Research Article: 2023 Vol: 26 Issue: 5
A study of Management Information System report of student′s performance in rural school of Ranchi in Jharkhand.
Devendra Nath Mahato, YBN University
Citation Information: Nath Mahato, D. (2023). A study of management information system report of student’s performance in rural school of ranchi in jharkhand. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 26 (5),1-10.
Abstract
In the school education, we mostly measure the academic performance of students in terms of % of marks, pass, fail, rank, division etc based out of the education provided. But now we should think beyond this parameter, an in-depth analysis of each student’s performance by evaluating the management information system reports. This MIS report will help to teachers, principal, students and parents who are the key stakeholder in school education to analyse the student’s performance. It also helps to School Management to develop policy and procedures which in turn improves the quality of education. This MIS reports will be prepared based out of raw data, which is easily available in our regular teaching classes. These raw data are processed and transformed into information using IT computation technique. This Paper explains the concept of data, related information and MIS. The importance of MIS, its rapid growth and latest trends in MIS are discussed in this paper. A MIS tool shall be developed to generate the MIS report automatically, after surveying the different schools of Ranchi to understand the teaching techniques. Right now, we have different manual techniques or pen and paper methods to maintain such students performance report. Now we have the technology era where information must be in finger tips. The parents or school management is also expecting the information as on demand
Keywords
Management Information, Student’s Performance, Rural School.
Introduction
Computers began to emerge in the 1940s and 50s, punch cards in 1970s were replaced by magnetic storage media like tapes and disks. Between the 1970s and the early 1990s, as computers got smaller, quicker, and more affordable, MIS expanded beyond accounting to include inventory, sales, marketing, production, and engineering. MIS mostly started to becoming a summarised report for the top management.
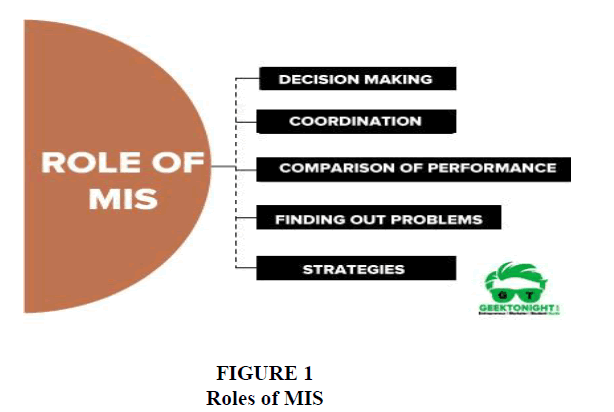
There are different kind of roles described in MIS and some of the important MIS roles are given below.
• Decision making: Management Information System (MIS) plays a significant role in the decision-making process of any organization. In any organization, MIS is a tool which can help to provide information about the organisation and this information is used further to make right decisions. Coordination among the department: Management Information System satisfy multiple need of an organization across the different functional department (Figure 1).
• Finding out Problems: As we know that MIS provides relevant information about every aspect of activities. In day-to-day, management Information Report is a summary type of report for all departments to understand the health condition of organisation. By seeing these reports, we can find out the problems, if any.
• Comparison of Business Performance: MIS store all past data and information in its Database. By extracting the past historical data, we can compare the organization performance with the current. By this approach we can increase the organisation performance.
• Strategies for an Organization: Today each business is running in a competitive market. An MIS is a great tool which helps the organization to evolve appropriate and right strategies for the business to achieve the organisation’s goal.
Definition of Management Information Systems
The study of people, technology, organisations, and their interrelationships is known as management information systems (MIS). MIS professionals help organisation realize maximum benefit from investment in personnel, equipment, and business processes. MIS is a people-oriented field that emphasises technology-assisted service.
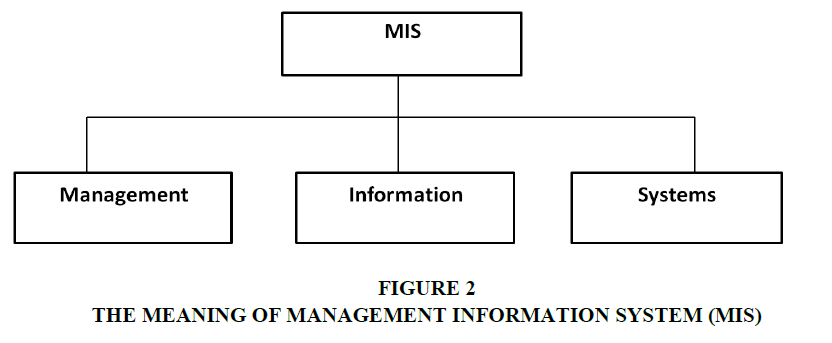
The phrase management information systems is made up of three elements; in order to comprehend the meaning of this term, you must first comprehend the meanings of management, information, and systems. It is preferable to comprehend each component of the term.
Management
Management is to achieve organizational goals efficiently and effectively through planning, organizing, directing and controlling organizational resources, it's ability to achieve the goals by others Al-Mamary et al. (2014) as stated by Al-Najjar. According to business dictionary (Al-Najjar, 2010). “Management is the organization and coordination of the activities of a business in order to achieve defined objectives.” Management is often known as a factor of production along with the key factors of any organisation like machines, materials, and money.
Data and Information
“Data is raw unprocessed facts and figure 2 that have no context or purposeful meaning and information is processed data that has meaning and is presented in a context”. According to Hardcastle (Einstein et al., 1935). “Data is a raw fact and can take the form of a number or statement such as a date or a measurement. information is generated through the transformation of data.” According to (Hasan et al., 2013).“Information as data that have been converted into a meaningful and useful context for specific end users.”
Types of Information
Hasan et al. (2013) suggested a classification of information into four categories: Descriptive Information, Diagnostic Information, Predictive Information and Prescriptive Information (Figure 3).
Descriptive Information
Staring point in the classification of information is the descriptive information, which is the base for all other types of information. Descriptive class of information scenario building of the business at a particular point of time. As an example of an School education system, it deliberates about:
a. Number of students enrolled,
b. Disciplines like Science, Commerce, Arts, Computer etc running at 10+2 level,
c. Placement and higher education,
d. Marketing strategy adopted and its impact on the enrolment.
Diagnostic Inforation
Diagnostic information provides insight in to the problems. What are the reasons of the problems? What has not been done? What should have been done? These are the areas of coverage of diagnostic information. The types of information needed in this class of information in case of the education institutes are:
a. Why the registration of students is below expectation?
b. Where is more registration and why?
c. What are reasons of students taking admission in this school?
d. Has the marketing strategy adopted given commensurate results?
e. Why students initially registered switched over to other schools?
f. Is the fees charged competitive in comparison to other contemporary schools?
Based on the diagnostic information education planners and regulators set norms and standards. Gap analysis is carried out to identify the areas of concerns as well as areas of opportunities. The information available is used for appropriate action plans.
Predictive Information
Predictive information is relating to question “What if….?” This class of information helps in analyzing the future strategies to be considered and adopted. This information attempts to identify the desirable outcomes. The predictive information is vital for forecasting, planning future strategies, looking for resource mobilization in coming years and what type of marketing strategies will be more practical. Budgeting techniques, simulation models and other management tools adopted by the organizations use predictive information extensively. Predictive information addresses the question of what should be done and what can be done. The basic source for such analysis is the domain of predictive information. The output of the predictive information is deliberated in the context of goals and values set for the organization.
For example, an school may offer integrated courses which ensure the students can prepare Engineering entrance or competition test at a later date when they have to go for higher education. The competition at that stage may be very critical. But a student of the same school will have more chances to get admission in higher courses due to intimate knowledge of the standard and norms of the school. Even the school have more confidence on the likely performance of its own students Figure 3.
System
According to Einstein et al. (1935) a system can be defined as a collection of components that work together towards a common goal. The objective of a system is to receive inputs and transform these into outputs. A set of policy and procedures helps who achieve organisation’s goal.
According to Hasan et al. (2013) a system is a set of five major interrelated components namely people, business processes, data, hardware, and software, with a clearly defined boundary, working together to achieve a common set of objectives by accepting inputs and producing outputs in an organized transformation process.
It’s a people process in order to improve business processes.According to Hasan et al. (2013) management information system is type of information systems that take internal data from the system and summarized it to meaningful and useful forms as management reports to use it to support management activities and managerial decision making. According to Kabir (2016) management information systems basically concerned with converting data from internal sources into information which is then communicated to managers at all the levels, in all functions to make timely and effective decisions for planning, directing and controlling the activities for which they are responsible.
Definition of the Problem
This research evaluates management information system report about student’s performance and its usage in schools by teachers, parents, principal and school management committee. It helps to deal on:
a. How to increase the quality of education ?
b. How It shows the path to make student’s attention towards education ?
c. Why More than 50% students in fifth grade are unable to read a second grade text book in Govt. School ?
d. How it influence the student’s productivity
e. How it improves the teaching technique ?
Research Objectives
To study the awareness level of MIS report among students, teachers, parents, principal and school management committee of schools in Ranchi, Jharkhand.
• To study the extent of usage of different similar MIS reports prepared either manual or computerised by schools in Ranchi, Jharkhand.
• To study the practices of teaching techniques in schools for parents.
• To study the students approaches and interest towards study.
• To study the overall analysis of rural school performance in Ranchi, Jharkhand
Scope of Work
This study is restricted to analyse the student’s performance based on different techniques used by schools within Ranchi, Jharkhand. The key stakeholders are students, teachers, parents, principal and school management committee of schools shall be engaged in this research.
Research Questions
• Research Question 1: What type of information parents expect about their children ? What are the challenges parents, teachers, school management facing about their students to improve the quality of education?
• Research Question 2: What are the different parameters required to evaluate student’s performance ?
• Research Question 3: What are the approaches taken to measure the student’s performance ?
• Research Question 4: What about the teacher’s comfort level regarding usage of IT for the implementation of MIS tool ?
Literature Review
A detailed review of collection of available knowledge from journals, conference papers, news papers has been done and found that the research in Management Information System field is mostly done in manufacturing industry sector. It is unique and original research where MIS tool shall be developed for school education sector. since similar work has not been carried out previously. So, this research will:
• Help school management committee in improving the quality of education thru MIS Report
• Help School Management to make their staff IT enabled
• Support in better implementation of Digital India to various educational institutes.
• Help policy makers of education department at State and Central government level to evaluate Students performance report.
Research Design
Here, the research design refers to the overall strategy that we choose to integrate the different components of the study in a coherent and logical way, thereby, ensuring we will effectively address the research problem; it constitutes the blueprint for the collection, measurement, and analysis of data.
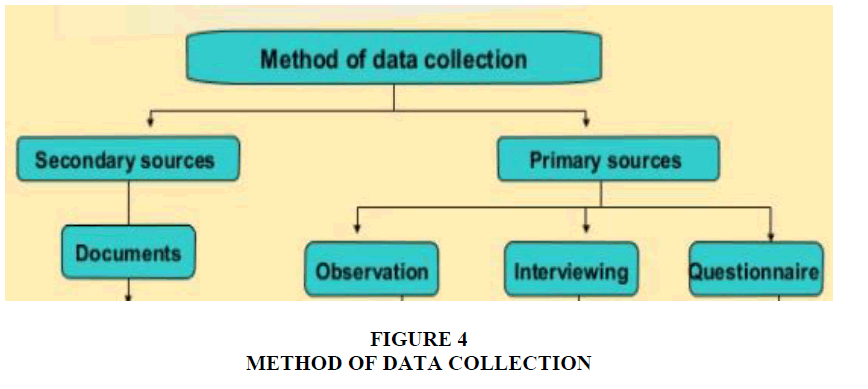
Data collection is a process of collecting information from all the relevant sources to find answers to the research problem , test the hypothesis and evaluate the outcomes Figure 4.
Most of the organizations collect data to make better decisions. Without data, it would be difficult for organizations to make appropriate decisions, and so data is collected at various points in time from different audiences. Although data is a valuable asset for every organization, it does not serve any purpose until analyzed or processed to get the desired results. Data collection is a real challenge for researchers and it requires much time and effort. For our research we have to visit schools of Ranchi where data to be collected. The data sources can be either the existing data or the new data. Existing data such as Report Card, Attendance Register, Teacher remarks on notebooks and other documents can be of great value in our research studies.
According to Basic Guidelines for Research (Kalhoro et al., 2019). We can categorize data collection methods into primary methods of data collection and secondary methods of data collection. The method of data collection is based out of the given techniques as mentioned in given diagram (Laudon & Laudon, 2004).
Primary Sources
Primary data is collected from the first-hand experience and is not used in the past but the best data source is student’s Report Card. The data gathered by primary data collection methods are specific to the research’s motive and highly accurate. For our research, we are mostly dependent of school students aging between 10 to 15 years so chances of data collection accuracy is little bit less whereas data collection accuracy becomes highly accurate when we collect data from teachers Figure 4.
Primary data collection methods can be divided into two categories: quantitative methods and qualitative methods.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative research presents data in a numerical format, enabling researchers to evaluate and understand this data through statistical analysis. It answers questions such as “who?”, “when?” “what?”, and “where?”. Common examples include interviews, Questionnaire , and case studies/document review. Generally, quantitative data tells us what respondents’ choices are and qualitative tells us why they made those choices. These methods of primary data collection are generally used to make long-term forecasts. Statistical methods are highly reliable as the element of subjectivity is minimum in these methods (O’Brien et al., 2011).
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods are especially useful in situations when historical data is not available. Or there is no need of numbers or mathematical calculations. Qualitative research is closely associated with words, sounds, feeling, emotions, colors, and other elements that are non-quantifiable. These techniques are based on experience, judgment, intuition, conjecture, emotion, etc.
Quantitative methods do not provide the motive behind participants’ responses, often don’t reach underrepresented populations, and span long periods to collect the data. Hence, it is best to combine quantitative methods with qualitative methods.
Observation
Observation technique is used to record the student’s behaviours and actions during class. Observational measurement can be unstructured or structured. Unstructured observations are done spontaneously and recorded as what is seen in words. Whereas, in structured observations, the researcher should carefully decide what to observe, how to observe, how long, and how to record the observed data. Observational measurement are usually more subjective than other methods of data collection. However, in some situations, observation may be the only way to collect information. In structured observations the specific behaviours of study subjects or the events to be observed or studied should be carefully defined.
In observation measurement, the observer plays an important role. A participant observer plays an active role and take part in the activity or event being observed. The nonparticipant observer adopts a passive role while observing the phenomena of interest. If observations are done by more than one data collector, establishing interrater reliability is vital. Here, Behaviours of student’s are measured in terms of Concentration on studies, Follow School Discipline, Attention etc.
Interviewing
In this method, the interviewer asks questions either face-to-face or through telephone to the respondents. In face-to-face interviews, the interviewer asks a series of questions to the interviewee in person and notes down responses. In case it is not feasible to meet the person, the interviewer can go for a telephonic interview, e-mail, WhatsApp. This form of data collection is suitable when there are only a few respondents. It is too time-consuming and tedious to repeat the same process if there are many participants.
Questionnaire
A questionnaire is a printed set of questions, either open-ended or closed-ended. The respondents are required to answer based on their knowledge and experience with the issue concerned. The questionnaire is a part of the survey, whereas the questionnaire’s end-goal may or may not be a survey.
Surveys
Surveys are used to collect data from the target audience and gather insights into their preferences, opinions, choices, and feedback related to their products and services. Most survey software often a wide range of question types to select. Here, we use a ready-made survey template to save on time and effort. Considering the Covid19, most of the surveys are being conducted online. Once the data is collected, survey software can generate various reports and run analytics algorithms to discover hidden insights. A survey dashboard can give us the statistics related data (Patterson, 2005).
Delphi Technique
In this method, market experts are provided with the estimates and assumptions of forecasts made by other experts in the industry. Experts may reconsider and revise their estimates and assumptions based on the information provided by other experts. The consensus of all experts on demand forecasts constitutes the final demand forecast.
Conclusion
Focus Groups
In a focus group, a small group of people, around 8-10 members, discuss the common areas of the problem. Each individual provides his insights on the issue concerned. A moderator regulates the discussion among the group members. At the end of the discussion, the group reaches a consensus.
Secondary Sources
Secondary source of data is the data that has been used in the past. Data collected from a source that has already been published in any form is called as secondary data. The review of literature in any research is based on secondary data. It is collected by someone else for some other purpose. The researcher can obtain data from the different documents, both internal and external, to the organization.
Internal Sources of Secondary Data
• School’s health and safety records
• Mission and vision statement
• Financial Statements
• School Magazines
• Report Card
• Attendance Register
External Sources of Secondary Data
• Government reports
• Press releases of Toppers name
• Journals
• Libraries
•Internet
The secondary data collection methods, too, can involve both quantitative and qualitative techniques. Secondary data is easily available and hence, less time-consuming and expensive as compared to the primary data. However, with the secondary data collection methods, the authenticity of the data gathered cannot be verified. Secondary data can be less valid but its importance is still there.
Sometimes it is difficult to obtain primary data; in these cases getting information from secondary sources is easier and possible. Sometimes primary data does not exist in such situation one has to confine the research on secondary data. Sometimes primary data is present but the respondents are not willing to reveal it in such case too secondary data can suffice.
References
Al-Mamary, Y. H., Shamsuddin, A., & Aziati, N. (2014). The meaning of management information systems and its role in telecommunication companies in Yemen.American Journal of Software Engineering,2(2), 22-25.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Najjar, F.G. (2010). Management information systems managerial perspective.
Beneke, R.R. (1955).Managing the farm business, 80 (3), 251.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., & Rosen, N. (1935). Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete?.Physical review,47(10), 777.
Hasan, Y., Shamsuddin, A., & Aziati, N. (2013). The impact of management information systems adoption in managerial decision making: A review.The International Scientific Journal of Management Information Systems,8(4), 010-017.
Kabir, S.M.S. (2016). Basic guidelines for research: An introductory approach for all disciplines. Book Zone Publication,4(2), 168-180.
Kalhoro, S., Rahoo, L.A., Kalhoro, M., & Nagar, M.A.K. (2019). The Meaning and Role of Management Information System in the Telecom Companies in Sindh Province.Intelligent Systems Engineering,10(3), 9-13.
Laudon, K.C., & Laudon, J.P. (2004).Management information systems: Managing the digital firm. Pearson Educación.
O’Brien, J.A., & Marakas, G.M. (2011). Foundation of information systems in business.Management Information Systems, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 65-67.
Patterson, A. (2005).Information systems: Using information. Intermediate 2; Higher. Learning+ Teaching Scotland.
Received: 29-Jun-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-13746; Editor assigned: 30-Jun-2023, Pre QC No. JMIDS-23-13746(PQ); Reviewed: 06-Jul-2023, QC No. JMIDS-23-13746; Revised: 20-Jul-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-13746(R); Published: 28-Jul-2023