Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 4S
Development of Evaluation Tool for Traditional Retail Businesses via Mobile Web Application
Supaporn Sompaiboon, Chulalongkorn University
Tatri Taiphapoon, Chulalongkorn University
Pakpachong Vadhanasindhu, Chulalongkorn University
Sipat Triukose, Chulalongkorn University
Abstract
The business evaluation is means of assessing their methodology and performance of business. Nevertheless, the traditional retail businesses do not implement evaluations in the auditing of their operations and therefore fail to identify flaws or good practices. The aim of this research is to study the need and problem of an evaluation tool for traditional retail business and to develop innovative prototypes of traditional retail evaluation tools that can be used via smartphones to solve the problems of traditional retail stores which often stick with legacy operating patterns and lack development, making it impossible to operate sustainably. This research using surveys and semi-structured interviews with entrepreneurs and representatives of organizations in the traditional retail business ecosystem. Based on the results of the data analysis and a review of the innovation thinking process conducted by a group of experts on technology and retail, the prototype presented is practical and suitable for mobile web application development. The entrepreneurs participating in this study were able to identify their potential level significantly more effectively than before using this evaluation tool. Moreover, the researcher tested the reliability by data triangulation that involved 1) comparing the data in terms of the location of data collection, 2) comparing trends in the correlation between evaluation results and income level by Box Plot, and 3) comparing the evaluation results from internal sampling and external sampling.
Keywords
Traditional Retail Business, Entrepreneur, Mobile Web Application
Introduction
Evaluations are carried out by many organizations to assess their performance and understand how it affects the results of their operations. Business evaluation is a measure of business performance and entrepreneurial potential based on academic principles. It provides guidance for solving basic business problems for entrepreneurs who want to self-assess their business. This is beneficial to all sectors, both public and private (Department of Business Development, 2018). At present, various business models have been developed, but these still lack understanding of to optimize evaluations (Tesch & Brillinger, 2017). In order to achieve the most effective assessment results, the development of a business evaluation system should include criteria that are consistent in terms of both objectives and users (Morita, Umezawa & Kubo, 2006).
Today, many large businesses are increasingly paying attention to their evaluation processes because they recognize that conducting assessments allows them to monitor how effectively they are performing and could be use the result of business evaluation to determine their business strategy and forecast the direction of change in organizational management effectively (Avdeeva, 2021). However, many traditional retail businesses, the majority of which are one-person operations run by an entrepreneur, still do not place emphasis on evaluations. Because most of the business evaluation tools are developed by organizations involved in business promotion with perspectives of academicians. Which the existing business evaluation tools are still less suitable for traditional retail entrepreneur in both the method and assessment questions. Moreover, when the assessment is complete, the entrepreneurs do not know the results of the business evaluation, thus making them less aware of the importance of evaluating and what the benefit of it.
While, the study about the traditional retail businesses in Thailand that found they have many weaknesses that making them unable to deal with the threats of modern retail businesses (Department of Business Development, 2018). Especially, they often stick with legacy operating patterns. Therefore, many researchers have studied the problems of traditional retail businesses but have focused on the factors of business success. There are few evaluations of the way to assess the chances of survival for businesses in this field (Fernández-Guerrero, 2012). However, some researchers also believe that a business evaluation can be a tool that helps entrepreneurs gain awareness of the potential level. Nevertheless, no traditional retail business evaluation tool has not yet been developed that is suitable for entrepreneurs to use. According to Papadakis & Education (Papadakis & Education, 2020) who found there are several evaluation tools currently available, the majority are not considered adequate for or specific to the nature of user group. Thus, the criteria when developing a business evaluation tool should be that it is easy to use and as consistent with user behavior as possible.
Therefore, this research aims to study the needs of entrepreneurs in terms of traditional retail business evaluation, including analyzing the problems or obstacles identified by past evaluations and identifying the expectations of the entrepreneurs in order to develop an innovative prototype of an evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses that utilizes appropriate technology and corresponds to the behavior of traditional retail business entrepreneurs to increase awareness about the benefits of business evaluation and apply them to sustainability in business operations.
Literature Review
The critical component in the development of a traditional retail business evaluation tool via mobile application for consistent in terms of both objectives and users are required to review the literature in 5 areas are as follows:
Concepts and Theories on Business Operations
The main point of an entrepreneurial venture is to create a good income for the entrepreneur. However, a good income or good turnover is the result of good practice and balance in the activities of the business venture. Therefore, it is necessary for the entrepreneur to understand business theory and adapt it into action. From the past to the present, there have been many business theories and concepts, but only some of them are appropriate for traditional retail businesses.
Financial Management Concept
The financial management concept can be applied to both individuals and businesses. As a traditional retail business is usually a small business, financial management is extremely important (Dunn & Liang, 2011) because a business that is not operating as efficiently as it should and lacks good financial management is more likely to fail. However, the majority of small business entrepreneurs still lack the knowledge and understanding of financial management methods, including personal money, business equity and non-ongoing financial audits, if there is a good financial planning, it will make the person and the business feel secure in normal situations, including being able to adapt or cope with emergency situations effectively make the accounting of income and expenditure easy (Dahmen & Rodríguez, 2014). It is a method that can help reduce the failures of business operations (Hussain, 2018).
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a term that emerged among Information Technology (IT) entrepreneurs and practitioners in the mid-1990s, and is used to describe options for technology customers (Parvatiyar, Sheth & Research, 2001). It is where businesses try to create satisfaction for customers by studying their needs and expectations as much as possible (Tao & Science, 2014; Jermsittiparsert, 2020). The benefits of managing customer relationships (Iyibildiren, Karasioglu & Research, 2018) are: 1) reducing the cost of finding new customers; 2) increasing sales revenue; 3) helping to develop accurate decisions by analyzing future trends in both the short-term and long-term ; 4) building a good relationship between customers and the business; 5) increasing customer satisfaction with the business; 6) providing a good service to customers and improving the work to respond immediately to customers’ needs; and 7) collecting detailed customer information systematically. This will allow customers to continue repeat to buy.
Retail Management Concept
The retail management concept is an important concept for retail business operations. Levy and Barton presented the concept of the retail mix, which is the activities and functions of retail stores. It consists of 6 components: location, merchandise assortments, pricing policy, marketing communication mix, store design and display, and customer service. This concept does not have the complexity to be adapted for large business operations, but is suitable for small stores with their own customer groups in order to generate income or turnover according to the next target. This includes the use of marketing methods to help incentivize customers (Dahana, 2020) to make repeat purchases and develop the desire to continue patronizing the store.
Knowledge Management (KM)
This concept involves using the collection of knowledge contained in the organization which is found in people or documents to develop a system so that everyone in the organization is able to access knowledge and develop themselves to be knowledgeable and to work efficiently (Jermsittiparsert, 2019; Saengchai, 2019). In this way, the organization achieves its highest competitiveness, and knowledge management is essential to the operations of the organization (Hislop, Bosua & Helms, 2018). Organizations that want to use the knowledge of personnel in a concrete way (Dalkir, 2017) can divide the knowledge into two categories: tacit knowledge and explicit knowledge. This theory often focuses on large corporations, but there are many small business entrepreneurs who are interested in applying knowledge management processes to enhance their business competitiveness (Bandera, 2016).
All of concepts and theories on business operations as mentioned above, they make sense that these can affect a business's income and sustainability without being overly focused on certain areas and ignoring others. It can be said that there should be a balanced approach. Which will present in balanced scorecard?
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard (Kaplan & Norton, 1996) is the most recognized system for organizations that not use only financial indicators. They present their ideas based on four metrics (Perspectives) to achieve the main mission of the organization according to the balance index. There will be 4 important indicators: 1) financial perspective, 2) customer perspective, 3) internal process perspective, and 4) learning and growth perspective. The four perspectives under the balanced scorecard concept are interrelated in cause and effect according to Michael E. Porter (Porter, 2011) who said that the competitiveness of the organization will stem from the ability to manage activities within the organization. If the activities are managed well, it will help to reduce costs for the organization. When the organization is able to reduce costs, it will increase profits. The organization has to work towards its destination of increasing profits by creating a value chain model. Thus, by balancing activities in all four areas, it can result in a good business performance and make the business more sustainable.
Evaluation for Retail Business
Business evaluations are important to businesses of all sizes. It is a process that assists an entrepreneur in reviewing the situation of the business. It improves their ability to operate the business (Birimisa & Wegener, 2013). Therefore, raising awareness of the importance of using business evaluations will be another way that entrepreneurs can operate their businesses more sustainably. Moreover, the evaluation techniques can be used to guide decisions that give businesses a competitive advantage. Currently, there are two patterns of business evaluation models: the first pattern is a checklist on a paper where entrepreneurs do not know the results after they have been evaluated because the evaluators will process them later, and the second pattern is an evaluation program via computer devices that can be conducted both online and offline. Nevertheless, most of them were published and used in modern retail group such as convenience stores and wholesale business.
The evaluation tools for small businesses in Thailand, such as traditional retail business, have been developed by the government and private organizations with academicians’ perspectives following a quality standard for retail and wholesale businesses in order to develop and upgrade a standardized management system (Department of Business Development, 2018). Thus, they may not be suitable enough for entrepreneurs to assess the potential of their traditional retail businesses and they may not be used as a guideline for effective business improvement and development.
Behavior of Thai People in Accessing the Internet via Smartphones
Regarding Thai people’s means of accessing the internet in 2015, it was found that 40% of internet access was by smartphones followed by 31% by personal computers and 16% by notebook computers with another 11% by tablets and 2% by feature phones (The National Statistical Office, 2018).
It is clear that there are opportunities for developing a traditional retail evaluation tool that is easily accessible and convenient to consumers. The development should focus on creating a responsive web design that can operate on various mobile devices such as smartphones, personal computers, notebooks, mobile phones and tablets. The paper-based evaluation should be adapted to fit the screen of a smartphone conveniently according to Perguna, Idis & Widianto who tried to offer a fundamental change in the process of learning from paper to the screen of smartphones. This approach offers freedom for learners to determine by themselves the way how they learn, which is consistent with the concept that mobile learning can contribute a new method. Furthermore, the different advantages of using a mobile application is that it can be used anytime and anywhere (Ewais, 2021).
Research Framework
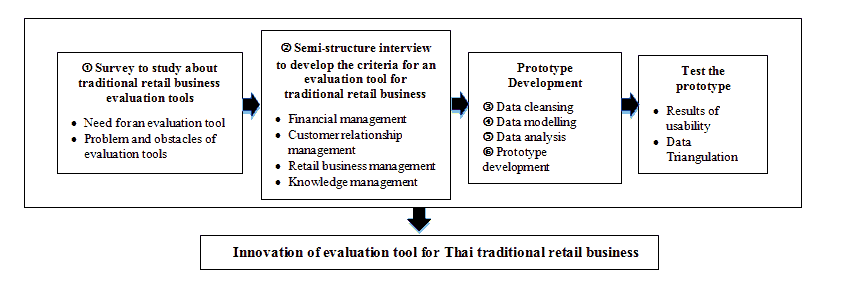
Figure 1 presents the framework of this research. First, the needs and problems of evaluation tools for traditional retail businesses were studied from the perspectives of traditional retail business entrepreneurs by survey. Next, the key success factors of traditional retail business were explored to identify the development criteria for an evaluation tool by semi-structure interview. After that, data cleansing, data modelling and data analysis were used to analyze the obtain data. Then, a prototype of an evaluation tool for traditional retail business was developed with appropriate technology according to innovation thinking process and, finally, tested in terms of the usability and reliability of the evaluation tool by using data triangulation.
Research Methodology
This research used both quantitative and qualitative methods for collecting data. The process is divided into 6 steps.
Step 1-Survey: This step focuses on studying the needs of traditional retailers for a business evaluation tool, the problems of using current evaluation tools, and the initial expectations in terms of the characteristics of the evaluation tool. The data were collected through a survey of traditional retail entrepreneurs with quota sampling of province number in each region in Thailand. The selection criteria for the 402 participants were qualified traditional retail operators who own a retail establishment or the person assigned the responsibility of managing such an establishment’s affairs who could be a relative but not an employee. Including, the retail stores are similar in size and there are a variety of physical store locations in each region. Then, the descriptive analysis was analyzed the quantitative by using descriptive statistics with frequency distribution (Percentage). The entrepreneurs had to answers the questions listed by choosing from the answer options in table 1. The questions are following as:
1. Do you have experience with business evaluations?
2. What are the benefits of conducting a retail business evaluation?
3. What problems or obstacles have you encountered in previous business evaluations?
4. Is there a demand for an innovative evaluation tool?
5. What are the benefits of a business assessment?
6. In which format should the traditional retail business evaluation model be developed?
Step 2-Semi-Structured Interviews: This step focuses on identifying the sample’s expectations in terms of the characteristics and performance of the evaluation tool in order to develop the appropriate criteria for evaluating the potential of traditional retail stores. Semi-structured interviews using an interview questionnaire were conducted with 35 entrepreneurs of traditional retail businesses from Bangkok and six regions in Thailand by purposive sampling. The selection criteria for the 35 participants were qualified the entrepreneur who were the sample in survey step and they were willing to participate in the research by giving an interview about their expectation of characteristics and performance of evaluation tool for traditional retail business. Include, five relevant responsible persons who are the experts from organizations in the traditional retail business ecosystem that have mission to help and support small businesses, including traditional retail businesses and have experience in retail business field not less than five years. The question about the participants’ expectations in terms of the characteristics and performance of a business evaluation tool used to evaluate the potential of traditional retail stores is “What are your expectations of the characteristics and capability of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail business? The answers were then used to inform the development criteria for a business evaluation tool for traditional retail business.
Step 3-Data Cleaning: The data cleansing method conducted by the researcher involved transcribing the data obtained from the 35 traditional retail entrepreneurs and five representatives from organizations operating in the traditional retail business ecosystem. Next, we selected the answers which related the activities that affect the income of the business. Then, the data were coded and mapped.
Step 4-Data Modelling: An affinity diagram was used to organize the number of ideas and consolidate the information related to the key success factors in order to develop the criteria for a business evaluation tool.
Step 5-Data Analysis: This step, thematic analysis was use to analyze the qualitative data because, it involves the ordering of the findings into descriptive categories around which most or all of the main elements of the data results can be presented. Including, identify the main topics from the interview data.
Step 6-Prototype Development: The data were analyzed in order to develop a conceptual prototype design which was validated by retail business experts and technology developers including Thai traditional retailers who had achieved success in their business by using an innovation thinking process to develop an evaluation tool for a traditional retail business. This step involved five sub-steps as follows; Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and test.
Research Results
Step 1-Survey
In this step, the descriptive analysis was analyzed the quantitative by using descriptive statistics with frequency distribution (Percentage). Information on the needs of an evaluation tool for traditional retailers, the problems of using current evaluation tools, and the initial expectations of the characteristics of the evaluation tool was collected from 402 entrepreneurs from Bangkok and 6 other regions of Thailand. The survey results are revealing the opinions of the 402 respondents, these results show that 370 respondents (92.04%) had never conducted a retail business evaluation, while only 32 respondents (7.96%) had done so. Of the 32 respondents who had conducted a retail business evaluation, 18 (56.25%) felt they had benefited from understanding the business potential, while the other 14 (43.75%) believed they benefited from understanding the entrepreneur’s potential. In terms of the obstacles or problems encountered by these 32 respondents, the main issue was being unable to answer some questions because their business operations were not in accordance with the question. However, 354 of the 402 respondents (88.06%) thought that they would like to use an innovative evaluation tool to develop their traditional business. In addition, the respondents expected that an innovative evaluation tool would be useful in terms of helping them develop their retail business to a higher level, identifying and addressing the flaws in their operations, and providing information that could serve as guidelines for the further operations. Furthermore, all of the respondents said that they would like the innovative evaluation tool to be accessible via mobile devices. Thus, this step identifies the research gap and opportunity for developing a traditional retail evaluation tool that fulfills the users’ needs and objectives by development the questionnaires easy for understand with accessible via mobile devices.
Step 2-Semi-Structured Interviews
The results from the interviews revealed a wide variety of opinions regarding entrepreneurial issues in past business evaluations, as well as expectations on the features that should be included in a business evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses. The raw data from the transcriptions was separated and grouped into similar issues that were shown detail in the data analysis step.
Step 3-Data Cleaning
In the data cleansing step, transcribing was used to convert audio to text. This text was then classified into significant messages on the same topic, which were then written down in text boxes. The results of this step are following:
1. The results of data cleansing after transcription and classification about expectations of the characteristics of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses according to entrepreneurs consist of 8 items.
2. The results of data cleansing after transcription about expectations of capabilities of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses according to entrepreneurs consist of 20 items.
3. The results of data cleansing after transcription about expectations of capabilities of innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses according to organization representatives consist of 12 items.
Step 4-Data Modelling
In this step, the affinity diagram was the tool used for classifying and grouping the data after cleansing. The results of this step are following as:
1. The results of data modelling with an affinity diagram about expectations of characteristics of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail business according to entrepreneurs from 8 items can be divided into 2 groups.
2. The results of data modelling with an affinity diagram about expectations of capabilities of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail business according to entrepreneurs from 20 items can be divided into 4 groups.
3. The results of data modelling with an affinity diagram about expectations of capabilities of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail business according to organization representatives from 12 items can be divided into 4 groups.
Step 5 - Data Analysis
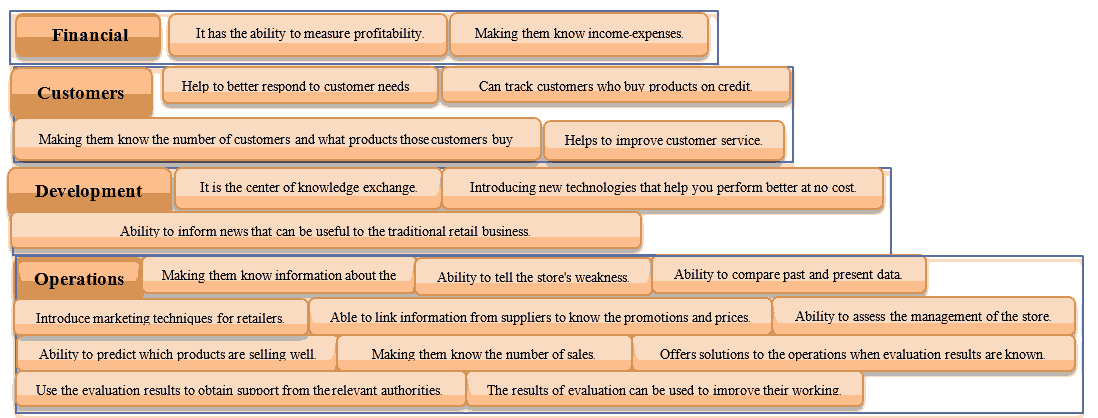
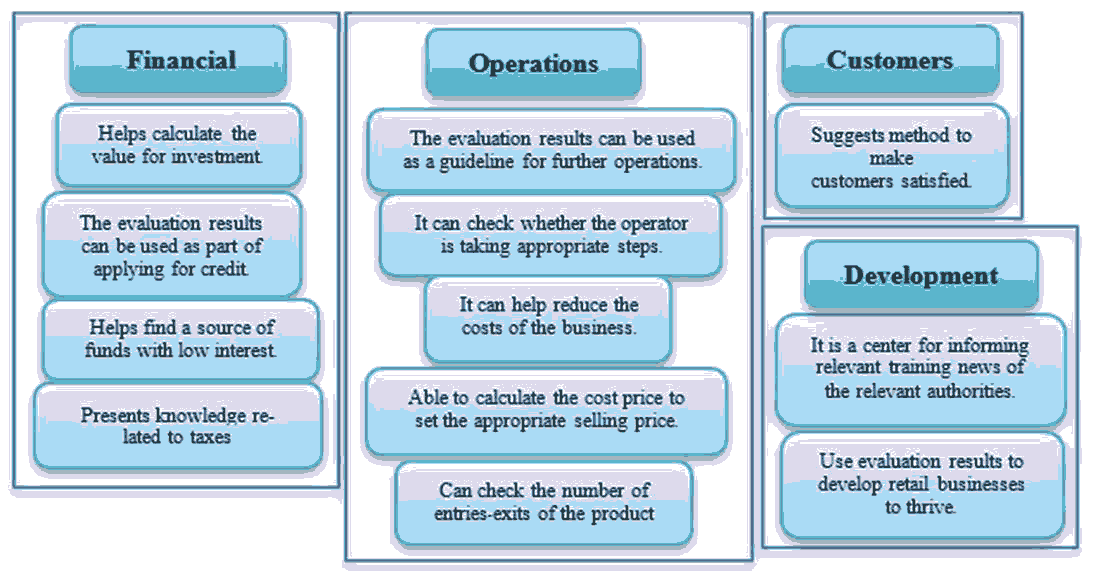
Thematic analysis was used as a tool to analyze the data and map entrepreneurs’ needs from a traditional retail business evaluation tool. The results of the data analysis are summarized below and shown in Figures 2-3.
Expectations of the Characteristics
The expected characteristics of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail business from the perspectives of entrepreneurs can be summarized into the following categories:
Category 1: Usability; easy access to the system, easy to use, works with all devices, keep evaluation results for later reading, fast assessment processing and the questions in the evaluation should be concise and easy to understand.
Category 2: Value; free of charge and reliable.
Expectations of the Capabilities
The expectations of the capabilities of an innovative evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses from the entrepreneurs and organization representatives are summarized into the following topics:
Topic 1: Financial
Topic 2: Operations
Topic 3: Customers
Topic 4: Development
Figure 2:Results Of Data Analysis Using Thematic Analysis: Expectations Of Capabilities Of An Innovative Evaluation Tool For Traditional Retail Business According To The Entrepreneurs
Figure 3:Results Of Data Analysis Using Thematic Analysis: Expectations Of Capabilities Of An Innovative Tool For Traditional Retail Business According To Organization Representatives
Step 6-Prototype Development
We analyzed the data to develop a conceptual prototype design with was validated by various professionals, including retail business experts and technology developers and by using an innovation thinking process to develop an evaluation tool for a traditional retail business. The results are as follows:
Empathize: Traditional retail businesses typically involve a single business owner who sticks with legacy operating patterns causing invisible problem.
Define: The main problem of traditional retail businesses is that the entrepreneurs have low awareness of their business potential because of the problem of the use and value of evaluation tools.
Ideate: The evaluation tool for traditional retail businesses should be easy to use and should be developed as a program that can be used on all devices including mobile phones. The questions in the evaluation form should cover all aspects of the business. Thus, they can be categorized into 4 main topics: 1) financial, 2) customers, 3) operations and 4) development as shown in the data analysis step.
Prototype: A prototype evaluation tool was developed that is suitable for the users with easy-to-understand questions covering retail business operations in 4 main topics—financial, customers, operations and development—that have a positive effect on their income or turnover.
The questionnaires were designed by use the result of data analysis that can arrange 4 topics. Next, researcher establish the question that relate the efficacy of retail business’s activities and easy to understand with 40 items with balance in 4 topics. Then, we had asked the experts who has researched on creating the evaluation tool and retail businesses review and comment on the quality of the questionnaire from their discretion regarding the content validity, the consistency and the comprehensiveness of the questionnaires in the definition and composition of the conceptual framework. The Index of Congruence (IoC) of the questionnaire for evaluation tool was 0.916. The reliability of the question by Cronbach's Alpha Coefficient was 0.974. The reliability for evaluate about financial perspective was 0.877, customer perspective was 0.834, operation perspective was 0.850 and development perspective was 0.986. This shows that the questions in this evaluation business is reliable. After that, we developed the method for calculating the results of evaluation business by finding the sum of the weighting and rating. Finally, compare the score level to know the potential level of their business.
Test: The researcher took the business evaluation form to the entrepreneurs who the same participants in semi-structure interview step to test in terms of its efficiency, suitability and acceptance. It was found after they used it that the mean of the perceived potential of the traditional retail business was significantly higher than before, at 0.05. The interesting results that were found after the entrepreneurs tested it showed that they see benefits in many areas, resulting in a significant increase in the importance of business assessments.
The development of the traditional retail business assessment was based on qualitative research. The data used to develop the questionnaire were obtained from interviews with retail business entrepreneurs. Therefore, the researcher sought to verify the data by using data triangulation: 1) compared the data in terms of the location of data collection (6 regions of Thailand and Bangkok), 2) compared trends of the relationships between evaluation results and income levels, and 3) compared the evaluation results from internal sampling and external sampling. The results of the analysis were as follows:
1. The results of comparing the data in terms of the location of the data collection (6 regions of Thailand and Bangkok) N=35 entrepreneurs. It can be seen that the mean performance levels of traditional retail stores under similar condition in different regions are close to each other, except the mean score of the central region that differs from the previously collected data. In fact, there was a significant drop in traditional retail sales during the Covid-19 pandemic, consistent with the results recorded by the researchers.
2. The results of comparing trends of the correlation between evaluation results and income level by box plot that shows the empirical data reveal that the score levels tend to be related to income levels.
3. The results of comparing evaluation results from internal sampling and external sampling. It was found that it was not statistically significant difference at 0.05, with the internal sample having a mean score of 3.85 and the external sample having a mean score of 3.97.
Discussion and Conclusion
This study was found the small businesses operated by one owner, such as traditional retail stores, often operate in the same way and have low awareness level of business evaluation. They tend to be blind to failures in their business operations consistent with the theory that has been preliminarily studied.
In addition, authority that has a mission to support traditional retail business has previously developed business evaluation tools that they believed could be used to evaluate all types of businesses in this ecosystem, which is in contrast to the opinion of traditional retail entrepreneurs, who said the current evaluation is not appropriate for themselves. Especially regarding the questions used in the evaluation, there are multiple activities that traditional retail businesses do not perform, such as systematic accounting and the purchasing system then make the evaluation is unsuitable to the user.
To develop the questions for a prototype evaluation tool, we used data obtained from interviews with 35 entrepreneurs and representatives from another 5 organizations operating in the business ecosystem of traditional trade. From the obtained data, we identified 2 main topics that relate to characteristics of an evaluation tool are usability and value. Including, 4 main topics that relate to the good performance of the business: 1) financial, 2) customers, 3) operations, and 4) development. The entrepreneurs focus on their operations and customers, which they believe will affect income, while the organization representatives focus on financial management the most. This contradicts Iyibildiren and Karasioglu (Iyibildiren et al., 2018) who present about business evaluation methods, which are based on only financial criteria, are not enough to evaluate the performances of the enterprises today. While, the balanced scorecard principle in which all four areas should be balanced to make the business operations more efficient and sustainable (Kaplan & Norton, 2007; Laketa, 2015). The validity of the questions was checked by Index of Consistency (IoC) of content validity and construct validity analysis. After the validity was confirmed, we incorporated the questions into an application form that could be accessed via computer, notebook or smartphone. Finally, we tested the evaluation tool on the entrepreneurs. From this testing, we found that the entrepreneurs’ awareness level of their business was significantly higher than before using this evaluation tool. One interesting result after the entrepreneurs tested the business evaluation form was that they could see benefits in many areas, resulting in a significant increase in their perceived importance of business evaluation that present. Moreover, it showed that the business evaluation tool was effective in helping them perceive their business potential level. Including, there was suitability for use and generate significant user acceptance.
It can be concluded that the appropriate business evaluation tool was developed via mobile web application can make them more convenient and easier to use including recognize the value of business evaluation from result that reflect their business potential level. Moreover, there are the suggestion that present in application can be used to guide effective business development. Which, they expressed their confidence that it would help them free from sticking to the old patterns that have been working on for a long time and help them to develop methods of operation that will make their business prosper and achieve sustainability.
However, to ensure confidence in the result of evaluation, the researcher applied data triangulation. The results of examine on all three s showed that the evaluation score scale tends to be related to income level that consistent with the observations of the researcher while visiting the area.
This research was limited because this evaluation tool was run on mobile and computer devices via the internet. Therefore, in some areas that have an unstable internet connection, the evaluation tool may not be used effectively. In addition, the elderly traditional retail entrepreneurs may have some restrictions on using mobile phones. They may also not be interested in business evaluations.
In future research, we would like to conduct a deeper study of the technological capabilities of traditional retailers in order to develop the business evaluation alert system for remind entrepreneurs to conduct an assessment when the assessment period is reached to make continuous business assessment. Including sending a message of potential level reports to remind them to work according to good operating practices to sustainability of their businesses.
References
- Avdeeva, I., Golovina, T. & Polyanin, A. (2021). Change management strategy for the activities of business organizations. Paper presented at the SHS Web of Conferences.
- Bandera, C., Bartolacci, M.R., & Passerini, K. (2016). Knowledge management and entrepreneurship: A contradictory recipe. International Journal of Knowledge Management, 12(3), 1-14.
- Birimisa, M.E. & Wegener, H. (2013). Tool for evaluation of business services. Google Patents.
- Dahana, W.D., Miwa, Y., Baumann, C., & Morisada, M. (2020). Relative importance of motivation, store patronage, and marketing efforts in driving cross-buying behaviors. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 1-29.
- Dahmen, P., & Rodríguez, E.J.N.A.E.I.Q.L. (2014). Financial literacy and the success of small businesses: An observation from a small business development center. Numeracy, 7(1).
- Dalkir, K. (2017). Knowledge management in theory and practice. MIT press.
- Department of Business Development (2018). Situation of Traditional retail business.
- Ewais, A., Hodrob, R., Maree, M., & Jaradat, S. (2021). Mobile learning application for helping pupils in learning chemistry.
- Fernández-Guerrero, R., Revuelto-Taboada, L., & Simón-Moya, V. (2012). The business plan as a project: An evaluation of its predictive capability for business success. The Service Industries Journal, 32(15), 2399-2420.
- Hislop, D., Bosua, R., & Helms, R. (2018). Knowledge management in organizations: A critical introduction. Oxford University press.
- Hussain, J., Salia, S., Karim, A., & Development, E. (2018). Is knowledge that powerful? Financial literacy and access to finance: An analysis of enterprises in the UK.
- Iyibildiren, M., Karasioglu, F., & Research, B. (2018). Balanced scorecard in business performance measurement and its effect on financial structure. Global Journal of Management and Business Research: C Finance, 18(2).
- Jermsittiparsert, K. (2020). The moderation effect of supply chain information technology capabilities on the relationship between customer relationship management with organizational performance of thai restaurants and hotels. New York: ACM. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on E-Education, E-Business, E-Management, and E-Learning.
- Jermsittiparsert, K. & Boonratanakittiphumi, C. (2019). The mediating role of knowledge management and the moderating role of additive manufacturing (Industry 4.0) in the relationship between knowledge management capability and firm performance: A Case of KPMG Thailand. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 8(8), 430-449.
- Kaplan, R.S., & Norton, D.P. (1996). Using the balanced scorecard as a strategic management system.
- Kaplan, R.S., & Norton, D.P. (2007). Balanced scorecard. Das Summa Summarum des Management: Springer.
- Laketa, M., Sanader, D., Laketa, L., & Misic, Z. (2015). Customer relationship management: Concept and importance for banking sector. UTMS Journal of Economics, 6(2), 241 254.
- Levy, M., & Barton, A. (2007). Weitz.
- Morita, M., Umezawa, T., & Kubo, O. (2006). Business evaluation supporting method. In: Google Patents.
- Papadakis, S. (2020). Tools for evaluating educational apps for young children: A systematic review of the literature. Interactive Technology and Smart Education, 18(1), 18-49.
- Parvatiyar, A., & Sheth, J. (2001). Customer relationship management: Emerging practice, process, and discipline, 3(2).
- Perguna, L., Idris, I., & Widianto, A. (2021). From paper to screen: Encouraging theory of sociology through sosiopedia by heutagogy approach.
- Porter, M.E. (2011). Competitive advantage of nations: Creating and sustaining superior performance: simon and schuster.
- Saengchai, S., Sawasdee, A., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2019). The knowledge management, product innovation, and process innovation as antecedents of sports manufacturing firms of Thailand. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise, 14(5 Proc), S2217-S2231.
- Santithon, P. (2011). Competitive marketing strategies for retail businesses.
- Tao, F. (2014). Customer relationship management based on increasing customer satisfaction. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 5(5), 256-263.
- Tesch, J., & Brillinger, A. (2017). The evaluation aspect of digital business model innovation: A literature review on tools and methodologies.
- The National Statistical Office (2018). Official statistics list: Number of people working in a retail business establishment.