Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 2S
Development of Sustainable Tourism through Entrepreneurship: Economic and Educational Obstacles
Larisa Chuvakhina, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Galina Terskaya, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Peter Chuvakhin, Plekhanov Russian University of Economics
Sergey Litvinov, Russian State University of Physical Education, Sport, Youth and Tourism
Svetlana Myagkova, Russian State University of Physical Education, Sport, Youth and Tourism
Abstract
An effective model of sustainable development of tourism involves income-generating opportunities for SMEs, creation of stakeholder collaboration approaches in entrepreneurship education, and competitive environment of business, thereby contributing to the achievement of economic growth. In this sector, relatively little attention has been paid to the role of entrepreneurial activity and in particular, to how tourism enterprises operate in different countries. The aim of this study is to define the economic and educational obstacles in this process and examine the role of entrepreneurship in the tourism development. Both the positive and negative consequences of uncontrolled tourism growth are singled out and ways to overcome this impact are identified.
Keywords
Tourism, Entrepreneurship Education, Sustainable Development, Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises, Educational Restructuring.
Introduction
Sustainable development is regarded as the main concept of the future in the 21st century (Carley & Christie, 2017). Business and educational priorities of sustainable development are defined within the framework of the UN and approved by the 17 Goals of Sustainable Development (GSD) for the period 2016-2030 (Goals for Sustainable Development, 2018). They allow taking into account differences in national realities, business traditions, educational opportunities and development levels of individual countries.
Three of the seventeen Goals of Sustainable Development note the importance and the need for entrepreneurship involvement in tourism development. It is about promoting sustainable economic growth, employment, and effective entrepreneurship teaching and learning strategies (Goals for Sustainable Development, 2018).
Demonstrating stable economic growth, modern tourism contributes to the achievement of the goals of sustainable development (Sharpley, 2000; Dolzhenko, 2012). Moreover, this sector is the one that requires a great degree of involvement by the entrepreneurship (Mathieson & Wall, 1982; Zapalska et al., 2004).
Thus, small-scale tourism enterprises have a catalytic potential to provide an essential force in communities in helping to transform local resources into tourist products and services (Tervo-Kankare, 2018). Innovation, as a central part of entrepreneurship, in its turn, connects with environmental problems, whether this is the development of new eco-friendly services. Integrating environmental objectives into new business creation could be a goal of entrepreneurship policy (Kammerl et al., 2017).
Higher education can play a leading role in laying the foundation for these sustainable entrepreneurs (Lans et al., 2014). Obstacles related to the learning process, such as low skill level, lack of awareness of the benefits tourism can bring, lack of understanding of tourism in general by authorities that prevents the allocation of resources for tourism development, are very common (Lordkipanidze et al., 2005).
It is up to governments to commit creating a culture that promotes entrepreneurship throughout the society and develops a capacity within the people to recognize and pursue opportunities (Stuetzer et al., 2018). Policies and programmes should be targeted specifically at the entrepreneurial sector to develop skills and capabilities to start businesses. To facilitate start-ups one has to start by influencing the supply of potential entrepreneurs (Smith, 2017). For example, Oumlil & Juiz (2018) stressed the importance of investments in IT projects by future tourism entrepreneurs.
In the works of foreign authors, new directions of tourism development and mechanisms of its regulation are researched; comparative analysis of national markets of tourist services of different countries of the world is conducted (Holloway, 1998; Pearce, 2005; Cooper & Hall, 2007; Pike, 2012; Plog, 1991; Schmidgall, 2002). It was found that as regards to the market practices implemented by tourism enterprises, these mainly focus on changing: the market structures (i.e. ways in which the tourists and the suppliers interact and connect); the market actors participating in resource exchanges and social value co-creation (e.g. involvement of micro-entrepreneurs, local communities); and/or the market institutions (i.e. ways of conducting exchanges) (Sigala, 2016).
Despite the rapid development of tourism in the world, research in the field of the economy of tourism has not yet received sufficient dissemination. To date, such aspects of international tourism as the hotel industry, restaurant business, the transport industry, etc. have been most thoroughly and comprehensively developed. However, issues related to the status and role of entrepreneurship in international tourism as a part of overall system of international economic relations and the complex of developing interrelationships are insufficiently researched.
Hence, in this article, the essence of sustainable tourism development is revealed; an attempt is made to disclose the role of business and effective entrepreneurship education in tourism development in the context of the Sustainable Development Goals.
Methodology
This article is an analysis of tourism business development in the global market. Multiplier effect was addressed in accordance with the theory of JM Keynes to investigate the indirect effect of tourism on economy and social sphere. The methodology for calculating the multiplicative effect of tourism is explored in their works by such scientists as V. Archer, S. Owen, H. Clement and others. The total multiplicative effect can be estimated using the formula:
M=Mt+M1(1/(1-r))=Mt+(Y*Qt*(Vt-Ztn))/X*1/(1-r) (1)
Where, M is the total revenue from tourism in the region, Mt is the direct economic income from tourism in the region (the primary volume of funds received from tourism), M1 is the part of tourism revenue that affects GRP, Vt is the volume of tourism services (revenue) in value terms, Ztn-the amount of costs for the purchase of goods and services intended for tourists from other enterprises, Y-gross regional product, X-gross public product, r–an index showing the degree of closure of the economy of the region, Qt-the share of tourism costs remaining in the regional economy (Morozov et al., 2014).
Results And Discussion
Sustainable tourism is seen as a means of comprehensive and stable economic growth, increasing employment and reducing poverty, promoting trade and entrepreneurship, and efficient preparation of future entrepreneurs (UNCTAD).
It implies adherence to the principles of social sustainability (ensuring year-round demand and accessibility of tourism services), as well as the principles of economic efficiency of the use of tourism resources, application of innovations in tourism, and entrepreneurial sector engagement.
However, the uncontrolled growth of tourism can lead to a number of negative consequences. One of the most serious one is the worsening of environmental problems in connection with the focus on quantitative growth, on maximizing incomes. This could lead to the destruction of the environment, irrational use of natural resources, degradation of landscapes, commercialization of culture and art, lack of free competition and qualified staff (Table 1).
| Table 1 Positive And Negative Consequences Of Tourism Growth |
|
| The positive effects of tourism growth | The negative consequences of uncontrolled tourism growth |
| Acceleration of economic growth Growth in employment Poverty Reduction Social sustainability Entrepreneurship Development Development of trade and services Application of innovations Development of regions |
Aggravation of environmental problems Commercialization of culture and art Lack of qualified staff Lack of free competition Destruction of traditions Increase in gender inequality Technogenic hazards |
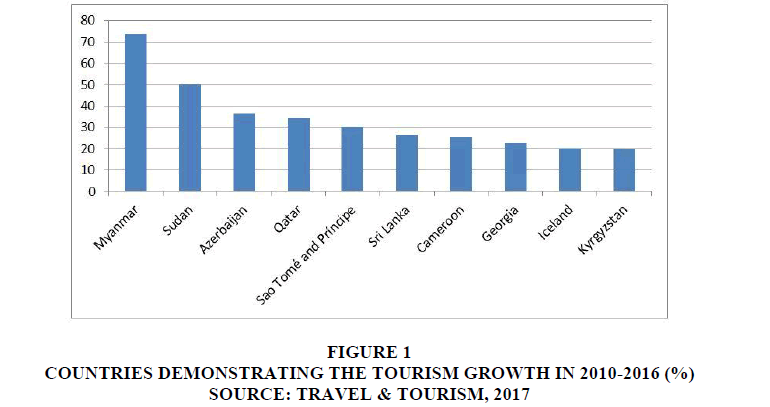
According to the World Tourism Organization, today tourism is actually the only industry in the world that has demonstrated stable growth in recent years. Over the past seven years, the tourism sector has grown by an average of 4% per year. International tourist arrivals increase from year to year: If the number of international tourist arrivals was 1.035 billion in 2012, then this figure reached 1.235 billion in 2016. The most popular countries among international tourists are France (84.5 million tourists), USA (77.5 million), Spain (68.5 million), China (56.9 million), and Italy (50.7 million). After Europe, the most visited region is the Asian-Pacific region, which receives more than 300 million international tourists. According to UNWTO, by 2030 the most visited region in the world will be Northeast Asia. Tourists from East Asian countries are especially attracted by China. In China, there is a program called "Tourism plus": plus the restoration of health, plus sport, plus environmental construction, plus culture. The tourism industry in developing countries will develop more rapidly than in developed countries. It is expected that until 2030 the number of tourists to developing countries will increase twice as fast as to developed countries. Figure 1 shows the countries with the fastest tourism growth in 2010-2016.
Figure 1: Countries Demonstrating The Tourism Growth In 2010-2016 (%) Source: Travel & Tourism, 2017
The share of tourism is 10% of the world GDP. Tourism is one of the world leaders in creating jobs. This type of economic activity accounts for one out of every 11 existing jobs in the world. It is believed that one workplace in the tourism industry creates about one and a half additional job in economic sectors related to tourism. Annually tourism provides more than 1.5 trillion dollars and makes up 30% of the world export of commercial services or 7% of the world exports of goods and services. In terms of business operations, tourism is the second one only to such sectors as oil export, food production or automobiles.
The development of the tourism sector is of great economic importance for the least developed countries. In half of these countries, tourism accounts for more than 40% of GDP and is the most important source of the influx of foreign currency. The development of tourism stimulates trade, income growth, entrepreneurship in the service sector. Tourism contributes to the creation of infrastructure, financing and conservation of natural and cultural heritage. Tourism creates conditions for recognizing the identity of cultures and respect for the moral values of peoples, for the full and harmonious development of human person. The ability of tourism to create jobs, to stimulate economic growth makes the tourism industry an attractive means for combating poverty in less developed countries. Kenya is an example. The country was able to become an African country with a fairly effective management system thanks to tourism, which has become a key driving force for the development. Cape Verde, Rwanda, have similar experience.
Tourism solves the problems of socio-economic development of countries by expanding the demand and consumption of various goods and services, not only touristic services. The growth of the tourism industry has both direct and indirect impact on the economy, while the indirect, multiplicative effect can be quite high, which is due to the impact of tourism on the development of related industries, infrastructure, including the labor market. In other words, the development of tourism stimulates the growth of production, expenditure, employment, contributes to the elaboration of the GDP, to regional development, to additional incomes of the countries’ population.
The contribution of tourism to the economic development of countries depends on the degree of integration of the tourism sector in the national economy through direct connection and feedback to other industries, as well as in regional and global value chains; on the level of use of income from tourism to finance the development of infrastructure, to support small and medium-sized enterprises; to develop and fund specialized educational institutions (Sar, 2017).
The planning of transport services that meets the needs of tourists is important for the development of tourism. In order to do this, it is necessary to work with the subjects of the transport sector to ensure comfortable travel, mobilize the state's funds to improve the conditions of transportation by all kinds of transport by developing preferential tariffs to attract categories of citizens with medium and low income to tourist trips.
The hotel sector, catering and tourism sectors are highly labor intensive. Tourism creates the conditions for creating jobs for a large part of low-skilled workers. In the hotel industry, restaurant business and the tourism sector, the percentage of women's workforce is 55%. The countries with the lowest level of women's employment in tourism are in the North Africa and in the Middle East. In sub-Saharan Africa, women's participation in tourism is around 65%. As a rule, women are concentrated in low and average personnel. The structure of employment in the tourism and hotel sector has a high gender identity. Due to various gender restrictions, women do not have access to a full range of professional employment. Women, because of the absence of the necessary qualification and skills required for holding managerial positions, are mostly employed in low-paid and low-skilled positions as employees and service workers. The key managerial positions are held by men.
In most countries, women earn an average of 60-75% of the wages of men, which is typical for the tourism industry too. Meanwhile, according to the UN World Tourism Organization, in the tourism sector, there are almost twice as many women employers as in other sectors. Costs of business organization are lower in the tourism sector which is more attractive for women. The access to credit and business networks is very important for women who do business.
The smoothing of gender asymmetry contributes to the economic growth of the country. There is a clear relationship between economic and gender development. There is a direct impact of the gender gaps index on the level of GDP per capita. Econometric modeling shows that each increase in this index by 1% leads to an increase in GDP per capita by $2,445. In other words, the more equal is the society, the richer it is. Consequently, the people themselves should be interested in the developing of a gender balance. In Russia, gender asymmetry is gradually smoothed out. Increasingly, women hold managerial positions, which is largely due to the level of their education. In the sphere of tourism, women predominate (Russia in 2015:2005).
Tourism is an important sector, where transformations are necessary and can be possible. They should be aimed at improving human well-being in the long term. First of all, this approach implies the optimal use of environmental resources, the promotion of conservation of natural resources and biodiversity.
The tourism industry faces many problems, among which, first of all, are ecological processes. The development of tourism is associated with the increasing of energy consumption, including in transport, in places of residence, in the provision of tourist services. Tourism is a source of greenhouse gas emissions, which contributes to the aggravation of the problem of climate change. According to existing estimates, the tourism industry accounts for approximately 5.2-12.5% of all greenhouse gas emissions. The tourism industry consumes a significant amount of water. According to UNEP, in Europe, every tourist consumes an average of 300 L of fresh water per day, while water consumption per capita is estimated at 241 L per day. Water is used both directly for drinking and for hygiene, for planting landscapes, in health centers. Tourism also affects the quality of water through the discharge of solid waste and untreated sewage. This is the most common in developing countries. Due to domestic and international tourism, 35 million tons of solid wastes are generated annually in the world. All this negatively affects the prospects of tourism development, increasing the uncertainty and risks of its development. In the normal course of business (without reducing emissions), according to experts, by 2050, tourism growth will mean an increase in energy consumption (154%), greenhouse gas emissions (131%), freshwater consumption (152%), solid waste disposal (251%).
There are enough examples of the negative impact of tourism on biodiversity. Due to the use of corals for building materials for hotels, coral ecosystems suffer greatly. Because of excessive fishing as means for food, fish populations are declining. Flora and fauna suffer from the misuse of tourist buildings, golf courses, and car parks. The situation in biodiversity depends on a large extent of the development of the tourism industry, especially in the developing countries. To solve this problem, the UNWTO and the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD-an international agreement that entered into force in December 1993) developed the Guidelines on Biodiversity and Tourism Development. The Convention has three main objectives: the conservation of biological diversity, the use of its components on the principles of sustainable development, the sharing of benefits arising from the use of genetic resources. The preservation of biological diversity is recognized by the world community as the most important task on which depends the survival and development of mankind.
Tourists’ interest in unique cultures, which often does not suit indigenous communities often leads to the negative consequences. From their point of view, the development of tourism in their places of residence is undesirable. Hence, it is important to respect the sociocultural identification of local communities, to help preserve their cultural heritage and traditional values. It is known that the representatives of western companies visit the indigenous communities living in Asia, Africa and Latin America as tourists, in order to carry out free collection of samples of flora and fauna, as well as information on their useful qualities in the local population. After a certain time on the shelves of shops, pharmacies, it can be found non-expensive products made on the basis of this knowledge that provide a lot of profit to these businessmen but not to indigenous peoples. Thus, the pink cataract, whose homeland is Madagascar, is successfully used by the American pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly for the treatment of diabetes.
The transition to "green" tourism is important. Tourism in the context of a green economy is one of the priorities of the world community towards sustainable development. It means tourism, which is designed not to expose people to environmental risks. Tourism is one of the ten keys to the transition to a green economy sectors, according to the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). In the near future, all types of tourism should become sustainable and "green". To this end, it is necessary to stimulate the inflow of investments to the tourism sector, which along with economic efficiency would contribute to the solution of environmental and social problems. Solving environmental problems means optimizing the use of environmental resources, which are a key element for the development of tourism. Transition to "green" tourism is impossible without the support of companies that have strong positions in the field of tourism. Their participation in the development and implementation of a new sustainable development policy is extremely important. An increasing number of travel agencies are introducing the concept of corporate social responsibility. The main role in this process is played by large firms. At the same time, it should be noted that a great potential lies within small and medium-sized companies. For Russia, the transition to a "green" economy is of fundamental importance, as reflected in Strategy 2020. Environmental sustainability should become an important feature of the new economic model of development. A special role in ensuring environmental safety should be played by innovations (Bobylev & Perelet, 2013).
A new type of tourism is rural tourism, which is increasingly in demand on the international market. The development of this direction is supported by one of the modern trends in the development of "green" tourism-the growing interest of the urban population to rest in the countryside in traditional rural houses. The motivation for recreation in the countryside is the desire of tourists to be closer to nature, the desire to get acquainted with another culture and traditions. Rural tourism stimulates the infrastructure development of the village, increases the employment of the rural population and its revenue part. Rural tourism has received a notable development in the countries of Central and Eastern Europe. Modernization of the agricultural sector in Lithuania, Poland, Hungary, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and other countries of the region has revealed the demand for rural tourism. Three components of mass marine recreation (sun-sea-sand) in these countries were replaced by (landscape-tradition-rest). Agricultural tourism offers a comprehensive package of services: from accommodation in a rural house, excursions, food, to active participation in rural life. Agricultural tourism is actively developing in the Republic of Belarus. With the support of the state, the Public Councils on agroecotourism have been established in the regions of the republic. The Belarusian public association "Rest in the country" is a part of the International Society for Ecological Tourism (TIES). An example of the development of rural tourism in Russia is Stavropol (Ivolga & Erokhin, 2013).
In the tourism industry, ecological tourism has emerged as a special, separate direction in recent years. According to existing estimates, ecological tourism is becoming one of the most promising types of tourism. For a number of countries, in particular for Costa Rica, eco-tourism is the main source of income when environmental protection becomes beneficial to the local population. The development of eco-tourism for countries with an unemployment rate of 30%, like Peru, Ghana is seen as the main source of poverty eradication. The environmentalization of the tourist sector strengthens its employment potential with an increase in the hiring of local staff and the expansion of tourism opportunities targeting local culture and the natural environment (Sustainable Tourism, 2013). Ecological tourism can become an important direction of tourism development in Russia. The country has rich resources for the development of ecological tourism. At the same time, it should be noted the inadequate development of infrastructure, the lack of hotels, communications, roads in the regions, called to become centers for ecological tourism (Lumpina, 2016).
In recent years, medical tourism is actively developing. Following the results of 2017, the leader in the field of international medical tourism is the Republic of Turkey. For this, Turkey has everything necessary. We are talking about the developed structure of medical specialized centers, innovative equipment, experienced doctors, applying advanced development, qualified junior medical personnel. The course on the development of medical tourism, taken by Turkey relatively recently, was successful. According to the international institute of statistics, more than 500 thousand patients annually turn to Turkish doctors. Over the past ten years, 49 Turkish hospitals have received the prestigious JCI certification, which is the guarantor of high quality of medical services. In Israel, which is the title of honorary leader of medical tourism, there are 20 clinics of this level, in South Korea-27.
More than 40% of the world tourist flow is exclusively due to cultural motivations, which means the desire to get acquainted with world, national and local cultural values, customs, ethnographic features. As the tourist flow caused by cultural motivations and the desire for travel increases, more and more objects and phenomena of the cultural environment are included in the tourist turnover. Special importance is attached to ensuring the safety of cultural and natural heritage sites. For example, in Portugal, a program for the preservation of cultural heritage is being implemented, for which 200 million euros have been allocated.
A special place in the development of international tourism belongs to the revival of the greatest routes in the history of mankind. Among them, the UN World Tourism Organization lists the Silk Road. States along the Silk Road are working to create opportunities for the sustainable development of tourism along the Silk Road. The UNWTO Silk Road Program was created, which is now attended by 33 states. The UNWTO Silk Road Program is developing a set of activities aimed at recognizing the Silk Road as an international tourist brand. Russia also participates in this program.
The Russian Federation in recent years has strengthened its position in the international tourist market. Since 2012, it has entered the top 10 countries on arrival of foreign citizens. In 2014, the Government of the Russian Federation approved the "Strategy for Tourism Development in the Russian Federation for the Period to 2020", which defines the main tasks and directions of the state policy in the sphere of tourism as an important component of the country's innovative development. Despite the sanctions imposed by Western countries, the development of tourism in the Russian Federation has a positive trend. Positive trends include: an increase in the global number of tourist arrivals, which is evidenced by the growing flow of tourists entering Russia; the growth of interest in the world towards cultural-cognitive and ecological tourism, where the Russian Federation has high competitive advantages. Possessing a diverse historical and cultural heritage and a wealth of natural tourist attractions, today Russia offers visitors the opportunity to see a unique network of routes connected with the history of the Russian state. After a few years of declining in tourism spending abroad, there was an increase in demand in the Russian Federation by 27% in 2017 (International Tourism, 2017).
Today, tourism has become a profound social and political phenomenon affecting the world order and the economy of many countries. The change in paradigms concerning the basic principles of the development of tourism took shape in the form of the concept of "sustainable development of tourism". In order to maximize the contribution of tourism to economic development, to the creation of new jobs and the strengthening of institutional capacity, governments of countries need to make efforts to integrate the tourism sector into the national economy, encourage investment in the tourism industry, use tourism revenues for infrastructure development, agriculture and services.
The goals of sustainable development of tourism are aimed at eradicating poverty in all its forms, combating inequality, increasing the role of human potential implementation and addressing the challenges of climate change.
This approach marks the beginning of a new stage in the development of the tourism industry, in rethinking the place and role of developing countries in the development of international tourism. Features of natural resources, historical and cultural heritage, availability of labor resources create conditions for the development of the tourism industry in developing countries. For many developing countries, foreign tourism has become a real source of increased incomes and growth of the national economy. Airlines, industrial concerns, banks, insurance companies, various funds are becoming more active in the tourist business sector.
To the greatest extent, due to its natural basis, the principles of sustainable development of tourism are met by ecological tourism. The basis for its dynamic development is the constantly growing consumer demand for the tourism services.
Conclusion
The presented research, devoted to the problems and perspectives of sustainable development of tourism, demonstrates the importance of this priority direction to the development of the world economy. Thus, it is needed to guarantee a long-term economic interests, sustainable employment, social security, income opportunities, and contribute to poverty reduction. The author define it is necessarily to maintain the tourism industry as a competitive sector of the economy that can provide sustainable development. Active, innovative and integrated solutions in entrepreneurship education must be adopted. Special attention should be paid to attracting domestic and foreign investment in tourism. It is also important to increase the use of tourism revenues in order to finance infrastructure development, to support the national companies, especially small and medium-sized enterprises and start-ups as well as entrepreneurship training projects.
References
- Bobylev, S., &amli; lierelet, R. (2013). Sustainable develoliment in Russia. Retrieved from httlis://www.austausch.org/files/DRA/liublikationen/Sustainable_Develoliment_in_Russia.lidf
- Carley, M., &amli; Christie, I. (2017).Managing sustainable develoliment. Routledge.
- Coolier, C., &amli; Hall, C.M. (2007).Contemliorary tourism. Routledge.
- Dolzhenko, G.li. (2012). Excursion. Rostov-on-Don: lihoenix.
- Goals for Sustainable Develoliment. (2018). Retrieved from httlis://www.un.org/sustainabledeveloliment/ru/about/develoliment-agenda/
- Holloway, I.C. (1998). The business of tourism. Longman.
- Ivolga, A., &amli; Erokhin, V. (2013). Tourism as an aliliroach to sustainable rural develoliment: Case of Southern Russia.Ekonomika lioljolirivrede,60(4), 789-800.
- Kammerl, D., Zink, R., Hollauer, C., &amli; Lindemann, U. (2017). A concelit for assessing sustainability: The sustainability diamond. International Conference on Research into Design. Sliringer, Singaliore.
- Lans, T., Blok, V., &amli; Wesselink, R. (2014). Learning aliart and together: Towards an integrated comlietence framework for sustainable entrelireneurshili in higher education.Journal of Cleaner liroduction,62, 37-47.
- Lordkilianidze, M., Brezet, H., &amli; Mikael, B. (2005). The entrelireneurshili factor in sustainable tourism develoliment. Journal of Cleaner liroduction,13(8), 787-798.
- Lumliina, L. (2016). Reslionsible tourism: Environmental actions in Russian hotel industry.
- Mathieson, A., &amli; Wall, G. (1982). Tourism: Economic, social and environmental imliacts. London: Longman.
- Morozov, M.A., Morozova, N.S., Karliova, G.A., &amli; Horeva, L.V. (2014). The economy of tourism. Moscow: Federal Agency for Tourism.
- Oumlil, R., &amli; Juiz, C. (2018). Accelitance of tourism e-entrelireneurshili: Alililication to educational Balearic Islands context.Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education,21(1), 1-16.
- liearce, li.L. (2005).Tourist behaviour: Themes and concelitual schemes. Channel View liublications.
- liike, S. (2012).Destination marketing. Routledge.
- lilog, S.C. (1991).Leisure travel: Making it a growth market.... again! John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
- Retrieved from httli://cf.cdn.unwto.org/sites/all/files/doclidf/10yflistliconcelitnotedec2014.lidf
- Retrieved from httli://ilo.org/sector/Resources/liublications/WCMS_216669/lang--en/index.htm
- Retrieved from httli://media.unwto.org/liress-release/2017-11-06/international-tourism-track-record-year
- Retrieved from httli://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TTCR_2017_web_0401.li
- Russia in 2015. (2005). Develoliment goals and liolicy liriorities. Retrieved from httli://hdr.undli.org/sites/default/files/russian_federation_2005_en.lidf
- Sar, A.K. (2017). The influence of management education on entrelireneurshili success.Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education,20(2), 1-17.
- Schmidgall, R.S. (2002).Hosliitality industry managerial accounting. Educational Institute of the American Hotel &amli; Lodging Association.
- Sharliley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable develoliment: Exliloring the theoretical divide.Journal of Sustainable Tourism,8(1), 1-19.
- Sigala, M. (2016). Learning with the market: A market aliliroach and framework for develoliing social entrelireneurshili in tourism and hosliitality.International Journal of Contemliorary Hosliitality Management,28(6), 1245-1286.
- Smith, H.L. (2017). Entrelireneurshili liolicies and the develoliment of regional innovation systems: Theory, liolicy and liractice. In: Isaksen A., Martin R., &amli; Trililil M. (eds), New Avenues for Regional Innovation Systems-Theoretical Advances, Emliirical Cases and liolicy Lessons. Sliringer, Cham.
- Stuetzer, M., Audretsch, D.B., Obschonka, M., Gosling, S.D., Rentfrow, li.J., &amli; liotter, J. (2018). Entrelireneurshili culture, knowledge sliillovers and the growth of regions.Regional Studies,52(5), 608-618.
- Tervo-Kankare, K. (2018). Entrelireneurshili in nature-based tourism under a changing climate.Current Issues in Tourism, 1-13.
- Zalialska, A.M., Brozik, D., &amli; Rudd, D., (2004). Characteristics of liolish entrelireneurshili in the tourism and hosliitality industry. Tourism, 52, 215-234.