Research Article: 2020 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
The Concept of Sustainable Development of Electronic Entrepreneurship in the International Business System
Stoyan Radev Koev, University of National and World Economy, Bulgaria
Pavel Blecharz, VSB-Technical University of Ostrava, Czech Republic
Kateryna Shafranova, Open International University of Human Development "Ukraine", Ukraine
Serhii Karpenko, Open International Human Development University "Ukraine", Ukraine
Yevheniia Morozova, Prydniprovs’ka State Academy of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Ukraine
Abstract
The article presents a scientific review and analysis of the conceptual foundations of sustainable development of electronic entrepreneurship in international business. The components of the use of information technologies in international entrepreneurship are determined and the components of the combination of electronic business and entrepreneurial activity are characterized. The role of the mobile business as a priority area for the development of electronic entrepreneurship is determined. The directions for leveling the main problems of organizing mobile electronic business are substantiated.
Keywords
Electronic Entrepreneurship, Mobile Electronic Business, E-Business, Information Technology, World Economy.
Introduction
The active penetration of information and communication technologies into all spheres of the life of the information society, which is being formed with the objective necessity of determination of the integrity of a new type of economic system, provides for the formation of fundamentally new markets and forms of entrepreneurial activity that are adequate to its conditions. Such an innovative form of entrepreneurship is presented by the electronic business, which is associated primarily with the use of the Internet (Johnson, 2014). The use of the Internet in traditional business is acquiring strategic importance not only for business entities. This is due to the exponential increase in the number of visitors to Internet resources and their transformation into the main sales channel for many sectors of international business.
Methodology
The following provisions and practices of conducting international business are the methodological basis of this study: (1) in the conditions of modern scientific and technological progress and increasing requirements for the speed of information exchange between entrepreneurial entities, an effective organization of the country's electronic business can increase their competitiveness; (2) in a modern market economy, the main task is not the optimization of commercial relations but a strategic increase in the country's effectiveness using electronic technologies; (3) electronic business plays one of the key roles in the field of achievement of global leadership by business entities, as well as successful integration into the world economy.
Literature Review
Electronic business is defined as a type of economic activity of entrepreneurial structures using computer networks in order to make a profit. Researchers (Chang et al., 2003; Rozwell et al., 2002; Drobyazko et al., 2019) define electronic business as the implementation of major entrepreneurial processes using Internet technology. The emphasis on automation of business processes in international entrepreneurship and business is made (Chong, 2008; Lee, 2008), noting that electronic business is an entrepreneurial activity based on Internet technologies, in which all business processes are automated. Another approach is more universal, combines the views of the authors (Gilmore et al., 2007; Garbowski et al., 2019) on electronic business as modern business processes that are carried out using information technology. According to the third approach, scientists (Halligan, 2014; Kidwell et al., 2000) do not focus on business tools at all.
Findings and Discussion
Information Technology and International Entrepreneurship
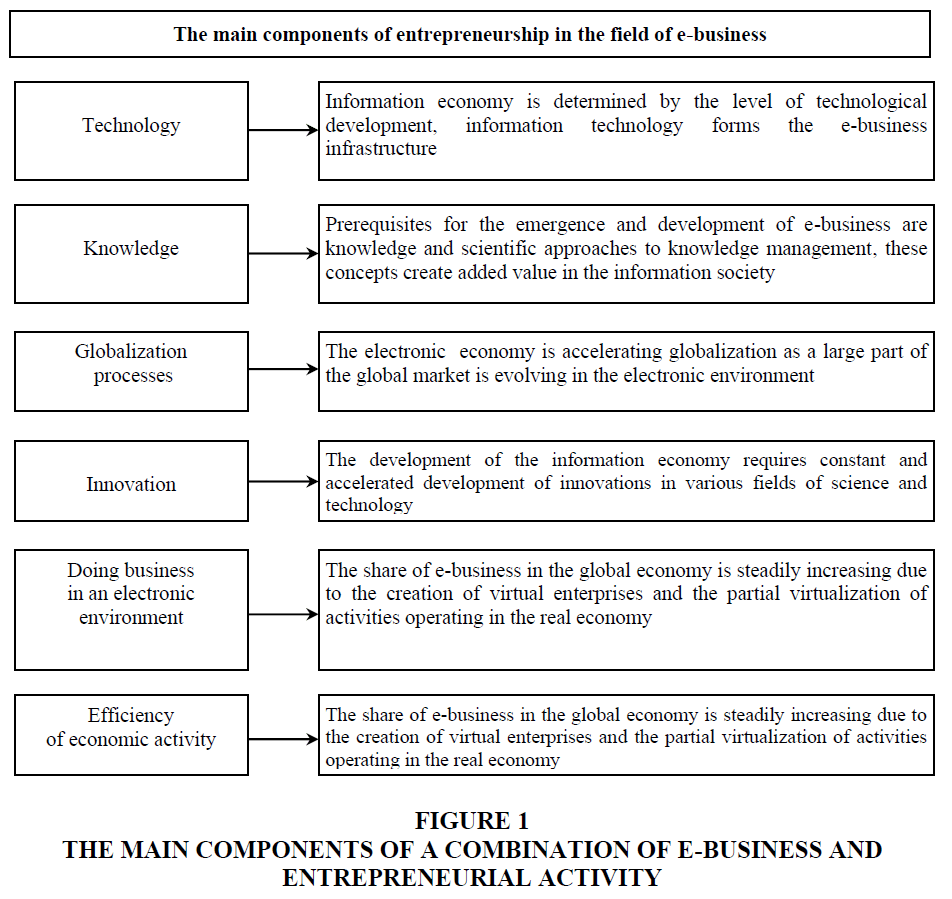
In recent years, the use of information technology has led to a sharp change in the structure of the business world. Having formed a system based on global transformations, the effect of the involvement of each of the economy sectors in the world of electronic business is actively developing (Phan, 2002) (Figure 1).
In today's world, the greatest potential of electronic business is in the B2B segment, which encompasses the interaction of business representatives with each other. If companies conduct their activity with the use of information and communication technologies, it is possible to work in the market more quickly (on average, the speed of conducting trading operations increases by 24.5%) and with higher profitability (the average cost reduction is 14.9%). This makes it possible to reduce costs for storage, wages, make direct payments (without intermediaries between seller and buyer), and decentralize administrative work (Tunde, 2014).
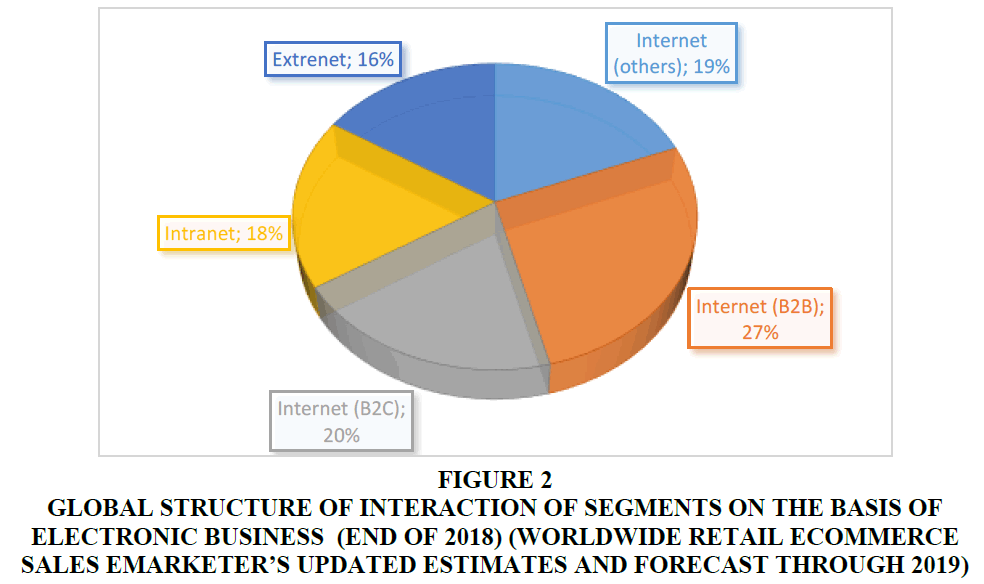
If we consider B2C, a segment of direct interaction between business representatives and consumers, then the end consumer is the client directly here (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Global Structure of Interaction of Segments on the Basis of Electronic Business (End of 2018) (Worldwide Retail Ecommerce Sales Emarketer’s Updated Estimates and Forecast Through 2019)
Due to the rapid development of information systems and technologies, more and more entrepreneurial structures find electronic business more acceptable as opposed to traditional methods of the trade organization. This is confirmed by the analysis of the world trade organization, according to which the growth rate of world virtual trade significantly exceeds the growth of world real trade as a whole. Thus, the rate of its development in 2018 exceeded the indicator for the first quarter of 2017 by 29.9%, while the growth in global trade amounted to only 4.1% compared to the previous year. Table 1 presents the factors that influence the efficiency of the development of electronic business, which are ranked according to the research of the authors (Diyan, 2012).
| Table 1 Significance of Electronic Business Impact Factors, 2018, % | ||
| Factor | small business representatives | middle business representatives |
| Legal framework | 13 | 12 |
| Role of the state | 7 | 11 |
| Infrastructure | 12 | 13 |
| Security | 21 | 20 |
| Competition in the market | 21 | 18 |
| Accessibility | 16 | 15 |
| Information literacy | 10 | 11 |
Mobile Electronic Business
Defining mobile business as a priority area for the development of electronic entrepreneurship makes it necessary to address the issue of its organization. It has been identified that, despite all the benefits of mobile electronic business, there may be a number of problems in the process of its creation and implementation that require prompt and preventive solutions (Rainer & Cegielski, 2011).
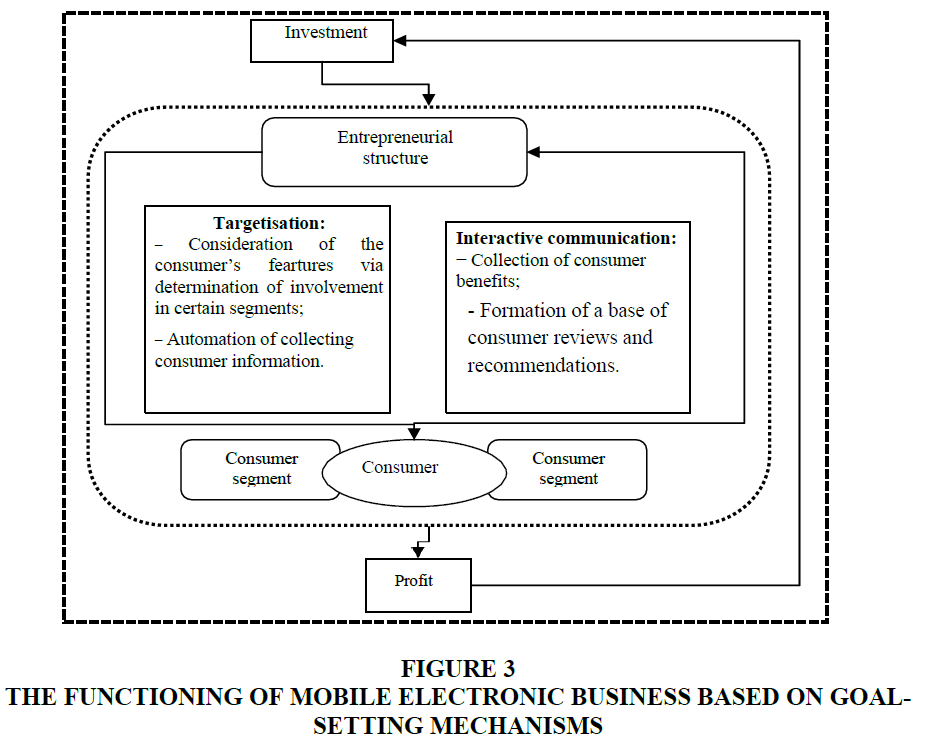
For today's business environment, the problem of skilled personnel is especially emphasized (Hecker, 2001). When organizing mobile electronic business, the fact that this business is new should also be taken into account. Thus, the problem of attracting and retaining customers is especially urgent. On this basis, it is concluded that the creation and implementation of mobile electronic business involve the use of mechanisms of targeting and interactive communication (Strauss & Frost, 2011). Interactive communication promotes the most accurate segmentation and reduction of sales risks due to the participation of the consumer in business processes as the initial link of business decisions (Figure 3).
In the most general form, the problems of organizing mobile electronic business are divided into two groups: organizational-economic and technical. The authors provide an analysis of these problems and possible ways to level them (Table 2).
| Table 2 Directions for Leveling the Main Problems of Organizing Mobile Electronic Business | ||
| Problems of organizing mobile electronic business | Directions for solving problems | Problem solving |
| Organizational and economic | ||
| Lack of qualified workforce | Selection of managerial decisions | Ordering the necessary software from specialized companies, retraining and training of specialists, attracting competent freelance specialists (complete development of business tools, partial development with further integration), formation of basic principles of activity, rights and obligations, and regulations for employees. |
| Unpreparedness of a large part of the population | Reflective promotion | Formation of an intuitive interface of a mobile business tool, making clear recommendations and rules for its use, reducing prices and providing discounts at the initial stage of operation |
| Differentiation of mobile platforms | Development of diversified software | Development of applications for all mobile platforms, development of universal web applications focused on mobile platforms |
| Difficulty of attracting and retaining customers | Active marketing | Active advertising, conducting promotions, granting additional bonuses, integration of technological systems of the business process (absolute automation of performed transactions), use of mechanisms of targeting and interactive communication, continuous improvement of mobile electronic business tool |
| Insufficient copyright protection | Preventive copyright protection | Diversified copyright registration, implementation and continuous improvement of the information security system |
| Technical and economic | ||
| Technical vulnerability | Comprehensive protection of information | Creation of backup system, implementation of automatic server change methods in emergency situations, use of differentiated methods of information security |
| Poor mobile performance | Transport localization of technical operations | Transferring databases and the process of performing basic operations to the server, reduction of the amount of necessary traffic due to the implementation of information archiving systems |
The priority of the development of mobile electronic business is primarily due to the fact that the orientation of the business on mobile devices involves the convergence of user and entrepreneurial interests. It is noted that convergence is two-level nature because, on the one hand, the most user-friendly features are integrated in mobile devices (differentiated types of communication, maximum portability, ease of payment function), and on the other hand, they are aggregated to minimize the costs of business structures related to implementation electronic business.
Recommendations
Although there is a positive trend in the world economy for the development of the electronic commerce market, there are a number of problems that impede its full potential. Developing an effective strategy for the development of electronic commerce business, solving technical issues, increasing public confidence in online commerce, optimizing the mechanisms of logistics and efficiency of postal services as well as payment systems will increase the level of development of the electronic business market.
The efficiency of electronic business development is confirmed by the data on the growth of profitability of business entities by reducing costs and forming integrated chains of the added value. The processes of electronic business development in the world reflect a steady tendency towards the transition of business entities to the electronic environment.
Conclusion
Thus, the electronic business world is a promising line of entrepreneurial activity, which is able to increase the level of competitiveness of both individual business structures, industries, and entire countries. In the century of accelerated development of information and communication technologies, the economy is constantly undergoing major transformations, gradually moving from "real" to "electronic". The development of the global electronic commerce market is one of the major achievements in this way. The world electronic business has good prospects; its further development requires a coherent policy of the business and public sectors of the economy in different countries, as well as the development of innovative approaches to improve the effectiveness of electronic platforms and marketing solutions, taking into account the successful experience of the leading countries in the development of electronic business.
References
- Chang, K., Jackson, J., & Grover, V. (2003). E-commerce and corporate strategy: An executive perspective. Information & Management, 40(7), 560-663.
- Chong, S. (2008). Success in electronic commerce implementation, A cross-country study of small and medium-sized enterprises. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 21(5), 468-492.
- Diyan, I. (2012). The impact of e-commerce on small-size companies in Sweden. Master Thesis of Karistand University, Sweden.
- Drobyazko S., Shapovalova A., Bielova O., Nazarenko O., & Yunatskyi M. (2019). Formation of hybrid costing system accounting model at the enterprise. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 23(6), 2019.
- Gilmore, A., Gallagher, D., & Henry, S. (2007). E-marketing and SMEs: Operational lessons for the future. European Business Review, 19, 234-247.
- Garbowski M., Drobyazko S., Matveeva V., Kyiashko O., Dmytrovska V. (2019). Financial accounting of e-business enterprises. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 23(2).
- Halligan, Brian (2014). Inbound Marketing. Attract, Engage, and Delight Customers Online.
- Hecker, D.E. (2001). Employment impact of electronic business. Monthly Labour Review, 3-16.
- Johnson, O. (2014). How e-commerce platform boosts SMEs
- Kidwell, J., Mattie, J., & Sousa, M. (2000). Prepareyour campus for e-business. Educause Quarterly, 2, 21-29
- Lee, M.R. (2008). E-ethical leadership for virtual project teams. International Journal of Project Management, 27(5), 456-463.
- Phan, D.D. (2002). E-business development for competitive advantages: A case study. Information Management, 40, 581-590.
- Rainer, K., & Cegielski, C. (2011). Introduction to information systems: Enabling and transforming business. Third Edition. Jonh Wiley & Sons Inc.
- Rozwell, C., Shu, L.J., & Reilly, G. (2002). Create E-business plans for competitive advantage. Gartner G2, 1-9.
- Strauss, J., & Frost, R. (2011). E-marketing (6th Edition). – Pearson Education International. New Jersey
- Tunde, K. (2014). How e-commerce platform boosts SMEs.