Research Article: 2018 Vol: 22 Issue: 3
Innovation of Entrepreneurship Learning With Business Model Canvas Game
Jajat Sudrajat, Bina Nusantara University
Muhammad Ali Rahman, Bina Nusantara University
Glory A Guzman, Bina Nusantara University
Michael Yoseph Ricky, Bina Nusantara University
Abstract
This study aims to produce entrepreneurship learning model using Business Model Canvas Games to improve information and communication technology content in entrepreneurship learning process. The expected benefit of this research is to be useful for educational institutions to develop entrepreneurial learning models, and the specific targets to be achieved from this research are expected to be useful for the Binus Entrepreneurship Centre (BEC) unit to create innovative entrepreneurship development. Learning process, Participants of this research are students of Binus Game Application Program who have taken EN001 and EN002 subjects. This research uses Research and Development method. The results prove that students can understand BMC by creating prototype BMC Games products, in the form of game software applications to facilitate socialization to students and lecturers EN001 and EN002. Based on a survey of 34 students who have attended entrepreneurial courses at Binus University, they found that 76.5% said it was interesting to learn entrepreneurship using the concept of games or business model applications on smartphones. 17.6% said unattractive, 5.9% did not comment.
Keywords
Learning Entrepreneurship, Business Model Canvas Games, Improve Learning.
Introduction
Indonesia President Joko Widodo wants social media to be used for productive things, encouraging creativity and innovation and improving people's welfare. The rapid development of information technology must be directed, utilized in a positive direction, towards the progress of the nation, to increase knowledge, broaden the horizons and spread positive values, hard work values, integrity values and honesty, the values of tolerance and peace, the values of solidarity and nationality. To encourage creativity and innovation, education plays an important role including entrepreneurship education to educate self-reliance. With this research, it is hoped that the result can accelerate student's independence through innovation of entrepreneurship learning that attract student interest through game or business simulation, where Innovation targets three categories: product, service and business model (Deschamp, 2005).
Innovation in learning entrepreneurship needs to be done because of various problems and challenges: Problems experienced by students so that this research is important, as one solution to answer student problems that is difficult to start a business, with many courses to take and tasks to be done on campus, their side is also motivated by entrepreneurship lecturers as well as their parents to dare to start a business. They have been given business lessons in entrepreneurship courses, where they are given the concept of Business Model Canvas as one of the solutions to understand business. Almost all students have a smartphone to support their day-to-day activities on campus; they are used to using social media to communicate. But the smart tool has not been optimized for learning and doing business. One of the solution of the students is given business applications using the concept of Business Model Canvas, this business application can help the prospective entrepreneurs, especially students, because in this application can learn how to do business and can find a business partner link.
In Indonesia, there are now 132 million active internet users or about 52% of the total population. Of 132 million internet users in Indonesia, 130 million internet users are social media users (We Are Social, 2018).
Of the 132 million internet users mentioned above, the majority used by productive age such as students. Social media for them is the main media to communicate. Ironic indeed, on the one hand, they must learn and on another many temptations and challenges are faced by young people today through smartphones. A few lecturers forbade students to activate the smartphone in class, although smartphone has a lot of useful information that supports their learning process. The phenomenon of Gojek application inspires the young generation to create an application that has an impact on employment, speed, convenience, transportation industry innovation and other positive impacts.
Indonesia Minister of Communications and Informatics, Rudiantara, plans 10.000 Technology Businesses Start Up. Minister of Research and Technology, Mohamad Nasir, is proud to inaugurate the Smartphone Rakyat Indonesia (Smartphone of Indonesian people).
Based on the president's wishes and followed by supporting programs in various ministries, authors as entrepreneurship lecturers develop continuous research in creating innovation to learn entrepreneurship to accelerate student independence.
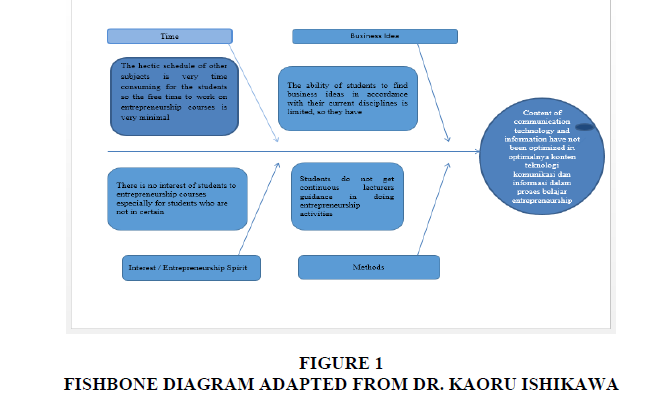
Currently, the fundamental problems experienced by students are as follows: (1) The hectic schedule of other subjects is very time consuming, so the leisure time to work on Entrepreneurship courses become very minimal; (2) The knowledge and experience possessed by the students in terms of entrepreneurship activities is limited; (3) Students do not get continuous lecturers' guidance in entrepreneurship activities.
Lecturers' opinions based on the observation and direct statement from the students are as follows: (1) It is not in the minds of students to engage in entrepreneurship activities to achieve bachelor degree; (2) Students do not have any interest in entrepreneurship course, especially for students who are not in certain disciplines (engineering, psychology, literature, and other faculties); (3) The ability of students to find business ideas in accordance with their current disciplines is limited, so they have difficulty to innovate according to their own expertise.
The purpose of this research is to create innovative learning of entrepreneurship through Business Model Canvas Games (BMC Games), where during two semesters, students of all study programs at Binus University must taking Entrepreneurship 1 (EN001) and Entrepreneurship 2 (EN002) courses. And one of the learning concepts is all students who have followed EN001 and EN002 should have a better understanding of the Business Model Canvas, whether for Start-up or business development. BMC Games is expected to facilitate students to learn while playing games so that their Smartphone becomes more productive and another expectation is this learning concept can also be accepted by other educational institutions in Indonesia. The targeted invention/innovation is to determine the model of entrepreneurship learning process using the concept of Business Model Canvas (BMC), so it can be better understood by students through BMC Games in Smartphone, and its application to support the development of science and technology-social and culture is to develop and improve the content of information technology and communication in Entrepreneurship learning process.
In this study provide inspiration for educators, researchers and policy makers on how to conduct an assessment that motivates students learning innovation and entrepreneurship (Seikkula-Leino et al., 2016). Business Model Canvas Game is one of the tools to motivate students so that they are motivated to learn entrepreneurship, as they are interested in playing games. In line with this research that the limitations of this study are descriptive and only based on educator perspectives (Seikkula-Leino et al., 2016). For that Business Model Canvas Game will provide more knowledge about the relationship between educator assessment and innovation and entrepreneurship learning outcomes by covering student perspective, because students will play Business Model Canvas games so they feel their experience.
High educational institutions should consider producing entrepreneur graduates. Entrepreneurship education in college must be fully reviewed and changed. Clear goals should be established on developing entrepreneur-oriented graduates, so that the education process will require a lot of restructuring to improve the development of entrepreneurship skills (Taatila, 2010). Business skills can be learned through the Business Model Canvas Game so that students' managerial competencies will develop, in particular, the relationships between entrepreneurial managerial competencies such as administrative, knowledge and technology competencies, network building competencies, communication skills, business development models and financial capacity achievement and start intentions self-employed and innovative investigated. (Motahareh and Sung, 2017).
Previous research that addresses the development of entrepreneurship education is the result of research on "Survey for Entrepreneurship Education Framework (Chris Parsley, 2010)". There are six dimensions of the survey which is a fundamental element in determining the framework of entrepreneurship education. Surveys are divided into several dimensions and sub dimensions as follows.
Strategy
Policies and objectives that describe undergraduate/postgraduate programs of an institutional commitment to entrepreneurship education:
1. The purpose of entrepreneurship: The goal of entrepreneurship is embedded in the institution's mission statement or the overall purpose of promoting entrepreneurship.
2. Entrepreneurship policy: A long-known policy within an institution or activity plan to support entrepreneurship.
3. Embedded strategy: Designated parties (assistant professors/lecturers/professors/deans/vice rectors and structural employees in the Entrepreneurship section) with management directives to oversee the implementation of policies and objectives.
Institutional Infrastructure:
Out-of-class support sources for those interested in entrepreneurship:
1. Approach: Access to entrepreneurship departments, entrepreneurship centres, facilities and technology transfer offices.
2. Appointment to entrepreneurship: Designated entrepreneurship responsibilities (permanent or non-permanent), excluding colleagues and assistant professors, to support entrepreneurship on campus.
3. Research in entrepreneurship: Research in entrepreneurship and entrepreneurship education.
4. Interdisciplinary Structure: A structure to allow students to receive credit towards their degree of entrepreneurship graduation. This sub-dimension also considers cross-faculty entrepreneurship activities to offer opportunities for different faculty students to work together.
Resources
Financing and resources available for entrepreneurship education:
1. Budget allocation: Financial support for entrepreneurship education and overall budget for entrepreneurship.
2. Source of income: Money that arises as a result of entrepreneurship education.
3. Type of Funding: An existing financial commitment to entrepreneurship education (short, medium or long term financing).
Teaching and Learning
The theoretical learning component of entrepreneurship education:
1. Subject: Number of credits from entrepreneurship education, with education level (diploma, bachelor and postgraduate).
2. Study Program: Access to study programs in entrepreneurship, with education level.
3. Curriculum: Methods used in developing an entrepreneurship curriculum, such as learning from other institutions (at home and abroad), in collaboration with practitioners or collaborations among faculties/disciplines.
4. Teaching methods: Lectures, case studies, practitioners, project teams, company visits, and/or practical work.
5. Extracurricular activities: Seminars, business plan competitions, company visits, meetings between students and outside business owners, training schemes.
Development
The processes given for evaluating and monitoring the effectiveness of entrepreneurship education:
1. Evaluation: A formal evaluation procedure.
2. User-based improvements: Evaluation of entrepreneurship courses to measure course outcomes from student and user perspectives (investors and business people, etc.).
3. Human resource management and development: Recognition of staff achievement in entrepreneurship education, staffing needs for entrepreneurial experience, inviting guest lecturers.
Outsiders
Relationships with communities and students related to experience of entrepreneurship:
1. Alumni: Staying in touch with alumni, alumni who are involved in entrepreneurship activities.
2. Stakeholder relationships: Existing relationships with foundations, private companies, entrepreneurs, governments, groups of scientists, incubators, or specialized institutions in entrepreneurship.
3. Community involvement: Students involved with practical work, project work, and business competitions to develop entrepreneurial thinking and skills.
There are three types of educators and entrepreneurial students: sceptics, followers and innovators. Student and educator's perception of entrepreneurship education, how they understand entrepreneurship as part of their future pedagogical work, so the most important and necessary to develop entrepreneurial education for future educators is to clearly explain the concept of entrepreneurship. A learning environment should enable students and faculty to approach the topic informally, allowing them to comfortably compare different critical views. Next maximizing the benefits of such an environment necessitates an informal coaching and encouraging the learning atmosphere, as well as the multi-professional cooperation.
In previous research on entrepreneurship education that entrepreneurship education contributes to complexity and heterogeneity in entrepreneurship education, thereby combining educational psychology with the perspective of entrepreneurship education research to understand how the assumptions of teaching guides. The research results understand that combining various learning theories and approaches in order to promote entrepreneurial awareness and mind-set. It is also necessary for entrepreneurship education to be student-centred and focused on life experience and practice learning, so that a variety of theoretical learning can be combined with practice experience (San Tan and Ng, 2006).
The concept of Business Model Canvas Game provides students with experience for business simulation so that a combination of practice and theory experiences can be integrated. Other research results suggest that entrepreneurship intentions for graduates are very low compared to working in companies, they are more interested in working first so that establishing the company will be done as they have experience. This appeals to curriculum makers and policymakers so that it becomes important information for the development of entrepreneurship education in the future. The positive effects of entrepreneurship education on the future plan of graduates to start a business are possible through independent selection so that the quality of educational content is entrepreneurial in terms of academic and teaching content as well learning methods require further attention. This would make more sense for some students to take entrepreneurial education comprehensively (San Tan and Ng, 2006).
Based on some previous research on entrepreneurial learning, it takes innovation and entrepreneurial learning methods that combine case studies and theory, where case-based methodology is an effective pedagogical approach to entrepreneurship education although it is generally recognized that entrepreneurship can be taught. It is found that case studies that stimulate entrepreneurial intuition within the classroom to enhance the appreciation and capacity of students for entrepreneurship. Pedagogical practice may not be significant as a viable means of enhancing the efficacy of entrepreneurship education, this case study is a sign of entrepreneurship education and researchers could be placed on developing innovative practices for entrepreneurship education (San Tan, 2016), in line with the concept of Business Model Canvas Game where each type business can be simulated based on business model (San Tan and Ng, 2006).
Methods
Research method to be used in this research is Research and Development method using Business Model Canvas Games (BMC Games). According to Dharma (2008), Research and Development Method is a series of processes or steps to develop a new product or refine existing products to be accountable. These products are not necessarily in the form of objects or hardware, such as books, modules, learning aids in the classroom or in the laboratory, but can also be software, such as computer programs for data processing, classroom learning, libraries or laboratories, or models of education, learning, training, guidance, evaluation, management systems, and others.
To identify the cause of the problem information and communication technology content have not been optimized in entrepreneurship learning process, the following are presented in the form of fishbone diagram (Figure 1) (Source: Jajat Sudrajat, 2017).
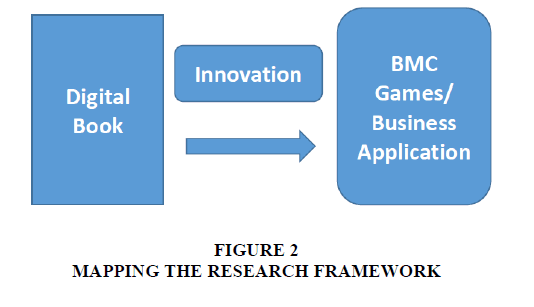
The following is the framework of Research and Development (Figure 2) (Source: Jajat Sudrajat, 2017).
Making the process in collecting data and analysing business applications model or business model canvas is as follows:
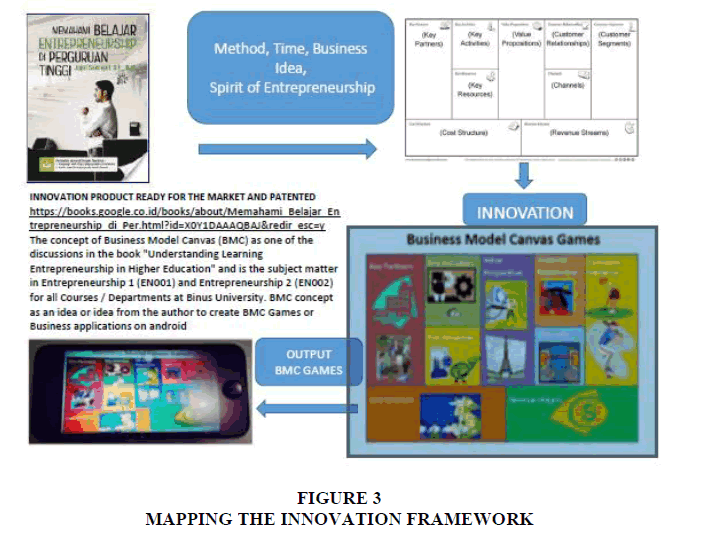
The framework of the stages (Figure 3) (Source: Jajat Sudrajat, 2017) in the process of implementation and manufacturing mechanisms rather than the Business Application Model follows the steps of software development life cycle (SDLC) waterfall and followed the long working time of each step are:
a) Needs analysis (2 days/2 meetings); Entrepreneurship lecturer discuss with Head of Department of Game Application Technology and Head of Visual Communication Design Department to formulate input, process and output of business model application. This is our first collaboration with different departments and competencies, as entrepreneurial courses are given to all majors.
b) System design (5 days/5 meetings); After the concept of business model application is made in accordance with the needs, followed by the system design process, where entrepreneurship lecturers meet again with lecturers and 7 students majoring in computer with the field of game application, to re-convey the concept of Business Model Canvas (BMC), where all students have get the course in 2 semesters, in this system design they will apply BMC in the form of game simulation or business model application.
c) Implementation and testing (1 semester/6 times progress report); in this stage, with the following process: (1) Create a business name or business theme Coffee Set and Coffee business type; (2) Gamification, Feature, Generate Assets, Balancing, Re-Balancing, Dummy Test Prototype, Valuing Mechanic; (3) Splash Screen; (4) Texturing; Fork, Spoon, Building (fastfood); (5) Model+Texture; (6) Progress so far: Create 3D model for game that is building and knick-knacks-Building model there are 15 pieces-3D building model not yet in un-erap live building: diner and accessories-for the knick-knacks made are; 3 trees, cars, fences-there will be additional models from the designer; (7) Gamification Features; (8) Player Mechanics.
d) Key Features: Entities; Business Partners & Competitors-Customers; Population & Demographics-Locations; Districts & Transports-Resources; Materials & Relationships-Variables; Trends & Events.
e) Supporting Features: Bank & Loan System-Procedural World; Generation-Evolving World; Conditions-Research Mechanic; Content Systems. Core Simulation: KP: Business partner systems-KA; Activity systems-KR; Material &am p; Asset system-CR; Media penetration system-CH; District channel system-CS; Community & Preparance system. Other: Banks & Courts-Random events; trends-All business owner’s behaviour.
Results And Discussions
Previous studies undertaken (Warhuus et al., 2017), (Taatila, 2010), (Seikkula-Leino et al., 2015), (San Tan and Ng, 2006), focus on entrepreneurship education and learning, not specific to innovation and application development using the Business concept Canvas Model. Besides, there has never been any innovation learning Business Model Canvas with game media. Based on a survey of 34 students who have attended entrepreneurial courses at Binus University, they found that 76.5% said it was interesting to learn entrepreneurship using the concept of games or business model applications on smartphones. 17.6% said unattractive, 5.9% did not comment. The results achieved in the implementation of this research, the prototype of BMC Game (Figure 4) (Source: The Pluto Project group at Game Application & Technology Laboratory Binus University, 2017) in the form of software, is an innovation of Learning Entrepreneurship as and input to use Smartphone or Android applications as a formal learning media.
The System Capabilities
Build More Cash lets players learn how to manage a business using the Business Model Canvas framework. Players play as the owner of a budding coffee business, where they have to apply these key Business Model Canvas principles: Key Partners: review and accept/reject partnership offers, Key Activities: research, devise and execute routine business activities, Key Resources: buy assets, materials, etc., Value Proposition: create coffee recipes, manage prices, Channels: build stores to increase sales, Customer Relationship: advertise to increase outreach, Customer Segments: review and target certain demographics, Cost Structure: review overall cost or operation and Revenue Streams: review business revenues Build More Cash helps aspirinf entrepreneurs and high school student in understanding and applying Business Model Camvas wheter in real business situations or in entrepreneurship classes.
Technical specifications of technological innovation products and technical data of innovation products including size, dimensions, components/raw materials of Business Model Canvas Game have specifications such as; Engine:Unity, Browser:N/A, Mobile:Android, PC:N/A, Wordspace:N/A, Domain:N/A and Resolution:1920x1080.
Product model business applications, currently in the form of prototype, because the test has not been tested error, before launched to the student. Still need work process until it can be upgraded on android device. This business model application product is the idea of an entrepreneurship lecturer delivered to the head of the Department of Game Application and Visual Communication Design, then followed up and made by 7 students in the Pluto Project group at Game Application & Technology Laboratory Binus University.
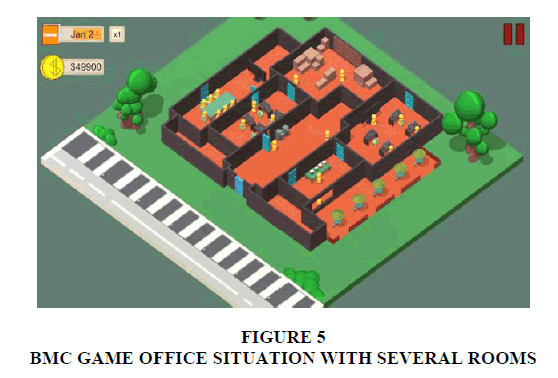
Example of BMC Game (Figure 5) (Source: The Pluto Project group at Game Application & Technology Laboratory Binus University, 2017) by describing the office situation with several rooms, 9 room describes the room based on the main function in the company is the financial department that is responsible for managing the Cost Structure and Revenue Stream in the concept of BMC Game and other functions. With these game students are expected to better understand the main functions of the parts within the company in general such as the financial, production, marketing, logistics and general, personnel or human resources. And can understand 9 blocks in Business Model Canvas concepts are Customer Segments, Customer Relationships, Value Propositions, Key Activities, Key Partners, Key Resources, Channels, Cost Structure and Revenue Streams.
Examples of Key Activies concept companies (Figure 6) (Source: The Pluto Project group at Game Application & Technology Laboratory Binus University, 2017), this concept describes the company's business model in conducting business activities. In this game exemplified the company in the field of coffee, of course the business model in the field of coffee a lot, ranging from a simple coffee shop, coffee cafe, coffee factory, coffee farmers, coffee traders, coffee exporters, each has a business model, so students will better understand how the activities of one company with other companies in serving customers.
Example of the Key Resource concept (Figure 7) (Source: The Pluto Project group at Game Application & Technology Laboratory Binus University, 2017), to illustrate how much resources are needed and how much it costs to pay for those resources, in accordance with its business model, as in this example the coffee shop business will certainly have less resources than coffee or coffee cafes, but if the business model of coffee shops there are 100 coffee shops in some places would require resources that are not small compared to coffee cafes that only 1 place. Students will better understand what key resources a business needs. Key Resource may be in the form of fixed assets such as buildings or other equipment, may also take the form of human expertise in a particular field.
The following are the research results generated according to the requirements of the research scheme: (1) Prototype already generated in the form of software; (2) Video of the prototype is made for promotion to student and lecturer to teach EN01 in odd semester 2017; (3) the authors use this method to test the following hypotheses: a) Students have the inspiration for the business idea by joining Entrepreneurship class; b) Students are interested in learning the concept of BMC with BMC Games/Business Applications.
In the research implementation, the activities are as follows: (1) Cooperation with Lecturers and Students of 3+1 Game Application Technology (GAT) Program to create BMC Game Prototype; (2) Meeting with Team Members to formulate BMC Games; (3) Each GAT Team periodically presents progress; (4) Socialization with other BEC Lecturers to get input, via the submitted videos in Whatsapp group of BEC Lecturer; (5) Invite other lecturers to work together to develop BMC Games
Conclusions
Based on long-term objectives in this research, that is to produce learning model of entrepreneurship by using Business Model Canvas Games, then the conclusion we can convey: the prototype is in the form of simulation software made technically by 3+1 student of Game Application Technology with lecturer guidance and the 3+1 program students consist of 6 people who have attended Entrepreneurship course. They can translate Business Model Canvas theory into a business simulation game.
The implications are:
1. For the development of BMC Game, it is expected that the next 3+1 program can continue the development of other game types.
2. The research across major will result in a more interesting BMC Game because BMC is studied by students of all majors.
References
- Abrams, R. (2008). What Business Should I Start? Yogyakarta: Kanisius.
- Deshcahamps, J.P. (2005). Strategy and Leadership. Emerald Insight, 33, 31-38.
- Kusumastuti, D. (2005). Analisa hubungan & pengaruh gaya belajar individu terhadap kompetensi entrepreneurship. Bandung: Fakultas bisnis & manajemen Universitas Widyatama.
- Lans, T. (2013). Learning for Entrepreneurship in Heterogeneous Groups: Experiences from an International, Interdisciplinary higher education student programme. Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 17(4), 383-399.
- Osterwalder, A., & Pigneur, Y. (2010). Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
- Parsley, C. (2017). The Teaching and Practice of Entrepreneurship within Canadian Higher Education Institutions.
- Smartphone Rakyat Indonesia. (2017). Retrieved from Ristekdikti: http://ristekdikti.go.id/smartphone-rakyat-indonesia/
- Sudrajat, J. (2016). Memahami Belajar Entrepreneurship di Perguruan Tinggi. Yogyakarta: Deepublish.
- Sudrajat, J. & Rahman, A. (2016). Entrepreneurship learning process by using SWOT analysis. The Winners, 17(1), 67-75.
- Summit Consulting, LLC. (2009). Toward effective education of innovative entrepreneurs in small business: Initial results from a survey of college students and graduates. Retrieved September 20, 2017, from U.S Small Business Administration.
- Wulandari, R. (2017). The impact of entrepreneurial leadership, culture and mindset in innovation strategy to obtain competitive advange: Study in non-formal english education industry in DKI jakarta. Dissertation, Doctor of Research in Management Program Binus Graduate Program.
- San Tan, S. & Ng, C.K.F. (2006). A problem‐based learning approach to entrepreneurship education. Education+Training, 48(6), 416-428.
- Seikkula-Leino, J., Satuvuori, T., Ruskovaara, E. & Hannula, H. (2015). How do finish teacher educators implement entrepreneurship education? Education+Training, 57(4), 392-404.
- Seikkula-Leino, J., Satuvuori, T., Ruskovaara, E. & Hannula, H. (2016). Assessment for learning in innovation and entrepreneurship education. Education+Training, 52, 3-29.
- Taatila, V.P. (2010). Learning entrepreneurship in higher education. Education+Training, 52(1), 48-61.
- Warhuus, J.P., Tanggaard, L., Robinson, S. & Ernø, S.M. (2017). From I to We: collaboration in entrepreneurship education and learning? Education + Training, 59(3), 234-249.
- Motahareh, Z. & Sung, E.C. (2017) Relationship between entrepreneur’s managerial competencies and innovate start-up intentions in university students: An Iranian Case. International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 21(3).