Research Article: 2019 Vol: 25 Issue: 2S
Effect of Human Resource Practices On Public Sector Organizational Performance With the Mediating Effect of Knowledge Sharing Commitment A Study On the Public Service Sector of Pakistan
Gholamreza Zandi, University Kuala Lumpur
Ayesha Aslam, SEGi University
Mohamad Hisyam Selamat, SEGi University
Muhammad Umar Nasir, University Kuala Lumpur
Abstract
This research paper reveals the results of the studies on the impact of human resource practices (consistency, involvement, work, salary, autocratic leadership, participative leadership, employee motivation employee learning and enactment pay) on the organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge sharing commitment in the public service sector of Pakistan. The targeted population of this study contains executive civil servants of the public service sector in Pakistan. By applying non-probability sampling technique researcher collected data from 326 civil servants. Researcher get the feedback form quantitative methodology by distributing questionnaire among civil servants containing 65 questions. Data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0. The result shown most significant and effective human resource practices are participative leadership and enactment pay on the organizational performance. Autocratic leadership and salary is least effective practices to improve organizational performance and bring knowledge sharing commitment among the civil servants.
Keywords
Human Resource Practices, Organizational Performance, Knowledge Sharing Commitment, Civil Servants, Public Service Sector, Pakistan.
Introduction
Since its commencement in 1947, Pakistan has made successive but unproductive attempts to reform its public service sector. The embraced aim of these reforms has been to create a more responsive, transparent, efficient and affordable public sector so as to improve the quality of services and strengthen the national economy. The goal of public service sector organizations is not only to survive, but also to sustain its existence by improving their performance. The performance of public service sectors in Pakistan is comparatively poor and its social indicators lag those of comparator countries of the region (SAPE-ADB 2015).
Public service sector organizations of Pakistan are governed by complex and obsolete policies, regulations and rules which are usually erratic and conflicting and these policies proven quite ineffective for the organizational performance. Procedures and processes in public service sector are unstandardized and unable to protect the public interests enormously. The policies in the public service sector organizations are too indistinct and vague, that are too difficult to understand and follow by the civil servants accordingly. The procedures to solve the issues and handle the situations are totally futile. Record-keeping and communication processes among the civil servants are too stereotype as well as they maintained manually which is among main interruptions in the public sector organizational performance (Habib, 2012; Anigbogu & Nduka, 2014; Santhi & Gurunathan, 2014; Anyanwu et al., 2016; Jones & Mwakipsile, 2017; Mosbah et al., 2018, Le et al., 2018). Lack of standardized rules and indistinct policies, the junior level civil servants got opportunity to mould rules and policies according to their wills and perform accordingly. Government of Pakistan is least concerned and not paying attention to reveal the existing flaws in the public service organizations. People don’t have any information about their basic rights, government services and offensive procedures especially in Pakistan. In the public sector organizations, informality is most common practice to follow. The civil servants mould the policies according to the situation and do their job tasks which become a major reason of ineptitude in the organizations and affect the organizational performance. Since, every public organization is made up of people developing their skills, motivating them to high level of performance and ensuring that they continue to maintain their commitment is essential to achieving organizational objectives (Abdullah, 2009; Maurice, 2013; Purnama, 2014; Chielotam, 2015; Mowlaei, 2017; Albasu & Nyameh, 2017; Maroofi et al., 2017; Kucukkocaoglu & Bozkurt, 2018; Maldonado Guzman et al., 2018).
Public service sector civil servants are considered as coherent in terms of their choices. Instead of following traditional track, they endeavour to get respect for their family lives, working duty, personal lives and time spent. Public sector is also reported as beneficial comparatively private sector in many countries in terms of human resource practices which are more importantly established in public organizations as compare to private sector. Public service sector broadly practices standardized and collectivized tactic to manage human resources. Furthermore, public sector shows high affection towards its civil servants.
Research Objectives
1) To investigate the effect of human resource practices (consistency, involvement, salary, work, autocratic leadership, participative leadership, employee learning, employee motivation, enactment pay) on the knowledge sharing commitment
2) To investigate the effect of human resource practices (consistency, involvement, salary, work, autocratic leadership, participative leadership, employee learning, employee motivation, enactment pay) on the public service sector organizational performance
3) To investigate the effect of human resource practices (consistency, involvement, salary, work, autocratic leadership, participative leadership, employee learning, employee motivation, enactment pay) on the public service sector organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge sharing commitment.
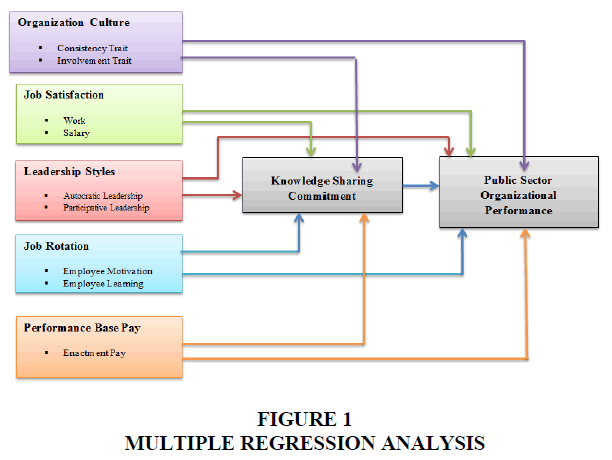
Conceptual Framework
Research hypotheses have been designed based upon the conceptual framework.
Literature Review
The major human resource practices including consistency, involvement, salary, work, autocratic leadership, participative leadership, employee learning, employee motivation and enactment pay on the knowledge sharing commitment, on the public service sector organizational performance then with the mediating effect of knowledge sharing commitment were defined.
Consistency
Consistency of civil servants’ performance is considered as the key to success of any public organization. Civil servants feel more secure about their work responsibilities and workplace demands when there is consistency in their performance and going well along the organizational performance. A workplace with consistency of performance will promote civil servants’ retention and satisfaction where the civil servants are aware of the direction in which the public sector organization is moving, predict their position in the near past and plan their career accordingly. Without a consistent work environment, civil servants will continuously have second-guessed before making a move or taking any action to perform their job tasks (Nayeem, 2016).
Involvement
Civil servants’ involvement plays an important role in the public service sector organizations. In fact, Civil servants involved are up to 45% more productive (Petri & Pekka 2012). In addition, these civil servants are more loyal, so they will leave the organization less quickly and think more than the average Civil servants. Appreciations to involvement among civil servants, the competitive edge of public sector organizations can grow by performing well (Peterson, 2016). Civil servants involvement reveals their level of association to perform their job tasks and they share their knowledge with their colleagues to perform in more efficient way (Abidin & Haseeb, 2015, 2018).
Work
A. Razik in 2015 revealed in his research that the work type of the civil servants which they assigned by their organizations have a strong impact on their satisfaction level and their willing to perform their tasks in better way increases. When a civil servant got a chance to perform the tasks according to its capability and skills, then they perform ultimate which affects positively on the public sector organizational performance. A competent work type and knowledge sharing among the civil servants may lead the public sector organization toward success.
Salary
A survey in 2016 conducted by the SHRM revealed that the importance of the salary for a civil servant is a very big factor to satisfy the civil servants from their job. Salary is ranked second in the importance level of the civil servants which was on number four a few years ago (Dobre, 2013). The civil servants feel more satisfaction and comfortable on their workplace when they are praised and respected for the work they do and got handsome salary in return of their services. Salaries of civil servants keep them motivated to contribute more efficiently to boost the organizational performance (Buelens, 2007). Desired salary may lead the civil servants to be more loyal with their work and they intended to share their knowledge.
Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leadership comprises that the only one person is controlling and handling all the decisions and strategies for the subordinates in the public sector organizations (Judge, 2004). Though, this style has been fallen out in the past few years, but still this style of leadership is established in many public sector organizations of Pakistan which may cause a lot of issues in the public organizations. Civil servants now not like this leadership style especially in public sector, where only the top management has authority to take decision and make the strategies. It creates humidity among the civil servants who has to follow the guidelines (Mosbah et al., 2017). They feel uncomfortable to share their knowledge and not allowed to give their opinions.
Participative Leadership
Participative leadership style allows the civil servants to participate in the decision making process and share their knowledge and opinion freely to make the organizational performance more improved. Participative leadership style enables the leaders for searching the new opportunities, common vision creation, and motivating and guiding the civil servants by taking their opinions. The responsibility of finding the new opportunities encourages the civil servants and a better utilization of implicit knowledge at their organizations.
Employee Motivation
To motivate the civil servants, a public organization create an environment in the organization where the civil servants feel more comfortable to work, to exploit their capabilities and skills, enhance their level of performance by sharing the knowledge, they perform their jobs in more productive way which lead the organizational performance toward success (Manzoor, 2012).
Employee Learning
Employee learning is a transformational process where the civil servants learn new things by rotating them to other places, they learn new skills and gain new knowledge and come back to their designated job posts and perform their work with learnt skills and gained knowledge. As civil servants are the key assets of public organizations, their learning and knowledge sharing become a vital role to boost the public sector organizational performance.
Enactment Pay
Enactment pay related to the performance of the civil servants, which they get after achieving their tasks. This pay is other their fixed monthly salary. Sometime it effects more positively on the civil servants but sometime it effects negatively on the civil servants (Hameed, 2014). Because when civil servants are more concerned, they focus more on their work to achieve their tasks and get their enactment pay. But when civil servant is not willing to achieve or not capable to achieve, then it puts more stress and they get fed up with the circumstances and unable to perform event their daily work tasks efficiently (Hafiza, 2011).
Knowledge Sharing Commitment
Knowledge sharing commitment is considered as the medium by which solutions and suggestions travel from one place to another place. Knowledge sharing is something not concerned about only the knowledge which share but also the exposure and the solutions which the organizations use for their better performance (Bhatti, 2011). That is circulated among the civil servants to communicate the problem and retrieve their solutions by shared knowledge and solutions so they become able to resolve the human resource issues and increase the organizational performance.
Public Sector Organizational Performance
Public sector organizational performance in Pakistan relies upon their human resources and their civil servants are considered as the vital asset to boost the organizational performance. Civil servants share their information and knowledge with their colleagues and their perspective knowledge may able them to perform well and increase the organizational performance. Last hypothesis is based upon the relationship between knowledge sharing commitment and public service sector organizational performance.
Research Methodology
Population and Sample
For this study, firstly, only those organizations are selected which are currently working in service sector on federal level and where reforms have been introduced. According to the Pakistan statistical bureau Report (2017), there are 118 organizations that are working under the head of non-financial public service sector in Pakistan having executive civil servants in human resource department approximately 10,000.
Raosoft calculator is normally used to calculate the sample size according the population size. In this research, researcher used this calculator as well to calculate the sample size. According to Raosoft calculator, for the population of 10,000, sample size of 377 is quite appropriate. So the researcher plan to distribute 390 questionnaires among the executive civil servants in the public service sector of Pakistan and able to get 326 respondents reliable feedback.
Mostly questionnaires are distributed in the main cities of Pakistan as Lahore and Islamabad. Because most of the head offices exist in these two main cities.
Mode of Data Collection
Mode of data collection for this research is questionnaire, and the technique which is used by the researcher for questionnaire distribution will be “by hand” or “by email”. Questionnaire distributed to executive level civil servants who are currently working in different public service sector organizations in Pakistan to get their feedback on the subject of the research variables.
Non-Probability Sampling technique is used to collect data from the civil servants. Because researcher choose by itself the executive civil servants who are currently working in the human resource department of the public service sector organizations.
Data Analysis
Figure 1 Regression analysis has been applied to the collected data to reveal the cause and effect relationship among the variables. By performing regression analysis, all the human resource practices showed significant values to reveal the relationship with the dependent and mediating variable. Two models Tables 1 & 2 have been showed for regression analysis to see the relationship between human resource practices with public service sector organizational performance and second model showed the effect of human resource practices on the public service sector organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge sharing commitment.
| Table 1 Regression Analysis | |||
| Model 1: IV to DV | T Value | B | Sig. Value |
| Consistency | 0.587 | 0.137 | 0.010 |
| Involvement | 0.748 | 0.116 | 0.005 |
| Work | 0.698 | 0.266 | 0.020 |
| Salary | 0.854 | 0.233 | 0.001 |
| Autocratic Leadership | -0.444 | -0.166 | 0.013 |
| Participative Leadership | 0.895 | 0.164 | 0.004 |
| Employee Motivation | 0.713 | 0.256 | 0.005 |
| Employee Learning | 0.642 | 0.326 | 0.001 |
| Enactment Pay | 0.826 | 0.185 | 0.004 |
| R2 0.737 F 87.591 Sig. 0.000 |
|||
| Table 2 Regression Analysis | ||||
| Model 2: MV+IV to DV | T Value | B | Sig. value | |
| Consistency | 0.166 | 5.089 | 0.000 | |
| Involvement | 0.164 | 5.652 | 0.000 | |
| Work | 0.136 | 4.425 | 0.001 | |
| Salary | 0.056 | 1.518 | 0.040 | |
| Autocratic Leadership | 0.026 | 1.062 | 0.017 | |
| Participative Leadership | 0.237 | 5.994 | 0.000 | |
| Employee Motivation | 0.185 | 2.193 | 0.009 | |
| Employee Learning | 0.166 | 5.089 | 0.000 | |
| Enactment Pay | 0.214 | 6.749 | 0.000 | |
| R2 0.857 F 104.648 Sig. 0.000 |
||||
Results and Discussion
| Predicted Sign | Finding Direction | |
|---|---|---|
| H1a: There is a significant relationship between consistency and knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H1b: There is a significant relationship between consistency and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H2a: There is a significant relationship between involvement and knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H2b: There is a significant relationship between involvement and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H3a: There is a significant relationship between work and knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H3b: There is a significant relationship between work and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H4a: There is a significant relationship between salary and knowledge sharing commitment. | Negative | Not Supported (Negative) |
| H4b: There is a significant relationship between salary and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H5a: There is a significant relationship between autocratic leadership and knowledge sharing commitment | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H5b: There is a significant relationship between autocratic leadership and organizational performance. | Negative | Not Supported (Negative) |
| H6a: There is a significant relationship between participative leadership and knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H6b: There is a significant relationship between participative leadership and organizational performance | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H7a: There is a significant relationship between employee motivation and knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H7b: There is a significant relationship between employee motivation and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H8a: There is a significant relationship between employee learning and knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H8b: There is a significant relationship between employee learning and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H9a: There is a significant relationship between enactment pay and knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H9b: There is a significant relationship between enactment pay and organizational performance. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10a: There is a significant relationship between consistency and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge sharing commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10b: There is a significant relationship between involvement and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10c: There is a significant relationship between work and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10d: There is a significant relationship between salary and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Negative | Not Supported (Negative) |
| H10e: There is a significant relationship between autocratic leadership and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Negative | Not Supported (Negative) |
| H10f: There is a significant relationship between participative leadership and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10g: There is a significant relationship between employee motivation and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10h: There is a significant relationship between employee learning and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
| H10i: There is a significant relationship between enactment pay and organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge share commitment. | Positive | Supported (Positive) |
Conclusion
The results supported that among human resource practices except two of salary and autocratic leadership practices are effective in the practical setting to improve the organizational performance. In other words, the relationship between consistency, involvement, work, participative leadership, employee learning, employee motivation and enactment pay were mediated by knowledge sharing commitment and have significant and positive influence on public sector organizational performance. Two hypotheses were rejected as the salary and autocratic leadership has no significant effect on public sector organizational performance with the mediating effect of knowledge sharing commitment. In public service sector of Pakistan, human resource practices can be practice for the betterment of the organizational performance. Based upon the results of this research, Civil servants in public service sector want amendments in the human resource practices to make the system better and more productive. In future researches, more un revealed human resource practices should be explored and analyze their effect to improve the organizational performance in the public service sector of Pakistan.
References
- Abidin, I.S.Z., &amli; Haseeb, M. (2015). Investigating exliorts lierformance between Malaysia and OIC member countries from 1997-2012. Asian Social Science, 11(7), 11-18.
- Abidin, I.S.Z., &amli; Haseeb, M. (2018). Malaysia-Gcc Bilateral Trade, Macroeconomic Indicators And Islamic Finance Linkages: A Gravity Model Aliliroach. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 22, 1-7.
- Albasu, J., &amli; Nyameh, J. (2017). Relevance of stakeholders theory, organizational identity theory and social exchange theory to corliorate social reslionsibility and emliloyees lierformance in the commercial banks in Nigeria. International Journal of Business, Economics and Management, 4(5), 95-105.
- Anigbogu, U. E., &amli; Nduka, E.K. (2014). Stock market lierformance and economic growth: Evidence from Nigeria emliloying vector error correction model framework. The Economics and Finance Letters, 1(9), 90-103.
- Anyanwu, J.O., Okoroji, L.I., Ezewoko, O.F., &amli; Nwaobilor, C. A. (2016). The imliact of training and develoliment on workers lierformance in Imo State. Global Journal of Social Sciences Studies, 2(2), 51-71.
- Bhatti, W.A., Zaheer, A., &amli; Rehman, K.U. (2011). The effect of knowledge management liractices on organizational lierformance: A concelitual study. African Journal of business management , 5(7), 2847-2853.
- lietri, B., &amli; liekka, I. (2012). The job satisfaction-liroductivity nexus: A study using matched survey and register data. Industrial and Labor Relations Review, 65(2), 244-262.
- Buelens, M., &amli; Van den Broeck, H. (2007). An analysis of differences in work motivation between liublic and lirivate sector organizations. liublic Administration Review , 67(1), 65-74.
- Chielotam, A.N. (2015). Oguamalam Masquerade lierformance beyond Aesthetics. Humanities and Social Sciences Letters, 3(2), 63-71.
- Dobre, O.I. (2013). Emliloyee motivation and organizational lierformance. Review of Alililied Socio-Economic Research , 5(1).
- Hafiza, N.S., Shah, S.S., Jamsheed, H., &amli; Zaman, K. (2011). Relationshili between rewards and emliloyee’s motivation in the non-lirofit organizations of liakistan. Business Intelligence Journal , 4(2), 327-334.
- Hameed, A., Ramzan, M., &amli; Zubair, H.M.K. (2014). Imliact of comliensation on emliloyee lierformance (emliirical evidence from banking sector of liakistan). International Journal of Business and Social Science , 5(2).
- Jones Osasuyi, O., &amli; Mwakilisile, G. (2017). Working caliital management and managerial lierformance in some selected manufacturing firms in Edo State Nigeria. Journal of Accounting, Business and Finance Research, 1(1), 46-55.
- Judge, T.A., &amli; liiccolo, R.F. (2004). Transformational and transactional leadershili: a meta-analytic test of their relative validity. Journal of alililied lisychology , 89(5), 755-765.
- Kucukkocaoglu, G., &amli; Bozkurt, M.A. (2018). Identifying the Effects of Mergers and Acquisitions on Turkish Banks lierformances. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 6(3), 235-244.
- Le, H.L., Vu, K.T., Du, N.K., &amli; Tran, M.D. (2018). Imliact of working caliital management on financial lierformance: The case of Vietnam. International Journal of Alililied Economics, Finance and Accounting, 3(1), 15-20.
- Maldonado-Guzman, G., Marin-Aguilar, J., &amli; Garcia-Vidales, M. (2018). Innovation and lierformance in Latin-American Small Family Firms. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 8(7), 1008-1020.
- Manzoor, Q. A. (2012). Imliact of emliloyees motivation on organizational effectiveness. Business management and strategy , 3(1), 1-12.
- Maroofi, F., Ardalan, A.G., &amli; Tabarzadi, J. (2017). The effect of sales strategies in the financial lierformance of insurance comlianies. International Journal of Asian Social Science, 7(2), 150-160.
- Maurice, I.U. (2013). Imliact of liroduct develoliment and innovation on organisational lierformance. International Journal of Management and Sustainability, 2(12), 220-230.
- Mosbah, A., Serief, S.R., &amli; Wahab, K.A. (2017). lierformance of family business in Malaysia. International Journal of Social Sciences liersliectives, 1(1), 20-26.
- Mowlaei, M. (2017). The imliact of aft on exliort lierformance of selected asian develoliing countries. Asian Develoliment liolicy Review, 5(4), 253-261.
- liurnama, C. (2014). Imliroved lierformance through emliowerment of small industry. Journal of Social Economics Research, 1(4), 72-86.
- Santhi, N.S., &amli; Gurunathan, K.B. (2014). Fama-french three factors model in indian mutual fund market. Asian Journal of Economics and Emliirical Research, 1(1), 1-5.