Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 3
Challenges and Opportunities for Fintech Startups: Situation in the Arab World
Ayman Mansour Khalaf Alkhaaleh, Middle East University
Abstract
Financial technology is one of the fields that has recently appeared in the finance and banking sector, and it has become imperative for the concerned sectors in all countries of the world to keep pace with this development. While the debate is still going on about financial technology as an Intruder, unregulated sector, this study was conducted with the aim of identifying the concept of financial technology, its characteristics, fields, and development and what it has achieved from global investments. It also aimed to identify the reality of financial technology in the Arab world, and the most important emerging projects in this field, available opportunities and challenges. One of the most important findings of this study that financial technology is a sector newly established which it would provide all kinds of traditional financial services but in a different style and shape more sophisticated, speedy and accurate. It has also been concluded that the countries of the world have made great strides in this field despite its recentness, While the use of financial technology and its volume of transactions in the Arab world is still modest when compared to the developed countries in the world despite Development of the future strategies, electronic payment, and electronic commerce that Arab countries put in place for economic diversification make them encourage the establishment of financial technology in their economies. The Arab world should take advantage of the available opportunities and face the challenges facing the application of this technology, especially the development of modern regulatory legislation that would create a business environment that supports the economy in general.
Keywords
Fintech, Financial Technology, Startups.
Introduction
Recent developments in the fields of technology, such as digital ledgers, big data, the spread of mobile smartphones and the use of the Internet, have pushed the process of innovation in the field of financial technology. Without any doubt, this technology has been able to change aspects of financial services, making them faster, cheaper, more transparent and safer. Especially for the larger segment of the population that does not deal with the banking system. In this regard and as it was reported by Value Add research firm, global investments in the field of financial technology have witnessed a remarkable rise, from 928 million dollars in 2008 to 4 billion dollars in 2013, then these investments have grown to 20 billion dollars in 2015, and it was expected to reach 46 billion dollars by 2020 (Rowadalaamal, 2017).
The importance of this study is reflected in the importance of the financial technology sector in its various fields and the resulting reversal of the financial sector scales and the modern technologies it brought, as well as its importance is evident in keeping pace with the global developments taking place and the extent to which Arab countries keep pace with these developments. For their part, Arab countries are trying to keep pace with this rapid development of financial technology, as it is a fast-growing sector that allows achieving strong investment returns that support the path of economic development throughout the region, and financial technology companies provide new solutions that the financial sector can employ to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of its operational processes Saeeda Harfoush, (2019). This study seeks to achieve a number of objectives, the most important of which is introducing the concept of financial technology, its characteristics, its most important services and fields. In addition to learning about the reality of financial technology in the Arab world, the size of the investments, the difficulties and challenges facing this industry in relation to global investments in this sector, and to what extent can Arab countries keep pace with this development and exploit the available opportunities. The approaches utilized are descriptive technique, collecting information through the internet, and taking data from existing journals accompanied. And also use former study correlated to FinTech and the effect of FinTech on Financial Institutions (Business Insider, 2018).
The Concept of Financial Technology, Characteristics, its Fields and Development
Financial Technology
Financial technology is a technique and innovation that aims to compete with traditional financial methods in delivering financial services (Lin, 2015). Studies have found that: Fintech is a new financial industry that applies technology to improve financial activities (Sanicola, (2017). Fintech is the applications, processes, products, or new business models in the financial services industry, which consist of one or more complementary financial services and are provided as a comprehensive process via the Internet (Schueffel, 2016). It can also be considered that Fintech is any creative ideas that improve financial services operations by proposing technological solutions according to different business situations.
Whereas in the aftermath of the financial crisis of 2008, a large number of bankers and merchants left the financial centers of the world and embarked on entrepreneurial adventures in order to reconsider the financing model through financial innovation (Les Fintech, 2018). And it appears that interest in and investment in financial technology has witnessed a massive turnout during the period between 2014 and 2018 due to its material and tangible impact on financial markets and institutions, and the financial services sector. In light of the rapid spread of virtual cryptocurrencies, crowdfunding, data analysis and artificial intelligence sciences, companies and institutions have turned towards the field of financial technology and investing in it, and benefiting from financial services provided by this field. Moreover, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision defines it as "any technology or financial innovation. It results in a new business model, process, or product that has an impact on markets and fainancial institutions (Abdurahim & Ben Qadour, 2018).
The Digital Research Institute in the Polish capital Dublin defines it as It is about modern technological inventions and innovations in the field of finance. These inventions include digital software that is used in financial operations for banks, which include: Transactions with customers and financial services such as transfer funds, currency exchange, interest rate and profit calculations, and knowledge of expected profits for investments and other banking operations (Alemam, 2018). Another perspective sees it as an evolution in financial services led by technology as there are changes in customer expectations, availability of financing with increased support from governments and regulators (KPMG, 2017).
Characteristics of Fintech
The most important characteristics of Fintech can be placed in that Fintech is a set of knowledge, skills, and financial and banking methods. Also, technology in its various concepts is not an end in itself, but a means used by financial and banking institutions to achieve their goals. Moreover, banking financial service is the main area of technology application. It is important to notice that the application of technology is not limited to financial and banking service performance but extends to administrative methods (Lazhari, Z & Nafisa, H 2018).
Fintech Sectors
Financial technology has been used in insurance, trading, banking, and automated risk management (Aldridge & Krawciw, 2017). According to the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision , the financial technology field is linked to three main sectors related to basic banking: These are: "Credit, deposit and capital raising; Payments, clearing and settlement; and Investment and wealth management"; Where the stages of financial technology development are divided into two waves, the first wave includes payment solutions and lending solutions, and the second wave includes the introduction of technology into international transfers, insurance, wealth management and financial investments. Fintech is reflected in the banking field as Personal finance where spending, savings, and credit, as well as tax liabilities, are monitored through the government technical services and database provision for the customer. It includes simple guided banking for individuals online, without any physical presence of the agency, at low costs; it also includes budget management solutions, as well as various tools for personal financial management. The second banking field is Payments / Transactions which are the most flexible and active banking activities that the fintech offers for many clients, providing them with a set of payment methods, the most important of which are the following: Mobile payment, Money transfers abroad are at the lowest cost – TransferWise and Exchange currencies at no cost- Kantox. Where financial technology provides services for transferring various values at any time and any size across the world through its primary business, it is thus safe and accurate distribution technologies based on cryptocurrencies and Block Chains (KPMG, 2017).
In the field of Investment and financing, Fintech attracts the savings of individuals, by offering simplicity in the offers; and providing crowdfunding platforms to companies in form of crowdlending or crowdequity. It aslo offer online counseling to help individuals manage their savings; and analyze risks, and to provide the client with various proposals in financial investments. In capital market trading operations, innovative electronic trading platforms facilitate online and real-time trading operations. Social trading networks allow investors to monitor the trading behavior of their peers and expert traders and follow their investment strategies in the currency and capital markets. The platforms require little or even no knowledge of financial markets, and the World Economic Forum has described them as "disruptive agents that" provide a low-cost and sophisticated alternative to traditional wealth managers (McWaters, et al., 2015).Robo-advisers who are a class of automated financial advisors that provide financial recommendation or investment management online without a middleman to reduce human interference (Lieber, 2014). These consultants provide the digital financial recommendation according to mathematical rules or algorithms, so they can provide a low-cost alternative to human advisors.
Insurance is considered as one of most important sector and in this aspect Financial technology contributes to the rapid development of the insurance industry according to its various stages through products with innovative solutions using data analysis and the internet of things and artificial intelligence, as customized insurance products were generated through P2P Insurance platforms in addition, through digital distribution platforms. Regarding to services for banks and companies as one of the bank fields that relate to tecnnology FinTech offers many services solutions for improving corporate governance, some is banking-oriented ones such as technology Blocks (Blocktech) which develops blockchain-based solutions with regard to the recording of transactions, as for the companies provided also FinTech solutions such as data-processing software, as well as procedures for controlling Information systems and risk management, tax administration, etc. In Business-to business (B2B) regards, Fintech works to create technological service solutions that are specifically targeted for companies and financial institutions, such as: Software used in financial operations that support security financial clients are like a blockchain. Moreover, regulatory technology (regtech) facilitates and improves regulatory consensus by exploiting new technologies such as big data analysis and Machine learning (ML) (KPMG, 2017). Fitech on the other side provides services to banks on a big data where it is progress solutions geared to the banking and banking sector, by gathering and analyzing a large base of data, which would improve the management of the relationship with the customer (buying behavior, saving, customer career path, solvency), and also works in the field of cyber security, and that is through early detection of any fraud in the customer's behavior, such as locating the geography of smartphones, or encryption of sensitive data and information. Fintech also analyzes risks and provides tools to assist in making decisions about management financial portfolios, and facilitating regulatory reporting.
Fitech Development
Financial technology is not a new and modern phenomenon, as are banking services and financial services institutions have a long history of using technology in their operations Consumers International, (2016). The first stage where at this point was placed the first trans-ocean cable was laid Atlantic, invented the automated teller machine; technology and finance have come together for exploding the first period of financial globalization. The second stage, fintech remained dominant by the traditional financial services industry, which has used technology financial for the provision of financial products and services, and this period witnessed the beginning of the introduction of electronic payments, clearing systems, automated teller machines, and online banking services. Lastly, the third stage since the global financial crisis, it has emerged new startups that are starting to offer financial products and services directly to companies and the general public.
The most important factors that have contributed to the embrace of financial technology in the world and the widespread absorption of its developments are represented in low cost in fintech and easy access to quality services without paying big costs and ease of access to wider segments of the population, through the virtual world and social media sites. In addition, Ease of dealing in the world of financial technology "fintech", compared to the traditional world in which dealing with at least the opening of bank accounts at home and abroad is required Ghalib 2018), The most prominent feature of financial technology is the absence of postural restrictions that can hinder its progress and in light of technological development, this contributed to an increase in the pace of this progress and acceptance, thus highlighting new possibilities. Governments and regulatory authorities by organizational supporting this type of technology contribute to reducing barriers to their investors .Some governments have recognized the important role of fintech companies in facilitating complementing the traditional roles of financial services companies, in 2016, governments across five countries announced Sanbox software development (Patel, 2018).
Financial Technology in World Countries
Over the past few years, the financial technology sector has revolutionized the global financial systems, as emerging companies in the field of financial technology have succeeded in providing a diverse package of financial services, including payments services, cryptocurrencies and money transfer, as well as lending, crowdfunding, and wealth management in addition to insurance services casts a shadow over the future of traditional financial services. Therefore, banks and financial institutions seek to introduce some changes in their business models by expanding the adoption of technology and investing in their own infrastructure, and perhaps entering into partnerships with emerging companies to improve their competitiveness and increase reliance on modern technology in providing financial services. Here, the importance of the availability of the legislative, regulatory and supervisory framework that allows the development and operation of financial technology and financial artificial intelligence business models, and which enables supervisory and regulatory authorities to reduce risks and provide growth opportunities in a competitive environment, while maintaining financial integrity and financial stability
International Investments in the Financial Technology Sector
Global investments in the financial technology sector have achieved rapid growth in the past few years, as their value increased more than tenfold between 2012 and 2018, and the volume of global investment in financial technology companies reached about $ 112 billion in 2018, with an increase of 120%. Compared to 2017, when the volume of financing and investment reached 50.8 billion US dollars. According to a report published by KPMG, the year 2018 witnessed the conclusion of 2,196 deals, after this number reached 2,165 in 2017, indicating that the geographical diversity of venture capital funds financing financial technology investments contributed to boosting the volume of deals, even at a time when the huge financial technology centers witnessed an intensity Higher investment under big deals. Investments in fintech startups are expected to increase during the next years, despite growing geopolitical uncertainty and commercial concerns, which may place a greater burden on investment in fintech
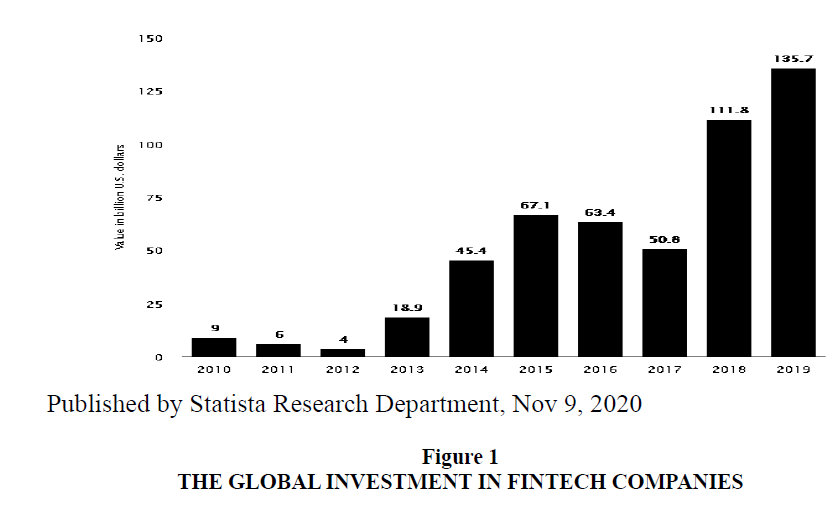
The volume of global investments in fintech has grown rapidly over the past few years, especially in the wake the global financial crisis of 2008, due to the lack of customer confidence in traditional financial services, especially banking. The following Figure 1 represents the size of global investments in fintech companies. This statistic illustrates the total value of investments into Fintech companies worldwide from 2010 to 2019. It can be seen that total investments on the global market reached 135.7 billion U.S. dollars in 2019.
During the period 2010-2019, it is noticed through this figure that the volume global investments in financial technology during the time from 2010-2012 have experienced a small decrease wherer it has increased continuously during the period 2013 - 2015, where the annual average increase in the volume of investment was significant. It is also noted that volume of investments have decreased in 2017, then increased in years 2018 and 2019, indicating that the value of these investments increased during the period as of general. Likewise, the percentage increase in transactions of more than $ 100 million increases at a faster rate than the increase in transactions of less than $ 100 million. Global investment in financial technology experienced a huge increase from $ 930 million in 2008 to more than $ 22 billion in 2015 Qatar Financial, Center, London's emerging fintech industry has experienced rapid growth over the past few years, according to the London Mayor's Office. Forty percent of London's workforce is employed in financial and technical services (Chance, 2017).
In Europe, $ 1.5 billion was invested in financial technology companies in 2014, with the volume of investment in London-based companies amounting to $ 538 million, Amsterdam companies $ 306 million, and Stockholm $ 266 million. After London, Stockholm is the second most funded city in Europe over the past ten years. Fintech deals in Europe increased fivefold, rising from 47 in the last quarter of fiscal 2015 to 47 in the first quarter of 2016 (Patel R. (2018); BAHRAIN. A). Lithuania is on the way to becoming a hub for fintech companies in Northern Europe after news broke out in 2016 that the UK might leave the European Union. Lithuania has issued 51 fintech permits since 2016, 32 of them in 2017 Fintech Consortium, (2018). Investments in fintech companies in the United States increased to reach $ 12.4 billion in 2018, an increase of 43% over 2017 Crown prince foundation. The Asia-Pacific region witnessed the opening of a new fintech center in Sydney in April 2015 Westlaw's Computer & Internet Journal (2015). Depending on KPMG in 2017, the financial services sector in Sydney contributed 9% of the national GDP, more than the financial services sector in Hong Kong and Singapore. In 2015, a Fintech Innovation Lab was opened in Hong Kong (Global IndraStra) In 2015, the Monetary Authority of Singapore launched an initiative called FinTech and Information Group to attract startups around the world. It pledged to spend $ 225 million in the fintech sector over the next five years. The size of investment in financial technology for Consecutive years, as North America tops the list, followed by Europe, and then Asia, Latin America is at the bottom of the ranking.
Development of Financial Technology in Arab World
The number of emerging fintech companies across the MENA region has grown-up promptly over the previous years, increasing in number at a faster rate than other segments. There is a growing emergence of financial technology solutions in Bahrain, Egypt and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with the introduction of many private and government enterprises to endorse this sector
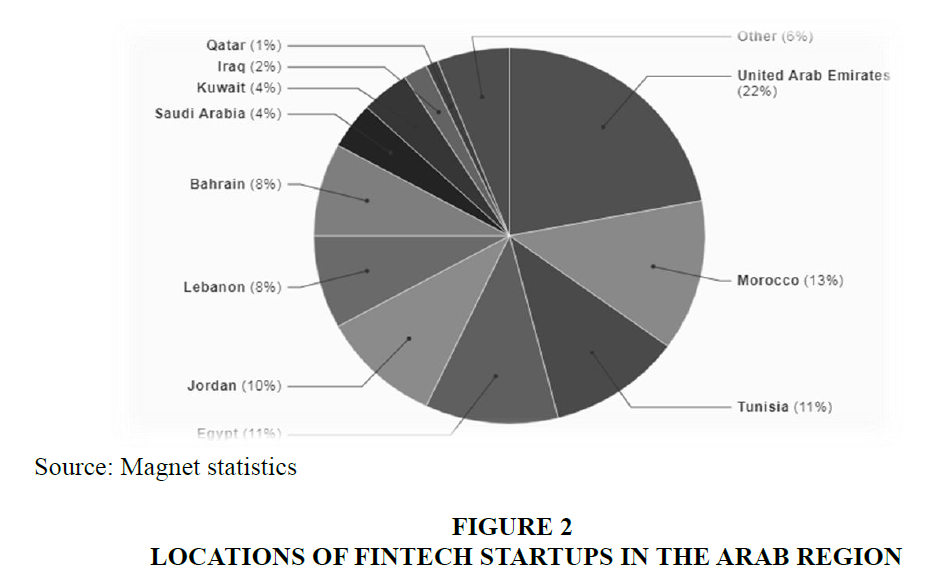
Since October 2019, it has been recognized that more than 330 technology startups operating in 22 countries in the Arab region. It is noted 75 percent of fintech solutions are concentrated in a few countries. The Gulf countries have situated themselves as front-runners, with the Emirates boasting more than 60 solutions. Levantine side, headed by Jordan and Lebanon follows the North Africa, led by Egypt, Morocco and Tunisia 29. Old Laws, New Models, (2014). Along with the sates listed in figure 1, startups were also found in Libya (1%), Oman (0.7%), Somalia (1.3%), Yemen (1%), Djibouti (0.7%), Syria (0.3%), Palestine (0.3%) and Algeria (0.3%) in Figure 2.
In the Middle East and North Africa region, fintech startups have made large investments, as the first half of 2019 witnessed 238 investments amounting to $ 471 million in financing startups, which is an excellent indicator, as it reflects an increase of 66%. In the value of investment during this period, compared to the first half of 2018, in which the value of investments amounted to 283 million dollars. The number of deals also reached a record level, recording an increase of 28% compared to the first half of 2018, indicating the continued demand for emerging companies in the region during all stages of investment. The United Arab Emirates maintained its lead by acquiring 26% of all startup deals based in the UAE, which took place in the first half of 2019, while it acquired 66% of the total funding provided to startups, and Tunisia recorded its ownership of the startup environment. The fastest growing number of deals in the first half of 2019, as it acquired the fifth largest number of deals, with 8% of all deals, an increase of 4% compared to the first half of 2018, while the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia recorded an increase of 2% in the number of deals, i.e. Reaches 11% of the total number of deals in the MENA region. The number of fintech startups in the MENA region is expected to reach about 96 companies during 2019 and 465 companies by 2020. Investments in the financial technology sector are expected to jump from $ 287 million in 2019 to 2.28. Billion dollars by 2022 GroundbreakingFinTech Innovations.
The Most Important Accelerator Projects for Expanding Fintech in the Arab Region
There are many successful business accelerators in the Arab world in terms of financial technology, which are beginnings and success stories. In the Egyption context, In March 2017, Pay Fort, the online payment engine, announced launch of fintech accelerator (Fintech Factory) to continue Pay Fort meet the demands of its merchants and innovate faster by investing and cooperating with Fintech startups. Previously , Egypt launched the "1224 Accelerator" in 2016, and the program aims to promoting the space for innovation in financial technology in Egypt, where participated the American University in Cairo and the Commercial Bank in the establishment of the (AUC Venture Lab Fintech) It is backed by the Commercial International Bank, and aims the new specialized program aims to develop and support startups in Egypt areas such as payments, lending and interface technology clients, retail trade, personal financial planning, investment and remittances
As usual, the Arab Gulf states, and because of their generally developed economy compared to the rest of the Arab countries, have multiple experiences in using financial technology to support economic success. The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA) also launched the “Saudi Fintech” initiative. This initiative aims to support the financial technology system to advance in the Kingdom, to become a center for financial technology, in order to support and increase financial inclusion and digital financial transactions in the Kingdom. It aspires to be a platform and a front of financial technology in Saudi Arabia, and it is counted on to accelerate the pace of growth and development of financial technology in the Kingdom, and turning the country into a destination for innovation in fields and technologies, such as artificial intelligence, block chain, and other technologies. The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency, (2018). The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has established regulatory sandboxes. This box is a "virtual" place to provide a temporary legal framework to qualify the category of creative technical owners of creative projects to obtain official approval, and later, they are granted the legal license to carry out business and services in an official and recognized capacity Ghalib A., It is an area where offers can be tested free of charge, due to the usual restrictions for financial technology in many innovative areas
In 2018, provided the Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA) a sandbox in which banks can try the USA Ripples blockchain solution for low-cost cross-border operations. In addition, in May 2018, The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency announced the launch of electronic invoicing nationwide (ESAL) to enhance the number of digital financial transactions and makes the economy of the country more competitive, as many companies have signed to join, including retail, insurance and healthcare services logistics. The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency noted that ESAL completely extends the life cycle of the bill - from time invoice reconciliation to settlement. This adds visibility to sales, automates settlements, and improves financial management.It will likely do much more in the future given that SAMA plans to add more jobs (Patel, 2018). The UAE Central Bank and the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority have announced plans to use blockchain technology to issue a cryptocurrency accepted in cross-border transactions between the two countries (Qatar Financial Center, 2018).
In Qatar, an exclusive section for the electronic financial system has been established at Qatar Central Bank, and a fintech strategy has been developed that aims to develop a collaborative and connected financial ecosystem to meet long-term goals, and as part of the strategy, Qatar Central Bank is working to create a modern regulatory environment, including a regulatory protection fund Supports innovation and market stability. The most important thing Qatar has done in the context of enhancing financial technology in was the conclusion of a partnership between the Qatar Financial Center creative European technology collaborative platforms B-Hive to develop the fintech industry. B-Hive brings together major banks, insurance companies and others to work together on joint innovation. This partnership will help in facilitating cooperation in many aspects, on the basis of promoting employment and exchange opportunities knowledge. It also notes the agreement the participation of the two parties in supporting the development of fintech-related societies. Additionally, work to explore potential joint ventures focused on developing financial technologies, as well as developing training and talent management programs (Chance, 2017).
In Kuwait, the situation is not as hoped where small number of fintech startups operate, particularly in the payments sector; to date, there have been limited regulatory developments, to address legal challenges and new developments arising from the digital revolution, such as the Kuwaiti National Assembly issuing Law No. 20 of 2014 concerning electronic transactions. The goal was to simulate traditional paper-based transactions in an organized, efficient and secure digital system, where the law governs electronic contracts and agreements (Patel, 2018).
Bahrain is the fastest growing financial technology centre, partly due to the environment surrounding modern financial services regulations. In Bahrain, the main player in the Islamic banking sector in the region, Al Baraka Banking Group, Bahrain Bank for Development and Kuwait Finance House - Bahrain announced December 2017 the establishment of a company dedicated to the research and development of compatible financial technology products Islamic Sharia (BAHRAIN. A) in which the world's first Islamic financial technology consortium was launched and named ALGO – Bahrain. Its goal was to accelerate technological solutions and the founders of this group is preparing to launch 15 financial financial planning platforms by 2022, across gulf countries (Fintech Consortium, 2018).
In June 2017, the Central Bank of Bahrain launched the Regulatory Sand box. Once approved, applicants are given a set period of up to nine months to test technology solutions to date, nine companies have been mandated to participate in the regulatory domain includes areas of foreign exchange, financial inclusion, wealth management, alternative lending, data analysis mega robotic consulting. The companies are local and international companies based in the Arab Emirates, United States, Malaysia, and India. Moreover, Bahrain Development Bank launched its first $ 100 million risk capital fund to assist companies and the aim of launching the "Oasis" fund is to support the incubating environment for projects emerging and technology-based not only in Bahrain but also in all parts of the Middle East, and to attract also funds to the region to help establish more innovative startups. Bahrain hopes to transform into a fintech hub, and opened Fintech Bay in 2018 to attract promising startups into its economic system to create much-needed jobs as this will work with leading institutions in the fintech sector, world leaders in addition to companies emerging locally, regionally and globally . However, Bahrain is required to compete with rival centers in Dubai and Abu Dhabi to attract high-quality fintech companies. Both Dubai and Abu Dhabi hope to establish themselves as a fintech hub in the region, and to make investments in a $ 2 billion financial technology market in the Middle East (Crown prince foundation).
In the Jordanian case, there are many experiences regarding the development and use of financial technology, for example (Changecom) platform. It is a Jordanian startup, established in 2019, that is developing a personal finance management platform, which will be the first of its kind in Jordan and the region with an expected global presence and relationships in the region in general. The importance of this platform comes as it is a solution targeting the people of the Middle East region that helps them save according to their daily spending habits, in addition to their access to the services that they were able to obtain earlier. Moreove, AlAhli FinTech Company, fintech business accelerator, innovation and proprietary investment arm completely by the Jordan National Bank, during the month of October of 2019 by choosing a company Whyise Inc. mong the number startups to participate in the first cohort of the Fintech Startup Accelerator Program. The Jordanian Entrepreneurship Fund (ISSF) invested the same amount in the company, due to the great belief of both AlAhli for Financial Technology and the Entrepreneurship Fund in the value of the company and its investment opportunities in the market. During the previous period, Whyise was able to verify the suitability of its business model to the needs of the market and the presence of the market to obtain the company's services and products in a sustainable manner, and it has proven its ability to accelerate growth in terms of revenues, number of customers, content and standards available through the platform and the ability to export its services outside Jordan. The International Financial Technology Leadership Association, a specialized incubator for building ecosystems, announced the launch of the “Jordan Bay for FinTech”. Jordan FinTech Bay aims to enhance partnerships among the players in the financial technology sector in the market, including government agencies, financial institutions, companies, investors and innovators, in recognition of the role of technology in achieving added value and future evidence of the financial industry in Jordan. Jordan Fintech Bay will provide a number of digital solutions and advisory services, in addition to a program to accelerate financial leadership and projects, and a talent program for national financial leadership.
The Strongest Startups in the Financial Technology Field in the Arab World
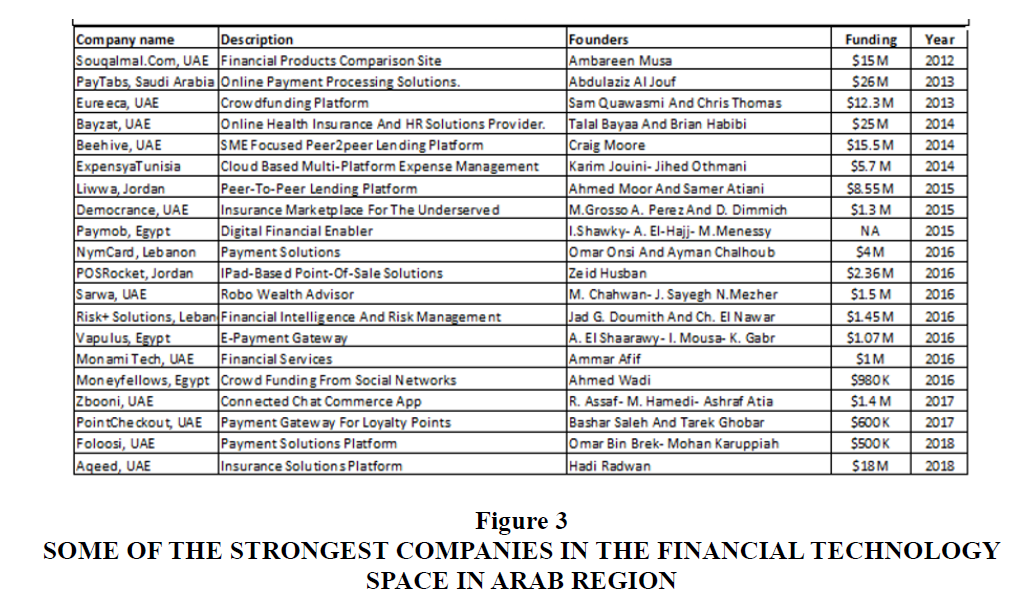
Financial Technology scene in the Middle East has grown so rapidly since 2015. The UAE hosts one-third of the region's Fintech start-ups, making it the biggest market in the Middle East. Th e next years, in particular, are expected to witness an exceptional interest in the Fintech sector, as a result of the radical changes that have occurred to our daily lives since the coronavirus pandemic has started. The limited travel options within or across countries in addition to the increasing shift to using technologies to facilitate financial services have been greatly impacting the industry.Moreover, the economic crisis that has been worsening, has sharply influenced investors' decisions as they look for safe, yet promising economic environments that can survive the global meltdown. Here are some of the strongest companies in the financial technology space Figure 3:
Challenges and Difficulties of Financial Technology in the Arab Region
In spite of the incentives available in the field of fintech in Arab region, there are still many major, structural and institutional constraints facing and limiting technology Finance growth in the Arab countries. The weak business environment that currently exists in general, and the problem of restrictions that still exist on the entry of foreign entities to the markets, impede the possibility of entering international financial technology companies that already operating in the markets. Additionally, the decline of private and investment capital, which is the basis for the existence and progress of financial technology in the economy, for any country has contributed to creating a challenge in this area. In fact, the difficulties that need to be overcome quickly may be the lack of an adequate level of legal legislation due to regulatory gaps impeding the growth of the financial technology sector, despite the ongoing work to develop regulatory frameworks for digital financial services, and the development of laws regarding the issuance of cryptocurrencies. On the other hand, Prices and quality of Internet and mobile phone service may be one of the factors that cause pressure and impediment in the financial technology sector despite the high penetration rates of information and communication technology in recent years. Unfortunately, the institutional support necessary to have an incubator environment for fintech remains below the required level, as a few Arab countries have established incubators and accelerators to help increase startups, which allow fintech companies and institutions to make traditional tests of innovations in the actual environment. From the demand side of fintech services the "confidence gap" and financial awareness levels is a major constraint for fintech startups where using fintech as a payment channel requires confidence to reduce uncertainty. In addition, there is the problem of promoting this type of services and the problem of the educational level for the customer in the Arab countries. Moreover, the problem of cyber risk, where cyber-attacks may lead to disruption of operation, incur financial losses, damage to reputation, and it may become a handicap restriction unless information security frameworks are strengthened. Rigorous enforcement of banking secrecy law and money transfer regulations is a constant threat to fintech companies IMF (2018). This called the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank jointly to submit proposals on the Bali Fintech Agenda in 2018 (Global, IndraStra) which consist of twelve elements that are used as guidelines for various governments and central banking institutions to adopt and disseminate “rapid progress in in fintech" (Bnaih & Alioush, 2018).
The Motives for Using Financial Technology in the Arab Region
In a region where access to financial services is not global, it is not surprising that slightly more than half of emerging solutions target the mass market, whether individuals or companies. As regulatory bottlenecks remain a major concern in many countries, a number of business-to-consumer (B2C) companies have ended up switching to business-to-business (B2B) or business-to business-to-consumer (B2B2C) models.Survival rates are difficult to calculate, especially given how difficult it is to open or close a company in the region. The World Bank's Doing Business 2019 score for the MENA region is 58/100, well below the OECD average of 78/100. The very tentative results seem to indicate a better fintech survival rate compared to the average startup in the region and beyond. This reflects the survival rate of 63 percent that was highlighted in Wamda's 2017 research on fintech.The incentive for companies and individuals to use financial technology in Arab world is next points (Old Laws, New Models, 2014).
Great interest in mobile payments where there is a more urgent change underway in mobile payments, and they are especially beneficial to residents’ non-collaborators in Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, where smartphone penetration is on the rise, and the two countries are moving toward cashless societies. The tech-savvy young generation in this region deals with mobile phone wallets.
Widespread financial exclusion has a high cost for everyone and governments while increasingly people seek to use some forms of financial services, the key to overcoming that are technology, and with the increasing use of technology in all aspects of life, and the increasing prevalence of smartphone, it is expected to increase the need for digital payments solutions.
The oil crisis and the adoption of economic diversification strategies where the economies of the Gulf states, as is well known, depend heavily on oil, and the recent oil crisis is following caused by a drop in oil prices, it made the oil-producing countries reconsider their accounts for not falling into such a bitter crisis others, the only solution is to adopt strategies based on economic diversification.
In spite of the relative contribution of e-commerce to the GDP, in countries such as Gulf Cooperation Council, but it is considered to be five times less compared to other countries with higher income, partly because customers prefer the payment option upon receipt even if they own credit and debit cards.
Lending to small and medium enterprises represents 8% of the credit loans provideed by Arab banks in the countries of the Middle East and North Africa compared to 18% in the countries of middle income in the world, and this despite the important role that small and medium-enterprises play in the region, providing a good perecentage of all private sector jobs
Economic strength and young human base: the Gulf Cooperation Council is a political and economic group of Arab countries in the Arab Gulf. Its maritime members are Qatar, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the Sultanate of Oman, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. This part of the Arab world ranks among the top 10 economies, larger than India, Russia and Brazil. The United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are ranked first among the top five countries in the world smartphone penetration rates, with more than two-thirds of its population between the ages of 15 and 24. This part is represented It is among the largest age group in the MENA region and is the most targeted group before financial institutions
The opportunities offered by financial technology to the financial and banking sector can be represnted by enhancing financial inclusion, providing better and more convenient banking services to customers, the potential positive impact on financial stability due to increased competition, and the role of regulatory technology in improving compliance processes in banks. On the other hand, the main risks that may arise from the application of technology in financial and banking operations include strategic risks, operational risks, and compliance risks, outsourcing risks, cyber-risk, and liquidity and financing risks. In addition to established competitors, fintech companies often face suspicions from financial regulators such as bond issuing banks and federal governments (Groundbreaking FinTech Innovations).
Results and Discussion
Fintech is a modern aspect that has taken its place worldwide and has been encouraged under the fear of its risks; Fintech is every innovation that relies on advanced technology to develop the financing sector, its services depend on ease and speed of technology.Moreover, and to experince high growth level in fintech, technology has to be spread over all the world and may the financial inclusion need to be enforced in all Arab countires.
Arab countries are trying to keep pace with the tremendous development in technology in the world. Some of the Arab countries realized the importance of the financial technology sector and see it as a way out to overcome crises especially Gulf countries where the development of the electronic payment sector through mobile devices helped its speed in dealing with financial technology.
The steps taken by the Arab states to adopt the financial technology sector are distinguished by governmental and official regulation which will end at reducing the negatives and risks of this sector. All Arab world governments are required to coordinate their efforts and to reach to abundle of regulation to intregate all financial transactions in systems that rely on technology as a part of the communication with the rest of world.
Several countries in the region have launched software and accelerators in financial technology, and Hive Fintech in Dubai and Bahrain Fintech Bay are among the most important of them. In this regards other Arab countries are invited to benefit from the two countries experice and to set up new business accleators to encourge the startups in fintech.
The use of financial technology in the Arab countries faces several difficulties, the most important of which are lack of business, venture capital, and legal woes and regulatory, as well as quality problems of Internet and communication services.It is important as one mass of Arab countries to colabborate to exchange buseness and to work closely to emply a new legstlations to move forward in this field.
There are many common features among Arab countries that make the search for service integration an easy matter, especially investing in common opportunities and converting difficulties into real opportunities through which integration between capital and human elements can be achieved to reach great breakthroughs in this field
Conclusion and Recommendations
Fintech offers tremendous opportunities for developing financial services, as well as helping to renew and develop traditional services. Arab countries are trying to occupy a position in the field of financial technology, by providing all the regulatory, legal and technological frameworks. Through this study, a set of results were reached, the most important of which are the following: Arab countries are trying to keep pace with the tremendous development in technology in the world, and the Gulf Cooperation Council countries occupy the first place in the Arab countries, and the UAE is the first. In the Arab world, with the exception of the Gulf countries, Egypt, Lebanon and Jordan, the rest of the Arab countries remain far from these important developments affecting the financial services sector. Fintech is a modern sector that has taken its place within the economies of developed countries and has been welcomed and encouraged under fears of its risks. Most Arab countries quickly realized the importance of the financial technology sector and saw it as a way out in light of the recent oil crisis. The development of the electronic payment sector through mobile devices in the Gulf countries has helped to accelerate the absorption of financial technology. The steps taken by the Arab countries to adopt the financial technology sector are characterized by governmental and official regulations that reduce the negatives and risks of this sector. It is very clear that the use of financial technology in the Arab countries faces several difficulties, the most important of which are weak business, venture capital, legal and regulatory problems, as well as problems with the quality of Internet and communications services. Banks have also realized the dangers of creating competitive institutions, so they have taken steps to make them a partner rather than a competitor. The study recommends the necessity of studying the opportunities and challenges well by the decision makers in the Arab countries and investing these opportunities and converting more difficulties into opportunities. This study recommends researchers in the future to conduct studies based on the reality of financial technology in each Arab country separately and trying to make benchmark comparisons to generalize the experience. Also, the impact of financial technology on different sectors and on economic growth can be measured.
References
- Abdurahim, W., & Ben Qadour, A. (2018). The Trends of Financial Technology in the Light of Successful Companies Experiences. Revue al-Ijtihed des Études Juridiques and Économiques, 434(6317), 1-18.
- Aldridge, I., & Krawciw, S. (2017). Real-time risk: What investors should know about FinTech, high-frequency trading, and flash crashes.
- Alemam, M. (2018). The role of financial technology in developing the performance of Islamic banks. https://islamonline.net/.
- Al-Latif H.E, Ahmed B. (2018). Fintech among the enormity of the concept the severity of the risks is an intervention presented at the National Forum on Financial Technology Startups, Challenges of Growth and Competition.
- BAHRAIN. A. The World’s First Fintech Launching Shari’a compliant FinTech solutions Consortium of Islamic Banks. Retrieved from: http://algobahrain.com/#WhatWeDo%20
- Bizri L, (2018). The State of Fintech in MENA, Retrieved from: http://news.arabnet.me/the-state-of-fintech-in-mena/
- Cai, C.W. (2018). Disruption of financial intermediation by FinTech: a review on crowdfunding and blockchain. Accounting & Finance, 58(4), 965-992.
- CGAP's research. (2019) Retrieved from
- Chance, C. (2017). FINTECH IN THE MIDDLE EAST, Retrieved from: https://financialmarketstoolkit.cliffordchance.com/
- Chaouadi, N., & Goumghar, N. (2018). L’impact de la bancarisation sur le développement socio-économique en Algérie: cas de la BNA de la wilaya de Tizi-Ouzou (Doctoral dissertation, Université Mouloud Mammeri).
- Consumers International, Coming together for change, Banking on the future; (2017), Retrieved from: https://www.consumersinternational.org/media/154710/banking-on-the-future-full-report.pdf
- Crown prince foundation, Retrieved from: https://www.cpf.jo/ar/media/press-release/
- Fintech Consortium. (2018).EDB Bahrain and Bahrain Fintech Bay, Bahrain Fintech Ecosystem Report , 39, Retrieved from: https://www.fintechgalaxy.com/storage/uploads/reports/2018/08/08/31b03ebdf443501b54fb107285a6da4f.pdf
- Ghalib, A. (2018). The Sand Fund, Organizational and Central Banks, the Research Center for Islamic Transactions Jurisprudence, online: https://www.kantakji.com/monetary-policy/
- Business Insider. (2018). Groundbreaking FinTech Innovations: Threat for banks, or opportunity of a lifetime?”.
- Bnaih, H., & Alioush, I. (2018). The reality of startups in the Middle East and North Africa, an intervention presented within the activities of the National Forum on: Companies Emerging fintechs -challenge competition and growth.
- Harfoush, S. (2019). Financial technology is a promising industry in the Arab world, afak Journal, 11(3),
- https://www.cgap.org/blog/mapping-fintech-innovations-arab-world
- Hutabarat, S., & Vermeulen, E.P.M. (2016). The Challanges for Development of Peer to Peer Lending Business in Indonesia's Financial World.
- KPMG. (2017) .value of fintech. Retrieved from: https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/uk/pdf/2017/10/value-of-fintech.pdf
- Lazhari, Z., & Nafisa, H (2018). Financial Technology Revolution of Financial Payment Reality and Prospects. Revue al-Ijtihed des Études Juridiques and Économiques, 434(6317), 1-20
- Lieber, R. (2014). Financial advice for people who aren’t rich. The New York Times, B1.
- Lin, T.C. (2015). Infinite financial intermediation. Wake Forest L. Rev., 50, 643.
- McWaters, R.J., Bruno, G., Lee, A., & Blake, M. (2015). The future of financial services: How disruptive innovations are reshaping the way financial services are structured, provisioned and consumed. In World Economic Forum, 125.
- Middle East and North Africa FinTech Projects Report. (2019). https://magnitt.com/research/209-mena-fintech-venture-report-ar-50676
- Munch, J. (2015). What is fintech and why does it matter to all entrepreneurs. Hot Topics.
- Old Laws, New Models. (2014). Taylor Wessing.
- Patel, R. (2018). Fintech: Don’t be analogue in a digital world. Deloitte, A Middle East Point of View, Spring Retrieved from: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/xe/Documents/About- Deloitte/mepovdocuments/mepov25/fintech_mepov25.pdf
- Qatar Financial Center. (2018). A partnership between the Qatar Financial Center. And B-HIVE to develop the financial technology industry. Retrieved from:http://www.qfc.qa/ar/MediaCenter/News/Pages/bhive-fintech-partner.aspx
- Rowadalaamal. (2017). Value of fintech. Retrieved from: https://www.rowadalaamal.com/
- Sanicola, L. (2017). What is fintech. Huffington Post.
- Schueffel, P. (2016). Taming the beast: A scientific definition of fintech. Journal of Innovation Management, 4(4), 32-54.
- Sergi, A. (2019). Polycephalous ‘ndrangheta: Crimes, behaviours and organisation of the Calabrianmafia in Australia. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Criminology, 52(1), 3-22.
- The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency, (2018). Retrieved from:http://www.sama.gov.sa/ar-sa/News/Pages/news30042018.aspx
- Wesley-James, N., Ingram, C., Källstrand, C., & Teigland, R. (2015). Stockholm FinTech: An overview of the FinTech sector in the greater Stockholm region. [online] Stockholm School of Economics.
- Yue, X.G., Cao, Y., Duarte, N., Shao, X.F., & Manta, O. (2019). Social and Financial Inclusion through Nonbanking Institutions: A Model for Rural Romania. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 12(4), 166.