder statements in accordance with the law. Meanwhile, the law lacks a wide range of different Stakeholders, including strategic Stakeholders that directly affect the entire business activities such as
The research topic has shown that there are many different BLQs affecting the management system of SOE respond covered up all the role of the Communist Party with many different organizations dominant party system administrators of PVN directly from inside and from outside, or indirectly governed through stakeholder different.
T drive organizational Party have very strong political power can intervene on the planning process, evaluate workforce or to influence the key leaders, the senior management of the SOE. Party organizations also decide business strategy of PVN through various resolutions in each period.
However, the functional role of Party organizations was not specified in charter operations as well as the documents related legal system to the administrator of the SOE. SOE is not disclosing the role of Party organizations.
SOE does not have a system of standards and regulations on ethical standards in integrity. N tokens behavioral intervention stakeholder, or the actions of the stakeholder has not been monitored adequately, promptly stop leads to many problems’ malfunctions in the work of administration. This creates a loophole for stakeholder to govern activities and use SOE as political tools.
System administrators of SOE incomplete, SOE not considered SOEs also not be considered as an organ of state in economic activities. The provisions on duty to regulate economic, or political mission is unclear and frequently changing difficult to predict.
The stakeholder makes governance decisions that do not respect the interests of other Stakeholders. Stake holders perform tasks administrators incorrect, incomplete, or perform an overlapping d sentenced to not timely detection of malfunctions in the system of governance of SOE should cause consequences loss of assets, reduction reputation of stakeholder.
International management experience also shows that political cohesion will make oil and gas corporations malfunction (China), while if they create a transparent mechanism and competitive environment, they will promote more efficiency. In the management of oil and gas corporations (Malaysia and Norway) respect the interests of Stakeholders weak
The stakeholder has the same power as the Party, State or PVN governance officials to respect and ensure the interests of the stakeholder have a weaker position.
State laws should specify the position of stakeholder, especially those who could directly intervene in strategic planning and personnel appointment, ensuring that these regulations are complied with and fully implement to be able to predict stakeholder intervention.
Disclosure of relationships with Stakeholders
PVN needs to develop a strategy to find out regularly about stakeholder. When the new CPC appears, the SOE needs to be publicly announced; especially it needs to announce the relationship of Party organizations, which is the political power very strong.
When unforeseen problems arise, the stakeholder must discuss with PVN to ensure the correct and complete implementation according to the applicable regulations at that time.
Learn and build a strategy to engage with stakeholder, especially with Party facilities to grasp the trend of intervention, expected appropriate responses to reduce damage, increase the likelihood of success.
Develop a monitoring mechanism for Stakeholders
Forming a clear monitoring mechanism, anybody can n À m start and participate in monitoring thereby depleting interventions stakeholder not compliant.
Ensuring the rights and interests of the supervisory agency, ensuring the safety of those who detect non-standard interventions ... to encourage the stakeholder to participate in monitoring each other.
Building ethical standards of business integrity, ensuring the ability to enforce the benefits and consensus of stakeholder.
Separate the political task to not form the focal political relations.
Admin members do not participate in political activities.
The Party participates in developing strategies and personnel based on effective governance goals only.
References
- Quốc Thanh. (2012). “Quốc hội chất vấn thủ tướng: đoạn tuyệt xin lỗi”. Access date 05/01/2019 at the address: https://tuoitre.vn/quoc-hoi-chat-van-thu-tuong-doan-tuyet-xin-loi-520446.htm.
- Donaldson& Preston. (1995). The_Stakeholder_Theory_of_the_Corporation_Concepts_Evidence_and_Implications.
- Elmore. (1982& 1985). "Elmore’s Approaches to Implementation Analysis".
- Farrokh Suntook & John A. Murphy. (2009). “The Stakeholder Balance Sheet_ Profiting from Really Understanding Your Market”.
- Freeman, Kujala, Sachs. (2017). "Stakeholder Engagement-Springer". International Publishing.
- Freeman, R.E. (1984). Strategic Management_ A Stakeholder Approach. (Pitman Series in Business and Public Policy)-Pitman Publishing (1984).
- Ian I.Mitroff & Richard O.Mason. (1983). Accounting, Organizations and Society. Department of Management and Policy Sciences, Graduate School of Business University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90007 U.S.A.
- Mendelow, A.L. (1981). "Environmental Scanning--The Impact of the Stakeholder Concept". ICIS 1981 Proceedings. 20.
- R Edward Freeman, Robert Phillips. ((1984 and 2010)). “Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach”, New York.: Cambridge University Press, .
- R. Edward Freeman, Johanna Kujala, Sybille Sachs, Christian Stutz. (2017). Stakeholder Engagement: Practicing the Ideas of Stakeholder Theory.
- Ronald K. Mitchell, Bradley R. Agle and Donna J. Wood. (1997). Toward a Theory of Stakeholder Identification and Salience: Defining the Principle of Who and What Really Counts. The Academy of Management Review.
- Russell Ackoff & Charles West Churchman. (1957). Introduction to Operations Research.
- Salamon, L. M. (2002). "The Tools of Government: A Guide to the New Governance". Trích theo Nguyễn Xuân Thành.
- SRI. (1963). Stake holder . Standford Research Institute.
- WB. (1994). "Governance (1994). The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development". Manufactured in the United States of America.