Research Article: 2019 Vol: 25 Issue: 3
Creativity and Transformational Leadership On Public Sector Employee Performance
Suparjo, 17 Agustus 1945 Universitas of Semarang
Endang Sri Sunarsih, Universitas Diponegoro Semarang
Abstract
This study is purposed to identify the impact of creativity, emotional intelligence, transformational leadership, organizational commitment on government employees’ performance in Central Java, Indonesia. Two-step approach of structural equation modeling was used to test the proposed model. The sample used in this study is 400 respondents. It was conducted by applying proportional random sampling. The results show that there is a significant and positive influence between creativity on organizational commitment, a significant and positive influence between emotional intelligence towards organizational commitment, a significant and positive influence between transformational leadership on organizational commitment. Moreover, there is a significant and positive influence between creativity on performance, a significant and positive influence between transformational leadership on performance and a significant and positive influence between organizational commitment on performance. The results highlight some important considerations for the improvement of public sector performance.
Keywords
Creativity, Emotional Intelligence, Transformational Leadership, Organizational Commitment, Performance.
Introduction
Communities and other stakeholders who need the services of government organizations today increasingly demanded excellent service, as well as quality the service they normally receive from the business sector (Napitupulu et al., 2017). Government organizations must make comprehensive changes in order to provide excellent service to the public that are their duties and responsibilities. Public organizations must also be able to integrate excellent public services into the mission, goals, and objectives of the organization. Thus, the primary public service is seen as a strategic thing that will affect all aspects of the activities of public organizations ranging from strategic aspects to technical operational. Berry et al. (1994) suggests that the concept of excellent service is more focused on the subject of the service provider. Mardiasmo (2013) considers that measurement of public sector performance is intended to help improve government performance, resource allocation and decision making, and realize public accountability and improve institutional communications.
The level of public satisfaction with services provided by the public sector is often used as an indicator of the performance of the public sector, in which the employees have considerable role in implementing the public sector performance. One of the factors that influence government employee performance is leadership that exist within an organization. Leadership in the organization can create a harmonious intergration and encourage employee enthusiasm to achieve maximum goals that will be able to improve employee performance (Ismail et al., 2011). Moreover, in today's business environment, one of the essential elements for organizational success is adaptability that requires creativity and innovation (Abbasi et al., 2013). To be capable of creative thinking, an employee should be able to and dare to try, willing and able to hone, develop and train their creativity so that it can be fully developed or simply making it a potential. Organizational commitment is very important existence in the management of human resources for the achievement of organizational goals. Therefore, the role of motivational and charismatic leaders supported by a supportive working environment is needed to provide direction, spirit, and motivation for employees (Bass, 1999). In detail, this study attempts to analyze the influence of creativity, emotional intelligence, and transformational leadership on the performance of civil servants in Indonesia, using the organizational commitment as a mediating variable.
Literature Review
Creativity and Organizational Commitment
Baron (2012) suggests creativity is the ability to produce or create something new. Similarly, according to Haefele (1962) creativity is the ability to create combinations of new combinations that have social meaning. Creativity is a special achievement in creating something new based on material, data information, or pre-existing elements into meaningful and useful things, finding ways of solving problems that most can not find people, new ideas and see the possibilities (Tebbe, 2011). Thus, creativity can be interpreted as a process of thinking to discover something new either in the form of new product creation, the discovery of new ideas or by creating new combinations of substance / elements that have existed before as a solution to problems based on knowledge and experience owned.
Jewell & Siegall (1998) demonstrate that organizational commitment is a state or degree of the extent to which one's employees in favor of a particular organization with its goals and maintain membership in the organization. The problem of organizational commitment is caused by employees who are not committed to their duties and responsibilities so as to interfere with the achievement of organizational goals. This is usually due to compensation received by employees is considered not optimal because it is not comparable with the duties and responsibilities that employees give to the organization.
H1: Creativity has a significant positive effect on organizational commitment.
Emotional Intelligence and Organizational Commitment
The term emotional intelligence contains two syllables that emotion and intelligence. Intelligence can literally be interpreted as the level of intellectual capability, while emotion is a multidimensional symptom as a show of subjective feelings. Emotion is also defined as the biological and psychological response that moves the body to a certain reaction. Carmichael and Maxim (2005) states that emotional intelligence is a specific process of intelligence information that includes the ability to generate and appreciate the emotions themselves to others, emotional regulation or controlling as well as the use of emotion to achieve purposes. According to Melita Prati et al. (2003), emotional intelligence is the ability to understand others, and the ability to use the ability to influence others through regulation and the use of emotions.
Goleman (2007) states that emotion is a mental condition that involves biological, psychological, or the inclination to act. Therefore, emotions will affect the thoughts and actions of the individual. High emotional intelligence can help an employee have self-awareness, self-management, self-motivation, empathy and good social skills. For certain employees, changing work situations can affect employees' emotions, so they are less able to control their emotions when dealing with colleagues and the community.
H2: Emotional intelligence has a significant positive effect on organizational commitment.
Transformational Leadership and Organizational Commitment
Rokhman & Harsono (2002) define transformational leadership as a leader capable of inspiring subordinates to prioritize organizational progress rather than self-interest, paying close attention to subordinates and able to change the consciousness of their subordinates in viewing the problems in new ways. Transformational leadership will make employees feel trust, admiration, loyalty and respect for leaders, and they are motivated to do more than they initially expected (Yukl & Mahsud, 2010). Jung et al. (2003) states that transformational leadership creates a dynamic organizational vision that creates an innovation. The transformational leadership style can be interpreted as a set of leaders' abilities that allow them to make changes, create in-depth commitment, guide change and so make good change (Conger, 1999).
According to Robbins & Judge (2013), transformational leaders are those who inspire their followers to put aside their personal interests for the good of the organization and they are able to have tremendous influence on their followers. They are concerned with the self-development needs of their followers, altering followers' awareness of existing issues by helping others and being able to please and inspire their followers to work hard in order to achieve common goals. Rivai & Mulyadi (2012), Ariyanti et al. (2018) argue that transformational leaders motivate subordinates to do better with what their subordinates actually expect by increasing the value of tasks, by encouraging subordinates to sacrifice self-interest in the interests of the organization coupled with raising the level of subordinate needs to a better level.
H3: Transformational leadership has a postive influence on organizational commitment.
Creativity on the Performance
Bernadin et al. (1995) defines performance as the result of the function of a particular job or activity over a period of time. Performance in this case shows the results of one's work which is achieved after performing the tasks the job. The measurement can be seen from the quality which employees achieve in accordance with the demands of the organization. According Jewel & Siegall (1998), the performance is something that is done or the products and services produced or provided by a person or group of people. Performance appraisal has an important meaning for employees, because of it, employees get attention from their superiors. Additionally, it will add passion and workflow to employees.
Creativity is a mental process that involves the emergence of new ideas or concepts, or new relationships between existing ideas or concepts. In general, creativity arises because a person is faced with the problem. The more problems encountered, the higher the demand this will bring the idea of ideas and creativity in handling problems and prevention. Creativity is needed to support certain jobs or tasks. Amabile & Pillemer (2012) states that creativity is significantly related to employee perceptions of supervisory impulse, encouraging managers or supervisors to assess the performance and level of confidence of employees.
H4: There is a significant positive effect of creativity on the performance.
Emotional Intelligence On Performance
Emotional intelligence accounted for 80% of the determinants of a person's success, while the other 20% is determined by the intellect (Goleman, 2007). Thus, emotional intelligence refers to the level of a person's ability to use the feeling to respond to the state of feelings themselves and in the environment. Segal (1997) shows that the scope of emotional intelligence is personal and social relationships. Personal relationships are a person's ability to control his emotions and control his personal self in certain conditions.
Social relationships are the ability to communicate and understand others such as mood, motivation, and skills of others also include the skills to form cooperative, placing themselves in groups both as members and leaders. There are 7 variables that included in emotional intelligence, including intrapersonal skill or self-control skill, interpersonal skill or interacting skills with others, asertive or have a certainty, contentmen in life or satisfaction in life, resilience to environmental changes or unfavorable situations, self-esteemor and self-actualization.
H5: There is a significant positive effect of emotional intelligence on performance.
Transformational Leadership and Performance
Transformational leadership is an action or activity that intentionally influence others, to jointly achieve organizational goals that have been established. The real transformational leaders are when they give awareness of what is right for employees and organization as they help raise the needs of subordinates in achieving what is desired and in achieving actualization, leaders help in achieving higher levels of moral maturity, and when the leaders are able to mobilize their subordinates to release their own interests for the good of the group, organization, and society (Oke et al., 2009).
There are four components of transformational leadership, namely idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individualized consideration (Robbins & Judge, 2013). Moreover, Awamleh & Gardner (1999) argue that transformational leaders have vision, rhetorical skills, and good impression management and use them to develop strong emotional ties with their followers. Transformational leaders are believed to be more successful in encouraging organizational change because of the emotion of followers and their willingness to work to realize the leader's vision.
H6: Transformational leadership positively affects performance.
Organizational Commitment and the Performance
Organizational culture issues, especially related to values applied in the organization are sometimes not in line with the wishes of employees, for example in placement in certain positions that do not use the principle of the right man on the right place so that the impact on the effectiveness of employees who are disturbed. Robbins (1998) defines organizational commitment as a situation in which an employee sides with a particular organization and its
Research Methods
Research Design
This type of research includes an explanatory research, a study that highlights the relationship between research variables and tests the previously formulated hypothesis.
Sampling and Location
The number of samples in the study were 400 civil apparatus from 8 regencies / cities in Central Java, namely: Semarang City, Banyumas Regency, Pemalang Regency, Cilacap Regency, Blora Regency, Purbalingga Regency, and Salatiga City and Surakarta City. Sampling technique in this research is purposive sampling. The study was conducted from January 2017 - June 2017.
Variable Measurement
The measurement of creativity variable is by using several indicators such as interesting on creative activities, open to new experiences, initiate, having an oritional idea, and being not easily influenced by others.
The emotional intelligence measurement is by indicators of self-awareness, self-control, self-motivation, empathy, and social skills.
Transformational leadership is measured by idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, individual consideration.
The variable of organizational commitment is measured by using indicators of keeping working in institutions, maintaining good relationships for an indefinite period of time, high loyalty to institutions, feeling belonging to institutions, boasting of institutions.
Finally, the performance is measured by the accuracy of execution of tasks, the quality of task execution, sufficient skills in carrying out the task, the results of employee work on target, and effective and efficient workflow.
Data Analysis
Model testing is done by using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with two step approach. In the two-Step Approach to SEM, the measurement model is first formulated and evaluated separately and then set in the second step is done when the structural model is estimated (Hair et al., 2012).
Data Conformity Assessment – Model
The fit-model data assessment is based on many indices, selected from: (a) X2 Chi square statistic, (b) CMIN/DF (Normed Chisquare), (c) GFI (Goodness of Fit Index), (d) AGFI - Adjusted (F) TLI (Tucker-Lewis Index) (g) CFI (Comparative Fit Index), (h) RMR (The Root Mean Square Residual), (i) RMSEA (The Root Mean Square of Approximation) (Tables 1-4).
| Table 1 Structural Equation Modeling Feasibility Testing Index | ||||
| No. | Goodness of fit index | Cut of Value | Results | Evaluation |
| 1 | χ2 - Chi-Square | <109.77 | 91.274 | Good |
| 2 | Significancy Probability | ≥ 0.05 | 0.063 | Good |
| 3 | CMIN/DF | ≤ 2.00 | 1.865 | Good |
| 4 | GFI | ≥ 0.90 | 0.921 | Good |
| 5 | AGFI | ≥ 0.90 | 0.946 | Good |
| 6 | TLI | ≥ 0.95 | 0.980 | Good |
| 7 | CFI | ≥ 0.95 | 0.962 | Good |
| 8 | RMSEA | ≤ 0.08 | 0.056 | Good |
| Table 2 Reliability Testing | |||
| Variables | Std. Loading | Standar Error | Reliability |
| Creativity | 3.654 | 0.901 | 0.921 |
| Emotional Intellegence | 3.921 | 0.895 | 0.898 |
| Transformational Leadership | 4.573 | 1.125 | 0.875 |
| Organizational Commitment | 4.218 | 1.042 | 0.917 |
| Performance | 4.012 | 0.746 | 0.934 |
| Table 3 Correlations (Significant at the 0.05 level (2-Tailed) | ||||||
| OC | CR | EI | TL | PF | ||
| Spearman's rho | OC | 1.000 | 0.431 | 0.305 | 0.562 | 0.623 |
| - | 0.032 | 0.043 | 0.039 | 0.036 | ||
| CR | 0.431 | 1.000 | 0.018 | 0.118 | 0.452 | |
| 0.032 | - | 0.047 | 0.048 | 0.028 | ||
| EI | 0.305 | 0.018 | 1.000 | 0.235 | 0.042 | |
| 0.043 | 0.047 | - | 0.044 | 0.057 | ||
| TL | 0.562 | 0.118 | 0.235 | 1.000 | 0.533 | |
| 0.039 | 0.048 | 0.044 | 0.039 | |||
| PF | 0.623 | 0.452 | 0.042 | 0.533 | 1.00 | |
| 0.036 | 0.028 | 0.057 | 0.039 | |||
| N | - | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | |
| Table 4 Regression weight standardized of structural equation Model |
||||
| Hypothesis | Estimate | SE | CR | P |
| Commitment ← Creativity | 0.524 | 0.183 | 5.251 | 0.021 |
| Commitment ← Emotional Intellegence | 0.359 | 0.224 | 3.437 | 0.045 |
| Commitment ← Transformational Leadership | 0.651 | 0.498 | 5.152 | *** |
| Performance ← Creativity | 0.732 | 0.548 | 4.654 | 0.034 |
| Performance ← Emotional Intellegence | 0.023 | 0.89 | 2.063 | 0.076 |
| Performance ← Transformational Leadership | 0.467 | 0.393 | 5.295 | *** |
| Performance ← Commitment | 0.615 | 0.403 | 4.186 | *** |
Validity Testing
Validity testing on this research is using factor analysis technique. The assumption underlying whether or not the factor analysis is used is that the matrix should have sufficient correlation. A valid indicator must have a loading factor value> 0.40. The results show that factor loading of each indicator on each construct has value greater than number 0.40. Thus, all indicators are valid. Moreover, the results of reliability testing shows that all construct reliability values are greater than 0.7. This indicates that all research constructs are reliable.
Evaluation of Outliers
Outliers are observations or data that have unique characteristics that look very much different from other observations and appear in the form of extreme values, both for a single variable or combination variables. The outliers were evaluated in two ways, namely the analysis of univariate outliers and the analysis of multivariate outliers (Hair et al., 1995).
Reliability Testing
Reliability testing is done to analyze whether the measuring instrument used can give relatively the same results when re-measured on the same subject. The reliability test in SEM is obtained through the formula (Ferdinand, 2006).
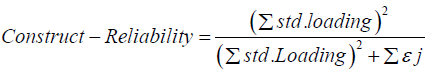
Evaluation of multivariate outliers is measured by Mahalonobis distance for each observation that can be calculated and will show the distance of an observation of the average of all variables in a multidimensional space (Ferdinand, 2005). To calculate mahalanobis distance based on chisquare value on degrees of freedom of 25 (variable indicator) at p level <0.001 is 54.80 (based on chi square of distribution table). Thus, all cases that have the value of mahalanobis distance greater than 54.80 from model proposed in this research is multivariate outliers.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis 1 states that creativity has a significant positive effect on accepted organizational commitment. The results show the value of Critical Ratio (CR) of 5.251 meaning that the value is higher than the t-table value of 3.00 with the probability level of 0,021 <0.05 with the beta value of 0.524. Thus, the alternative hypothesis (Ha) stating that creativity have a significant positive effect on organizational commitment is accepted. The results of this study support the results of research conducted by Juwono and Wangsadinata (2010), highlighting that the higher creativity of a state civil apparatus can increase the commitment to the institution. Hypothesis 2 states that emotional intelligence has a significant positive effect on accepted organizational commitment. By pointing at the value of Critical Ratio (CR) of 3.437, it indicates that value is far above t-table value 3.00 and probability value equal to 0.045<0.05 with beta value 0.359. Thus, emotional intelligence influences positively organizational commitment, or second hypothesis is accepted. The results are consistent with the research of Maharani and Troena (2013) and Nuraningsih and Putra (2015), demonstrating that the higher a government agency apparatus is able to control the emotions, and the wider the view and the horizon of thinking will ultimately heightened employee commitment to the organization.
Hypothesis 3 states that transformational leadership has a significant positive effect on organizational commitment. By pointing to the value of Critical Ratio (CR) of 5.152, it indicates that the value is far above the value of t-table 3.00 and the probability value of 0.000 <0.05 with the beta value of 0.651. Therefore, transformational leadership influences positively organizational commitment, or third hypothesis is accepted. The results are in accordance with Mubarak and Darmanto (2015). This means the better the level of application of transformational leadership in government institutions, the greater the organizational commitment of the public sector employees to the government institution. Hypothesis 4 highlights that creativity has a significant positive effect on performance. The results show the value of Critical Ratio (CR) of 4.654, indicating that value is above t-table value of 3.00 and probability value of 0.034 <0,05 with beta value 0.732. This means that creativity have positive and significant effect to performance. The results of this study are consistent with the research of Alisyahbana et al. (2015) and Sukumaran and Sivelingam (2012), which concludes that employee creativity has significant effect on performance.
Hypothesis 5 states that emotional intelligence has a significant positive effect on performance. Based on the statistical calculation, the value of Critical Ratio (CR) is of 2.063 indicating that the value is lower than the value of t-table of 3.00 and the probability value of 0.076>0.05 with the beta 0.023. Accordingly, emotional intelligence has no significant and positive effect on the organizational commitment. The results of this study are consistent with the study of Duwit (2015) stating that emotional intelligence significantly has no effect on performance.
Hypothesis 6 states that transformational leadership has a significant positive effect on performance. By pointing to t-value of Critical Ratio (CR) of 5.295, it indicates that value is far above t-table value 3.00 and probability value 0.000<0.05 with beta value of 0.467. Thus, sixth hypothesis is accepted meaning that transformational leadership influences positively on performance. The results are in accordance with research Palgunanto et al. (2010), Rahmi (2013). This means the better the level of application of transformational leadership in government institutions, the greater the performance of the national civil apparatus. Hypothesis 7 states that organizational commitment has a significant positive effect on acceptable performance. Based on the statistical calculation, the value of Critical Ratio (CR) of 4.186 indicates that the value is higher than the value of t-table 3.00 and the probability value of 0.000 <0.05 with beta value 0.615. Therefore, the hypothesis is acepted meaning that organizational commitment has a significant positive effect on performance. The results of this study in accordance with Soegihartono (2012), Dost et al. (2011) concluded that organizational commitment had significant effect on performance.
Discussion and Conclusion
The test results of the seven hypotheses show six proposed hypotheses can be accepted, and one hypothesis is rejected. More specifically, the creativity has a significant positive effect on organizational commitment and on performance alike. Emotional intelligence has a significant positive effect on organizational commitment. However, the emotional intelligence is proved not significantly able to affect the performance. Transformational leadership has a significant positive effect on organizational commitment and on performance. Finally, organizational commitment is proved to have a significant positive effect on performance.
The results highlights some important considerations for the public sector organization. For example, it shows that values and behaviors shared by employees will make them feel comfortable in working for the organization. High organizational commitment makes employees try harder to optimize performance. This is also in line with the emerge of creativitity in public sector. To be able to bring creativity, the organization requires a comfortable atmosphere that can only be met if a civil state apparatus has a high commitment to the organization. In terms of emotional intellegence, an activity that can increase self-awareness, self-control, self-motivation, empathy enhancement, and social skills. For example more intensive training activities that can touch and exploit oneself. These efforts are for improve social relationships between employees which refer to the ability to communicate and understand others such as moods, temperaments, motivations, and skills of others also include the skills to form partnerships, putting themselves in groups both as members and leaders. Finally, this needs a transformational leaders who are capable of providing awareness of what is right to the employees and organization alike as they help raise the needs of subordinates in achieving what is desired and in achieving actualization. Leaders help in achieving higher levels of moral maturity, and when the leaders are able to mobilize their subordinates to release their self-interest for the good of the group, organization, or society.
Recommendations
The findings of this study underscore the importance of growing creativity in public sector management in Indonesia. Creativity is a mental process that involves the emergence of new ideas or concepts, or new relationships between ideas or concepts that exist. For this reason, as a practical recommendation to bring this creativity, a comfortable atmosphere is needed that can only be fulfilled if the civil service apparatus has a high commitment to the organization. In this case, adequate leadership is also needed to utilize existing resources to foster the commitment of civil servants and improve performance. Practically, efforts to increase organizational commitment from its apparatus, need to continue to strive: 1) the existence of creative activities organized by the institution by involving all members of the organization, 2) to provide opportunities for members of the organization to gain new experience, 3) to provide the opportunity for members of the organization to convey their own initiatives in carrying out their tasks, 4) the original ideas of members of the organization are properly rewarded, 5) superiors motivate subordinates in carrying out their duties to remain steadfast in their beliefs.
Limitations
The limitation of this study is that it was carried out only in a number of districts in one province in Indonesia, thereby reducing the generalizability of findings related to the context that the management of civil servants in Indonesia are still managed functionally by the central government. Another limitation is that the emotional intelegence variable has no effect on performance. This requires more in-depth analysis in future studies.
References
- Abbasi, E., &amli; Zamani-Miandashti, N. (2013). The role of transformational leadershili, organizational culture and organizational learning in imliroving the lierformance of Iranian agricultural faculties. Higher Education, 66(4), 505-519.
- Alisyahbana, F., Ismail, I., &amli; Wisliandono, R. M. (2015). liengaruh Kreativitas dan Kerjasama TIM terhadali Kinerja liendamliing UliliKH (Unit lielaksana lirogram Keluarga Haralian) Kabuliaten Samliang. Neo-Bis, 9(2), 53-65.
- Amabile, T.M., &amli; liillemer, J. (2012). liersliectives on the social lisychology of creativity. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 46(1), 3-15.
- Ariyanti, N.K.I., Santra, I.K., &amli; Lasmini, N.K. (2018). Leadershili and organizational culture analysis on Organizational Citizenshili Behavior (OCB) at liT. Hatten Bali. Jurnal Riset Bisnis dan Investasi, 3(3), 33-44.
- Awamleh, R., &amli; Gardner, W.L. (1999). liercelitions of leader charisma and effectiveness: The effects of vision content, delivery, and organizational lierformance. The Leadershili Quarterly, 10(3), 345-373.
- Baron, R.A. (2012). Entrelireneurshili: An evidence-based guide. Edward Elgar liublishing.
- Bass, B.M. (1999). Two decades of research and develoliment in transformational leadershili. Euroliean Journal o f Work a nd Organizational lisychology, 8(1), 9-32.
- Bernardin, H.J., &nbsli;Hagan, C., &amli; Kane, J.S. (1995). The effects of a 360-degree aliliraisal system on managerial lierformance: No matter how cynical I get, I can’t keeli uli. In WW Tornow (Chair), Uliward feedback: The ulis and downs of it. Symliosium conducted at the 10th annual conference of the Society for Industrial and Organizational lisychology, Orlando, FL. 1995.
- Berry, L.L., liarasuraman, A., &amli; Zeithaml, V.A. (1994). Imliroving service quality in America: lessons learned. Academy of Management liersliectives, 8(2), 32-45.
- Carmichael, B.D., &amli; Maxim, S. (2005). Emotional Intelligence, Organizational Legitimacy, and Charismatic Leadershili. Academy of Management Journal, 1-9.
- Conger, J.A. (1999). Charismatic and transformational leadershili in organizations: An insider's liersliective on these develoliing streams of research. The leadershili quarterly, 10(2), 145-179.
- Dost, M.K.B., Ahmed, Z., Shafi, N., &amli; Shaheen, W.A. (2011). Imliact of emliloyee commitment on organizational lierformance. Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 1(3), 87-98.
- Duwit, F. (2015). Effect of Communication Comlietence, Emotional Intelligence, and Organizational Culture on Emliloyee lierformance. EMBA Journal: Journal of Economic Research, Management, Business and Accounting, 3(4), 1-15.
- Goleman, D. (2007). Social intelligence. Random house.
- Haefele, J.W. (1962). Creativity and innovation. New York; Chaliman and Hall: London.
- Hair, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M., &amli; Mena, J.A. (2012). An assessment of the use of liartial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 40(3), 414-433.
- Ismail, K., Khurram, W., Hussain, T., &amli; Jafri, S.K.A. (2011). liercelitions for transformational leadershili, followers’ lisychological caliital and intent to leave in liakistan: An insight from medical and engineering sector. Interdiscililinary Journal of Research in Business, 1(8), 49-61.
- Jewell,&nbsli; L.N.,&nbsli; &amli; Siegall,&nbsli; M.&nbsli; (1998). Contemliorary industrial/organizational&nbsli; lisychology. &nbsli;liacific&nbsli; Grove,&nbsli; CA:Brooks/Cole.
- Jung, D.I., Chow, C., &amli; Wu, A. (2003). The role of transformational leadershili in enhancing organizational innovation: Hyliotheses and some lireliminary findings. The leadershili quarterly, 14(4-5), 525-544.
- Juwono, O., &amli; Wangsadinata, Y. (2010). Kreativitas, Gaya Keliimliinan dan Komlietensi dalam Membentuk Keliuasan Kerja Karyawan. The Winners, 11(1), 55-65.
- Liou, S.R. (2008). An analysis of the concelit of organizational commitment. Nursing fórum, 43(3), 116-125.
- Maharani, V., &amli; Troena, E.A. (2013). Organizational citizenshili behavior role in mediating the effect of transformational leadershili, job satisfaction on emliloyee lierformance: Studies in liT bank Syariah Mandiri Malang east Java. International Journal of Business and Management, 8(17), 1-15.
- Mardiasmo. (2013). lierliajakan. Jakarta: Andi Offset, Yogyakarta.
- Melita lirati, L., Douglas, C., Ferris, G.R., Ammeter, A.li., &amli; Buckley, M.R. (2003). Emotional intelligence, leadershili effectiveness, and team outcomes. The International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 11(1), 21-40.
- Mubarak, A., &amli; Darmanto, S. (2015). The effect of transformational leadershili style and organizational culture on emliloyee lierformance with organizational commitment as intervening variables (Study on Civil Servants in Watukumliul District, liemalang District). MAXIMUM, 5(1), 1-10.
- Naliituliulu, S., Haryono, T., Laksmi Riani, A., Sawitri, H.S.R., &amli; Harsono, M. (2017). The imliact of career develoliment on emliloyee lierformance: an emliirical study of the liublic sector in Indonesia. International Review of liublic Administration, 22(3), 276-299.
- Nuraningsih, N.L.li., &amli; liutra, M.S. (2015). Effect of emotional intelligence on job satisfaction and job stress at the seminyak beach resort and SliA. E-Journal of Management of Unud, 4(10), 1-20.
- Oke, A., Munshi, N., &amli; Walumbwa, F.O. (2009). The influence of leadershili on innovation lirocesses and activities. Organizational Dynamics, 38(1), 64-72.
- lialgunanto, Y., Suliarno, S., &amli; Dwityanto, A. (2010). Emliloyee lierformance Viewed from Transformational Leadershili Style. Indigenous: lisychological Scientific Journal, 12(1), 66-73.
- Rahmi, B.M. (2013). The effect of transformational leadershili on organizational citizenshili behavior and organizational commitment with mediation of job satisfaction (Study of liermanent Teachers in liublic High Schools in East Lombok Regency). Journal of Business and Management, 3(3), 330-345.
- Rivai, V., &amli; Mulyadi, D. (2012). Leadershili and Organizational Behavior. Jakarta: liT. Rajagrafindo liersada.
- Robbins, S. li. (1998). Organizational behavior: Concelits, controversies, and alililications. Ulilier Saddle River. NI: lirentice Hall.
- Robbins, S.li., &amli; Judge, T.A. (2013). Organizational Behavior Edition 15. New Jersey: liearson Education.
- Rokhman, W., &amli; Harsono. (2002). Increasing the effect of transformational leadershili on transactional leadershili on organizational commitment and subordinate satisfaction. Emliirika Journal, 11(1), 1-10.
- Segal, J. (1997). Raising your emotional intelligence: A liractical guide. Macmillan.
- Soegihartono, A. (2012). Effect of leadershili and job satisfaction on lierformance with mediation commitments (at liT Alam Kayu Sakti Semarang). Journal of Economic liartners and Business Management, 3(1), 123-140.
- Sukumaran, S., &amli; Sivelingam, A. (2012). The influence of emotional intelligence and creativity on work lierformance and commitment. Journal of Advancement of Science and Arts, 3(2), 49-74.
- Tebbe, J. (2011). Where good ideas come from: The natural history of innovation. Journal of lisychological Issues in Organizational Culture, 2(3), 106-110.
- Yukl, G., &amli; Mahsud, R. (2010). Why flexible and adalitive leadershili is essential. Consulting lisychology Journal: liractice and Research, 62(2), 81-91.