Research Article: 2018 Vol: 22 Issue: 4
The Moderating Effect of Business Environment on the Relationship between Entrepreneurial Skills and Small Business Performance in Iraq
Yousif Aftan Abdullah, Universiti Utara Malaysia
Dr. Mohd Najib Bin Mansor, Universiti Utara Malaysia
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to examine the moderating role of business environment on the relationship between Entrepreneurial Skills (ES) and business performance of Small Business (SB) in Iraq, Baghdad. This study aims to resolve the inconsistencies found in the contemporary literature regarding the relationship between ES and business performance. Questionnaire using a 5-point Likert scale was adopted from previous work to ascertain the responses of the respondents. Survey research design was adopted, and self-administered questionnaires were used to collect the data from small business owners in 9 districts in Baghdad the capital of Iraq. The analysis was conducted using SPSS version 23.0. The direct relationship and hierarchical regression analysis were spent to exam the hypothesis with moderating influence of Business Environment on the Relationship between Entrepreneurial Skills and Small Business Performance. The major findings reveal that that business environment moderates the relationship between entrepreneurial skills and small business performance. The study has useful recommendations for Iraqi Government and policy making institutions.
Keywords
Business Environment, Entrepreneurial Skills, Small Business, Business Performance.
Introduction
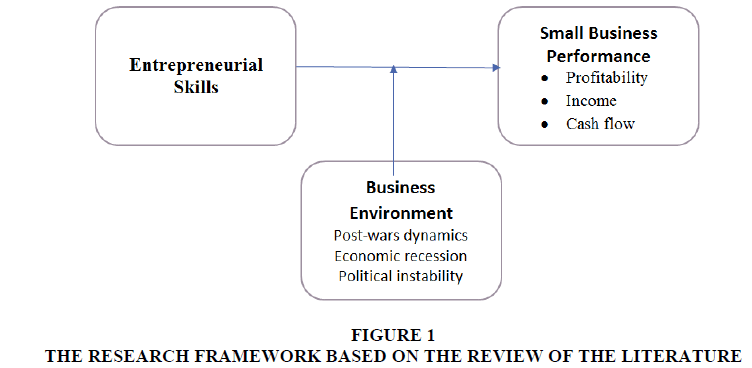
Based on the private sector development strategy of Iraq, between the period of 2013- 2030 stated that the private sector will be dominated by small and medium businesses and also very small business which are mainly operating in retail and trade, construction and transportation and the majority of the business are owned by sole proprietors and family business and many employees of the small business lack entrepreneurial training and also are unskilled and short term labourers (PSDSI, 2013). Although the role of small and medium size business in the economic development is highly recognized but on the same time the small and medium size business are also facing various challenges which had been widely acknowledged in the previous research literature on the subject (Harash et al., 2014). Below listed are some of the key challenges for small and medium size business identified by (OECD, 2009). Small and medium size business are challenged on multiple internal and external aspects of like lack of management expertise, insufficient access to financing options, government ineptitudes and lack of infrastructure. Figure 1, is indicating the Key Challenges for small businesses during Evolution Process from inception, development and maturity (Enterprises, 2013).
The performance of Small businesses in Iraq ordinarily experience many ill effects and there are many challenges confronting the development of the sector particularly during an economic recession, downturn, and unstable political crisis (Lohrke et al., 2015). This period of recession creates an unfavorable environment that limits small business productivity, profitability, and expansion which have a negative impact on the economic as a whole (Berisha- Namani, 2009). In the mid of any economic recession, the small business sector has been identified as the most hit harder among other sectors. This is because there will be a decline in sales and profits where consumers will be unwilling to buy products. Thus, when small businesses are struggling, this implies, the employment rate will be reduced which results in high unemployment and crime rates. The significance of the study coming from the role of small businesses and will help the Iraqi policy making institutions specially, where SMEs contribute significantly in employment generation and contribute towards the gross domestic products. This study is an effort to highlight the role and benefits of entrepreneurship specially in the Iraqi economy. Therefore, this present study investigates the critical success factors that enable an improved economic environment for small businesses in Iraq to thrive and growth in economic recession and downturn.
Prior Studies and Hypothesis Development
The investigation into the different factors that contribute towards the success of business or project in any environment has been seen to be of germane importance (Ram & Wu, 2013; Daniel et al., 2012). This is as a result of the impact that businesses have on virtually almost all aspects of every individual. However, small businesses have been seen to have more impact, especially with respect to the masses and the economy as a whole, thus there is need to investigate the factors necessary to grow the small business sector. This study tends to investigate the impact of moderating Effect of Business Environment on the Relationship between Entrepreneurial Skills and Small Business Performance in Iraq, due to the challenges faced by the country (Al-Ansari et al., 2014), such as economic imbalance (Hanna et al., 2014), and civil unrest (Abbass & Jassam, 2015). such as economic imbalance (Hanna et al., 2014), and civil unrest (Abbass & Jassam, 2015). Although many studies have been conducted in the field of entrepreneurial behavior but very few exist in the Arab countries, in particular.
Entrepreneurial skills is defined as the entrepreneur ability to make difference in creating something new which possess a value with the aim and zeal of devoting effort and time and other like finance, psychic, social risks and obtain the resulting rewards of monetary and personal satisfaction and independence (Hisrich & Peters, 2002). The skills acquired by the entrepreneur is essential in achieving a great success, the study conducted by Gomezelj and Antoncic (2008) to determine the critical entrepreneur knowledge dimension for the Small and medium firms’ performance using 168 firms in Slovenia, established a model which hypothesized the relationship among the entrepreneurial knowledge and performance were mainly support, thus reflecting the positive effect of the entrepreneurial knowledge and all its dimension on the small business performance and suggested that generalizability should be employed in order to test the model in other places.
The knowledge dimension which also constitutes the entrepreneurial skills is vital to the success and performance of the small business in the period of the global competitiveness, although, the entrepreneurs do not pay more attention to the importance of knowledge (Gomezelj & Antoncic, 2008). Typically, entrepreneurs are regarded educated, but lacks some certain knowledge and skills related to the market, but on the other hand, knowledge shortage and also the belief about the capacity and the ability to tackle and solve the problems usually represent the obstacle on the success path of the small business (Rowley, 2000).
Another issue regarding the entrepreneurs is that, it is difficult to ascertain which skills they lack and the specific knowledge they are to acquire in order to manage and improve their business performance (Tajnikar, 2000). Hence, it is important for entrepreneurs to determine what skills and knowledge is required in order to improve their knowledge, there is no limit to the entrepreneur knowledge, previous studies discovered that entrepreneurs in their early stage of their entrepreneurial activities lacks some specific knowledge and skills but even with this obstacle they can still succeed. Several entrepreneurs obtain their entrepreneurial skills not through formal education during their work, the entrepreneurs develop several practical skills related to the comprehending the business situation and problem which includes the understanding of the market, developing their vision and also in their quest to succeed, the entrepreneurs will acquire the required knowledge in order to succeed in their business (Lassen, 2007).
Moderating Environment and Small Business Performance
The business environment plays a vital role in the growth and economic development of every country and it enhance and create chance for individuals to engage in different business venture in order to improve the quality and standard of their living (Ohanemu, 2006). Small business around the world operates within a business environment (Adidu & Olanye, 2006). Furthermore, the term business environment does not necessarily mean the physical surrounding but rather the total forces and factors that influence and affect the business performance in a business environment (Adidu & Olanye, 2006). Hence, this implies that, the small business owners must interact with those forces that influence their small business firms in order for their business to perform and be successful (Ukaegbu, 2004).
The study conducted by Kuye (2004) stated that, there is a need to study the business environment as its important considering the fact that, the business firms do not operate in a vacuum but rather in business environments which are dynamic. The business environment is vital for the survival of the small business and their performance and also there is a need to explore success factors that can enhance small business performance during the economic recession, downturn, and crisis in order to create an appropriate economic environment for the growth of small business (Dockel & Ligthelm, 2015). For instance, the financial sector in Iraq is facing serious recession due to the unrest and interstate war (Mahmoud et al., 2014). This has a huge negative effect on the financial sector of the country whereby both the foreign and domestic financial transactions cannot take place (Levitt, 2014). This has affected the closure of most financial firms in the country, whereas government cannot meet her budgetary obligations to her citizens. The consequence of this is greatly felt by small businesses whose enormously depend on the financial sector like the bank for their survival and daily running.
Many studies have expressed these concerns for instance; Jabeen (2014) investigated Total Quality Management (TQM), Entrepreneurial Orientation (EO), Market Orientation (MO) and External Environment (EE) on the performance of SMEs in Pakistan. It was aimed to provide answers to SMEs problems particularly in Pakistan by contributing to factors that will make SMEs perform better. It was discovered that TQM and MO are important drivers that contribute to higher performance in the context of SMEs in Pakistan while external environment truly plays the role of moderator between entrepreneurial orientation and performance and market orientation and performance of SMEs. However, entrepreneurial orientation had no significant association with performance. Similarly, there was no moderating role of EE found on the relationship amid TQM and performance.
Similarly, Yeow (2014) examined the rationale for the shortage of entrepreneurial competencies, capabilities, and skills among the SME owners in the Malaysian business environment. It was concluded in the study that SMEs owners in Malaysia need to engage more in strategic entrepreneurship activities and skill development in order to sustain the competitive advantages thereby shoring up their performance in the global market. Likewise, Husien (2012) explored the role of Strategic Human Resources Management (SHRM) in the performance of SMEs in Iraq. It specifically investigated the relationship between SHRM practices and the business performance in Iraq. The study contributed that factor like line manager, compensation, alignment, employee participation and performance appraisal are impotent in the prediction of Iraq SMEs success in which if the HRM can be taken more seriously then it will improve their companies’ performance. Thus, this study examines the moderating role of business environment towards the entrepreneurial factors and the small business performance in Iraqi.
Moreover, the performance of a small business firm is unpredictable, especially in countries facing poverty, war, natural disaster and civil unrest (Jenning and Beaver, 1997). These situations have profound consequences on economic growth, not only with large businesses but also with small businesses that are the backbone of the economy. Generally, businesses will be affected by such factors as the diversion of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), disruption to trade, the destruction of social overhead capital, loss of human capital, the displacement of people, and the reallocation of resources to less productive activities (Lowry & Chapman, 2015).
However, Iraq is a good example of such country which is faced with poverty, war, natural disaster and civil unrest and had disturbed not only the peace of the country but also the business environment, which in turn affect the small business operations. Based on a report from the Trade Economic (2014), Iraq GDP fell to 4.21 percent in 2015. Also, according to World Bank (2014) report of countries that is convenient to successfully start a small business, the country is ranked 156 positions among 188 countries. The insecurity in the country is creating an untold hardship both to businesses and the citizens at large. Similarly, the drop in oil prices on global markets and the deduction of the northern oil revenues from Iraq’s crude oil production due to the military operation in the country is causing a huge problem to both government and private business in the country.
Additionally, the Iraq business environment is characterized by a lack of transparency and efficiency (Embassy, 2014; Cordesman & Khazai, 2014; Looney, 2008; Suder, 2004). The labour market is suffering from government interference and control which has been severely affected by the devastating conflicts (Looney, 2008). In order for the government to strengthen the economy, oil revenues are used as subsidies for basic goods and services which resulted in maintaining tight price controls on food and medicine (Balke et al., 2014; Ross, 2011). This type of government policy is further discouraging the free flow of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Trade Investment (FTI) (Balke et al., 2014). Thus, the dubious security environment in the country caused blockage to international commerce and trade. Several previous studies also demonstrate that exportation has a positive effect on the growth of small businesses in developing countries (Coad & Tamvanda, 2012).
Accordingly, Damages were done on the oil installations and facilities which increased production cost and exposure the domestic market to import of goods. To complicate the situation in the country, the present activities of the militia Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) is creating an untold hardship on businesses. This created an unsafe environment both for businesses and economic development which led to the relocation of businesses to other safe environment neighboring these countries (Lowe, 2003). Thus, these conditions are part of the suffering and hardship that the Iraq small businesses are facing. Also, inadequate supervision, political uncertainty, and a lack of security have severely undermined the small business survival in the country. Likewise, the country has high start-up expenses and meagre government subsidy which makes life difficult for small businesses (Nasr & Rostom, 2013; White, 2012; Alsaaty, 2011). Also, interminable power and water deficiencies, continuous security concerns and high traditions taxes have all made it troublesome for a small business division to develop in the Iraq business environment (Nasr & Rostom, 2013).
Thus, restoring Iraq's small business industry is critical in order to restore and revives the economy and the creation of employments. Moreover, the small businesses in Iraq contributed 0.5 percent to GDP (Kami & Chaudhr, 2011), but there was a short fall to 0.421 in 2015, due to unfavourable business environment caused by crises (Trade Economic, 2014). The study will investigate the moderating effect of business environment towards entrepreneurial behaviour and business performance of the small business in the Iraqi business environment in post-war and economic recession period.
Business Environment as a Moderator
The study of Naser et al. (2009) asserted that, for small businesses to flourish there is a need for a conducive business environment and regulations, satisfactory essential framework administrations, access to short and long haul financing at sensible rates, valuation and funding, counseling help, and learning about business opportunities. The study of Awe (2012) and Yusuf (1995) identified Consumer confidence, country economic state, environmental impact, government intervention, currency strength, and interest rate business environment as a critical success factors for small business performance.
The study of Adidu and Olanye (2006) established a significant relationship between small business and business environment and asserted that small business around the world operates within a business environment. In a related study the findings of Ukaegbu, (2004) stated that, the small business owners must interact with those forces that influence their small business firms in order for their business to perform and be successful. Based on the literature consulted none of the previous study integrate market orientation, knowledge management, entrepreneurial orientation and firm performance with the moderating and mediating variables of business environment and organizational culture into a single model. Based on these arguments, this study seeks to propose the hypothesis:
H1: Business environment moderate the relationship between entrepreneurial skills and small business performance in Iraq.
The Theoretical Underpinning
The theories employed for the research are mainly theories that are concern on how firms generate profitability and achieve performance through employing entrepreneurial behavior towards business growth and performance. There are several theoretical approaches for studying available resources and firm performance. Hence, this study adapts the entrepreneurial cognitive theory, resource based view theory and contingency theory. The entrepreneurial cognitive theory discusses on how the entrepreneurial behavior helps the entrepreneurs in the identification of opportunities for the creation of businesses and business growth. While, the resource-based view theory explains the relationship between the entrepreneurial factors as the independent variable and the firm performance as dependent variable. The contingency theory is also adapted to support the resource-based view and entrepreneurial cognitive theory due to the dynamics in the business environment in which the small business performs and operates.
Methodology
Sampling and Data Collection
The method of data collected was by means of a self-administered questionnaire survey which was completed by small business owners using simple random sampling selected from the sampling frame of small business owners in the nine districts of Baghdad in Iraq. The sampling frame is a representation of all small businesses in the district of Baghdad. Even though, there are some shortcomings of using questionnaire survey-based research, the benefits arising from cost savings, convenience, and reduced interview biased seems to outweigh the limitations. There is also the risk of common method bias as a result of self-report data, and as such the results of this study should be viewed as representing the small business owners’ perceptions which could provide the most accurate assessment of the condition of their small business (Lyon, et al., 2000). Based on the data of the Employment and Vocational Training Department in the Ministry of Labour and Social Security (2017), there are “11302” small businesses in the district of Baghdad, Krejcie & Morgan (1970) table for sample size determination is employed. A sample of “375” small business owners from the sampling frame was administered with the questionnaire, and “300” usable responses were duly completed and returned, giving a response rate of 80 percent. The response rate was considered adequate, which might be related to the researcher’s ability to convince the respondents for them to participate in the survey actively.
In addition, in dealing with the issues of non-response bias which is pertinent to a survey method of data collection. In which non response bias exists when there are significant differences between the surveys responses of those who have responded early and those who do not respond. This study followed the convention of comparing the respondents of the first wave with those of the second wave (Armstrong & Overton 1977). The early wave group consisted of “186” responses whereas the final wave group consisted of “114” responses. The independent sample test (T-tests) conducted on the responses of these two groups yielded no statistically significant differences on demographic characteristics in the survey. Thus, it can be concluded that there is no significant non-response bias in this study (Oppenheim, 1966; Lin & Schaeffer, 1995).
Operationalization and Measurement of Variables
The entrepreneurial factors are referred to those factors that provide the entrepreneurs with the opportunities to establish their business in order to success and meet their needs and help in building the economy. The entrepreneurial factors assist in the business growth from different perspectives ranging from the local community to the urban areas. The items measured under the entrepreneur factor includes the motivation, functional skills, training, mind-set and aspiration in aiming high in the entrepreneurship activities. The measurements of these concepts are adapted from the previous literature (Amabile et al., 1994; Krasniqi & Tullami, 2013; Botha, 2006; Jayawarna et al., 2013; Carland et al., 2015; Davis et al., 2015). The item is used to measure the variable (entrepreneurial skills).
Entrepreneurial skills measures
1. I’m focused on the long term (Future Focus).
2. Sometimes the idea just bubbles out of me (Idea Generation).
3. I have a reputation for being able to take an idea and make it work (Execution).
4. I’m sensitive to others’ feelings (Interpersonal Sensitivity).
5. I am a self-confident person (Self-Confidence).
6. Even when things are not going well I look on the bright side (Optimism).
7. I do not give up easily (Persistence).
8. I feel comfortable when taking risk in my business venture (Risk Taking).
9. I believe I have a high locus of control (Locus of Control).
10. I believe in my problem solving and creativity ability (Self Esteem).
Business Environment
The business environment is vital and essential for the performance of the small business, the immediate environment and area of doing business, plays a vital role in the overall development of the Iraqi business environment and economy, due to the fact that most of the region in Iraqi have a specific product of small business they deal with in their surroundings, this contribute enormously to the overall growth of the economy. The items used to measure the Iraqi business environment include the post war dynamism, economic recession and the political instability of the country. Business environment as the moderating variable between the entrepreneurial behaviours and small business performance items are adopted from the previous studies conducted by Ward et al., 1995; Olszak & Ziemba, 2012; Peifer et al., 2012 and Leonidou, 2004. The instruments used to measure the construct are as follows:
1. Lack of access to financing affect small businesses.
2. Government instability affects business environment and performance.
3. Economic recession creates unfavourable business environment.
4. Shortages of skilled labour affect small business performance.
5. Rising cost of materials affect business performance.
6. Rise in utility cost affect business environment.
7. Declining demand in local market affect business environment.
8. Low profit margins affect business performance.
9. Declining in foreign market affect business environment.
10. Lack of access to advertisement of product affect business performance in a business environment.
Small business performance
The SMEs performance in Iraqi is crucial due to the effect of the long-lasted war and the country is still trying to recover from the previous damage done to the country. The presence of certain critical success factors such as the entrepreneurial factor like motivation, skills, training and mindset are vital towards the small businesses in Iraq, the measurement is adapted from the previous studies conducted by Abdul-Maksoud et al. (2008); Feldman (2014) and Rody & Stearns (2013) and the performance is measured based on the small business cash flow, profitability and the small business income. Below are the constructs used to measure the variables:
1. The level of profitability of small businesses has improved significantly.
2. There is an increase in operating income growth of small businesses.
3. There is a significant increase in sales profit growth of small businesses.
4. The cash flow growth rate has increased significantly.
5. Significant increase in yearly sales.
6. There is an increase in total asset of the small businesses.
Testing Of Hypothesis
The Table 1 in the below indicates the hierarchical regression results between entrepreneurial skills and small business performance. The independent variables were first entered in step 1; explain 26.2 percent of the variance. After entering business environment at step 2, the total variance explained by the model was 34.9 percent. In step 3, the interaction terms were inserted, which result to additional increase of 36.8 percent of the variance explained in the model. However, the significant F-change at step 1 to 2 and from step 2 to 3 at 1%, 5% and 10% were all significant. Inspection of the individual interaction term between ES×Business environment (t=2.922, p=0.004). This shows that business environment moderates the relationship between entrepreneurial skills and small business performance, hence H1 is supported.
| Table 1 Hierarchical Regression Result: The Moderating Effect Of Business Environment On The Entrepreneurial Skills And Small Business Performance |
|||
| Independent Variables | Std. Beta 1 | Std. Beta 2 | Std. Beta 3 |
| Entrepreneurial Skills Interaction | 0.512 | 0.23 | 0.246 |
| ES × Business environment | 0.138 | ||
| R2 | 0.262 | 0.349 | 0.368 |
| R2 change | 0.262 | 0.087 | 0.019 |
| F-change | 102.918 | 38.842 | 8.539 |
| Note: Significant level P<0.001***; P<0.05**; P<0.1*. | |||
Results And Discussion
The current study was conducted in order to investigate the relationship between the moderating effect of the business environment on the relationship between entrepreneurial skills and small business performance was equally investigated. The Quantitative method of data collection was employed, which involved the use of a well-structured questionnaire which was adopted and adapted from previous studies. A self-administered questionnaire was used which allows the researcher to have face to face interaction with the respondents. A total of 400 sets of questionnaires were distributed to owner/managers of small business with a population of 11302. Hence, having distributed 400 questionnaires, 350 were completed and returned. Out of which 300 were retained for further analysis. A total of 50 questionnaires were considered not suitable as a result of both uni-variate and multivariate outliers’ cases. The 300 questionnaires data were keyed into SPSS Version 23 and the analysis was conducted by start checking for missing values and outliers. Hence, the study do not recorded a missing value in the data set, as this was related to researchers curiosity right from the field in ensuring that all items were duly responded by the respondents, and at the same time, the researcher’s ability to key in any questionnaire collected within the shortest possible time. The principal component analysis was conducted to enable the researcher to assess the factor validity of the instruments.
Similarly, the reliability test was conducted for the purpose of assessing the internal consistency of the measures through the Cronbach’s alpha. In Table 2 the hypotheses of the direct relationship was established between entrepreneurial skills and business performance.
| Table 2 Multiple Regression Results Between Entrepreneurial Skills And Small Business Performance |
|||||
| Model | Standardized Beta | T | Sig. | Collinearity Tolerance | VIF |
| Constant | 5.46 | 0 | |||
| ES | 0.126 | 1.617 | 0.107 | 0.368 | 2.72 |
| R | R2 | Adj R2 | R2-Change | F-Change | |
| 0.6 | 0.361 | 0.352 | 0.361 | 40.454 | |
Tested using multiple linear regression, whereas, the hypotheses for indirect relationship (moderation) were tested using hierarchical regression analysis. The result of the factor analysis of small business performance as the dependent variable indicated that, the construct is measured with one component. Entrepreneurial skills, business environment were all measured as one dimensional and their respective reliability coefficient stood above 0.6 which is the minimum benchmark. In regard to the hypothesis testing for direct relationship using multiple regression analysis, the result showed that, H1, was the hypotheses developed on the moderating effects of the business environment on the relationship between entrepreneurial skills, and small business performance.
Conclusion
The hierarchical multiple regressions showed that, the business environment was a moderator of two of the hypotheses developed, which were entrepreneurial skills and small business performance because the interaction between variables was significant.
References
- Abbas, M.A., & Jassam, R.S. (2015). The problems of rebuilding a state in Iraq 2003-2015.Open Journal of Political Science,5(4), 247.
- Abdel-Maksoud, A., Asada, T., & Nakagawa, M. (2008). Performance measures, managerial practices and manufacturing technologies in Japanese manufacturing firms: State-of-the-art. International Journal of Business Performance Management, 10(1), 1-16.
- Adidu, F.A., & Olannye, P.A. (2006). Basic small business entrepreneurship: A modern approach. Agbor: Royal Pace Publishers.
- Al-Ansari, N., Ali, A., & Knutsson, S. (2014). Present conditions and future challenges of water resources problems in Iraq.Journal of Water Resource and Protection,6(12), 1066-1098.
- Amabile, T.M., Hill, K.G., Hennessey, B.A., & Tighe, E.M. (1994). The work preference inventory: Assessing intrinsic and extrinsic motivational orientations.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,66(5), 950-967
- Berisha-Namani, M. (2009). The role of information technology in small and medium sized enterprises in Kosova. InFulbright Academy Conference, 1-8.
- Balke, N., Plante, M., & Yücel, M. (2014). Fuel Subsidies, the oil market and the world economy (1407).
- Carland Jr, J.W., Carland, J.A.C., & Carland, J.W.T. (2015). Self-actualization: The zenith of entrepreneurship. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 6(1), 53-66.
- Carland, J.C., Carland, J.W., & Stewart, W.H. (2015). Seeing what's not there: The enigma of entrepreneurship.Journal of Small Business Strategy,7(1), 1-20.
- Chimezie, C. (2014). Critical feasibility study skills required for effective entrepreneurial development: Implications for Business Education Programmes.International Journal of Business and Social Science,5(10).
- Cordesman, A.H., & Khazai, S. (2014). Iraq in crisis. Rowman & Littlefield.
- Daniel, S.J., Cieslewicz, J.K., & Pourjalali, H. (2012). The impact of national economic culture and country-level institutional environment on corporate governance practices. Management International Review, 52(3), 365-394.
- Döckel, J.A., & Ligthelm, A.A. (2015). Factors responsible for the growth of small business.South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences,8(1), 54-62.
- Department of Economics (2009).OECD economic outlook(No. 85-86). Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
- Embassy, U.S. (2014). State Dept. on ISIL Claims of a Massacre in Tikrit, Iraq.
- Gomezelj Omerzel, D., & Antoncic, B. (2008). Critical entrepreneur knowledge dimensions for the SME performance.Industrial Management & Data Systems,108(9), 1182-1199
- Hanna, G.F., Hammoud, M.S., & Russo-Converso, J.A. (2014). Foreign direct investment in post-conflict countries: The case of Iraq’s oil and electricity sectors.International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy,4(2), 137-148.
- Hair Jr, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E., & Tatham, R.L. (2006).Multivariate data analysis,(6th Edition).
- Harash, E., Al-Timimi, S., & Alsaadi, J. (2014). The influence of finance on performance of small and medium enterprises (SMES).Technology,4(3), 161-167.
- Hisrich, R.D., & Peters, M.P. (2002). Entrepreneurship. McGraw-Hill.
- Husien, W.A. (2012). Role of Strategic Human Resources Management on SMEs’ Performance in Iraq. Doctoral Dissertation, Universiti Utara Malaysia.
- Jabeen, R. (2014). Moderating effect of external environment on performance of SMES in Pakistan. Doctoral Dissertation, Universiti Utara Malaysia.
- Jennings, P., & Beaver, G. (1997). The performance and competitive advantage of small firms: A management perspective.International Small Business Journal,15(2), 63-75.
- Kami, A., & Chaudhr, Z. (2011). Foreign direct investment in post-war Iraq: An investor's introductory guide to the legal framework. Internation Law & Management Review, 9, 141.
- Krejcie, R.V., & Morgan, D.W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities.Educational and Psychological Measurement,30(3), 607-610.
- Krasniqi, B.A., & Tullumi, M. (2013). What perceived success factors are important for small business owners in a transition economy. International Journal of Business & Management Studies, 5(2), 21-32.
- Lowry, J.R., & Chapman, J. D. (2015). Critical business problems and advisors. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 11(1), 64-73.
- Lohrke, F.T., Franklin, G.M., & Kothari, V.B. (2015). Top management international orientation and small business exporting performance: The moderating roles of export market & industry factors. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 10(1), 13-24.
- Lyon, D.W., Lumpkin, G.T., & Dess, G.G. (2000). Enhancing entrepreneurial orientation research: Operationalizing and measuring a key strategic decision making process.Journal of Management,26(5), 1055-1085.
- Leonidou, L.C. (2004). An analysis of the barriers hindering small business export development.Journal of Small Business Management,42(3), 279-302.
- Leonidou, L.C. (2004). An analysis of the barriers hindering small business export development. Journal of Small Business Management, 42(3), 279-302.
- Mahmoud, N., Ahmed, E.M., & Al-Sammarraie, N.A. (2014). Technology capabilities effects on Iraqi private banks risk management and financial performance. Pensee, 76(11).
- Nasr, S., & Rostom, A.M. (2013). SME contributions to employment, job creation and growth in the Arab world. Job Creation, and Growth in the Arab World.
- Ohanemu, C.N. (2006). The complete entrepreneur: Managing the small industry.
- Oppenheim, A.N. (1966). Questionnaire design and attitude measurement. New York: Basic Books, Inc.
- Peltier, J.W., Zhao, Y., & Schibrowsky, J.A. (2012). Technology adoption by small businesses: An exploratory study of the interrelationships of owner and environmental factors. International Small Business Journal, 30(4), 406-431.
- Rowley, T., Behrens, D., &Krackhardt, D. (2000). Redundant governance structures: An analysis of structural and relational embeddedness in the steel and semiconductor industries.Strategic Management Journal,21(3), 369-386
- Salucci, I. (2005). A people's history of Iraq: The Iraqi communist party, workers' movements and the left, 1924-2004. Haymarket Books
- Suder, G.G. (2004). Terrorism and the international business environment: the security-business nexus. Edward Elgar Publishing
- Tajnikar, M. (2000).Pripojitve, spojitve in prevzemi.
- Ukaegbu, V. (2004). The problem with definitions.Drama Research,3.
- World Bank (2015).The world bank annual report 2015. Washington, DC. © World Bank.
- Yeow (2014). The relationship between strategic entrepreneurship and performance of small medium enterprises in Malaysia. Doctoral Dissertation, Universiti Utara Malaysia.
- Wu, Z., & Chua, J.H. (2012). Second order gender effects: The case of US small business.