Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 2S
A Systematic Review on Business Success Factors of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
Maheran Zakaria, UiTM Kelantan
Wan Noraswaniaty Wan Ahmad, UiTM Kelantan
Mohd Arpi Arifin, Kelantan State Secretary Office
Ida Rosnidah, Universitas Swadaya Gunung Jati
Nor Balkish Zakaria, UiTM Malaysia
Keywords
Business, Enterprise, Success, Micro, Small, Medium, Literature, Review
Abstract
Success in business venture is critical for the survival of Micro, Small And Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). However, gaining success is not an easy task. Majority of them failed explicitly in the startup phase. Abundances of studies have been conducted to find a solution on what would make the enterprises successful. Therefore, a thorough analysis of literature that identifies the antecedent factors is critical to be explored, which has less been emphasized. To fill this gap, the objective of this study is to comprehensively carry out a systematic literature review as to examine antecedent factors of business success among MSMEs highlighted by an extensive body of knowledge. The study also analyses the suggested areas for future research endeavor. Approximately ninety articles across the selected bases and search engine discussed the examined topic specifically. From the analysis, findings indicated that the factors are classified into internal and external. The internal factors are further divided into personal and organization, while the external factors are social, financial, societal, and contextual. Findings would provide valuable insights for researchers, entrepreneurs, government, and policymakers to incorporate those factors in formulating research framework, policies, training, and financial assistance at individual, institutional and societal levels. Hence, it is hoped that the initiatives would expedite the success of MSMEs' business and eventually stimulate the growth of the world’s economy.
Introduction
Majority of the firms are under Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) categories which contribute significant roles to the global economy (Chittithaworn et al., 2011). Success is crucial to SME in determining their strength, resilience, sustainability, and survival due to their vulnerability (Zakaria, 2009). Moreover, being successful would empower MSMEs or entrepreneurs to become financially autonomous, alleviate poverty, and enjoy a decent quality of life. Indeed, among the strategies in eradicating poverty taken by nations with emerging economies is to provide productive funds and assistance to underprivileged groups to venture into business or become entrepreneurs.
Despite receiving myriad financial assistance and government support, many MSMEs failed, especially in the startup phase (Klimas et al., 2020). This issue has triggered abundances of studies to examine what factors would lead to their business success. Literature published in leading academic journals develops a comprehensive body of knowledge and overview concerning the business success factors. Although a multitude of factors have been highlighted, there are no consensus and thus, so far inconclusive.
Interestingly, prior studies had been conducted in many approaches and different theoretical foundations which offered directions for future research. Several studies showed a partial overview of business factors. Other studies explored themes, while some provided empirical evidence of what factors constituted business success. Although a literature review is compelling and essential to be carried out, it has less likely been emphasized. The collection of literature can facilitate understanding and create a longitudinal overview of the area of interest that can guide researchers in the future.
To bridge this gap, the objective of this study is to systematically review the literature on antecedent factors of MSMEs business success. The study will synthesize through research recommendations. This study will also contribute profound insights into examining business success factors which lead to future research avenues.
Accordingly, two questions guide the review:
RQ1: What are the antecedent factors of entrepreneurial business success?
RQ2: What are the directions for future research?
The article continues with a brief explanation of the background and definitions of the phenomenon of interest, namely business success. It is followed by a description of the methodology. The following section presents the key findings by stream and contextual perspectives. It is then trailed with the discussion and synthesis of the literature by positioning the streams according to their potential research recommendations. Managerial and theoretical implications are also discussed. Finally, the paper concludes the review based on the research questions and fruitful suggestions for future research.
Literature Review
Literature is unequivocal when it defines business success. Indeed, every business is established to gain profit and success. Entrepreneurial business success is defined as attaining the complex relationship between strategy, processes, and business performance, and these elements align and work together for the betterment of stakeholders (Dahari et al., 2019). Prior literature indicated that various factors influence business success. Nevertheless, there is no consensus and thus, inconclusive as to which factors are significant for business success (Yeoh & Popovic, 2016).
This study aims to identify the findings indicated by prior literature on the factors that contribute significant impacts to business success via multiple approaches and perspectives. The compilation of the research findings will provide valuable insights to other researchers in the future. Furthermore, the findings can assist reviewers and editors of journals when examining the degree to which a submitted article has been undertaken with a thorough systematic review of the available research.
Methodology
A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) attempts to identify, select and critically appraise prior studies to answer specific research questions (Dewey & Drahota, 2016). It comprises series of processes that guide the researchers in formulating the objectives and planning how articles are retrieved and conveyed (Machado, 2017).
The SLR method is different from traditional literature reviews, which apply replicable, scientific, and transparent method (Cook et al., 1997; Wetzstein et al., 2016). The method is chosen due to three reasons. First, SLR intends to trace, identify and evaluate related research confined to the specific research questions. Secondly, the SLR method can lessen bias and mistakes; thus, it can provide high-quality evidence (Tranfield et al., 2003). Thirdly, a systematic and transparent synthesis of existing research boosts knowledge creation and hence, it is of equal importance as novel research (Cooper, 2010), apart from providing the best possible solution in solving a scientific problem (Wetzstein et al., 2016).
The study emulates a research protocol conducted by Aboo-Moghli, et al., (2019) on a systematic literature review regarding women entrepreneurs' opportunities and challenges in Saudi Arabia
Database Selection
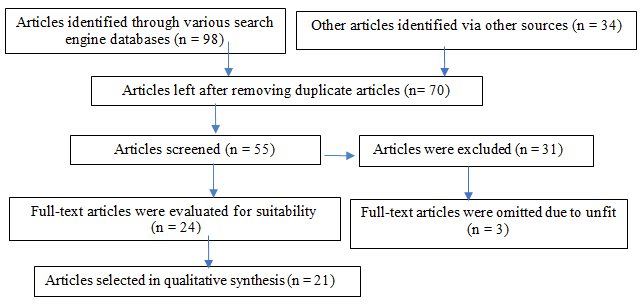
The quality of SLR depends on the sources of data selected for analysis (Ghadge et al., 2012). Using several keywords, the data were traced from various search engines, namely Google scholar, EBSCO, ProQuest, Emerald, and Scopus database. The keywords were within the search strategy, separately and in combinations, including but not limited to entrepreneurs, technology, ethics, small-medium enterprise, business development, and more specifically, business success. These keywords were checked from the year 2016 to 2021. As a result, nine-eight articles were discovered across the database.
The search was limited to articles in peer-reviewed journals. Other publications that include books, chapters in a book, conference proceedings, thesis, and dissertations were excluded. The identified articles were reviewed. Additionally, thirty-four articles were identified through other sources. Any similar articles extracted from different search engines and other sources were excluded, in which only one was chosen to proceed for analysis, leading to seventy articles selected for further analysis. Initially, the researchers screened the articles by reviewing their titles and abstracts. Thirty-one articles were excluded because they did not specifically examine and explore the factors of business success.
The remaining twenty-four articles were reviewed and screened based on the following criteria: Cohort, cross-sectional, empirical and exploratory studies, indicating the contribution factors towards business success. However, three articles were omitted due to a mismatch with the requirements. Finally, twenty-one articles were selected for qualitative synthesis. Figure 1 depicts the search process adopted by the present study.
Evaluating the Risk of Bias
The quality of the selected articles was evaluated based on two criteria. First, the articles were assessed in terms of their study design and analysis. Second, the selection was based on its conceptualization and representatives.
The bias was assessed on a scale in the continuum from the lowest value of 0 to the highest value of 9. This study was rated at a lower risk, with a score of 6 representing good quality. Meanwhile, the bias risk was rated at a moderate level with a score between 3 to 5 which illustrated an acceptable quality. This study emulated the assessment carried out by Abou-Moghli et al. (2019) and Moher et al. (2015).
Study Protocol and Registration
The protocols adopted by this study are aligned to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement and previous studies (Abou-Moghli et al., 2019; Moher et al., 2015).
Findings
Based on the inclusion criteria, a total of twenty studies proceeded for systematic literature review analysis. Although plenty of studies were identified initially, many were omitted. This was due to either not providing a clear description or insufficient research to evaluate the MSMEs' business success. For the analysis, information that included publication authors, date, title, and study was identified.
- The analysis of the selected studies indicated that most of them were cross-sectional (Ezennia & Mutambara, 2021; Shroder et al., 2021; Ullah Khan et al., 2021; Maduku & Kaeeram, 2021; Mielniczuk & Laguna, 2020; Pranowo et al., 2020; Profirioa, 2020; Sumihah & Anantanyu, 2020; Al-Kwifi et al., 2019; Dahari et al., 2019; Sadeh & Dvir, 2019; Soomro et al., 2019; Hossain et al., 2019; Batool & Ullah, 2017; Eschker et al., 2017; Barhatov & Belova, 2017), followed by exploratory (Kanapathipillai & Azam, 2019; Santoro et al., 2020; Salazar & Gonzales, 2018, Albu et al., 2017), systematic review (El-Adailah & Foster, 2019; Santisteban & Mauricio, 2017) and mixed-mode (Kerpitak, 2017; Sreih et al., 2019). Table 1 illustrates the information of the selected studies.
| Table 1 Characteristics of Selected Studies |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Year of Publication | Title | Type of Study |
| Ezennia & Mutambara | 2021 | Entrepreneurial Factors Influencing the Need for High Achievement on African Immigrant-Owned Micro Businesses in Durban, South Africa. | Cross-sectional |
| Shroder, et al., | 2021 | Determinants on success of businesses of female entrepreneurs in Taiwan | Cross-sectional |
| Ullah Khan, et al., | 2021 | Factors affecting women entrepreneurs’ success: A study of small- and medium sized enterprises in emerging market of Pakistan | Cross-sectional |
| Maduku & Kaeeram | 2020 | Success indicators among black owned informal small micro and medium enterprises’ (SMMEs) in South Africa | Cross-sectional |
| Mielniczuk & Laguna | 2020 | Positive affect mediates the relationship between self-efficacy and innovative behavior in entrepreneurs | Cross-sectional |
| Pranowo, et al., | 2020 | The entrepreneurial competency, innovation capability, and business success: The case of footwear industry in Indonesia | Cross-sectional |
| Porfírioa | 2020 | Family business succession: Analysis of the drivers of success based on entrepreneurship theory. | Cross-sectional |
| Sumihah & Anantanyu | 2020 | Empowering poor-household women on productive economy businesses in Indonesia | Cross-sectionals |
| Santoro, et al., | 2020 | Self-efficacy and Success of Disadvantaged Entrepreneurs: The Moderating Role of Resilience. | Exploratory |
| Al-Kwifi, et al., | 2019 | Determinants of female entrepreneurship success across Saudi Arabia | Cross-sectional |
| Dahari, et al., | 2019 | Key Success Factors of Home-Based Business among Female Entrepreneurs in Saudi Arabia | Exploratory |
| Kanapathipillai & Azam | 2019 | Women entrepreneurs path to success: An investigation of the critical success factors in Malaysia | Exploratory |
| Soomro, et al., | 2019 | The influence of demographic factors on the business success of entrepreneurs: An empirical study from the small and medium-sized enterprises context in Pakistan | Cross-sectional |
| Sreih, et al., | 2019 | Differences in management style, levels of profitability, and performance across generations, and the development of the Family Business Success Model | Explorative and Cross-sectional |
| Hossain, et al., | 2018 | A study on female entrepreneurs in Malaysia | Cross-sectional |
| Salazar & Gonzalez | 2018 | Entrepreneurial characteristics in women, the key to business success | Exploratory |
| Albu, et al., | 2017 | Impact of ethics upon business success | Exploratory |
| Abd. Rani & Hashim | 2017 | Factors that influence women entrepreneurial success in Malaysia: A conceptual framework | Systematic Review |
| Batool & Ullah | 2017 | Successful antecedents of women entrepreneurs: A case of underdeveloped nation | Cross-sectional |
| Eschker, et al., | 2017 | Rural entrepreneurs: What are the best indicators of their success? | Cross-sectional |
| Kerdpitak | 2017 | Factors leading to success of tourism business in Bangkok Thailand | Explorative Cross-Sectional |
| Barhatov & Belova | 2017 | External success factors of small and medium-sized enterprises of Russia: economic aspect | Cross-sectional |
| Vier Machado | 2016 | Growth of small businesses: A literature review and perspectives of studies. | Systematic review |
It was observed that based on the titles, the selected studies focused on the factors of MSMEs' business success in multi contexts. Table 2 presents the findings and conclusions of every investigation.
| Table 2 Detail Classification of Selected Studies |
||
|---|---|---|
| Author | Findings | Conclusion |
| Ullah Khan, et al., | Internal factors such as the need for high achievements, risk-taking, self-confidence, and external factors namely economic and socio-cultural are significant factors of women entrepreneurs’ business success in Pakistan | It concludes that enthusiastic entrepreneurs would accomplish an excellent job with high achievement and thus lead to higher performance and success |
| Ezennia & Mutambara | The need for high achievement is a significant factor of business success among African immigrant-owned micro businesses. | It concludes that entrepreneurs who are enthusiastic would accomplish good job with high achievement and thus lead to higher performance and success. |
| Shroder, et al., | Fear of failure and personal network are significant factors of the business success of Taiwanese women entrepreneurs. | It recommends a comparative study to deliver some interesting insights. |
| Maduku & Kaeeram | Education status, income, employment growth, business age, experience, financial literacy, advertising and access to capital are indicators of business success of black owned MSMEs in South Africa. | This study recommends that the government provide training to small businesses as to enhance their financial literacy. Also, small business owners should spend on advertising for the firm’s success. |
| Mielniczuk & Laguna | Self-efficacy is a factor of business success, while work related effect (enthusiasm, comfort, anxiety and depression) mediates the relationship between self-efficacy and business success. | The mediation analysis confirmed that their work-related positively mediated the relationship between self-efficacy and business success. |
| Pranowo, et al., | Competency and innovation capability positively influence entrepreneurial business success of the Indonesian footwear enterprises. Innovation capability mediates the relationship between competency and business success. | The study suggested that the government provides extensive training on technology to make the entrepreneurs become competent and innovative and elevate the business success. |
| Porfírio, et al., (2020) | Entrepreneurs' characteristics, organizational characteristics, and product diversification relate to family business success in six nations: Portugal, Italy, Greece, Cyprus, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria. | The findings are essential to strengthen the success of a family business and thus would promote their future growth and sustainability. |
| Suminah & Anantanyu | A learning process, social support and self-efficacy are factors of business success of poor-household women entrepreneurs in Indonesia. Self-efficacy mediates the relationship between the learning process and social support with business success. | Business success among poor household women entrepreneurs can be maximized if they are socially supported and provided with appropriate training. |
| Santoro, et al., | Self-efficacy improves entrepreneurial business success. Resilience moderates the relationship between self-efficacy and business success of entrepreneurs with specific disadvantages (those with physical challenges, mental limitation such as dyslexia and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder) (ADHS). | The most successful of those disadvantaged entrepreneurs are those who have the greatest self-efficacy. Business success is suggested to be measured using objective performance such as turnover, profit, profitability indices. Future studies are recommended to examine the business success of high-tech ventures. |
| Al-Kwifi, et al., | Business knowledge is the most impactful factor that leads to business success of women entrepreneurs in Saudi Arabia. | It suggests initiating programs for development of women, their advocacy as well as learning about entrepreneurship. |
| Dahari, et al., | The findings revealed that access to funding, sufficiency of savings and the influence of the intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in starting the business contribute to the success of women entrepreneurs in Saudi Arabia. | It recommended banks to be lenient in policies and procedures so that more women would have access to funding and services. The study also suggests future research to examine organizational factors such as level of stress at work. |
| Kanapathipillai & Azam | Level of education, access to financial capital and innovative are significant factors for women entrepreneurs’ business success in Malaysia. | It serves as guidance to other Malaysian women of the factors that make them rise against all the odds faced in their quest to achieve success. |
| Soomro, et al., | Demographic profiles of entrepreneurs such as age, level of education and working experience significantly impact entrepreneurs’ business success. | The study provides beneficial insights to the government to upgrade entrepreneurial education by continuously providing them with various training programs. |
| Hossain, et al., | Resource, personal, economy, politics and culture are factors of women entrepreneurs’ success in Malaysia | The findings would be useful for government, local authorities and entrepreneurs to empower women and hence reduce gender inequality. |
| Salazar & Gonzalez | Personal challenges, ethical values and development of competencies will lead to business success | The study concludes that entrepreneurs should be ready to face challenges, competence and embrace ethical values. |
| Albu, et al., | Ethics emerged as an essential theme of business success. | Ethical culture should be embedded within MSMEs from the top down and all members should embrace ethics in their working culture that lead to business success. |
| Abd.Rani & Hashim | The need for high achievement, risk raking, self-confidence and innovative to influence business success. | It concludes on the importance of understanding the factors of business success for women entrepreneurs. |
| Batool & Ullah | Motivation, personality traits, creativity, funds, social support are women entrepreneur’s success in Pakistan. Social support has a strong mediation effect. | It concludes that women in an underdeveloped society are generally not warmly supported by their families to become entrepreneurs. To succeed, they should possess strong personalities, be creative, and equipped with sufficient funding. |
| Eschker, et al., | Experiences with previous business ownership and social support have a positive impact on business success. | The study concludes that social support and business experience are essential to the success or failure of a small business. |
| Kerdpitak | Marketing innovation, tour program arrangement and marketing strategies are factors of business success in tourist industry in Thailand. | It concludes a business should focus on marketing innovation, followed by customer satisfaction and finally its efficiency in pursuit of success. |
| Vier Machado | Identifying and understanding the phenomenon of the growth of small businesses presented by prior literature and their suggestions for future research | It shows the complexity of the phenomenon from the perspective of business growth and success. |
Review from 2020 to 2021
Ezenie & Mutambara (2021) investigated the business success factors of African immigrant micro-entrepreneurs in Durban, South Africa. They conducted a quantitative study using 338 respondents. Findings were divided into two factors of internal and external. The internal factors were high achievement, the requirements to support family, and the desire to increase the business size. Meanwhile, the external factors were peer pressure, economic and political stability. They concluded that entrepreneurs who strive for high achievement are committed and passionate with their businesses, which would make them succeed and achieve competitive edge.
Another research carried out by Shroder, et al., (2021) examined determinant factors of business success among Taiwanese women entrepreneurs. They utilized secondary data with 1098 observations and analysed them using a logistic regression model. Findings showed that an internal factor, namely fear of failure and an external factor, networking, correlated significantly to business success. Findings provide valuable insights for women to shun their fear of failure. They must be ready to face risks in pursuit of success. Women also need social support and business networking. The study recommended future studies to investigate the influence of other factors such as financial resources and innovation on business success.
Maduku & Kaseeram (2021) investigated business success factors among black-owned Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in South Africa. Data were collected from 390 MSMEs in Johannesburg and analysed them using an ordered logistic regression. Findings highlighted those internal factors such as education status, income, experience, financial literacy, advertising budget, employment growth, and center of operation influenced the business success. The study suggested that the government provide continuous training. This would improve financial literacy, knowledge, and experience. Apart from that, the business should allocate a budget for advertising.
Ullah Khan, et al., (2021) examined the antecedent business success factors among Pakistani women entrepreneurs. They gathered data from 181 SMEs in Pakistan. Analysed with SPSS and AMOS, the findings indicated that the business success was due to internal factors. The internal factors include the need for high achievements, risk-taking, and self-confidence, while external factors are economical and socio-culture. The study recommended that the government offer incentives and supports by emphasizing both internal and external aspects. Future studies are suggested to examine financial literacy as a moderator that moderates the relationship between internal and external factors with business success.
Santoro (2020) explored the antecedent business success factors among disabling entrepreneurs with specific disadvantages such as dyslexia and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in Italy. Data were collected from 114 respondents and analysed using Ordinary Least Square regression. Findings revealed that internal factors, namely entrepreneurial self-efficacy, have positive impacts on business success. Furthermore, another internal factor of resilience was found to moderate and strengthen the relationship between self-efficacy and business success. Future studies are suggested to focus on high-tech and new business ventures, replicate the research, and examine other contexts.
Mielniczuk & Laguna (2020) examined factors of small enterprises' success. They conducted a longitudinal study on 206 entrepreneurs. Analysed with AMOSS, the findings indicated that internal factors, namely self-efficacy and innovative behaviour, affect business success. Additionally, the mediation analysis confirmed that the relationship between self-efficacy and innovative behaviour with business success is mediated by work-related positive manifested by comfort and enthusiasm.
Pronowo, et al., (2020) studied business success factors concerning entrepreneurial competence and innovation capability among the footwear industries in Indonesia. A total of 340 questionnaires were analysed using Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). Findings showed that business success was influenced by internal factors of entrepreneurial competency and innovation capability. Additionally, the findings indicated that innovation capability mediates the relationship between entrepreneurial competency and business success. In other words, those who are competent can innovate, which makes them succeed in business. Therefore, they concluded that the entrepreneurs must innovate and be competent in pursuit of success.
Porfírio, et al., (2020) explored the factors of family business succession. It was analysed with Fuzzyset qualitative comparative analysis (FsQCA) on a sample of 383 family businesses from 6 countries, including Portugal, Italy, Greece, Cyprus, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria. They found that internal factors, namely personal and organizational characteristics, would determine the succession of family businesses. Findings were essential to strengthen the growth and sustainability of family businesses. The findings would also provide insights to each country in formulating specific public policies to support family businesses succession and success.
Shakeel, et al., (2020) investigated on business success factors of women entrepreneurs in Pakistan. Data were collected from 190 respondents. The findings indicated that internal factors such as individual personalities and external factors, namely environments and support, positively influence business success. In addition, another external factor of national culture was found to moderate and strengthen the relationship between entrepreneur's personalities and help with business success.
Sumihah & Anantanyu (2020) examined the effect of self-efficacy on the business success of poor household women in Indonesia. Data were collected through a survey gathered from 250 respondents engaged in productive economic activities. The respondents were from 80 villages of five regencies in Central Java. Findings showed that internal factors that include the learning process and self-efficacy, namely social support, significantly impact business success. Additionally, self-efficacy mediates the relationship between the learning process and social support with business success. The study concludes that business success can be maximized if the poor household women are provided with social support, a learning program, and belief in their capability.
Review from 2018 to 2019
Al-Kwifi, et al., (2019) examined the factors that affect the business success of female university students in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. A total of 507 students from six universities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia responded. Findings showed that an internal factor, namely business knowledge, was the most influential business success factor. Therefore, it is recommended that the government initiate programs for women's development, their advocacy and educate them on all matters of entrepreneurship.
Dahari, et al., (2019) explored business success factors among women entrepreneurs who run home-based business in Saudi Arabia. They interviewed 11 respondents, and the findings revealed that internal factors such as sufficiency of savings and intrinsic motivations, and external factors that are funding and extrinsic motivations would lead to business success. As a result, the study recommended that banking institutions reduce their lending requirements. This is to assist entrepreneurs in funding their business besides providing continuous support from intrinsic and extrinsic motivations. The study also suggested that future research examines organizational factors, stress coping, and growth strategies on business success.
Kanapathipillai & Azam (2019) investigated critical business success factors of Malaysian women entrepreneurs. Data were gathered from questionnaire distributed to 313 respondents. Findings from logistic regression analysis showed that business success is influenced by internal factors such as education status and innovation, and external factor of access to capital. The findings served as guidance for women entrepreneurs to rise against all the predicaments they face in pursuit of success. The study foresees that successful women entrepreneurs would earn better income, improve their socio-economic status, and attain competitive edge.
Soomro, et al., (2019) examined the business success of SMEs in Pakistan. The survey was carried out on 230 entrepreneurs in Pakistan based on convenience sampling technique. Findings indicated that entrepreneurial success is related to internal factors of demographic profiles such as gender, age, education, and experience. Hence, to bolster the business success, the study suggested that the government and policymakers provide the entrepreneurs with appropriate education and training according to their gender and age.
Hossain, et al., (2018) researched the factors that affected the business success of Malaysian women entrepreneurs. Data were collected from 300 respondents. Findings of multiple regression analysis indicated that personal, economic, political, and culture affected the success of women's business. They suggested that future studies replicate the research and be conducted in other nations or contexts.
Salazar & Gonzalez (2018) explored the characteristics of women entrepreneurs in Popayan, Colombia, who were successful in business. Data were gathered from in-depth interview of 20 women respondents. Findings indicated that internal factors such as personal challenges for safety and well-being, ethical values, and competencies would lead the women entrepreneurs to succeed.
Review from 2016 to 2017
Albu, et al., (2017) explored business success factors using a qualitative approach, adopting an in-depth interview of semi-structured questions on 20 entrepreneurs. The interviews were transcribed for content analysis. Several themes emerged, such as internal factors manifested by ethical values and social responsibility were essential factors for business success. It concluded that ethical culture should be embedded and practiced within an enterprise. Lack of ethical culture may cause severe problems in a business which affect employee performance, employee work relations, enterprises image, and credibility.
Abd Rani & Hashim (2017) did a literature review on the factors that influence the business success of Malaysian women entrepreneurs. Based on prior literature, they found four internal factors were highlighted to influence business success: the need for achievement, risk-taking, self-confidence, creativity, and innovation. The study concluded that understanding the success factors is essential to enable women entrepreneurs to broaden their business successfully in a globalized environment.
Batool and Ullah (2017) investigated the relationship between motivation, personality trait, creativity, capital, family factors, and women's entrepreneurial business success in Pakistan. Data were gathered through purposive sampling techniques. Analysis of the data revealed that all the proposed antecedent factors play a positive role in the success of women entrepreneurs. Family support also appears to have a strong mediation effect on the success of women entrepreneurs but in a negative relationship. Thus, women in under-developed societies are generally not warmly supported by the family to become entrepreneurs. In light of this, the study recommended that the government support women entrepreneurs and increase their participation in economic growth.
Eschker, et al., (2017) examined the factors that lead to either success or failure of newly started small businesses operating within 3 to 4 years. Using a probit regression analysis, findings revealed that women owners, family help, and experience with the previous business owner had a distinct impact on the business success. The study concluded that internal factors such as experiences and external factors, namely social and financial supports, are needed for a business to succeed.
Kerdpitak (2017) researched the factors of success among tourism businesses in Thailand. The study conducted a mixed-method approach. First, the data were collected based on simple random sampling. Samples consisted of 339 tourism business operators and managers. Second, data were analysed using SPPS multiple regression. Findings indicated that the business success was due to internal factors, namely marketing innovation, tour program arrangement, and competition strategies. Meanwhile, the results from the interview stated that there are 45 business success factors. These factors are also grouped into three dimensions: marketing innovation, tour program arrangement, competitive strategies, and differentiation.
Machado (2016) reviewed the literature to examine the phenomenon on the growth of small businesses. The study reviewed 16 journal articles of small enterprises' development and business success factors within the last fifteen years. The reviewed studies highlighted several internal factors. These factors were further classified in terms of personal and firm characteristics. The individual elements were experience, educational level, position, age, fear of failure, personal aims, internal locus of control, growth aspirations, motivations, expectations, growth intentions, equilibrium between work and family.
Meanwhile, the firm characteristics were size and duration of the enterprise, location, mission, and commitment to growth, innovation, and development in products and services. Entrepreneurs must be provided with training and support at the institutional and societal levels. This would assist them in achieving the desired success threshold in the entrepreneurial world.
Managerial Implications
The study provides implications to the MSMEs and entrepreneurs on the importance of enhancing their knowledge on entrepreneurship, striving for high achievement, and believing in their capabilities in pursuit of success. The study also offers implications to governments and policymakers in formulating policies, programs, training, and assistance to help MSMEs' survival, growth, viability, and development.
Theoretical Implications
The study compiles the findings of prior literature to guide and provide direction for future research avenues. In addition, the compilation of an extensive body of knowledge would enrich the robustness of the existing literature on antecedent factors of business success.
Conclusion
The present study carried out a systematic literature review on the quest of finding the antecedent factors of business success among Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) for six-year period of 2016 to 2021. From 20 selected studies, the findings are classified into internal and external factors. The internal factors are further divided according to individual and business characteristics. The individual elements are the need for high achievement, self-efficacy, innovation, competency, resilience, ethical values, creativity, fear of failure, business knowledge, education, and experiences. Meanwhile, part of the business characteristics is business size, type, duration, and location.
Additionally, the external factors are social, and government supports, funding, economic and political interventions. A contextual setting would also make the findings different as no one size fits all solutions. In other words, significant factors in a particular nation might not be influential in another context. The study also offers suggestions on the influence of other factors on business success. Hence, it is hoped that the study can assist many quarters, namely entrepreneurs, academicians, governments, and policymakers, in identifying the relevant factors of business success for the betterment of MSMEs.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the management of Universiti Teknologi MARA Kelantan for their support and funding the research grant (600-TNCPI 5/3/DDN (03) (011/2020).
References
Abd Rani, S.H., & Hashim, N. (2017). Factors that influence women entrepreneurial success in Malaysia: A conceptual framework. International Journal of Research in Business Studies and Management, 4(1), 16-23.
Abou-Moghli, A., & Al-Abdallah, G.M. (2019). A systematic review of women entrepreneur’s opportunities and challenges in Saudi Arabia (2019). Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(6). 1-14.
Al-Kwifi, O.S., Tier Khoa, T., Ongsakul,V., & Ahmed, Z.U. (2019). Determinants of female entrepreneurship success across Saudi Arabia. Journal of Transnational Management, 1-27.
Albu, R., Suciu,T., & Mandru,L. (2017). Impact of ethics upon business success. Vision 2020: Sustainable Economic Development: Innovation Management and Global Growth, 203-211. Google scholar
Batool, H., & Ullah, K. (2017). Successful antecedent of women entrepreneurs: A case of underdeveloped. Entrepreneurship Research Journal.
Barhatov, V., & Belova, I. (2017). External success factors of small and medium-sized enterprises of Russia: Economic aspect. Eurasian Studies in Business and Economics, 5, 453-468.
Chittithaworn, C., Islam, M.A., Kewwchana, T., & Muhd Yusuf, D.H. (2011). Factors Affecting Business Success of Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Thailand. Asian Journal of Social Science, 7(5), 180-190.
Cook,D., Mulrow,C. & Haynes, R. (2010). Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann. Intern. Med., 126(5), 376-380.
Crossref, Google scholar, Indexed at
Cooper, H. (2010). Research synthesis and meta-analysis: A step-by-step approach. (4th Edition), Sage, Los Angeles, CA (2010).
Dahari,Z., Abu Bakar, A.R., & Al-Gosaibi, S. (2019). Key success factors of home-based business among female entrepreneur in Saudi Arabia. Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Review, 3(2), 43-66.
Dewey, A., & Drahota, A. (2016) Introduction to systematic reviews: Online learning module Cochrane Training. https://training.cochrane.org/interactivelearning/module-1-introduction-conducting-systematic-reviews.
Ezennia, J.C., & Mutambara, E. (2021). Entrepreneurial factors influencing the need for high achievement on African immigrant-owned micro business in Durban, South Africa. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(10), 1-11.
Eschker, E., Gold, G., & Lane, M.D. (2017). Rural entrepreneurs: what are the best indicators of their success? Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 24(2), 278-296.
Hossain, J., Jahangir, N., & Nur-Al-Ahad, M. (2018). A study on female entrepreneurs in Malaysia. Business Ethics and Leadership, 2(3), 67-73.
Kerdpitak, C. (2017). Factors Leading To Success Of Tourism Business In Bangkok Thailand. Journal of Applied Business Research (JABR), 33(3), 501-508.
Kanapathipillai, K., & Ferdous Azam, S.M. (2019). Women entrepreneurs path to success: An investigation of the critical success factors in Malaysia, 3(1), 106-128.
Klimas, P., Kraus, S. Kailer, N. & Maalaoui, A. (2020). Entrepreneurial Failure: A Synthesis and Conceptual Framework of its Effects. European Management Review, 18(1), 167-182.
Maduku, H., & Kaseeram, I. (2021). Success indicators among black owned informal small micro and medium enterprises (SMMEs) in Africa. `Development Southern Africa.
Mielniczuk, E., & Laguna, M. (2020). Positive affect mediates the relationship between self-efficacy and innovative behavior. Journal of Creative Behavioe, 54(2), 267-278.
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew,M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L.A. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic review, 4(1).1.
Portfirio, J.A., Feliciio, J.A., & Carrilho, T (2020). Family business succession: Analysis of the drivers of success based on entrepreneurship theory. Journal of Business Research, 1-8.
Pranowo, A.S., Sutrisno, J., & Sulastiono, P. (2020). The entrepreneurial competency, innovation capability, and business success: The case of footwear industry in Indonesia. Quality, Access to Success, 21(178),
Santoro, G., Ferraris, A., Del Giudice, M., & Schiavone, F. (2020). Self-efficacy and success of disadvantaged entrepreneurs: The moderating role of resilience. European Management Review, 17(3), 719-732.
Salazar, M.E.S., & Gonzalez, M.F.G. (2018). Entrepreneurial characteristics in women, the key to business success. La Clave Del Exito Empresarial, 34(18), 1452-1478.
Schroder, L., Bobek, V., & Horvat, T. (2021). Determinants of success of business of female entrepreneurs in Taiwan. Sustainability, 13, 1-25.
Shakeel, M., Yaokuang, L., & Gohar, A. (2020). Identifying the entrepreneurial success factors and the performance of women-owned businesses in Pakistan: The moderating role of National Culture. Sage Open, 2, 1-17.
Sreih, J.F., Lussier, R.N., & Sonfield, M.C. (2018). Differences in management styles, levels of profitability, and performance across generations, and the development of the family business success model. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 22(1), 32-50.
Suminah S., Anantanyu, S. (2020).Empowering poor-households women on productive economy businesses in Indonesia. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(9), 769-779.
Tran?eld, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003).Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management, 44(3), 207-222.
Ullah Khan, R., Salamzadeh, Y., Ali Shah, S.Z., & Hussain, M. (2021).Factors affecting women entrepreneurs’ success: A study of small and medium-sized enterprises in emerging market of Pakistan. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 10(11).
Vier Machado, H.P. (2016). Growth of small businesses: a literature review and perspectives of studies. Gest. Prod. Sao Carlos, 23(2). P.419-432.
Wetzstein, A., Hartmann, E., Behton, Jr, W.C., & Hohenstein,N. (2016).A systematic assessment of supplier selection literature – State-of-the art and future scope. International Journal Production Economic, 182, 304-323.
Yeoh, W., & Popovic, A. (2016).Extending the understanding of critical success factors for implementing business intelligence systems. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 67(1), 134-147.
Zakaria, N.B. (2009).Dynamic and static corporate liquidity measurement: a case of Malaysian Small and Medium Enterprises. International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, 6(4), 479-493.
Received: 15-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. IJE-21-7733; Editor assigned: 17-Dec-2021, PreQC No. IJE-21-7733(PQ); Reviewed: 26-Dec-2021, QC No. IJE-21-7733; Revised: 07-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. IJE-21-7733(R); Published: 15-Jan-2022