Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
A Comprehensive Study of Performance Appraisal of the Business Entity
Giriraj Kiradoo, Government of Engineering College
Nik Alif Amri Nik Hashim, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
Shah Iskandar Fahmie Ramlee, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
K.M.Ashifa, Istanbul GelisimUniversity- Istanbul
Abstract
Purpose: Performance appraisal is described as the measurement of outcome to generate reliable data on its effectiveness and efficiency. Performance appraisal measures the business activities and implements a strategy to bring them back to the desired position. This paper is useful in presenting a systematic understanding of the performance appraisal concept of the business entity.Research Methods: The Study of performance appraisal of a business entity has been performed using the literature review and case study analysis, interviews, and personal observation as the secondary source of data.
Keywords
Performance Appraisal, Performance Appraisal Criterion, Performance Appraisal Techniques, Performance Appraisal Process, Performance Appraisal System
Introduction
The research paper has been designed to study the concept of performance evaluation for the business entity (Albanese, 1978). The study's primary purpose is to understand how performance assessment or financial analysis affects overall growth and performance. In enterprise management, the commercial decision is considered arduous (Erich, 1977). Increasing overall performance and running effectively with available financial resources is one of the best tools to regulate such processes with limited resources. Although considerable research has been done on this topic, some conclusions regarding companies' performance evaluation and effectiveness have still been drawn. It is necessary to review the matter critically. It has been planned to do research with data collected and presented in theoretical formats through literature review, industrial analysis, and personal observation.
Methods of Research
The following methods have been adopted for research to get a complete insight into the organisation's (Francis, 1980). overall performance appraisal scenario.
Case Studies
Through the case studies as a research method, a holistic analysis of past events has been carried out in various industries regarding performance assessment and has affected organisations' functioning. These case studies reflect different approaches to deal with the situation and find better solutions to deal with them timely.
Interview
Having one-on-one connects with industrial experts to consider the importance of performance appraisal and its impact on its overall performance has been extremely important. There were severe sets of questions that we prepared to answer questions about the topic, including the meaning of their performance evaluation and how their company has opted for it.
Overview
One of the most practical and influential ways is observation. It collects information by looking at trends of industries, market and conclusions based on the same. It helps create an approach on the subject and ends based on individual observations rather than research or literature.
Literature Review
Meaning & Concept Related To Performance Appraisal
Concept & Meaning of Performance
Studying an organisation's performance means analysing the organisation's behaviour, and improving the execution, enhancing the individual's behaviour. Implementation of an organisation means attaining its strategic objective, which can be stated as the actual meaning for efficiency. This concept is known to form a systematic, rational model that makes the organisation perceived as mechanical, which says that efficiency must be implicitly considered. Performance regarding business entity is viewed as the creation and significant reason behind describing the concept of determining the dimensions and properties (Gresternberg, 1960). These considerations thus have a proper reference to the overall performance of the company's strategy. Concurrently, (Hant & Donaldson, 1966). Performance appraisal measures the company's effectiveness quantitatively (Helfert, 1977).
Performance can also be stated as a precarious balance between effectiveness and efficiency. It can even be termed as the state of competitiveness for the enterprise attained through efficiency and effectiveness, which helps maintain its presence in the market. (Howard & Upton)
The concept of performance even involves the economic idea regarding creating value and wealth for the organisation (Pandey, 1983). Thus, performance has been stated to be a relationship between the benefit derived from the cost incurred. (Kennedy & Me Millan, 1962). Two of the central concepts which have been dominating modern management are performance and value. The performance measure is for assessing the value and knowing the primary cause that generates the actual value (Kohlar, 1979).
Concept & Meaning of Appraisal
Appraisal has been termed to conduct unbiased evaluation and analysis of the assets for any organisation or business or evaluate the performance based on defined criteria or standard (Kothari, 1997). There are various kinds of appraisals that have been brought to the picture by multiple researchers, and they include the following:
Business Asset
Business Assets are appraised in situations where the business plans to cease its operation. In such a case, the company must determine the assets' overall value for paying off the liabilities.
Capitalizing the Earning
One of the most popular means of appraising the business is determining its earning. While capitalising on the earning, the well documented earning record from the past is considered and given weightage.
Future Earning
The future earning is meant to look at the future anticipated figures that the business plans on making in future. The company uses the discount rate after the determination of projected earnings.
Meaning & Concept of Performance Appraisal
Performance appraisal in terms of business entity ensures that the outputs and activities meet the required business goals most effectively and efficiently. It focuses on the system's overall performance, employees, department, or even managing tasks in the organisation. Business managers, (Lloyed, & Don, 1975). Senior leaders, and task owners generally decide these standards for performance appraisals. The method includes specification in terms of functions and the related outcome of any job, including giving proper coaching and feedback, comparing the performance with other organisation's performance in the same industry, and giving away rewards for achieving target goals (Nigam, 1989).
Objective and Importance of Performance Appraisal
Having a business appraisal has been essential for any organisation. Instead, it has been considered indispensable for various reasons, including the following:
Selling & Buying Business
It is necessary to have the business's appraisal done to get a systematic and accurate value before planned to be acquired or any company is intended to be bought or sold or a business merger.
Setting up of Legal Disputes
Having legal disputes in business are familiar, which are majorly caused due to breach or disagreement of any contract (Antino, 2014). In such cases, the companies get involved in taking legal actions that are considered a highly effective means of settling disputes. While such disputes are handled, the court requires the details on the business appraisal. It is necessary if funds are to be re-allocated, assets are to be liquidated, or business is to be sold (Kulkarni, 1983). The details required for the same are much handy with the help of business' performance appraisal.
Determination of the Actual Value of Intellectual Property
Most people assume that the only aspect of the business's performance appraisal is its tangible assets, and there is no way to appraise intangible asset like intellectual property. However, such determination has been deemed vital as it has an overall contribution to the business value (Robert, 1978).
Raising Fund
When the business wishes to convince and attract investors to contribute money to the company, its performance appraisal data helps straightforwardly. If the company's value is high, the investors are driven to make investments in the company (Anasica & Sweta, 2020).
Basis of Performance Appraisal
Business performance appraisal has also been recognised as the business unit's financial performance appraisal as an objective evaluation in terms of financial strength and profitability. Financial statement analysis and financial performance appraisals are used as synonyms by researchers. All kinds of techniques of financial statement analysis are being used by companies for economic appraisal. (Richard, Wilson & Gerard, 1987).Thus, a financial appraisal applies various financial statement analysis techniques to make a comparative, relevant, and critical evaluation of any firm's financial health and profitability. The accounting system is overly concerned with recording, classification, and presentation to summarise any financial data. Such data is thus analysed for appraisal and evaluation of the performance of the company (Demirdağ, 2021).
The financial statement analysis is defined as an attempt to unveil the significance and managing various items classified under the balance sheet and profit and loss account. It assists the management in informing the operational and financial policies. It also shows all the crucial facts regarding profitability, strength, weaknesses, efficiency, solvency, managerial performance, and other related factors (Thornfon, 1979). These financial appraisal techniques are used to analyse the accounting data for answering the various question on the company's safety of investment, the profitability of the firm, solvency status, reserves, and growth prospects of the company.
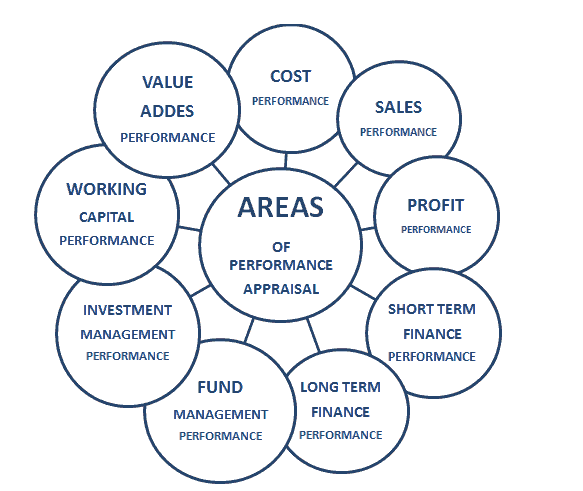
Areas of Performance Appraisal
Businesses' performance can be analysed on the following various areas identified during research (Figure 1):
Cost Performance
Measurement of cost performance involves cost variance, earned value management, and performance index. Cost variance indicates the change between the value gained and the actual cost. Earned value provides information about the extent to which the project has been completed in terms of cost and time. Moreover, the ratio of earned value to the actual cost is known as performance as a cost price index.
Sales Performance
Sales performance measures the actual sales for the budgeted sales plan over the year. The variance is calculated to evaluate the strategy drafted for the sales target.
Profit Performance
Profit performance provides an insight into the business's ability to operate a profitable venture. The profit performance is calculated with the financial statement's data, and it includes critical information about the companies earning capacity. The profit performance has four types: gross profit, net profit, operating profit, and margins. Gross profit indicates the total revenue earned net of the cost of goods sold. Using profit is the gross profit net of operating expenses (Tripathi, 1978). At the same time, net profit is calculated by deducting the operating profit's irregular business expenses. Margin is a ratio that provides information about profit percentage to sales revenue.
Short Term Financial Performance
Short-term financial performance indicates the firm's ability to fulfil its short-term liabilities. The short-term financial performance could be calculated monthly to ascertain and compare the company's financial performance in the period. The short-term financial performance is mainly related to the performance of the current asset and current liability. Various liquidity ratios are some of the means to measure the short-term financial performance of the business entity.
Long Term Financial Performance
Long-term financial performance indicates the firm's ability to fulfil long term obligations. The long-term performance could be calculated on the trends of the last five or ten-year basis. It could be measure with return on equity or retune on investment ratios, which provide information about the return made on capital, debt, or equity over more than a year.
Fund Management Performance
Fund management is a performance appraisal method that provides information on the organisation's efficiency to manage the fund. Fund management is generally related to the firm's cash flow, considering financial, operating, and investment activities. However, it is majorly associated with its investment activities and decision to cultivate liquidity for operation and enhance its share's value concerning financial activity.
Investment Performance (Investor's point of view)
Investment performance provides information about the investment portfolio's excess return. It could be measure in two manners, namely yield and rate of return. Yield includes information about the return on the investment made. In contrast, the return rate specifies the total return over time (mostly annually) over the investment. Yield does not include the capital gain in its calculation; however, the rate of return does. Mutual funds, stock, and bonds are some of the securities that produce yield and return.
From an investor's perspective, the investment performance provides information about the excess value of an investment earned over the period. It is the most common performance measurement mean adopted by the investors to make the investment decision. Therefore, the yield and return rate are two primary tools to gain more investment from the potential and current investors from the company's perspective.
Working Capital Performance
Working capital performance provides information concerning to evaluate the company's working capital management. Efficient working capital management could be performed with an improvement in cash-in-flow. The working capital represents the net current asset required to sustain the ordinary business course routinely. Efficient working capital management releases the extra cash flow bounded for the operation. The same could be invested in any other manner for a better return by the company. Therefore, working capital performance ascertains the efficiency with which the cost of day-to-day operation has been managed and cut down.
Value-Added Performance
Value-added performance provides information about the value created by the organisation. The value-added performance is calculated as Economic Value (EVA) and Market Value (MVA) performances. The EVA is a total return rate over the firm's capital cost. Simultaneously, the economic value-added calculates its net wealth as the difference between operating profit and capital cost with tax adjustment. EVA helps to calculate the value the firm has generated over the investment fund in the business.
However, market value is calculated as the difference between the entity's market value and the investors' capital contribution. Market value provides information about the capital invested, including the market value of the debt and equity. It includes information about the company's capacity to enhance its investment over the period. A high MVA indicates strong value-added performance with strong operational capabilities. A low MVA demonstrates that the management's operation creates less value than the shareholders' capital contribution. However, MVA could not be the only indicator of management performance during the bull market. The stock prices are high while low in the bear market.
Techniques of Performance Appraisal
Business performance appraisal is performed using various techniques, and a few of the most popular ones include the following:
Management Accounting Techniques
The management accounting technique helps in identifying, measuring, analysing, and interpreting the information in accounting for supporting the managers in making a crucial decision for managing the operation of the company. It helps in reporting the company's financial transaction for making various business and financial decisions correctly. It involves analysis like margin analysis, constraint analysis, capital budgeting, inventory valuation, trend forecasting, and analysis.
Statistical Techniques
There are majorly two statistical techniques that are used for analysis and performance appraisal. These include descriptive statistics that help summarise the data using the sample with the help of indexes and inferential statistics, which is used while data is looked in as a systematic subclass for a defined population.
Other Modern Techniques
Various other techniques are used for the performance appraisal of the company, and it may include the following:
Management by Objective
It is termed to be a technique in which employees and managers identify the plans and communicate the objectives to focus on the company's appraisal.
Financial Software
The software helps combine the financial and accounting data in a single place and investigate an accurate financial picture. It helps in scaling up the financial functions of the company and helps the company grow with time.
Process Of Performance Appraisal
The performance appraisal methods need to create an alignment between the operation and strategies. The business performance must be analysed based on a different level. At the top level, the performance measurement should provide an insight into the strategic performance based on its vision. The second level includes the business's objective, which is needed to be measured in terms of market and financial terms. The third level comprises measurement based on the operating system regarding customer satisfaction, flexibility, and productivity. While the bottom level of size includes the operational objectives of quality, delivery, cost, and process time.
Another process that could be considered is the Balanced Score Card (BSC) Performance measurement. The BSC model has four components: financial performance, customer performance, internal business process performance, and performance related to its learning. BSC model helps to synergise the long-term objectives (Strategy) to the short-term target (Operations).
Findings and Discussion
As can be understood from the comprehensive study done above, the performance appraisal is highly dependent on various financial aspects and the company's performance. The company's financial health can be one of the best indicators of its growth potential in the longer run. To improve the company's financial position and ensure proper business appraisal, the company needs to have an appropriate business analysis, which is inclusive of the five areas given in Table 1.
| Table 1 Appropriate Business Analysis, Which Is Inclusive Of The Five Areas |
||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Revenue | Revenue has been termed to be the most critical source of cash in the company. The quality, quantity and timing of revenue can help in recognising the long-run success of the company. The revenue is analysed based on revenue growth over the period, revenue made from each client, and revenue generated by each employee. |
| 2 | Profits | The company needs to be producing quality profits for surviving in the longer run. The profits are analysed based on the Gross profits margin, net profit, and operating profit. Gross profits reveal the production efficiency of the business, and operating profits indicates operational efficiency. The net profit proves the overall efficiency of the business. |
| 3 | Operating Efficiency | It helps recognise the appropriateness with which the company's resources are being used. If there is no proper operating efficiency in the business, the company makes smaller profits and generates weak market growth. The company's operating efficiency is recognised, employing accounts receivable turnover and inventory turnover of the company. |
| 4 | Capital Solvency and Efficiency | It includes the payments to interest to the investors and lenders. How it gets repaid helps determine the business's financial stability to judge the company's overall performance. The company considers calculating return on the company's equity shares and its power to repay all its debts with its existing equity to calculate the same. |
| 5 | Liquidity | This specific analysis represents the company's ability to generate cash to cover its overall cash expenses. Even increased revenue and profits cannot compensate for the low liquidity of any business. Liquidity is measured with the help of the interest coverage and current ratio of the company. |
The most important part of the Performance Appraisal of the Company is the financial analysis. It is performed with the help of comparison to determine if the company can align itself to the overall benchmark that it was asked to observe. It works in the case of all the data points and even helps judge its overall financial position.
Conclusion
As can be well understood from the comprehensive study done about performance appraisal, it forms an essential part of the business organisation. It helps the business management recognise its worth in terms of the market and industry and thus work on business strategies. Business performance appraisal allows companies and investors to invest in the company, which helps stabilise its position in the business market. Performance appraisal helps with conducting the financial report analysis and understanding the various aspects of business performance. It ensures future growth and even analyses efficiency to make profits in the longer run. Business performance appraisal is considered as well-known financial appraisal, which helps the company raise the need for investment in front of the financial institution and ensure that they can get all the funds required to expand their business into the new market company.
Limitation of Study
Though even after having all the essential information to study the topic and make the necessary conclusion, certain aspects limit the scope of the study of this topic, and they include the following:
Limited Literature
Though various researchers have done an in-depth study on the topic, the scope of literature around the subject remains limited in terms of its vastness. Most of the literature is concentrated on appraising tangible assets without considering the importance of intangible assets for the organisation, which also impact the company's overall performance in a various manner. The literature around the subject is limited and thus limits the scope of the study.
Generic Study
The topic is quite generic regarding its nature and the industry to which it belongs. However, each sector may have different parameters for recognising their business performance, highlighted in the literature. Thus, a vital aspect has been highly ignored in this case.
Further Scope of Research
Various other areas can be explored as part of the comprehensive study of literature around the topic, and this includes the following:
Considering the Study of Good Will
One of the most important intangible assets is goodwill, which helps build trust in the brand and attract more profits. It can be further analysed as part of the study of this topic. Also, literature is limited around the subject as various assumptions are to be made while studying it.
Nature of Business
Considering various forms of business and how they can be upraised is another field to improve the scope of the study of this topic. The industrial analysis shall help evaluate the business analysis's further coverage and ensure that each business form is investigated with the different standard's help.
References
- Albanese, R. (1978). "Managing towards accountability for performance". Richard D. Irwin Inc, Home wood. Illinois. 13-14.
- Erich, A. (1977). Helfert "Techniques of Financial Analysis" (4th Edition). Richard D. Irwin Inc., Homewood Illinois, 53.
- Francis, P. (1980). "The foundations of financial management". Arnold Heinemann, New Delhi, 25.
- Giriraj, K. (2003). "Performance Appraisal of Ceramic Industries of India". Ph.D. Thesis, MDS University Ajmer, Kiradoo, Giriraj, Use of Statistical Techniques in Ceramic Industry to Reduce Complexities. 2020 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 993, 012112.
- Gresternberg, C.W. (1960). "Financial Organization and Management of Business" (4th edition). Asia Publishing House, New Delhi, 365.
- Hant, W., & Donaldson. (1966). "Basic business finance, text & cases" (Third Edition). Homewood Illionois Richard D. Irwin Inc., 141.
- Helfert, E.A. (1977). "Techniques of Financial Analysis" (4th edition). The Richard D. Irwin inc., Homewood, Illinois, 53.
- Howard & Upton. (n.d). "Introduction to Business Finance". International student edition Me Graw Hill Book Co. Ltd., New York, 61.
- Pandey, I.M. (1983). "Management Accounting". Vikash Publishing House, 89
- John A.T. (n.d). "Fundamentals of financial accounting" (Second Edition). John Willy R Sons, 605.
- Kennedy, & Me Millan. (1962). "Financial statements: Form analysis and interpretation", (4th edition). Richard D. Irwin inc., Illinois, 7.
- Kohlar, E.L. (1979). "A Dictionary for Accountants", (4th edition). The Prentice Hall ofIndia Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi. 315.
- Kothari, C.R. (1997). "Research Methodology". Wishwa Prakashan, New Delhi.85.
- Lloyed, R.A., & Don, A. (1975). Egg in Fion, "Management Accounting". Long Man Group Ltd., 62.
- Nigam, S. (1989). "Financial efficiency". Print Well Publishers, Jaipur, 5.
- Antino, M. (2014). Customer satisfaction analysis based on customer relationship management. International Journal of New Practices in Management and Engineering, 3(01), 07 - 12.
- Kulkarni, P.V. (1983). "Financial management". Himalaya Publishing House, Second Edition, 146.
- Robert, A. (1978). "Managing towards accountability for performance". Richard D. Irwin Inc., Home wood, Illinois. 13-14.
- Anasica, S., & Sweta, B. (2020). Analysing the factors involved in risk management in a business. International Journal of New Practices in Management and Engineering, 9(03), 05 - 10.
- Richard, M.S., Wilson & Gerard, Mc.H. (1987). "Financial analysis – A managerial introduction". Cassers Educational Ltd., 63.
- Demirdağ, S. (2021). The mediating role of life satisfaction in the relationship between time management and communication skills. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice, 27(1), 967-984.
- Thornfon, N. (1979). "Management accounting". London Allied Publishers Pvt. Ltd., Indian Reprint Edition, 149.
- Tripathi, P.C. (1978). "Research methodology". Sultan Chand & Sons, New Delhi, (1991) p. 108.
- Meigs, W.B. (n.d). "International accounting". Mc Graw Hill Book Co. Ltd., 1049.