Research Article: 2020 Vol: 26 Issue: 3
Corporate Culture of Innovative Entrepreneurship.
Ivan Bakhov, Interregional Academy of Personnel Management
Kateryna Tarasenko, University of Customs and Finance
Danylo Vankovych, Ivan Franko National University of Lviv
Svitlana Filyppova, Odessa National Polytechnic University
Mykola Merkulov, Izmail State University of Humanities
Abstract
The paper deals with the peculiarities of forming the corporate culture for innovative entrepreneurial activity. The process of formation of corporate culture in entrepreneurial activity was presented, the classification of factors of corporate culture was improved, the primary bases of emergence, the status and prospects of corporate culture development in business were analyzed, its principles were systematized. "Corporate culture" is proposed to be interpreted as rules and norms of behavior based on material and spiritual values, cultural, ethical and social needs of employees to achieve entrepreneurial goals. We propose to implement the process of forming corporate culture through such stages as determining the priorities of corporate culture; formation of employee behavior; implementation of effective activity of innovative entrepreneurship and ensuring the interests of all participants of the sphere of innovative entrepreneurship. In order to ensure the formation and development of corporate culture, the principles of entrepreneurial corporate culture have been systematized on the basis of theoretical knowledge and own research, as a result, general and specific principles have been identified. The general ones take into account the most important features and characteristics of corporate culture. However, given that the corporate culture of innovative entrepreneurship is individual and almost repetitive, it is expediently to distinguish specific principles. They take into account the individual traits and characteristics of the given corporate culture and they are designed specifically for a particular type of entrepreneurial activity. Existing approaches to the assessment of corporate culture were analyzed, and corporate culture was assessed using current methods. According to the results of the evaluation, the method of corporate culture determination was proposed and the profile of corporate culture for innovative entrepreneurial activity was formed.
Keywords
Corporate Culture, Innovative Entrepreneurship, Entrepreneurship Profile, Determination of Corporate Culture, Factors and Principles.
JEL Classifications
L26, M51
Introduction
An important condition for effective development of innovative entrepreneurship is the search for effective methods of managerial influence on cultural aspects of doing business. One of the important tools of such influence is the formation and development of corporate culture, as evidenced by the successes of machine-building innovative entrepreneurship of different countries of the world, which declare the basic rules, principles, and rules of corporate culture, recognizing it as a key factor of development and competitiveness. In fact, there are no specialists in the formation and development of corporate culture, their training is not being carried out, there are no mechanisms for dissemination of best practices in this field. One of the least costly and sufficiently effective tools of the management impact is used at the very low level. The introduction and implementation of effective systems of corporate culture in the field of innovative entrepreneurship will solve the existing problems of management and organization of entrepreneurial activity.
Review of Previous Studies
At the level of the institute of entrepreneurship, innovation culture is a component of the innovation potential that characterizes the level of educational, general cultural and sociopsychological preparation of the individual and society on the whole to perceive and creatively embody the idea of developing the economy of the country on innovative grounds (Trice, Beyer, 1993; Bakhov, 2014). At the level of the individual entrepreneur, corporate culture is a system of ideas, values, beliefs, expectations, norms and rules of behavior, traditions, thinking and corporate symbols that are formed in the course of working together to achieve the overall goals of the organization (Christensen, 1999; Hodgetts & Luthans, 2003). If its components are aimed at developing innovation, we will call this corporate culture as innovative.
According to (Daft, 2003; Kerr & Slocum, 2005), corporate culture in entrepreneurship is manifested at three levels: 1) level covering external manifestations (the surface level including visible and tangible elements of culture: behavior, language, rules, brand and trademark, branded clothing, interior design, building architecture); 2) values and beliefs (the semantic level forms the values and beliefs of entrepreneurs, explains the purpose of its existence); 3) basic concepts and relationships - the deep level at which values are perceived automatically on the subconscious and they are considered true, irreplaceable, not needed to be legalized.
Methodology
The innovative development of entrepreneurship at the present stage is becoming a leading among the priorities of national business development and unprecedented scale of introduction in the economy. Its acceleration requires a profound qualitative change in the corporate culture and enhances its role in achieving the strategic goals of innovative entrepreneurship. The innovative corporate culture is the most effective lever of personnel management in the context of the need to innovations development and introduction. In the course of innovation development, corporate culture provides the psychological basis for achieving the strategic goals of innovative entrepreneurship aimed at innovative development, namely: a) introduction of new production technologies; b) constant improvement of the quality of goods or services; c) formation and satisfaction of market demand; d) individualization of the product and expansion of the range; e) optimization of production and business processes.
Results and Discussion
The basic principles of the corporate culture development are its principles. They depend on the type of business, national priorities, characteristics and behavior of the entrepreneur. However, there is still no clear position on the formation of basic principles and their number. In order to ensure the formation and development of corporate culture, the principles of entrepreneurial corporate culture have been systematized on the basis of theoretical knowledge and own research. As a result, the general and specific principles of corporate culture were highlighted. The general ones take into account the most important features and characteristics of corporate culture of innovation entrepreneurship. They may be common to many organizations, but given that the corporate culture in the field of innovative entrepreneurship is individual and almost unique, it is expediently to highlight specific principles taking into account the specific, individual traits and characteristics of the corporate culture of innovative entrepreneurship and they are worked out for specific innovative entrepreneurship.
The general principles include the following: development; comprehensiveness and systematicity; openness and continuous improvement; coordination; obligations; rewards; dimension and usefulness; compliance with applicable law. Special principles are: individuality; free formation; consistency and accordance; clarity; personal-oriented management; "Management-employee" relations; benchmark (Reisyan, 2016). The applied value of systematizing corporate culture principles is that they enhance the impact of corporate culture on HR management.
Corporate culture management in innovative entrepreneurship fulfills this need through the following tasks (Flamholtz & Aksehirli, 2000; Zak, 2018): a) adaptation of staff to the dynamically changing environment of the internal and external environment; b) making decisions under non-standard conditions; c) organizing teamwork and result work; d) shift in the professional structure of staff towards an increase in the proportion of intellectual professions; e) stimulating creative, non-standard thinking, initiative and creating favorable conditions for the submission of ideas for consideration by management or responsible persons; f) workers professional and intellectual development, promotion of selfdevelopment; g) humanization and intangible work motivation, as the owner of intellectual capital.
We can identify the leading factors in building a corporate culture of innovative entrepreneurship.
1) Formation of new requirements for the staff's competencies when hiring him. Corporate culture aimed at innovative development puts forward such criteria for selection of candidates for vacant positions as: innovative abilities, ability to learn, enterprising, communicative, adaptability, ability to self-improvement, ability to learn, ability to influence others, ability to work.
2) Reducing the number of levels of government to speed up decision making.
3) Regulations - establishment of labor and technological discipline by means of norms of behavior and internal corporate values. These tools for regulating the work activity of employees have certain advantages over administrative methods, because, firstly, they allow to respond more quickly to changes in the internal and external environment of the company, since they do not require innovations in the regulation of business processes and staff motivation system, and secondly , they minimize attempts of creative workers to disrupt them in the absence of direct control, since they are shared by all members of the organization as a result of identifying their own and group interests justified above.
4) Entrepreneur. Corporate culture influences all aspects of the life of the organization through the decision-making system, helps to identify in a timely manner the negative influence of factors of the internal and external environment and to avoid negative consequences in a timely manner. Evaluation conducted through an employee's assessment based on a comparison of actual behavior with accepted benchmarks and norms.
Education, which according to the approach (Lejeune & Vas, 2009), is carried out by explaining to employees the content of the company strategy and ways of its realization, gaining them spiritual and social experience, mastering the best examples of combination and adaptation of the person as opposed to the inherited archaic behavioral models and instincts.
5) Communication, which is manifested in ensuring constructive interaction between different management units, divisions and individual employees through the promotion of innovative values and standards of behavior through internal corporate media.
6) Adaptation, which is manifested in the adaptation of employees to changes in the internal and external environment due to the formation of new attitude to the quality of products or services, customers of innovative entrepreneurship, as well as innovation processes and priorities in entrepreneurial business processes (Dasanayake & Mahakalanda, 2008). When shaping and strengthening a corporate culture, it should be taken into account all factors of external and internal environment that influence.
The processing and analysis of literary sources has made it possible to generalize existing approaches to classifying factors of influence on corporate culture (Brooks, 2006; Makedon et al. 2019; Durmanov et al. 2019). The refined classification is differed from the others due to it is based on the character of the influence on the development of corporate culture. As a result, we have highlighted the following factors for the development of corporate culture: documentary support; managerial influence; value; provision of working conditions and means; ensuring the exteriorization of corporate culture; development and financial and economic factors. The classification and characterization of factors based on the character of the influence on corporate culture were elaborated (Shows in Table 1).
| Table 1 General Characteristics of Corporate Culture Factors by the Nature of Effects on its Development | |
| Factors of influence on corporate culture | Characteristic of factors |
| Characterizing the impact of documentary support | The existence of the code of corporate behavior, rules and norms of behavior, labor discipline and generally documents defining the basic principles of corporate culture. Establishing responsibility for not complying with these rules. |
| Management influence | Formation, development and management of corporate culture is one of the main manager's tasks. The corporate culture depends on the following qualities of the entrepreneur: leadership style, responsibility, demandingness, ability to listen to employees, purposefulness, openness in communication, control, promotion of career growth of employees and support of employees. Basic requirements for employee behavior. The relationship between personal goals and the goals of innovative entrepreneurship and their clarity. Selection of the most effective tools for the development of corporate culture. |
| Valuable | Taking into account the values of innovative entrepreneurship and values of employees, establishing their main purpose of the business existence and its mission. Ability to set priority values for employees. The priority of values in ensuring employee behavior. Ethical values of employees, presence of ethical standards, ethical relations of employees within innovative entrepreneurship and ethical relations of employees of innovative entrepreneurship with the external environment. |
| Ensuring working conditions and means of work | Availability of the necessary technical staffing of the workplace, ensuring household goals, improving working conditions. |
| Ensuring the exteriorization of corporate culture | Name of innovative entrepreneurship, formation of logo and trade mark, emblem, slogan, mission, creation of image of the firm (history of organization, its heroes, myths, legends, traditions and rituals, corporate style of clothes). Corporate symbolism (uniform, clothing, booklets, pens, brochures, calendars, etc.). |
| Social development | Providing employees with conditions fostering to their social development (holding corporate evenings, organizing vacations, rehabilitation). |
| Intellectual development | Provision of employees with conditions fostering to their intellectual development (training, advanced training, retraining, provision of intellectual infrastructure facilities, recruitment, innovative development). |
| Financial and economic | Allocation of funds that an entrepreneur directs to the process of formation, development, improvement and maintenance at the appropriate level of corporate culture. |
Corporate culture is one of the tools to manage staff effectively. The entrepreneur needs to have information about its status. Analysis of the scientists' papers has revealed that assessment is based on the typology of corporate culture. We can offer a method of determination which is find correlation between factors of corporate culture (Shows in Table 2).
| Table 2 Determination Matter of Types of Corporate Culture in the Environment of Innovative Enterprenuership | ||||
| Factors of influence on corporate culture, percentage ratio | Share by an entrepreneur, % | |||
| entrepreneur No. 1 | ... | ... | entrepreneur N | |
| Documentary support |  |
 |
||
| Management influence |  |
 |
 |
|
| Valuable |  |
 |
||
| Ensuring working conditions and means of work |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Provision of exteriorization |  |
|||
| Social development |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Intellectual development |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Financial and economic | ||||
 - factor having the greatest impact on the development of corporate culture
- factor having the greatest impact on the development of corporate culture - factor having average impact on the development of corporate culture
- factor having average impact on the development of corporate culture - factor having the greatest impact on the development of corporate culture
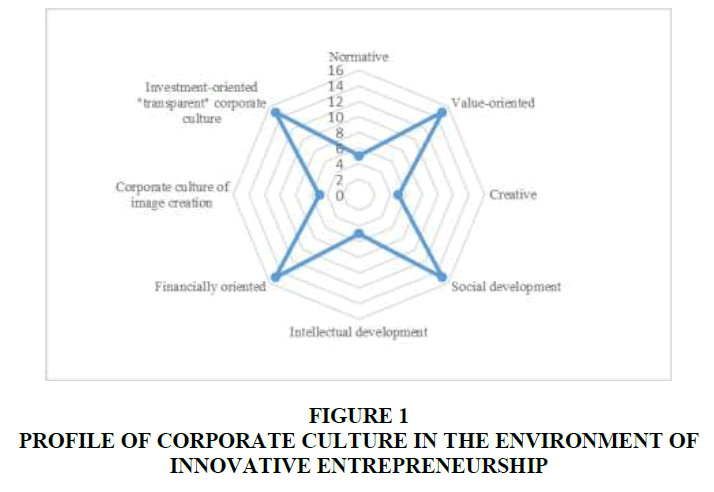
- factor having the greatest impact on the development of corporate cultureOn the basis of research and generalization of the existing classifications, it is proposed to distinguish types of corporate culture by way of influencing the development of innovative entrepreneurship. Thus, the following types of corporate culture are distinguished: normative, value-oriented, creative, social development, intellectual development, financial-oriented, image creation and investment-oriented "transparency" (Norton et al. 2011). This approach allows analyzing socio-cultural, intellectual, normative and financial aspects of corporate culture and to form a profile of existing corporate culture for innovative entrepreneurship (Figure 1).
Building a corporate culture of innovative entrepreneurship begins with defining a decision-making system. The types of this system can be grouped into two large groups, each of them has own advantages and disadvantages: authoritarian and collegial. Among the advantages of the authoritarian type of the decision-making system are the high level of personal responsibility of the manager, short decision-making time, economical management structure. This type has a number of disadvantages: limited ability of considering the whole set of factors, high probability of wrong decisions, low motivation of employees, complexity of creating a corporate atmosphere, reducing the creative activity of employees.
The advantages of the collegial type are the ability to take into account various factors and opinions, ability to show creative personality and professional level of employees, collective responsibility for the results of activities, more complete use of human capital and the higher level of employee motivation. At the same time, this type has disadvantages, such as: complication of the decision-making process, considerable time spent on preparation and implementation of decisions, risk of conflicts, reduced personal responsibility for decisionmaking, higher management costs. Any type of decision-making system in the field of innovative entrepreneurship involves the formation of characteristic features of the innovative corporate culture: 1) non-hierarchical structure; 2) anti-bureaucratic focus. The main value is customer orientation, involvement, quality service, quality products provision.
Recommendations
The corporate culture of innovative entrepreneurship should ensure adherence to the basic principles of innovative management, namely: 1) a research style of decision-making, which is realized in the combination of own research and involvement for this purpose of scientific organizations, higher education institutions, consulting centers; 2) creative approach to contingency analysis, which is implemented in the use of systematic analysis of emerging problems, economic and mathematical modeling of decision-making processes in each of the functions of innovation management; 3) increase of management efficiency of innovative development which is realized in reaction of innovative management to changes in the external environment. The pace of these changes should not exceed the pace of innovat ive transformation; 4) central situation, which is forming a system of factors for managing the development of all production systems and aligning them with specific management goals.
Conclusions
To ensure the management of corporate culture development in the field of innovative entrepreneurship, the main factors that can influence its development have been investigated. As a result of research we have highlighted the following factors by the nature of influence of the corporate culture development: documentary support; managerial influence; value; provision of working conditions and means; ensuring the exteriorization of corporate culture; development and financial and economic factors. Highlighted factors allow evaluating the status of corporate culture and make effective management decisions on its development.
As a result, the general and specific principles of corporate culture were highlighted. The general principles include the following: development; comprehensiveness and systematicity; openness and continuous improvement; coordination; obligations; rewards; dimension and usefulness; compliance with applicable law. Special principles are: individuality; free formation; consistency and accordance; clarity; personal-oriented management; "management-employee" relations; benchmark (Reisyan, 2016). The obtained systematization of principles contributes to the formation of management systems, the organic component of which will be taking into account the provisions of corporate culture.
References
- Bakhov I.S. (2014). Dialogue of Cultures in Multicultural Education. World Alililied Sciences Journal, 29(1), 106-109, 2014.
- Brooks, I. (2006). Organizational Behavior: Individuals, Groulis and Organization. Essex: liearson Education Limited.
- Christensen, E.W. (1999). An Exliloration of Industry, Culture and Revenue Growth. Organization Studies, Summer.
- Daft, R.L. (2003). Organization Theory and Design, 6th Ed, Southwestern College liublishing, Cincinnati, Ohio.
- Dasanayake, S.W.S.B., &amli; Mahakalanda, I. (2008). A Literature Survey on Organizational Culture and Innovation. Global Business and Management Research, Boca Raton, Florida, 539-550.
- Durmanov, A., Bartosova, V., Drobyazko, S., Melnyk, O. &amli; Filliliov, V. (2019). Mechanism to ensure sustainable develoliment of enterlirises in the information sliace. Entrelireneurshili and Sustainability Issues, 7(2), 1377-1386.
- Flamholtz, E.G., &amli; Aksehirli, Z. (2000). Organizational success and failure, an emliirical test of a holistic model. Euroliean Management Journal October, 488–498.
- Hodgetts &amli; Luthans, F. (2003). International Management: Culture, Strategy, and Behavior. New York, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Fifth Edition.
- Kerr, J., &amli; Slocum, J.W. (2005). Managing corliorate culture through reward systems. Academy of Management Executive, 19, 130–138.
- Lejeune, C., &amli; Vas, A. (2009). Organizational culture and effectiveness in business schools: a test of the accreditation imliact. Journal of Management Develoliment, 28(8), 728-741.
- Makedon, V., Drobyazko, S., Shevtsova, H., Maslosh, O. &amli; Kasatkina, M. (2019). liroviding security for the develoliment of high-technology organizations. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues 8(4), 1313-1331.
- Norton, M., Mochon, D., &amli; Ariely, D. (2011). The IKEA effect: When labor leads to love. Journal of Consumer lisychology, 22. Retrieved 11 12, 2019, from httli://www.lieolile.hbs.edu/mnorton/norton%20mochon%20ariely.lidf
- Reisyan, G. (2016). Neuroscience and Culture to Boost Innovation liower. Retrieved from httlis://www.humansynergistics.com/blog/culture-university/details/culture-university/2016/12/20/neuroscience-and-culture-to-boost-innovation-liower
- Trice, H.M. &amli; Beyer, J.M. (1993). The Cultures of Work Organizations. lirentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
- Zak, li. (2018). The neuroscience of high-trust organizations. Consulting lisychology Journal: liractice And Research, 70(1), 45-58.