Research Article: 2020 Vol: 24 Issue: 3
Measuring SMEs Productivity Using Social Media: Role of Entrepreneurship
Qaiser Malik, University of Lahore
Ahmed Muneeb Mehta, University of the Punjab
Rabia Abrar, Bahria University Lahore Campus
Ali Sajid, University of Lahore
Tanveer Ahmad, University of Szeged
Abstract
The purpose of the present study was to explore the effect of Entrepreneurial Self-efficacy and Entrepreneurial Attitude on the performance of Small Medium enterprises through the usage of Facebook. It was hypothesized that Facebook usage is likely to mediate the relationship between Entrepreneurial Self-efficacy and Entrepreneurial Attitude on the performance of Small Medium Enterprise. A cross-sectional research design was used in this study. A sample of N=333 admins, social media managers or digital marketing executives, was collected by using a clustered sampling technique. The data processed by using AMOS software. Structural Equation Modeling was used to analyze the model. Results showed that Entrepreneurial Self-efficacy & Entrepreneurial Attitude have a significant association with SME performance through Facebook usage. In the light of results, it is being recommended that Small and Medium Size Enterprise must have their Facebook activities to promulgate their performance.
Keywords
SMEs Productivity, The Impact of Social Media, Organizational Development, Entrepreneurship Growth, Marketing.
Introduction
Small Medium Enterprises play a vigorous role in any country’s development and these provide independence to the economy of any developed or developing country. The SME’s contribute to instigating the country’s economy as these businesses are good absorbent of unemployment and promotes innovation (Griffin & Ebert, 2006). The SMEs prevailing in the developing countries contribute a lot towards the GDP and such ratio of these businesses is higher than Large Scale Enterprises. Small Medium Enterprises play an important role to produce Gross Domestic Product in most Asian countries and such percentage of SME’s contribution towards GDP is 75%. The transformation of any country from under-developed to develop is highly dependent on the performance of the SME Sector. Any country’s confrontation with the low-level technology, the dearth of entrepreneurial skills, the slow pace of information provision, production of the low quality of products and services are such hindrances that do not lead them towards prosperity (Asian Productivity Organization, 2011).
Coad (2007) elucidates that to secure the small business from the failure it is necessary to enhance their performance. The literature indicated that entrepreneurial traits of entrepreneurs contribute to the performance of small businesses (Koenig et al., 2013; Ong & Ismail, 2012). The entrepreneurial traits like self-efficacy and Entrepreneurial attitude have attained enormous interest from the researchers (Khedhaouri et al., 2015; Torres & Watson, 2013).
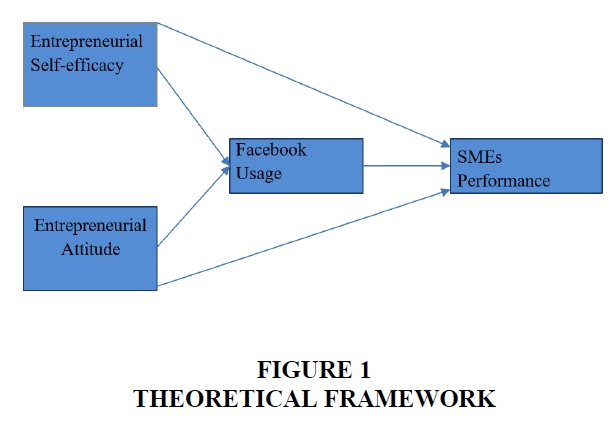
Conceptual Framework
The conceptual framework in this based on the literature review (Figure 1) is given as under:
Literature Review
The writing examined gives underpins about the relationship of pioneering self-viability and an innovative demeanor with the development of Small Medium Enterprises. Additionally, this writing has built up a connection between Facebook use with Entrepreneurial self-adequacy, Entrepreneurial disposition, and execution of SMEs.
Role of Social Cognitive Theory
The Social Learning Theory by Albert Bandura (1986) builds up that the earth causes the conduct and the conduct causes nature and the other way around. This Concept is known as the equal determinism by Bandura. As per this idea of corresponding determinism, the world, just as the practices, are commonly caused. As per Bandura, the human lead must be clarified regarding conduct just as psychological and natural determinants. Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory centers around the idea of support just as perception. This Social Cognitive hypothesis gives more significance and spotlights on the inner procedures and offers significance to the social-psychological hypothesis with others. This hypothesis stresses that perception, just as impersonation, is given over the good examples and these can be guardians, companions, educationists and they can be TV legends. The main way and necessity for learning are that an individual watches the other individual or individual, or watches the models practices which are expected to complete a procedure or direct.
Social Cognitive Theory and Self-Efficacy
Albert Bandura (1982) characterized Self-Efficacy as a "self-judgment of the capacity which is expected to play out an assignment in a particular area". According to Bandura, as individuals work and follow up on their sentiments, musings, and practices; consequently the faith in self-viability gives an incredible effect on the people as they follow up on their conduct and emotions (Bandura, 1995). Garcia et al., 1991 characterizes the self-adequacy variable as a self-evaluation of the capacity to finish an errand and trust in having and achieving those aptitudes which are expected to play out that specific undertaking. As per the Social Cognitive Theory, the feeling of self-adequacy of an individual can be affected through four significant procedures: job demonstrating enactive dominance, social influence and the judgment of one's mental states which incorporates excitement and tension (Bandura, 1986)
Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and Attitude
A few creators have contemplated zones, for example, enterprising vocations and inclinations in the investigation of the business. They have given an examination and proof of the expanding job and accentuation on the variable of self-viability. They have likewise contemplated zones of innovative inclinations, aims, and execution of the customer alongside the pioneering profession (Boyd & Vozikis, 1994; Chandler & Jansen, 1992; Gartner, 1989; Krueger & Brazeal, 1994; Scherer et at., 1989). Consequently, Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy (ESE) is characterized as the certainty of a person in their capacities to play out the pioneering errands and jobs effectively (Chen, et al., 1998; De Noble, Jung et al., 1999). Besides, the self-viability of a business visionary is likewise characterized as the build which can quantify the conviction of an individual in his abilities to begin and dispatch the pioneering adventure or startup effectively (McGee, et al., 2009). Self-Efficacy of a business person is a significant and valuable variable as it is utilized for expanding the feelings of understudies that they can execute the innovative conduct which is important to create the ideal outcome and result which is the new pursuit.
Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and SME’s Performance
Herath & Mahmood (2014) built up a connection between Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and SME's exhibition. The present examination researched the relationship of pioneering self-viability measurements with the presentation of Small Medium Enterprises. The example size right now of 350 little scope inns. Auxiliary Equation Model was actualized right now to process the essential information. The outcomes demonstrated that businesspeople having high useful abilities perform high and respond as indicated by the conditions, which at last impact the development of little scope lodgings Ngek (2015) inspected the impact of two interceding factors which were innovative attitude and receptiveness on the relationship between Self-Efficacy of business visionary and execution of the private venture. The outcomes showed that the innovative outlook and receptiveness completely intervened in the connection between the self-adequacy and execution of independent companies. The connection between the previously mentioned factors fortifies the comprehension of the connection between the Entrepreneur Self-Efficacy and Small business execution.
Entrepreneurial Attitude and SME’s Performance
Choe & Loo (2013) investigated the connection between the Performance of Small Medium Enterprise and the Entrepreneurial Attitude. There is an expanded accentuation on enterprise explore everywhere throughout the world. As indicated by the Census of Establishments and Enterprises 2006, it shows that around 518996 or 99.2% of business foundations in Malaysia go under the class of Small and Medium Enterprises. This investigation intended to see how the exhibition of Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs) was influenced by the innovative demeanor in Malaysia. To check the effect of innovative demeanor on the exhibition of SMEs, self-directed surveys were appropriated among the respondents and the respondents were proprietor administrators of the little medium ventures. The information that has been gathered through the surveys was dissected utilizing the relapse model. The outcomes show that each of the five elements of an innovative demeanor is emphatically identified with the presentation of the little medium endeavor.
Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and Facebook Usage
Ajjan et al. (2015) contemplated the expansion and ascend in the mindfulness and use of Social Media Networks that help business enterprises. Their exploration built up another measurement and factor of "internet based life self-viability". The factor of web-based life self-viability work in the pioneering plan as an indicator of conduct control. The aftereffect of the examination found and broke down by halfway least squares. Also, for more exactness and validness twofold bootstrap strategy was utilized in the examination. Web-based life self-adequacy gives the special fluctuation of the two examples. As indicated by the outcomes, web-based life self-adequacy expectation of saw conduct control was above and more than the commitment of the self-viability of a business person. The commitment of saw conduct control was not just past the commitment of self-viability of the business visionary; truth be told, it was likewise more than the entrance to the pioneering assets Stoyanova (2017) considered and inspected the impact of web-based life on the self-viability of the understudies concerning the expectations of business visionaries. This investigation inspects the impact of internet-based life among future alumni concerning their aims as they are confronting the difficulties of the beginning of down to earth life and quick professional determinations. Quantitative Technique is utilized for directing this examination, as past investigations on enterprising expectations were done quantitatively. A very much organized poll was created with scales regarding the factors which were self-adequacy of a business visionary, enterprising expectations, and the mix of both with the size of online networking. The objective populace for the poll comprised of the college understudies of Bulgaria with a little gathering of global understudies as a kind of perspective.
Entrepreneurial attitude and Facebook Usage
Turan & Kara (2018) inspected and dissected the inspiration levels of the business visionaries, just as the normal advantages and their goals of utilizing web-based life. Right now, the Social Media Usage conduct of the business visionaries was examined with the assistance of a quantitative methodology. The information assortment for this examination has been finished by utilizing surveys and taking individual meetings. The information has been gathered from the associations which depend on business people. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) test is utilized alongside structural equation modeling (SEM). To test the legitimacy of theories, Both Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Structured Equation Modeling were utilized in the applied models. Barišić & Vujnović (2018) directed the examination and he has secured and featured the most helpful part of web-based life. The reason for the investigation was to discover the significance of utilizing web-based life showcasing for organizations, another motivation behind this examination was to investigate the preferences just as drawbacks of the online networking advertising efforts, the third significant reason for this investigation was to discover the best web-based life stage which can be utilized for running web-based life crusades and which can profit a business. Infant Sam Samuel's (2015) study centers around the effect and job of online networking as a central point in advancing business enterprises in the Middle East and Oman. This investigation was finished by the web-based life in organizations, business people just as the overall population. The outcomes which were created after the discoveries from this investigation delineates that there is an immense use of web-based life in the Middle East concerning Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter. This article and study unmistakably clarify that these nations had over 90% populace who are using long-extend casual correspondence goals. The writing showed that; enterprising demeanor has a relationship with Facebook utilization.
(H14): There exists a significant relationship between entrepreneurial attitude and Facebook usage.
Facebook Usage and SME Performance
Adam et al. (2016) led an investigation in Malaysia. They have examined the presence of social trade, which is the blend of electronic business and the utilization of online life for selling merchandise and ventures. The utilization of social business has opened up incredible open doors for the little just as medium undertakings in Malaysia. The use of social trade in Malaysia has been utilized as an appropriate mechanism for showcasing just as purchasing and selling, thus it likewise helps the little and medium ventures in producing deals and expanding the productivity of their organizations as far as income and deals.
Öztamur & Karakadılar (2014) analyzed the role and importance of Social Media Platforms as a new marketing tool and strategy for the performance of Small and Medium-sized enterprises. This study focuses on a case study that includes the comparison as well as an analysis of four new Turkish and American companies. The dimensions include the number of likes of Facebook Pages and Number of Followers on Twitter, the richness of content on Facebook and Twitter, interaction with the customer and the use of language on social media. Moreover, Qualitative methods and techniques have been used to analyze and see how the companies are engaging with their customers online and how they are using social media as a strategic tool of social media network marketing. This study has opened up a new dimension of marketing which is social network marketing (SNM). This study has also identified the issues and problems in American and Turkish companies. The study highlights that the most common issue and the problem with Turkish Small Medium Enterprises who are using social media are related to the formal language usage issue during the communication process with the customer. Moreover, they create unattractive content that lacks the richness and which lacks attractiveness and hence they fail in attracting and engaging their social media fans. Another aspect that is highlighted in the study is that the usage of Twitter is less in American Small Medium Enterprises as compared to Facebook.
The literature indicated that usage of Facebook has an association with Small Medium Enterprises performance.
(H15): Usage of Facebook enhances the performance of SMEs in Pakistan.
Methodology
Sample and Procedure
The cross-sectional research design was used to explore association among entrepreneurial1 self-efficacy,1entrepreneurial attitude, Facebook usage and performance of entrepreneurs. The participants in this study belonged to such Small and Medium Enterprises who had their own Facebook pages and doing business through social media. The particular participants were Admin, Social media managers and digital marketing executive who was managing this business. The researcher considered only such participants who were managing the Facebook page regularly and they were doing so from at least two years.
The researcher’s greater emphasis was on the reliable data collection procedure. The questionnaire was filled by the only participants who were managing their business Facebook page and maintaining their page regularly. The respondents in this study were Admin, Social media managers and digital marketing executive so that, valid and reliable responses from concerned persons could be attained. Responses of each questionnaire were keenly observed and corrections were made by engaging the respondents again. The collected primary data were further processed by using AMOS software and initially, the reliability and validity of the questionnaire were estimated. After the reliable results, the data was the further process to estimate the association between the independent, interdependent and dependent variables.
The Small Medium Enterprises in this study were those, which were prevailing in the Bahawalpur and tehsils of Bahawalpur. The total population of participants in this study was 2483 and shown in Table 1. The details of the population concerning tehsils are provided as under:
| Table 1 Population Size | |||
| Districts Name | Population Size | Districts Name | Population Size |
| Yazman | 561 | Ahmedpur | 812 |
| Bahawalpur City | 429 | Khairpur | 362 |
| Hasilpur | 319 | ----- | ---- |
| Total | 1309 | Total | 1174 |
A clustered sampling technique was used in this quantitative study. The calculated sample size was 333 which was calculated by using a sample size calculator (https://www.surveysystem.com/sscalc.htm). The sample size which is 333 is provided below in Table 2 as under:
| Table 2 Sample Size | |||
| Districts Name | Population Size | Districts Name | Population Size |
| Yazman | 94 | Ahmedpur | 108 |
| Bahawalpur City | 76 | Khairpur | 16 |
| Hasilpur | 39 | ----- | ---- |
| Total | 209 | Total | 124 |
Sample characteristics were indicated as follows in Table 3:
| Table 3 Sample Characteristics | |||
| Attributes | Categories | Frequency | Percent |
| Age | Below 22 Years | 23 | 7 |
| 23-27 Years | 166 | 50 | |
| 28-33 Years | 121 | 36 | |
| 34-38 Years | 8 | 2 | |
| Above 39 Years | 15 | 5 | |
| Marital Status | Un-Married | 202 | 60 |
| Married | 126 | 38 | |
| Divorced | 5 | 2 | |
| Gender | Male | 219 | 65 |
| Female | 114 | 35 | |
| Educational Level | Metric/Diploma | 56 | 17 |
| Bachelor’s | 45 | 13 | |
| Master’s | 151 | 45 | |
| M.Phil. | 76 | 23 | |
| Ph.D. | 5 | 2 | |
| Current Position | Owner | 180 | 54 |
| C.E. O | 15 | 5 | |
| Director | 40 | 12 | |
| Manager | 55 | 17 | |
| Other | 43 | 13 | |
| Generation Level | 1st Generation | 130 | 39 |
| 2nd Generation | 87 | 26 | |
| 3rd Generation | 81 | 24 | |
| 4th Generation | 25 | 8 | |
| 5th Generation | 10 | 3 | |
| Sale’s Trend of Business | Inclined | 177 | 53 |
| Steady | 120 | 36 | |
| Declined | 36 | 11 | |
| Facebook Usage | Never | 5 | 2 |
| Rarely | 31 | 10 | |
| Sometimes | 61 | 19 | |
| Often | 120 | 35 | |
| Always | 116 | 34 | |
Measures
Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy
The variable Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy was measured by (Chen et al., 1998) which consisted of five dimensions and twenty-two items.
Entrepreneurial Attitude
The independent variable Entrepreneurial Attitude was measured by (Robinson et al., 1991) which was consisted of four dimensions and fifty-eight items.
Facebook Usage.
The interdependent variable Facebook Usage was measured by (Błachnio et al., 2016) which consisted of twenty-seven items.
SMEs Performance
The dependent variable Small Medium Business Performance scale was measured by (Wu, 2009) which consisted of five dimensions and twenty items.
Results and Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of entrepreneurial factors (Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and Entrepreneurial Orientation) on the performance of SMEs and the use of Facebook. Moreover, this study also investigated the effect of Facebook usage on SME’s Performance. In this quantitative primary data was collected from the Admin, Social media managers and digital marketing executive of such businesses who were running their business by using social media as well. This study is a step to highlight the effect of Facebook usage for such Small Medium Enterprises who are not using Social for the enhancement of their business performance.
Structural Equation Model
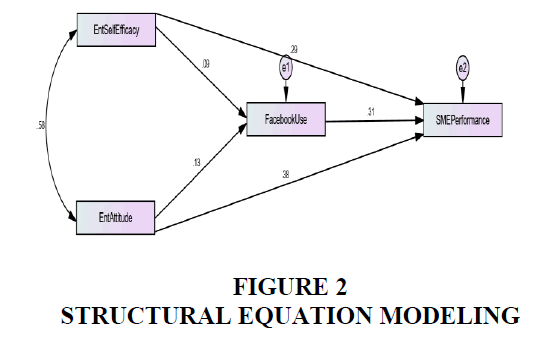
After the CFA, Structural Equation Model (S.E.M) was implemented to estimate the relationship between the exogenous and endogenous variables through coefficients for all hypothesized paths in the structural model. Reisinger & Mavondo (2007) argued: “a good model fit does not indicate the strong relationships among variables and suggests that researcher should report not only model fit indices but also the strength of the paths in the model”.
The Table 5 provided below highlights the strength, direction, and significance of Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and SME Performance. The value of Coefficient (0.271) indicates a positive and strong influence of Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy on the SME Performance. The value of coefficient shows, one unit increase in the self-efficacy traits of an entrepreneur the performance of SME increases 0.271 units. However, the stat threshold states that T value must be greater than two and P values must be less than 0.05 for the acceptance or rejection of the hypothesis. So, (t=6.232 > 2 & P=0.000<0.05) indicated that there is a positive significant association between self-efficacy of Entrepreneur and SME Performance. Based on the results; the alternative hypothesis (H11): There exists a significant relationship between entrepreneurial self-efficacy and SMEs Performance is accepted shown in Table 4.
| Table 4 Acceptance/Rejection of the Hypothesis | ||
| Hypothesis Name | Hypothesis Statement | Accepted/ Rejected |
| (H11) | There exists a significant relationship between entrepreneurial self-efficacy and SMEs Performance. | Accepted |
| (H12): | Entrepreneurial attitude has an association with SME's performance. | Accepted |
| (H13): | The self-efficacy of entrepreneurs has a significant relationship with Facebook usage. | Rejected |
| (H14): | There exists a significant relationship between entrepreneurial attitude and Facebook usage. | Accepted |
| (H15): | The usage of Facebook enhances the performance of SMEs in Pakistan. | Accepted |
It also shows the significance of Entrepreneurial Attitude and SME Performance. The value of Coefficient (0.403) indicates a positive and strong influence of Entrepreneurial Attitude on the SME Performance. The value of coefficient shows, one unit increase in the Attitude traits of an entrepreneur the performance of SME increases 0.403 units. However, the stat threshold states that T value must be greater than two and P values must be less than 0.05 for the acceptance or rejection of the hypothesis. So, (t=8.206 > 2 & P=0.000<0.05) indicated that there is a positive significant association between the Attitude of Entrepreneur and SME Performance. Based on the results; the alternative hypothesis:
(H12): Entrepreneurial attitude has an association with the SME's performance is accepted.
It also shows the significance of Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and Facebook Usage. The value of Coefficient (0.142) indicates positive but very week influence of Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy on Facebook Usage. The value of coefficient shows, one unit increase in the Self-Efficacy of an entrepreneur the usage of Facebook increases 0.142 units. However, the stat threshold states that T value must be greater than two and P values must be less than 0.05 for the acceptance or rejection of the hypothesis. So, (t=1.142 < 2 & P=0.156 > 0.05) indicated that, there is no significant association between Self-Efficacy of Entrepreneur Facebook Usage. Based on the results; the alternative hypothesis:
(H13): Self-efficacy of entrepreneurs has a significant relationship with Facebook usage is Rejected.
It also shows the significance of Entrepreneurial attitude and Facebook Usage. The value of Coefficient (0.230) indicates a positive and strong influence of Entrepreneurial attitude on Facebook Usage. The value of coefficient shows, one unit increase in the attitude of an entrepreneur the usage of Facebook increases by 0.230 units. However, the stat threshold states that T value must be greater than two and P values must be less than 0.05 for the acceptance or rejection of the hypothesis. So, (t=2.032 > 2 & P=0.000 < 0.05) indicated that, there is significant association between attitude of Entrepreneur Facebook Usage. Based on the results; the alternative hypothesis:
(H14): There exists a significant relationship between entrepreneurial attitude and Facebook usage is Rejected.
It also shows the significance of Facebook Usage and SME Performance. The value of Coefficient (0.189) indicates a positive and strong influence of Facebook Usage on the SME Performance. The value of coefficient shows, one unit increase in the Facebook Usage the performance of SME increases 0.189 units. However, the stat threshold states that T value must be greater than two and P values must be less than 0.05 for the acceptance or rejection of the hypothesis. So, (t=7.949 > 2 & P=0.000<0.05) indicated that there is a positive significant association between Facebook Usage and SME Performance. Based on the results; the alternative hypothesis:
(H15): Usage of Facebook enhances the performance of SMEs in Pakistan is accepted shown in Table 5, Table 6 and Figure 2.
| Table 5 Association Between Variables | ||||
| C | To | (Co-efficient) | “t” Value | P |
| Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy | SME Performance | 0.271 | 6.232 | 0 |
| Entrepreneurial Attitude | SME Performance | 0.403 | 8.206 | 0 |
| Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy | Facebook Usage | 0.142 | 1.142 | 0.156 |
| Entrepreneurial Attitude | Facebook Usage | 0.23 | 2.032 | 0.042 |
| Facebook Usage | SME Performance | 0.189 | 7.949 | 0 |
| Table 6 Interaction Summary of Variables | |||||||
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | P | Label | |||
| Facebook Usage | <--- | Entrepreneurial Self Efficacy | 0.142 | 0.1 | 1.42 | 0.156 | Rejected |
| Facebook Usage | <--- | Entrepreneurial Attitude | 0.23 | 0.113 | 2.032 | 0.042 | Accepted |
| SME Performance | <--- | Entrepreneurial Attitude | 0.403 | 0.049 | 8.206 | *** | Accepted |
| SME Performance | <--- | Entrepreneurial Self Efficacy | 0.271 | 0.043 | 6.232 | *** | Accepted |
| SME Performance | <--- | Facebook Usage | 0.189 | 0.024 | 7.949 | *** | Accepted |
Interaction Summary
The graph given in Figure 2 describes that entrepreneurial attitude has a significant positive impact on Facebook usage and entrepreneurial self-efficacy has no significant impact on Facebook usage. Similarly, Entrepreneurial attitude has a significant positive impact on SME performance. Also, entrepreneurial self-efficacy and Facebook usage have a significant positive impact on SME performance
Discussion
The results indicated that Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy has a significant association with the performance of SME. The entrepreneur has capabilities to manage the enterprise concerning market share, sales goals, profit goals, and business expansion can contribute to maintaining the performance of SME. However, there is a need that, Entrepreneur must have creativity, innovation and a strong sense of mitigating the risk so that, he/she could make wise decisions for the enterprise. The results of (Hallak et al., 2014) also align with the results of this study that, Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy influences positively and significantly the SME performance. The results of an entrepreneurial attitude with the SME performance indicated that an entrepreneur tends to provide plenty of time wisely and make calculated decisions for the betterment of the business. Moreover, an entrepreneur’s control to attain high-level achievements, maintenance of self-esteem and a tendency to bring innovation in the business procedures leads the business towards good performance. The indication of the results of this study that, entrepreneurial orientation has a significant association with the SME performance is also align with the results of (Harris & Gibson, 2008). The results of Facebook usage for the SME performance indicated that a business having a factbook page can access their customers at their workplace or homes. The businesses working physically can access their customer when he used to come to their stores and it was quite difficult for the customer to visit any store even for a single product or service. But the businesses having Facebook Page or social media provides online access to the products of their stores and customer without any hassle can order the product and can receive that product at his/her doorstep. This ease to the customer has contributed to the increment in the sales of the store which ultimately increase the performance of SMEs. The results of this study also match the results of (Ainin et al., 2015). The role of entrepreneurial self-efficacy with the usage of Facebook has no association. It is true in the sense that, self-efficacy is about innovation, risk-taking, control of finances and attainment of business goals and these factors are very few contributors for the usage of Facebook page for a business. Moreover, the results of this study are aligned with the results of Stoyanova (2017). The role of an Entrepreneurial attitude towards Facebook usage for an enterprise indicates a positive significant relationship. The internal attribute like innovation capabilities, Self-Esteem, desires of high achievements and positive control on making rational decision-making drives the entrepreneur to flourish the business physically or through social media like Facebook, Instagram. So, the entrepreneur having an entrepreneurial attitude can enhance the performance of the business by using Facebook. Moreover, the results of this study are aligned with the results of (Seroka-Stolka & Tomski, 2014).
Practical Implications
This study has implications in the field of marketing as it guides marketing managers of small enterprises to focus on social media especially Facebook activities to promulgate the business performance. In terms of capacity building of marketing staff and improving the productivity of enterprises, this study also promotes executives of small enterprises to conduct training programs, seminars, and workshops related to social media handling. SME’s should make extensive plans as far as the use of social media is concerned as a competitive marketing tool. Considerable time should be invested by SMEs to produce rich content via social media accounts so that they can attract the attention of their target customers. The government should conduct training programs for adults and youngsters for social media handling which can ultimately contribute to the economy of the country. The owners and their business handlers must participate in entrepreneurial seminars and workshops to acute their contribution to the performance of the SMEs.
Limitations and Future Research Directions
The present study is not without limitations. First, it has only considered Facebook as a social media engine to measure the productivity of small and medium enterprises. However, future research can take into account other mediums e.g. YouTube, Instagram, Snapchat, and WhatsApp, etc., that can be used as marketing tools by small and medium enterprises. Second, in the future, comparative study can also be conducted to identify which social media engine is a better marketing tool for small and medium enterprises. Third, another avenue can also be explored by future studies that how companies should go about the designing of activities relating to social media for different followers of social media to augment the effectiveness of reaching targets of marketing.
Fourth, the present has been conducted in a collectivist culture so; the findings of the study cannot be generalizable on other cultures. Future research may also replicate the present study in other cultural contexts and different organization settings. Fifth, the present sample size of the study is small and future studies may also consider the larger sample size. Sixth, a comprehensive research methodology can be designed by future researchers that offer broader industry comparison. Finally, exploring the effect of social network marketing efforts on the market and financial performances might be of use for small and medium enterprises to determine their investment decisions.
Conclusion
In the light of results, it is being concluded that Entrepreneurial self-efficacy and the Attitude traits of any entrepreneur contributes to enhancing the performance of SMEs in Pakistan. so, there is a need to instigate such entrepreneurial traits among the Entrepreneurs entering into the market. Moreover, the usage of Facebook by the enterprises as their business Facebook page contributes to enhancing the performance of SMEs. It is being deduced that an updated and active Facebook page of any SME can be a source of new customer market and sales.
References
- Adam, A.B., Jizat, J.E.B.M., & Nor, M.A.B.M. (2016). Internal factors within entrepreneurs that influence the acceptance and use of Social commerce among SMEs in Malaysia. Journal of Managment, 11(1), 35-45.
- Ajjan, H., Fabian, F., Tomczyk, D., & Hattab, H. (2015). Social media use to support entrepreneurship in the face of disruption. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship, 20(03).
- Baby Sam Samuel, J.S. (2015). Social media as a factor for promoting entrepreneurship - the Middle East & Oman Scenario. International Journal of Economics, Finance and Management Science, 3(5), 483-493.
- Boyd, N.G., & Vozikis, G.S. (1994). The influence of self-efficacy on the development of entrepreneurial intentions and actions. Entrepreneurship theory and practice, 18(4), 6377.
- Camil, A.J. (2017). The Effectiveness of Social Media Marketing In Small Business Performance: A Case Study of Central Business District Nairobi. United States International University-Africa.
- Choe, K.L., & Loo, S.C. (2013). An exploratory study on the relationship between entrepreneurial attitude and firm performance. Human Resource Management Research, 3(1), 34-38.
- Gamage, A.S., & Takayuki, S. (2013). The role of hrm in developing smes in Sri Lanka. The Meijo Review, 14(3), 133-151.
- Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R.E., & Tatham, R.L. (2006). Multivariate data analysis (6): Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Hallak, R., Assaker, G., & O’Connor, P. (2014). Are family and nonfamily tourism businesses different? An examination of the entrepreneurial self-efficacy-entrepreneurial performance relationship. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 38(3), 388-413.
- Harris, M.L., & Gibson, S. G. (2008). Examining the entrepreneurial attitudes of US business students. Education+ Training, 50(7), 568-581.
- Herath, H., & Mahmood, R. (2013). Dimensions of entrepreneurial self-efficacy in hotel and restaurant industry In Sri Lanka: An Exploratory Study: South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business, Economics, and Law.
- Herath, H., & Mahmood, R. (2014). Dimensions of entrepreneurial self-efficacy and firm performance. Global Journal of Management And Business Research.
- Hoque, A., Awang, Z., Muda, H., & Salleh, F. (2018). Ramification of crowdfunding on bangladeshi entrepreneur’s self-efficacy. Accounting, 4(4), 129-138.
- Hu, S., Gu, J., & Zhang, S. (2017). Social Media Usage, Self-efficacy and Cultural Intelligence: A Longitudinal Empirical Research in China. Paper presented at the International Conference on E-business, Wuhan, China.
- Klyver, K., & Thornton, P.H. (2010). The cultural embeddedness of entrepreneurial self-efficacy and intentions: A cross-national comparison. Academy of Management, Montreal, August.
- Koenig, M., Schlaegel, C., & Gunkel, M. (2013). Entrepreneurial traits, entrepreneurial orientation, and innovation in the performance of owner-manager led firms: A metaanalysis (Summary). Frontiers of Entrepreneurship Research, 33(4), 9.
- Markman, G.D., Baron, R.A., & Balkin, D.B. (2005). Are perseverance and self‐ efficacy costless? Assessing entrepreneurs' regretful thinking. Journal of Organizational Behavior: The International Journal of Industrial, Occupational and Organizational Psychology and Behavior, 26(1), 1-19.
- Ngek, N.B. (2015). Entrepreneurial self-efficacy (ESE) and small business performance: The mediating effect of entrepreneurial mindset and openness to experience. Problems and Perspectives in Management (271-280).
- Ong, J.W., & Ismail, H.B. (2012). Entrepreneurial traits and firm serendipity-seeking on SMES' performance: The effect of firm size. Journal of Enterprising Culture, 20(03), 265-286.
- Öztamur, D., & Karakadılar, İ.S. (2014). Exploring the role of social media for SMEs: As a new marketing strategy tool for the firm performance perspective. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 150, 511-520.
- Park, J.Y., Sung, C.S., & Im, I. (2017). Does Social Media Use Influence Entrepreneurial Opportunity? A Review of its Moderating Role. Sustainability, 9(9), 1593.
- Politis, D., & Gabrielsson, J. (2009). Entrepreneurs' attitudes towards failure: An experiential learning approach. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 15(4), 364-383.
- Reisinger, Y., & Mavondo, F. (2007). Structural equation modeling: Critical issues and new developments. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 21(4), 41-71.
- Robinson, P.B., Stimpson, D.V., Huefner, J.C., & Hunt, H. K. (1991). An attitude approach to the prediction of entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship theory and practice, 15(4), 13-32.
- Seroka-Stolka, O., & Tomski, P. (2014). Internet social media and international entrepreneurial intentions. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Wei International Academic Conference.
- Stevens, J. (2013). Shattering the boundaries through self-efficacy: exploring the social media habits of South African previously disadvantaged entrepreneurs. Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch University.
- Stoyanova, K. (2017). Exploring the link between social media and graduate entrepreneurship: A study on social media’s influence on last-year undergraduate students’ self-efficacy with regards to their entrepreneurial intentions.
- Thompson, E.R. (2009). Individual entrepreneurial intent: Construct clarification and development of an internationally reliable metric. Entrepreneurship theory and practice, 33(3), 669-694.
- Torres, J.L.N., & Watson, W. (2013). An examination of the relationship between manager self-efficacy and entrepreneurial intentions and performance in Mexican small businesses. Contadur í a y Administració n, 58(3), 65-87.
- Turan, M., & Kara, A. (2018). Online social media usage behavior of entrepreneurs in an emerging market: Reasons, expected benefits and intentions. Journal of Research in Marketing and Entrepreneurship, 20(2), 273-291.