Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 4S
Benchmarking Proposals in the Macroeconomic Policies of Peru and Singapore in the Last 20 Years
Raul Alberto Rengifo Lozano, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos
Ricardo Fernando Cosio Borda, Universidad Privada del Norte
Elmo Ramón Zavala Sheen, Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal
Raúl Ernesto Porras Lavalle, Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal
July Ana Yovera Vargas, Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas
Juan Martín Campos Huamán, Universidad César Vallejo
Citation Information: Lozano, R.A.R., Borda, R.F.C., Sheen, E.R.Z., Lavalle, R.E.P., Vargas, J. A.Y., & Huaman, J.M.C. (2022). Benchmarking proposals in the macroeconomic policies of Peru and Singapore in the last 20 years. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S4), 1-11.
Keywords
Singapore, Macroeconomic Policy, Economic Growth, Economic Indicators, Simulation Models
Abstract
The results achieved by Singapore in terms of development levels are recognized by different international organizations. Recently, WEF (Word Economic Forum) published its Global Competitiveness Report of 2019 where it is evident that Singapore has surpassed many countries that previously held the top positions in several of the factors that together generate the global competitiveness index. For this reason, it was decided to benchmark the macroeconomic policies of Singapore and Peru according to which a set of macroeconomic policies are proposed for Peru that would be based on the success achieved by Singapore. In each country, a series of variables have been identified that would support the great difference in scenarios, and according to this, a set of macroeconomic policies are proposed for implementation in Peru. This article presents a simulation model to analyze and prioritize the proposed macroeconomic policies.
Introduction
According to Espinosa (2020), Benchmarking is a continuous process by which the services or work processes of leading companies are taken as a reference, to compare them with those of your own company and then make improvements and implement them.
For Collado & Rojas (2015), Singapore is a sample of a great economic success as a result of having created favorable institutional conditions for investment, job creation and raising the average income of its nationals, and the many foreigners who work there. Therefore, macroeconomic policies and their main indicators would constitute a model for analysis and evaluation of the development of benchmarking and lessons learned.
According to Santander (2020), Singapore's economy is characterized by its excellent finances and high degree of openness which gives rise to the high dependence on international trade.
Martínez (2015) points out that despite the fact that in Singapore some of the essential civil liberties such as expression, association, press or sexual orientation are violated, the Asian country has become a world reference in terms of economic policy. In this sense, Lee Kuan Yew was able to devise a master plan almost six decades ago about what his country should do to become a very prosperous nation in Southeast Asia.
It should be noted that the central axis of this plan is related to quality education and economic freedom. Today, Lee Kuan Yew's son, Lee Hsien Loong is the one who holds the reins of the country as prime minister of the People's Action Party, following the same ideology as his father.
As can be seen, the growth indicators show that the Gross Domestic Product of the Asian country has and will have a sustained growth, possibly slowed by the current situation of the pandemic; on the other hand, another very important data is related to GDP per capita where you can also see a sustainable growth which places it as the country with the most important income worldwide.
As far as Peru is concerned, the growth indicators show a constant GDP growth that, like Singapore, will be slowed down by the pandemic situation. Where there is a difference is in the GDP per capita, where in our country, in spite of having a sustainable growth in this index, the Asian country does not exceed it enormously.
Material and Methods
The focus of the study is a review; in this context, "a systematic review is considered a "special" type of article or scientific document that, without being original, summarizes the current state of research on a particular topic, through a rigorous and reproducible systematic process" (Sobrido & Rumbo, 2016). Likewise, it has a descriptive and explanatory scope, while the design is non-experimental and longitudinal in nature.
According to the bibliographic research and the results of other research carried out, a proposal will be made on the main macroeconomic policy measures for Peru, according to the references of decisions adopted by Singapore and presented in the research.
It is clear that both countries have important differences; therefore, it is necessary to consider some variables as part of the scenarios of both countries. Among the variables that could mark the differences are:
• Culture and philosophy of life
• Informality
• Political Scenario
• Geostrategic location
• Population and social strata
• Country Geography
• Respect and values
Results
After the search for information, the different macroeconomic policies implemented by Singapore were identified, according to Huapaya and Naranjo (2018) cited in Siddique and Kumar (2010), the policies are detailed below.
Strengthening Legislation
Government agencies and their social programs and policies were strengthened by the development of legislation with well-established principles, which contributed greatly to Singapore's growth. It should be noted that in Singapore, the Board of Directors and its powers are well defined in the legislation, which allows government agencies to make decisions without much interference from the Ministry. Also, certain measures were implemented to safeguard the security of the legislation. For example, the Central Provident Fund was created for controlling the provisions for the salaries of both public and private employees and they apply certain measures so that these payments are not made unpunctually.
It should be noted, that in Singapore they completely banished the model where government entities sought support from ministries as this creates bureaucracy. "Part of the reason is to remove the associated bottlenecks, as important issues such as technology and research cannot afford to wait for funds throughout the annual budget cycle."
Adhere to Consistent Trade Policies
In Singapore, there is a single political party in power since the beginning of the reform, i.e., a single vision for the short, medium and long term. The advantage of this is that a single economic model has been applied throughout the reform process up to the present. Thanks to the Singaporean people, the style of government administration in Singapore has been dominant in all these years, which has made it possible to set goals not only in the short term, but also to analyze the barriers that have to be overcome for long-term growth, thus creating a strategic vision of what the country wants to achieve not only by looking at the internal environment but also the external environment. This is a very important point, because one of its best-known trade policies was the opening that Singapore had towards the world even being in the crisis in which it was, which benefited the country significantly and contributed to its economic growth.
Table 1 shows the ranking of the Peruvian and Singaporean economies in terms of ease of doing business, with Singapore ranking 2nd and Peru 76th.
| Table 1 Ease of Doing Business |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economy | Global Rank | Opening a business | Handling of construction permits | Obtaining Electricity | Property Registration | Obtaining Credit | Protection of minority investors | Payment of taxes | Fulfillment of contracts |
| Singapore | 2 | 4 | 5 | 16 | 16 | 10 | 2 | 7 | 2 |
| Peru | 76 | 133 | 65 | 88 | 55 | 37 | 45 | 121 | 83 |
Source. World Bank. (2019). Classification of economies. Retrieved from https://espanol.doingbusiness.org/es/rankings
It is important to highlight that "due to its small domestic market and its historical role as a regional trade center, this country has a clear export vocation, which has gone hand in hand with extensive economic liberalization" (Ramos, 2006).
A trained and Reliable Group of People
For Lee Kuan Yew, the group of people who were going to lead the main ministries in charge of Singapore's economic growth had to be highly specialized in the issues they had to deal with, since Singapore was in search of a nation-state and one of the gears to achieve it was to have officials properly trained in their areas, and who are trusted not only by the government, but also by the population, so that the right decisions are made on important issues of investment, finance, foreign affairs and economic development.
| Table 2 Comparison Between Singapore and Peru on the Corruption Perceptions Index |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore | Peru | ||||
| Rank | Punctuation | Change of places | Rank | Punctuation | Change of places |
| 4/198 | 85/100 | -1 | 101/198 | 36/100 | +4 |
Source. Transparency International (2019). Corruption Perceptions Index. Retrieved from https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2019/results/sgp
Source: Transparency International (2019). Corruption Perceptions Index.
Retrieved from https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2019/results/sgp
Source: Transparency International (2019). Corruption Perceptions Index.
Retrieved from https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2019/results/sgp
Incorporate Policies That Have Worked In Other Countries
When an economy wants to grow, but it is still third world, what you have to start looking at are the trade policies applied in first world countries, so that, with the model seen, you can propose improvements in those deficiencies that you have. Likewise, the study has to start analyzing what the country can offer to the world and create trade agreements with countries abroad. In the following table, it can be noted that the Global Competitiveness Index of Peru and Singapore in 2019 measures how a country uses its resources and capacity to provide its inhabitants with a high level of prosperity (Datosmacro, 2019).
| Table 3 Comparison of the Global Competitiveness Index for Peru and Singapore |
|
|---|---|
| Peru | Singapore |
| Peru obtained 61.66 points in the Competitiveness Index, published by the World Economic Forum. It has improved its score with respect to the previous year's report in which it obtained 61.26 points.It is in 65th place in the global competitiveness ranking, out of 141 countries analyzed. It has worsened its situation, as it was ranked 63rd in 2018. | Singapore has obtained 84.78 points in the Competitiveness Index, published by the World Economic Forum.This score makes it considered the most competitive country in the world. It has improved in this latest report, as it was ranked #2 in 2018. |
Source: (Datosmacro, 2019; Datosmacro, 2019a).
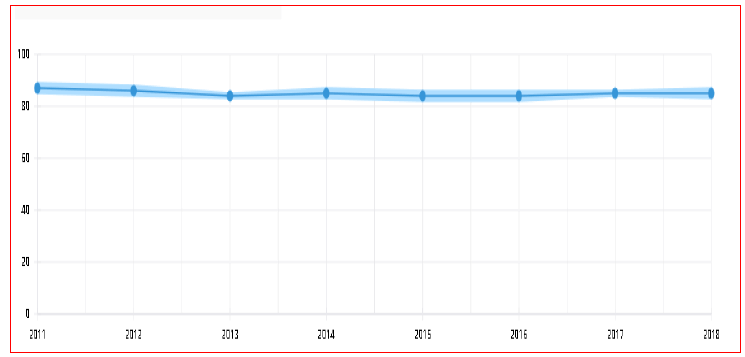
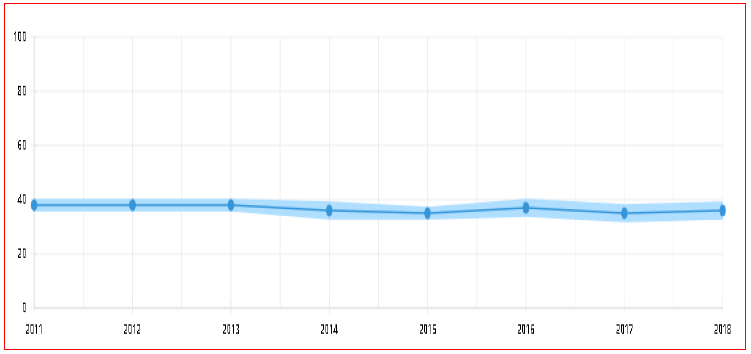
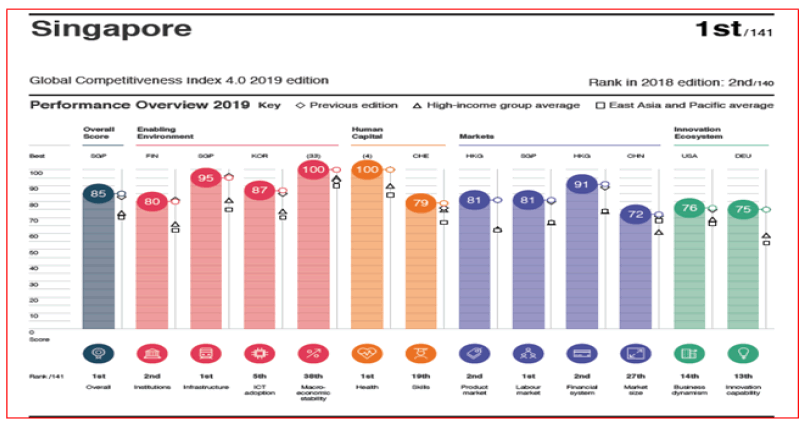
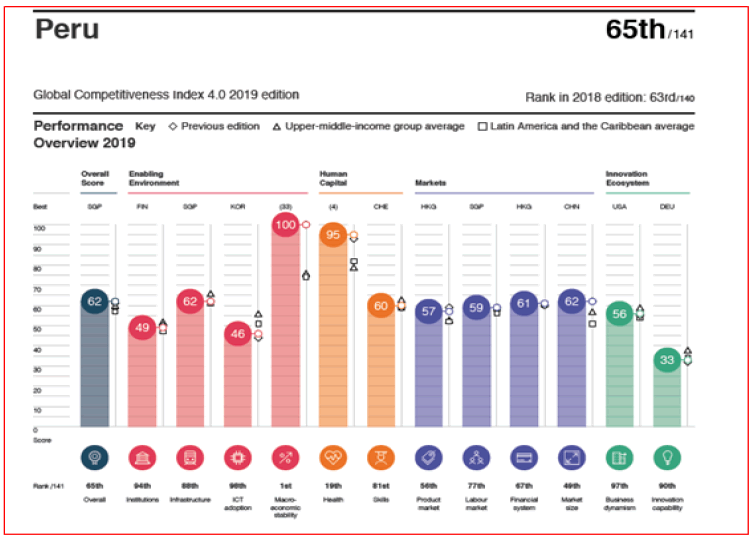
Figures 3 and 4 show the results achieved by Singapore and Peru in the twelve factors of the global competitiveness index according to the 2019 report of the World Economic Forum WEF. It is meritorious what has been achieved by Singapore has position 1 in the global competitiveness index this position corresponded to Switzerland on several occasions, not only that as it also achieved very impactful positions in Institutionality position 2, Infrastructure position 1, Health Position 1, Labor market position 1.
Source. World Economic Forum. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf
Source: World Economic Forum. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf
Compensation Administration
In terms of remuneration, Singapore currently has a salary range above several countries. According to the portal Libre Mercado (2018), a minister earns $650,000 per year. That said, one of the policies that Singapore implemented, for the fight against corruption and for productivity to increase, was to link the performance that each public official had with the remuneration they would receive.
Regarding the private sector, the following table 4 shows the comparison of average salaries between Peru and Singapore.
| Table 4 Comparison Between Remunerations in the Private Sector Between Peru and Singapore |
|
|---|---|
| Peru | Singapore |
| The average monthly income of workers in Metropolitan Lima stood at 1,324.2 nuevos soles, if income from the main activity is taken as a parameter. | The average net salary is 2,779.44 euros in the capital of Singapore. It is one of the most expensive cities in the world to live in. |
Source: La Vanguardia (2017); Tusalario (2019).
National Research Foundation (NRI)
One of the most important aspects of Singapore becoming the powerhouse it is today is linked to investment in research and development. Singapore's national R&D agency is the National Research Foundation, and to make good use of investment in research infrastructure, this agency introduced the National Research Infrastructure framework to guide the development of selected research facilities to be operated as a national resource, open to all researchers in Singapore. This foundation also encourages continuous investment in infrastructure upgrades so as to further drive the development of leading research and technology in a cost-effective way. In Peru, the National Council for Science, Technology and Technological Innovation (CONCYTEC) is the governing institution of the National System of Science and Technology and Technological Innovation, SINACYT, composed of Academia, State Research Institutes, business organizations, communities and civil society. It is governed by the Science and Technology Framework Law N° 28303; but unlike the National Research Foundation, it does not subsidize innovation projects.
| Table 5 Comparison in the Global Technology Innovation Index Between Peru and Singapore |
|
|---|---|
| Peru | Singapore |
| Peru ranks 69th in the Global Technology Innovation Index with an average score of 32.93. | Singapore ranks 8th in the Global Technology Innovation Index with an average score of 58.3 |
Source. World Intellectual Property Organization (2019). Rankings. https://www.wipo.int/edocs/pubdocs/en/wipo_pub_gii_2019-intro4.pdf
Intensive Manpower Training and Investment in Education
One of the objectives of Singapore's reform was to be called a "hub", not only commercial but also technological. One of the means by which it sought to achieve this goal was the search for foreign professionals whose high knowledge and skills could contribute to the different industries within the country, which ended up developing the financial, consulting, accounting and communications services in which Singapore specialized over time (Carrion & Saez, 2007).
From the systematic review of literature and research the study shares the results of the Economic and Commercial report developed by the Economic and Commercial Office of Spain in Singapore where they highlight that "since independence in 1965, after being a British colony and a brief integration into the Malaysian Federation, political life has been dominated by the People's Action Party (PAP) and its founder Lee Kuan Yew. Although the formalities of electoral processes are respected and there is a judicial system, the Government/Party tends to assimilate its ideology and performance with those of the State. The Government exercises some censorship of the media and limits the distribution of foreign publications. The situation could be summarized as a "Strong State", not based primarily on coercion, but on a broad systematic consensus, and on the great capacity of the Government to unite wills and mobilize the population towards the objectives set by the executive power".
It is important to note that the Government of Singapore is characterized by its rapid action in economic matters, which significantly differentiates it from Peru, where the decision makers often do not have the capacity and skills to carry out a strategic process of impact, as well as the credibility is an issue that does not allow to face the various crises with relative ease and success.
Discussion
According to the descriptive research carried out on the macroeconomic policies of Singapore developed and the results obtained, the following approach will be made on a group of macroeconomic policies for Peru with which it would be expected to achieve development in the country. The proposals would be the following:
| Table 6 Macroeconomic Policies Proposed for Peru's Development |
|
|---|---|
| Policies | Brief description |
| Long-term future building plan | The example of Singapore clearly demonstrates that in addition to having a single political party its basis elaborates a plan for the future that considers goals for different times, but with periodic checks, this way the plan is shaped to be monitored to validate the achievement of key development goals or milestones. |
| Sustained work on institutionalism | Institutionalism is a key issue for any country and is related to assertiveness of the powers and in the case of Singapore according to WEF 2019 has the position 2 and Peru according to the same reference is in position 94. It is clear that the different powers and entities must give confidence not only to nationals but the international image that will proceed under the same guidelines and would have similar results. |
| Strengthening legislation | It is recommended that the Legislative, Judicial and related Branches have and approve legal frameworks that do not represent generation of uncertainties and that the existence of legal risks in the country cannot be qualified either, since this would generate uncertainties. |
| Clear and consistent business policies | Trade operations between countries require full compliance with the provisions of the WTO and similar bodies in addition to adhering to the International Associations that frame trade operations between countries. |
| Highly competent team | Human capital is a simulated production factor that depends not only on the quantity, but also on the quality, degree, training and productivity of the people involved in a productive process; therefore, a development plan requires an intense improvement of skills and competences. |
| Strengthened electoral system | The confidence of a country in its electoral system is key not only for the internal management, but it is also key for the international image; therefore, it is of utmost importance that it is strengthened and enriched with all the technological advances to achieve in the shortest term the electronic non-face-to-face voting. |
| Basic and applied research and innovation | Every country that aspires to be developed requires to strengthen its research and innovation system must be strengthened only in this way to improve all the variables and stakeholders that are related to the development of research and especially with the proper exploitation of their progress. |
| Intensive training of human capital | As mentioned above, the national human capital requires a real and comprehensive improvement of competencies and capacities; for this reason, it is necessary to identify the needs for improvement in the shortest possible time, for which it will be necessary to allocate budget allocations as a priority to cover these needs. |
| Future-oriented education system and country development | The national education system requires public policies that are very clearly oriented towards development in a direct way. Of course, all the existing gaps must be considered in order to adopt the necessary public policies that consider working in synergy as a key issue and priority for the country. |
| National Information System | It is known that to date the country does not have an adequate system that would allow having information with the quality, solidity and validation for all areas of the country. Decisions taken at the State and Sector level need to be made based on reliable and trustworthy data that allow for the monitoring of such decisions. |
| National Public Policy Laboratory | Any public policy that you decide to develop will be carried out according to the approved and current plan for the future. But before approval and implementation it will be subjected to simulation under simulation exercises and game theory. In this way, there will be more certainty of achieving the goals and objectives foreseen. |
| Digitization and connectivity at the highest level | In today's world (2020), Estonia is a clear example of the levels achieved by comprehensive digitization. This country is an example in terms of digitization of all public services. Just as an example it is mentioned that the elections are electronic not face-to-face and according to recent publications has been achieved not only excellent economic ratios costs, but most importantly the participation of population is much better. According to publications of social networks there is a significant difference in costs between non-face-to-face electronic voting and conventional voting, in addition to the advantages of the digitization of society-oriented operations. |
Source: Own elaboration
Conclusion
The results achieved by Singapore are worthy of admiration and recognition; for this reason and in the opinion of those who have conducted this research, Singapore becomes a country and situation of study. And why not tell him the convenience of looking for the formula to help other countries to achieve this combination of factors, involved, variables and especially appropriate and timely decisions. But as it is known this is not possible and it was decided to make a benchmarking between macroeconomic policies and results achieved in the last twenty (20) years.
This research brings many questions about the variables and key decisions that achieved the results shown by the latest WEF 2019 report where results worthy of recognition and imitation if possible are appreciated. The benchmarking carried out allows highlighting among the most important actions and strategies the following facts: having a single political party, assigning salary to ministers of $US 650,000 per year, having a single leader for several decades and having a plan for the future. Perhaps these are the main variables, but it is necessary to point out that this scenario in the case of Peru will not be possible to achieve since there are many differences starting with the philosophy of the Asian quasar; therefore, for the purpose of proposing macroeconomic policies, a series of variables have been considered that would justify the adoption of complementary policies.
Parallel to the above and considering other research that has been done, it is planned that a new sequential article will develop a simulation model in which the proposed macroeconomic policies are analyzed and through the simulation using the VENSIM software, a better analysis and prioritization will be made. This will motivate a new complementary article.
Finally, and considering that any sustainable macroeconomic policy and any government plan is developed from highly trained political and public managers and with a superior scale of ethical and moral values, the compact and adequate human group of the Asian country who lead the different ministries in charge of the economic and social growth of Singapore stands out. In that sense, to achieve an efficient and sustainable nation-state, the main gear to achieve it is to have officials properly trained in their areas, and who are trusted not only by the government, but also by the population, so that the right decisions are made on important issues of investment, finance, foreign affairs and economic development.
References
References
Amalu, H.I., Agbasi, L.O., Olife, L.U., & Okechukwu, A. (2021). Responsiveness of service sector growth to financial development in Nigeria: Evidence from 1981-2019. Journal of Advanced Research in Economics and Administrative Sciences, 2(3), 1-12.
Carrion, A. & Saez, V. Singapur: politica comercial y politica de desarrollo. Contraste de teorias. Santiago, Chile. Universidad de Chile. Facultad de Economia y Negocios. Faculty of Economics and Business.
Datosmacro (2019). Peru - Indice de Competitividad Global.
Datosmacro (2019a). Singapore - Global Competitiveness Index
Fuente: Datosmacro (2019c). Comparar economia paises: Peru vs Singapur. Recuperado de (Compare economy countries: Peru vs Singapore. [Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
El Economistaes (2014). El exito de un modelo economico liberal: Singapur multiplica por 5 su PIB en 25 anos [Crossref], [Google Scholar], [Indexed]
Huapaya, A., & Naranjo, P. El modelo comercial de Singapur de la segunda mitad del siglo xx: una referencia para el Peru. Lima, Peru: Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (Singapore's business model in the second half of the twentieth century: A reference for Peru. Lima, Peru: Peruvian University of Applied Sciences)
La Vanguardia (2017). Salaries in Singapore.
Martínez, P. (2015) Como se convirtio Singapur en el pais mas rico del mundo?
Kumar, S., & Siddique, S. (2010). The Singapore success story: Public-private alliance for investment attraction, innovation and export development. United Nations Publications.
Portal Libre Mercado (2018). Como Lee Kuan Yew acabo con la corrupcion en Singapur
Ramos, J. (2006). Economy and Trade.
Santander (2010). Singapur: politica y economia.
Santander (2010). Peru: Politics and economy.
Sanad, S., & Anitha S. (2021). The impact of participative decision-making on organizational commitment: A study among employees of mobile telecom companies in Yemen. Journal of Advanced Research in Economics and Administrative Sciences, 2(3), 75-88.
Sobrido, M., & Rumbo, J. (2016). La revision sistematica: Pluralidad de enfoques y metodologias. Enfermería Clínica, 28 (6), 387-393.
Tusalario (2019). Salarios promedio (Average wages).
Wei, S.-Y., & Lin, L.-W. (2021). The influence of Taiwan electronic production company’s proprietary data products on the interaction of company effectiveness. Journal ofAdvanced Research in Economics and Administrative Sciences, 2(3), 40-74.
Received: 28-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. AEJ-21-8538; Editor assigned: 30-Dec-2021, PreQC No. AEJ-21-8538 (PQ); Reviewed: 10-Jan-2021, QC No. AEJ-21-8538; Revised: 20-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-21-8538 (R); Published: 28-Jan-2022