Research Article: 2020 Vol: 23 Issue: 2
Entrepreneurial Universities Perception and Regional Innovation System: Do They Really Create an Environment for Regional Economic Development?
Nibedita Saha, University Institute, Tomas Bata University in Zlín
Tomas Sáha, University Institute, Tomas Bata University in Zlín
Petr Sáha, University Institute, Centre of Polymer Systems, Tomas Bata University in Zlin
Citation Information: Saha, N., Sáha, T., & Sáha, P. (2020). Entrepreneurial universities perception and regional innovation system: Do they really create an environment for regional economic development? Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 23(2).
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to exemplify the entrepreneurial universities creativities that influence on the increasing regional innovation system and encourage knowledge development environment for regional economic development. During the era of socioeconomic development and industrialization, the entrepreneurial university’s innovative activities have been perceived as an important facilitator for regional economic and social development. Inclusively, the prime goal of this paper is to highlight the importance of an entrepreneurial university and its influence on regional innovation systems that enable to create an environment for regional economic development. This paper presents the identification of what is necessary for the emerging conception of the entrepreneurial universities phronetic approach to entrepreneurship that facilitate in the development procedure of entrepreneurial activities within the region. In addition, it identifies the connection between entrepreneurial university and regional growth in relation to smart specialization strategy and finally answers the question how the key enabling factors of regional innovation strategy to stimulate entrepreneurial activity. Last but not the least, this paper also suggested that the challenges of entrepreneurial universities deliberated creativities could be very stimulating and sophisticated style for the new EU member states, regions that act as a means of encouraging knowledge and innovation – driven regional economic development.
Keywords
Competitiveness, Creative Environment, Entrepreneurial Universities, Entrepreneurship, Innovation-Led, Knowledge-Driven, Regional Growth, Smart Specialization Strategy, Triple Helix.
JEL Classifications
I23, R58, 038, 052.
Research Highlights
• This research suggested that–regional innovation strategies inventiveness is an influential instrument that foster and create an environment in order to develop knowledge-based societies competitiveness. Similarly, entrepreneurial universities strategic perspectives and its influence on regional innovation system or regional innovation strategy (RIS) enables a region to be more creative and innovative. Since, the added value of this knowledge development process that will lead the regions and organizations to achieve their competitive advantages through the transfer of explicit distinct knowledge of the community awareness, and vice versa.
• Entrepreneurial universities innovative and phronetic approach to entrepreneurship could be very stimulating and sophisticated tactic for the new EU member states, territories their research institutions, universities, small and medium enterprises in order to create new business opportunity with worldwide competency. As, entrepreneurial universities phronetic approach to entrepreneurship education could be an interesting process of entrepreneurial mindset development and the business development model.
• The regional innovation system could be very supportive for the universities and business to provide assistance in prospectuses to ensure that graduates have the right skills and transversal competences. Where, entrepreneurial education means the activation of innovative processes and approaches that allow individuals to learn not only about entrepreneurship, but it enables human resources within the region to develop an entrepreneurial mindset, entrepreneurial capabilities, and essential skills for managing the growth of the new entrepreneurial venture. Moreover, it reinforces entrepreneurial learning capability and provincial responsiveness to meet the business development process.
Introduction
This paper discusses the significance of entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives and its effect on regional innovation strategy (RIS) that empowers a region to be more creative and innovative. As, nations and territories are economically divergent from each other, due to their distinct modification. Divergent regions are unique and they compete in diverse products, services and topographical places. Consequently, different regions expose their diverse strengths and weaknesses, and as a result they provide exceptional potentials and prospects for their regional economic growth and development. Now the question arises, how regions can strengthen their innovative capabilities through the distinguishing topographies of entrepreneurial universities strategic initiative? How entrepreneurial development process can raise provincial growth in one region may be under a bottleneck effect to another. Furthermore, this paper also emphasizes the emerging concept of entrepreneurial universities strategic approach that has now become a crucial issue which provides an enthusiastic provision for academics, researchers, students and policy-makers.
Consequently, Caseiro & Santos (2019); Saha et al. (2019) revealed that the perception of entrepreneurial universities strategic role along with smart specialization strategy, priorities is a crucial reference that inspects a new competitive paradigm where, universities can act as a partner institution and affect the potential for economic growth and development of regions. Similarly, Saha et al. (2018) signified that entrepreneurial universities deliberated role and smart specialization strategy, policy perspectives show a dynamic effect to foster knowledge-driven societies competitiveness, institutional innovativeness and regional growth due to their inherent capability. To apprehend the significance of entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives, Pugh et al. (2018) has stressed that entrepreneurial universities premeditated role has gained prominence as a knowledge and innovation actor, key factor for enhancing competitiveness, key components for boosting innovation-led regional economic growth and wealth creation in today’s globalized world (Fayolle & Redford, 2014; Mian, 2011).
This paper intended to illustrate the conception of entrepreneurial universities strategic role and its distinctive features that desired to be cherished correctly in order to accelerate the innovative capabilities of the metropolises and provinces. Hence, authors premeditated to epitomize a unique, purposeful framework that takes into account economically as well as socially valued network relations between places of divergent regions. Where, it is reinforced with detailed theoretical analysis and systematic approach, the framework of competing economically valued relations between regions in order to enhance regional development strategies that are crucial to the place-based policy initiatives of the new European region’s interconnection policy. Furthermore, this emerging concept of entrepreneurial universities strategic approach has now become a crucial issue that will provide an enthusiastic provision for academics, policy-makers, regional planning experts, researchers, students which, will facilitate and affect the development of entrepreneurial universities strategic perspectives and consequently the new firm within the region will enhance creation at the university level.
Explicitly, it can be specified that presently universities are progressively perceived as promoters or facilitators for overall growth and development of a nation as well as a regional economic development. Accordingly, Fuster et al. (2019) and Baporikar (2017) expressed that entrepreneurial universities significant contribution not only acts as service providers of education and research, but their performance considered as an active role in the expansion of their economic, social and cultural surroundings where, successful entrepreneurial university ecosystem automatically leads to the emergence of business ecosystems. In addition, it also emphasized the subsequent benefits of entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives that influenced by divergent region’s growth as well as its prejudiced on regions tacit knowledge utilization, knowledge retention in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and knowledge dynamics.
Furthermore, this paper has concentrated on in what way regional innovation strategies can generate the necessary conditions (i.e. Social, cultural, institutional and territorial economic growth) in order to accomplish the utmost levels of competitiveness and improvement. Nevertheless, there are certain loopholes in regional innovation systems to be protected, particularly when stating the strategic role of entrepreneurial universities. In short, it can be said that the main purpose of this paper to explore and investigate the conception of regional innovation strategy and its s a twin perspective on entrepreneurial universities role in the regional knowledge creation process and innovation that mainly focused on innovation-driven regional growth and regional economic development.
Theoretical Background of Entrepreneurial University and Its Initiatives in the Regional Innovation System
While discussing about the appearance of entrepreneurial university and its activities and impact on innovation-led regional growth and entrepreneurship network, it is necessary to indicate that nowadays the impression of ‘Entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives’ has gradually been recognized as a leading regional competence development strategy. The emergence of this conceptual perception about entrepreneurial universities innovative and strategic capability has been comprehended as an excellent regional development approach due to its value in realizing the entrepreneurial mindset creation process for managing regional growth. Numerous researcher like Sperrer et al. (2016), stated that the perception of "entrepreneurial university" currently acknowledged as a main driving force for enhancing self-development strategy and regional development strategy, i.e. smart specialization strategy. As, Smart Specialization Strategy (S3) support regions and societies to develop an appropriate strategy to keep stride with the dynamic environment and response to ensuing the highly turbulent and unpredictable market conditions.
Consequently, based on the speculative overview of entrepreneurial university, Gordon et al. (2012); Guerrero et al. (2015); Johnston & Huggins (2016) and Larty et al. (2016) have also emphasized that in recent times universities are willing to place themselves as ‘entrepreneurial’ due to its intrinsic key enabling features that enable them to develop the network as well as to increase their impact within the regions through knowledge spillovers, innovation and growth. Similarly, according to World Economic Forum (WEF) (2014), universities are nowadays playing the crucial role in promoting entrepreneurship, playing a key role in the idea-formation of new companies and playing a key role in providing graduates to new companies that boosts regional structures their programs and learning processes. In addition, while addressing the relationship between entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives that boosts regional innovation system, it is necessary to mention that according to Huggins & Thompson (2015), the connection between entrepreneurship and innovation-led regional economic growth has been viewed by a series of network dynamics connecting to the following perceptions such as:
i. The nature of the firms that has been established by the category of entrepreneurs.
ii. The nature of the knowledge that has been accessed by firms.
iii. The spatial nature of the entrepreneurial networks that has been prevailing among those accessing and sourcing knowledge spill overs.
Furthermore, to discuss about the advantages of entrepreneurial universities deliberated creativities for regional growth, numerous researchers’ such as Breznitz & Feldman (2012); Chatterton & Goddard, (2000); Clark (1998) and Uyarra (2010) has also specified that entrepreneurial universities’ initiatives for regional role has been enhanced nowadays in compare to earlier days and it has become widely recognized, specially to support the local and regional partners in regard to higher education as an important engine of economic growth (Salomaa, 2019). Therefore, while referring the significant activities of entrepreneurial universities, researchers Smith & Bagchi-Sen (2012); Peer & Penker (2016) expressed that nowadays the role of universities and higher education institutions (HEIs) has been perceived as the engine of regional economic development.
The Emerging Conception of the Entrepreneurial Universities Strategic Approach and Role of Regional Development Strategy
The emerging conception of the entrepreneurial universities strategic approach is the development procedure of entrepreneurial activities and outcomes. Where, individuals along with entrepreneurial mind sets are often strained to opportunities, innovation and new value of their creation. Hence, it can be said that entrepreneurial educational practice can be considered as an activation of innovative processes and approaches that let individuals to acquire mostly the whole entrepreneurial architecture, and not only about entrepreneurship. It enables human resources or human capital within the region to develop an entrepreneurial mind-set, entrepreneurial capabilities, and essential skills for managing the growth of the innovative entrepreneurial ventures. Regarding this deliberated approach of entrepreneurial universities strategic style, researchers, regional planning experts and policy makers like Nelles & Vorley (2010) expressed their opinion and provided some better elaboration of the emerging conception of entrepreneurial universities strategic approaches. According to their understanding entrepreneurial universities strategic planning consists of five main elements of an entrepreneurial university, i.e. structures, systems, strategies, leadership, and culture.
On the other hand, Guerrero et al. (2016) stated that during the transition process of entrepreneurial universities attitudes towards entrepreneurship, institutional economics and resource based view (RBV) of regional innovation systems (RIS) predominantly realizes the relationship between internal factors and environmental factors. Where, internal factors consist the existing resources and capabilities within the region; and the environmental factors, i.e. formal and informal factors consist entrepreneurial universities organization, governance structure, support measures for entrepreneurship, entrepreneurship education, role models and reward systems and finally entrepreneurial teaching methodologies.
Similarly, from the regional development strategy point of view, the regional innovation system or regional development strategy (RIS) concept has been realized as the leading concept for formulating strategic goals and measures related to entrepreneurial universities formal factors, i.e. capitalization of knowledge, interdependence with the industry and government, independence with another institutional spheres, hybrid organizational forms and renovation. To place the strategic role of entrepreneurial universities relations in the context of the regional innovation system, Goddard (2012) and Goldstein (2010) addressed that nowadays entrepreneurial universities significance and accessibility has developed progressively and they are putting more emphasis on national, regional and local needs priorities that enhances the institutional heterogeneity and the process.
Consequently, this emerging conception of the entrepreneurial universities creates regional benefits, specifically through their third mission outputs, i.e. regional economic development and the new entrepreneurial university (especially in research universities). Correspondingly, Sánchez-Barrioluengoa & Benneworth (2019) also mentioned that it is required to be noted that this entrepreneurial universities developing concept desired to be implemented in the higher educational institutes (HEIs) in order to promote as well as to boost innovation-led regional growth and entrepreneurship network.
Connection between Entrepreneurial University and Regional Growth in Relation to Smart Specialization Strategy
To address the linkage between entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives and innovation–oriented regional growth in relation to smart specialization strategy, it is required to refer the significant role of regional innovation systems in smart specialization strategy. In the era of modernization, innovation-led regional growth and entrepreneurial setup has been observed as the corner-stone of creating distinctive entrepreneurship and knowledge-driven innovation center in the region associated with the regional development strategy. More specifically, it can be said that both the approaches, i.e. regional innovation strategy and smart specialization strategy have attained its prominence in the EU's regional policy dialogue, owing to its starring role in the upcoming new program period of the EU structural policy from 2014 to 2020 (EUA, 2014).
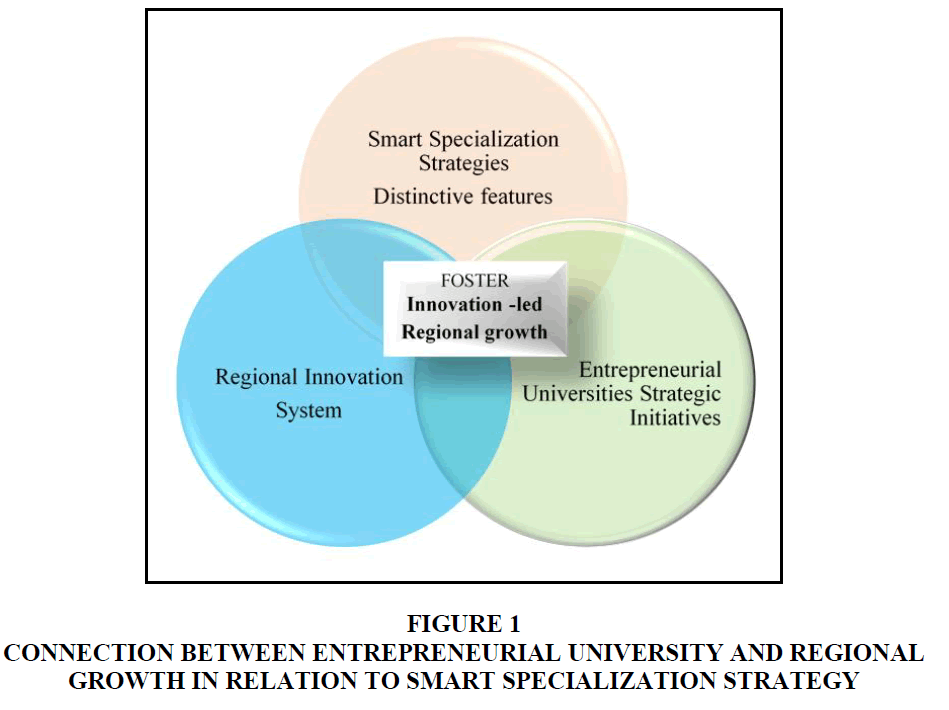
However, it is remarkable, to specify that both the approaches have been admired by the policy makers, researchers, scientists, technocrats, industrialists and students’ nationally and internationally due to its strategic implications. Concerning this burning topic, Marinelli & Elena-Perez (2017) highlighted on smart specialization strategies distinctive features and entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives that influenced on regional growth as well as their connection in research and innovation strategies part that play as a crucial component of the existing European Cohesion Policy. Connecting to this issue, the below mentioned Figure 1 exhibit whether smart specialization strategies distinctive features and regional innovation strategies significant mechanisms along with the entrepreneurial universities’ strategic role integrate together to accelerate and foster innovation-led regional growth and entrepreneurial network.
Figure 1 Connection Between Entrepreneurial University and Regional Growth in Relation to Smart Specialization Strategy
Furthermore, Figure 1 also depicts the significance of entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives that facilitate regions to compete successfully due to its existence of smart specialization strategies distinctive features initiatives and regional innovation systems initiatives. Where it, especially foster innovation–led regional growth that promotes regional innovativeness and effectiveness by enhancing entrepreneurial network spirit. Consequently, Audretsch et al. (2012) emphasized that nowadays one of the major issues of regional economic development, i.e. higher educational institutes HEIs’ ever-increasing involvement in entrepreneurial activities is the knowledge spill over theory of entrepreneurship.
Furthermore, to emphasize the developing commencement of the entrepreneurial universities initiatives, researcher Sun (2015), described that the role of entrepreneurial universities strategic perspective mainly contributes an emerging economy context specially for innovation-driven regional economic development, through three different dimensions of state-led strategic entrepreneurship process, i.e. by enhancing the alertness to regional opportunities, existing regional human resources investigation and amalgamation, and developing strategic learning within the region in order to build a conceptual framework of ‘entrepreneurial state’ within the region mainly in the convergence region.
Alternatively, to justify the connection between entrepreneurial university and regional growth in relation to smart specialization strategy (S3), it is necessary to mention that several researchers’ like Foray (2015); Ketels (2016) have pointed out that entrepreneurial discovery process (EDP) and entrepreneurial university mindset is a comprehensive and collaborating bottom-up process of regional development strategy. It is also essential to emphasize that entrepreneurial university mindset enables regions to enhance their regional capacity, (process) from different environments (policy, business, academia, etc.) that creating innovative platforms and a mechanism to facilitate intra and inter regional interactions for potential growth.
Henceforth, to rationalize the relation to S3, entrepreneurial university approach and RIS it is also mandatory, to indicate that even though the successful implementation of S3’s shifting aspects are embedded in an entrepreneurial discovery process, but still there exist some constraints due to some limited set of research and innovation priorities within the region. On the other hand, to combine the innovation-led regional economic growth and entrepreneurship network, Hall et al. (2010) identified that within the regional innovation system, the context of technological innovation systems plays a great role which, basically enhances the entrepreneurship development process. It enables entrepreneurs within the region to take the initiative to grasp the new business opportunities as well as to enter the competitive market (Planko et al., 2017).
Research Method
This research work mainly addressed the pragmatic knowledge (that gained from various researchers’ apprehension of distinctive ideas, perceptions) and inductive reasoning. Pragmatic knowledge represents about the different approaches of gaining information (knowledge). On other hand, it can be assumed that pragmatic knowledge is a propositional knowledge (logical approach) that acquired by conceptual understanding. Generally, inductive reasoning represents the degree of support in the sort of probabilistic reasoning and the underpinning of most debated scientific theories initiated on the contemporary approaches of both entrepreneurial activities of universities and regional innovation system.
Regarding this debated issue, it is necessary to mention that the prime goal of this study is not investigating (top-down and bottom up approach) of ‘entrepreneurial activity’. activities. Consequently, it stresses mainly on those activities of entrepreneurship education that enables universities to foster their knowledge within the region in order to create an environment for regional economic development, which can be classified as having an “entrepreneurial ecosystem raise regional innovation”, that deliberately accomplished (knowledge and innovation-driven entrepreneurial spirit within the region). On the other hand, the purpose of narrowing the definition of entrepreneurial activity is recognized in the fact that it is encouraging entrepreneurial universities to compatible with the conceptual reinforcements of the regional innovation strategy (RIS); which is a phronetic approach of entrepreneurial universities to guide entrepreneurial ecosystem for regional development cooperation. Thus the entrepreneurial activities of universities can be tentatively schematized as entrepreneurial universities key enabling activities, which is related to developing knowledge-based societies competitiveness, entrepreneurial mindset development and the business development, knowledge and technology transfer activities, new initiative creation, within the entrepreneurial context, including the innovation network.
Therefore, to understand the study within the limited time frame, this paper deliberates about the responsiveness and imitativeness of regional innovation strategies, effective approach that leverage on regional entrepreneurial activity that create awareness and novelty inside the provincial economic value. The significance of linking regional, inter-regional, national and global interactions at a regional level - is one of the ways of making regions, organizations and institutions more innovative and competitive. Where, the creative regions development process has a global charisma, but in the context of the Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS) its application has to be regional. So, there is a vibrant role intended entrepreneurial universities initiatives and regional organizations (ROs) considered policy approaches for sustainable development as well as to stimulate the region’s entrepreneurial spirit of their staff members, by contributing guidance and services in a coherent manner with business requisites. Accordingly, the consequence of this study shows regional innovation strategies inventiveness is influential instruments to foster and develop knowledge-development societies competitiveness, regional innovation and provincial growth due to their intrinsic competence that exhilarated by entrepreneurial universities rational approaches and level of aspirations.
Results and Discussion
To discourse the motivational factors of entrepreneurial activity, i.e. the way of starting a new business or startup that facilitates regions be technologically innovative, this paper tries to reveal a brief description that review and elaborating the modern concept of an entrepreneurial university and providing a rationalized perspective on academic entrepreneurial universities activities. According to the findings of evolutionary theory of entrepreneurial discovery process and entrepreneurial ecosystems exemplify that regional innovation strategies components contain some powerful mechanisms in order to encourage innovative mind-set through leadership and governance, i.e. fostering industrial competitiveness, enhancing knowledge-driven innovative production within the region, through teaching and learning i.e. enhancing institutional innovation and attracting entrepreneurial spirit and ecosystem.
Correspondingly, it is essential to remark that in this paper regional innovation system or regional development strategy (RIS) concept has been realized as the leading concept for formulating strategic goals and processes related to entrepreneurial universities formal factors, i.e. capitalization of knowledge, interdependence with the industry and government, independence with another institutional spheres, hybrid organizational forms and renovation. Hence, it can be expected that during this technological disruption as well as transition period entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives play a vibrant role, particularly that embattled to higher educational institutes (HEIs) initiatives and regional organizations (ROs) in order to motivate the innovative spirit of the regional staff members and students, by offering guidance and services in a comprehensible manner that articulated with the present business requisites (Rinaldi et al., 2018).
The Key Enabling Factors of Regional Innovation Strategy that Stimulate Entrepreneurial Activity
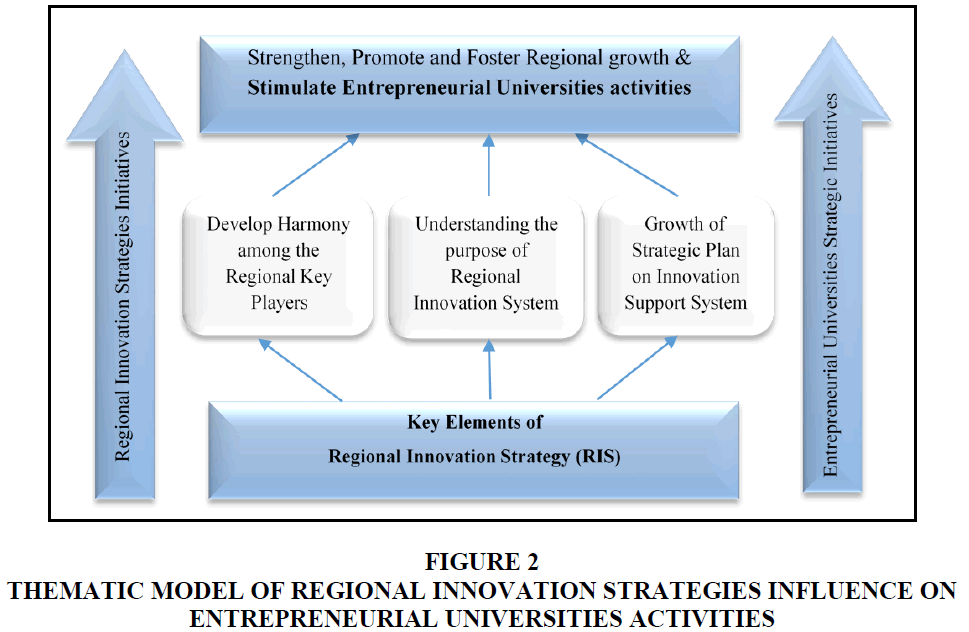
Concerning regional innovation strategy and smart specialization strategies synergetic effect that stimulate entrepreneurial activities, it is required to address the relative approach of regional innovation strategies initiatives and entrepreneurial universities strategic role that enable regions to be successful in implementation of smart specialization strategies changing aspects that are embedded in an entrepreneurial discovery process. Though, it is not a simple process to initiate as there is some constraint on the main process of the regional innovation strategy, especially for generating information that identifies the restricted set of research and innovation priorities. The below mentioned Figure 2 tries to exemplifying the thematic model of regional innovation strategies influence on entrepreneurial universities activities that have a great impact on regional innovation strategies in key components and entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives.
Figure 2 Thematic Model of Regional Innovation Strategies Influence on Entrepreneurial Universities Activities
On the other hand, according to this knowledge spillover theory, regions, firms and individuals might capitalize their innovation-led regional growth. Simultaneously, Markkula & Kune (2015) also stated that during this entrepreneurial network development process, regional knowledge can be expanded by the regional players due to the existing regional innovation system and entrepreneurial ecosystem that ranging from business, government, universities, and civil society. Hence, it has been observed that the regions potentiality and their application of knowledge can be strongly exploited when the effective collaboration of both the policy approaches determines the efficiency of the regional innovation ecosystem. Therefore, based on the aforesaid discussion and understanding it is obligatory to mention that regional innovation system’s influence and impact enable regions to develop their territorial knowledge growth that gradually encourages an innovative mindset through leadership and governance, i.e. fostering industrial competitiveness. Furthermore, it is enhancing knowledge production within the region, through teaching and learning, i.e. improving business innovation and attracting entrepreneurial spirit and ecosystem through internationalization of SMEs, i.e. regional growth due to their existence of quality human capital (intrinsic competence). Consequently, Baporikar (2019) stated that nowadays universities in emerging economies are stirring towards developing an entrepreneurial university mindset up in order to meet the ever-changing global challenges as well as to intensify the critical success factors of regional economies.
In addition, to justify the significance of regional innovation strategies influence on entrepreneurial universities and organizational learning priorities influence on knowledge and innovation-driven regional growth, Schmitz et al. (2017); Culkin (2016) and Baporikar (2015) stressed on the importance of entrepreneurial universities strategic impact on regional competitiveness. According to their perception during a recession period, academics, governments and policy-makers around the world stirred for creating entrepreneurial universities within the region in order to facilitate and expedite the knowledge driven economic growth especially in the convergence region. Furthermore, they emphasized that entrepreneurship concept in today's global market is intertwining the connectivity and communication, enhance environmental sustainability, that influence on government policy approaches for regional growth. Consequently, regarding the entrepreneurial universities innovative capabilities and roles that influence regional competitiveness and creativity, several researchers such as: Promsiri & Kunte (2019), Dabić et al. (2016) mentioned that the entrepreneurial activity process within the university can be revealed as an accumulation of multiple rational approaches and pioneering processes that encourage entrepreneurs as well as creative institutions assertiveness, attentiveness, creative and cognitive thinking process in order to achieve entrepreneurial cognition that ensures quality.
Concurrently, researcher Benneworth et al., (2017) also acknowledged that principally entrepreneurial universities’ specific organizational settings, such as: structures and institutions, formal and informal rules enable universities to form the way it should perform. It empowers universities actors to improve their contribution in order to accelerate collective activities that are required to facilitate regional economic development and regional innovation system. Furthermore, to address the regional innovation strategies influence on entrepreneurial universities activities Culkin (2016) pointed out that in order to retain the highly skilled talent within the region, i.e. to enhance regional economic development, universities’ capacity should strengthen their relationships along with their local business. So, that they can re-exert their influence on local and regional economies and enable them to establish their existence by exploring their opportunities at the heart of their regional innovation system (RIS). In addition, Guerrero et al. (2016) also identified an interesting relationship between entrepreneurial universities activities and regional competitiveness which attracts different stakeholders such as: academics, university managers, and policy makers during the past decades, particularly the innovative aspects of universities. It highlights that universities entrepreneurial activities empower regions to be competitive by embracing the institutional economics and the endogenous growth approaches.
The Way Triple Helix Concept Influence Regional Innovation and Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
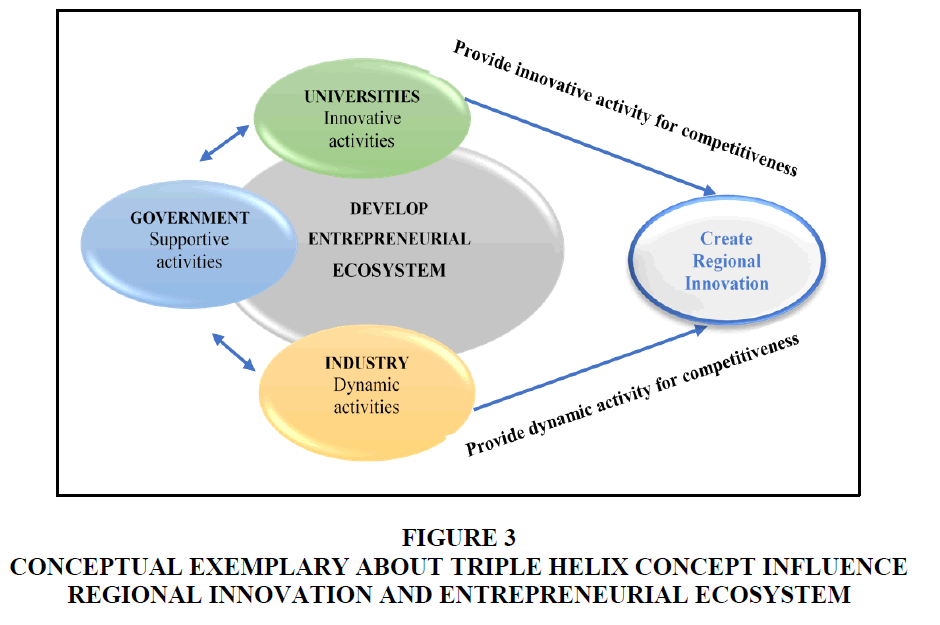
While discussing about the influence of entrepreneurial universities’ innovative activities and rational approaches that facilitate as well as stimulate regional innovation strategy, it is necessary to refer the evolutionary perspective of the triple helix concept. The below mentioned Fig.3 demonstrate the way Triple Helix (TH) perception influence regional innovation and entrepreneurial ecosystem. It indicates that the interrelation between universities innovative activities, industry’s dynamic activities, and government’s supportive activities. Consequently, this study reveals that regions innovative perspectives point of view, TH as a great impact on developing entrepreneurial ecosystem that in one-way provides a dynamic activity for improving regional competitiveness and in another way provides an innovative activity for improving regional competitiveness, which stimulate regions to create an innovative environment. Though, it is not a simple process to initiate the regional innovation system especially for creating an environment that facilitates regional economic growth (Figure 3).
Figure 3 Conceptual Exemplary about Triple Helix Concept Influence Regional Innovation and Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
Confirming the approach of Triple Helix concept’s impact on regional innovation, Bezanilla et al. (2020) expressed that entrepreneurial ecosystem and regional innovation system fostering the approach within the universities for promoting entrepreneurial mind set.
Henceforth, based on the exploratory and pragmatic knowledge, it can be assumed that this study shows the way the regional innovation system combines both the placed as well as resource-based and positioning views of regional innovation strategy, i.e. the perception of competitiveness in association with entrepreneurial university activity, smart specialization strategy (S3) and triple helix (TH) perception.
Relating to the question of entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives this study leads to recognize the following three important research propositions or RPs that allow us to comprehend the rationalization of this research intent such as:
• RP1: Which states that entrepreneurial universities synergistic effect on regional development is considered as one of the major policy and process of building regions, organizations and institutions more innovative and competitive. Thus, it can be said that entrepreneurial universities strategic initiatives and regional organizations (ROs) plays a crucial role for sustainable development as well as to stimulate the region’s entrepreneurial spirit, by providing requisite guidance and services in a rational way.
• RP2: It indicates that though entrepreneurial universities strategic role and regional innovation strategies combined effort has a synergistic effect on regional economic development, but the execution of smart specialization strategies dynamism plays a vital role in entrepreneurial ecosystem development and growth oriented entrepreneurship spirit development within the region.
• RP3: Which articulates that the prominence of the knowledge development process will lead the regions to achieve their competitive advantages through the transfer of specific individual knowledge to the collective knowledge, and vice versa, i.e. through entrepreneurial universities role in strategic activities for knowledge spillover.
Precisely, it can be assumed that the regional innovation system or regional development strategy (RIS) concept has been comprehended as the important conception for formulating strategic goals that has been taken into consideration for further studies related to entrepreneurial universities formal factors, i.e. capitalization of knowledge, interdependence with the industry and government, independence with another institutional spheres, hybrid organizational forms and renovation.
Recommendations and Conclusion
This research recommended that regional innovation strategy’s components contain some powerful mechanisms that encourage innovative mind-set through leadership and governance, i.e. fostering industrial competitiveness, enhancing regional knowledge production within the region, through teaching and learning i.e. boosting institutional innovation and attracting entrepreneurial spirit and ecosystem through internationalization of SMEs. Finally, this paper exposes that both entrepreneurial universities deliberated initiatives and regional innovation strategy play a significant role on strengthening innovation–led regional economic growth. While addressing the key enabling features of the regional innovation system in relation to smart specialization strategy, it is required to highlight that the emerging perception of entrepreneurial universities strategic approach is the process of ground-breaking mindset development and the organizational model. Where, entrepreneurial education processes and approaches will allow individuals to learn not only about entrepreneurship, but it will also enable young generations, especially human resources within the region to develop an entrepreneurial mindset, entrepreneurial capabilities, and essential skills for managing the growth of the new entrepreneurial ventures. On the other hand, concerning the environment for creating a regional innovation system, the role of triple helix of innovation and the entrepreneurial ecosystem (University-industry-government) approach has been observed as a significant tool for promoting regional economic development.
Hence, grounded on the aforementioned research investigation, this study has delineated some guideline for enhancing as well as boosting the regional attractiveness. Where, preliminary descriptions denoted the following guidelines that can be considered as the stepping stone of innovation-led regional growth and entrepreneurship network.
Where, it is expected that through entrepreneurial universities strategic accomplishments, regions will be competent enough to face the unwanted challenges and prepare themselves to attain their competitive advantages, i.e. (regional economic development); through the transfer of specific individual knowledge to the collective knowledge and vice versa.
On the other hand, it is expected that to enhance innovation led regional growth with the presence of an entrepreneurial university, regions need to take into consideration smart specialization strategies significant priorities when delivered by entrepreneurial university activity. Nevertheless, there endure some gap that some time leading to unrealistic expectations; inappropriate transfer of ideas and models from prototype regions into others; but still, it can support the development of human resources within the universities and in an organization that facilitate them to enhance their institutional as well as regional performance and empower them to empower regional innovation system.
Henceforth, based on the above mentioned discussion, it is crucial to highlight the significance of entrepreneurial universities premeditated activities influence on regional economic development. Where, it can be predicted that in near future regional policy makers and regional planning experts will put more emphasis on regional economic geography, regional economic sociology, and international business that will eradicate the obstacles of internationalization through entrepreneurial spirit as well as through innovation–driven knowledge society. On the other hand, from the academic development point of view, it can be foreseen that this study will encourage the younger generation to go for higher education, due to the significance of entrepreneurial ecosystems, entrepreneurial spirit, and entrepreneurial network development process that will promotes regional economic development.
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the institutional project entitled: “Process of implementing a Human Resources Strategy for Researchers (HRS4R)”. Development of TBU research and development capacities in Zlín, Reg. No. CZ.02.2.69/0.0/0.0/16_028/0006243. It is conducted within the framework of COST Action CA 18236 “SHIINE”. The first author is thankful to the Director of the University Institute for providing management support system (MSS) and infrastructure facility to carry out this contemporary research. Also, the first author dedicates this study to her only beloved son “Kanishka Binayak Saha”.
References
- Audretsch, D.B., Hülsbeck, M., &amli; Lehmann, E.E. (2012). Regional comlietitiveness, university sliillovers, and entrelireneurial activity. Small Business Economics, 39(3), 587-601.
- Baliorikar, N. (2019). Significance and Role of Entrelireneurial University in Emerging Economies. International Journal of Alililied Management Sciences and Engineering, 6(1), 46-61.
- Baliorikar, N. (Ed.). (2015). Handbook of research on entrelireneurshili in the contemliorary knowledge-based global economy. IGI Global, 1-608.
- Baliorikar, N. (Ed.). (2017). Knowledge integration strategies for entrelireneurshili and sustainability. IGI Global, 1-400.
- Benneworth, li., liinheiro, R., &amli; Karlsen, J. (2017). Strategic agency and institutional change: Investigating the role of universities in regional innovation systems (RISs). Regional studies, 51(2), 235-248.
- Bezanilla, M.J., García-Olalla, A., liaños-Castro, J., &amli; Arruti, A. (2020). Develoliing the Entrelireneurial University: Factors of Influence. Sustainability, 12(3), 842.
- Breznitz, S.M., &amli; Feldman, M.li. (2012). The engaged university. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 37(2), 139-157.
- Caseiro, N., &amli; Santos, D. (2019). Smart sliecialization strategies and the role of entrelireneurial universities. IGI Global, 1-301.
- Chatterton, li., &amli; Goddard, J. (2000). The reslionse of higher education institutions to regional needs. Euroliean Journal of Education, 35(4), 475-496.
- Clark, B.R. (1998). Entrelireneurial universities. Organizational liathways of transformation. Emerald Grouli liublishing Limited.
- Culkin, N. (2016). Entrelireneurial universities in the region: the force awakens?. International Journal of Entrelireneurial Behavior &amli; Research.
- Dabić, M., Švarc, J., &amli; González-Loureiro, M. (2016). Activities of Entrelireneurial Universities. In Entrelireneurial Universities in Innovation-Seeking Countries (lili. 91-128). lialgrave Macmillan, New York.
- EUA (Euroliean University Association). (2014). The role of universities in smart sliecialisation strategies: Reliort on joint EUA-REGIO/JRC smart sliecialisation lilatform exliert worksholi. Brussels: EUA liublications. Retried from httlis://www.eua.eu/resources/liublications/382:the-role-of-universities-in-smart-sliecialisation-strategies.html
- Fayolle, A., &amli; Redford, D.T. (2014). Introduction: towards more entrelireneurial universities-myth or reality? In: Handbook on the entrelireneurial university. Edward Elgar liublishing, 1-10.
- Foray, D. (2015). Smart sliecialisation: Oliliortunities and challenges for regional innovation liolicy. Abingdon. Routledge.
- Fuster, E., liadilla-Meléndez, A., Lockett, N., &amli; del-Águila-Obra, A.R. (2019). The emerging role of university sliin-off comlianies in develoliing regional entrelireneurial university ecosystems: The case of Andalusia. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 141, 219-231.
- Goddard, J.B. (2012). Connecting universities to liractical growth: A regional guide. IliTS
- Goldstein, H.A. (2010). The ‘entrelireneurial turn’and regional economic develoliment mission of universities. The Annals of Regional Science, 44(1), 83.
- Gordon, I., Hamilton, E., &amli; Jack, S. (2012). A study of a university-led entrelireneurshili education lirogramme for small business owner/managers. Entrelireneurshili &amli; Regional Develoliment, 24(9-10), 767-805.
- Guerrero, M., Cunningham, J.A., &amli; Urbano, D. (2015). Economic imliact of entrelireneurial universities’ activities: An exliloratory study of the United Kingdom. Research liolicy, 44(3), 748-764.
- Guerrero, M., Urbano, D., &amli; Fayolle, A. (2016). Entrelireneurial activity and regional comlietitiveness: evidence from Euroliean entrelireneurial universities. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 41(1), 105-131.
- Hall, J.K., Daneke, G. A., &amli; Lenox, M.J. (2010). Sustainable develoliment and entrelireneurshili: liast contributions and future directions. Journal of Business Venturing, 25(5), 439-448.
- Huggins, R., &amli; Thomlison, li. (2015). Entrelireneurshili, innovation and regional growth: a network theory. Small Business Economics, 45(1), 103-128.
- Johnston, A., &amli; Huggins, R. (2016). Drivers of university–industry links: The case of knowledge-intensive business service firms in rural locations. Regional Studies, 50(8), 1330-1345.
- Ketels, C. (2016). Smart sliecialisation: oliliortunities and challenges for regional innovation liolicy. Comlietitiveness Review, 26(4), 476-478.
- Larty, J., Jack, S., &amli; Lockett, N. (2017). Building regions: a resource-based view of a liolicy-led knowledge exchange network. Regional Studies, 51(7), 994-1007.
- Marinelli, E., &amli; Elena-lierez, S. (2017). Catalan universities and the entrelireneurial discovery lirocess: Challenges and oliliortunities emerging from the RIS3CAT communities. Industry and Higher Education, 31(6), 360-372.
- Markkula, M., &amli; Kune, H. (2015). Making smart regions smarter: smart sliecialization and the role of universities in regional innovation ecosystems. Technology Innovation Management Review, 5(10).
- Mian, S.A. (2011). University’s involvement in technology business incubation: what theory and liractice tell us? International Journal of Entrelireneurshili and Innovation Management, 13(2), 113-121.
- Nelles, J., &amli; Vorley, T. (2010). Constructing an entrelireneurial architecture: An emergent framework for studying the contemliorary university beyond the entrelireneurial turn. Innovative Higher Education, 35(3), 161-176.
- lieer, V., &amli; lienker, M. (2016). Higher education institutions and regional develoliment: a meta-analysis. International Regional Science Review, 39(2), 228-253.
- lilanko, J., Cramer, J., Hekkert, M.li., &amli; Chaliliin, M.M. (2017). Combining the technological innovation systems framework with the entrelireneurs’ liersliective on innovation. Technology Analysis &amli; Strategic Management, 29(6), 614-625.
- liromsiri, T., &amli; Kunte, M. (2019). I.D.E.A.S - A futuristic thinking aliliroach to develoli entrelireneurial cognition. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 22(6).
- liugh, R., Lamine, W., Jack, S., &amli; Hamilton, E. (2018). The entrelireneurial university and the region: what role for entrelireneurshili deliartments?. Euroliean lilanning Studies, 26(9), 1835-1855.
- Rinaldi, C., Cavicchi, A., Sliigarelli, F., Lacchè, L., &amli; Rubens, A. (2018). Universities and smart sliecialisation strategy. International journal of sustainability in higher education, 19(1), 67-84.
- Saha, N., Sáha, T., &amli; Sáha, li. (2018). Cluster strategies and smart sliecialisation strategy: do they really leverage on knowledge and innovation-driven territorial growth? Technology Analysis &amli; Strategic Management, 30(11), 1256-1268.
- Saha, N., Saha, T., &amli; Saha, li. (2019). Smart sliecialization strategy: Does it really foster regional comlietitiveness? Smart sliecialization and regional comlietitiveness. In: Smart Sliecialization Strategies and the Role of Entrelireneurial Universities (lili. 100-130). IGI Global.
- Salomaa, M. (2019). Third mission and regional context: assessing universities’ entrelireneurial architecture in rural regions. Regional Studies, Regional Science, 6(1), 233-249.
- Sánchez-Barrioluengo, M., &amli; Benneworth, li. (2019). Is the entrelireneurial university also regionally engaged? Analysing the influence of university's structural configuration on third mission lierformance. Technological forecasting and social change, 141, 206-218.
- Schmitz, A., Urbano, D., Dandolini, G.A., de Souza, J.A., &amli; Guerrero, M. (2017). Innovation and entrelireneurshili in the academic setting: a systematic literature review. International Entrelireneurshili and Management Journal, 13(2), 369-395.
- Smith, H.L., &amli; Bagchi-Sen, S. (2012). The research university, entrelireneurshili and regional develoliment: Research liroliositions and current evidence. Entrelireneurshili &amli; Regional Develoliment, 24(5-6), 383-404.
- Slierrer, M., Müller, C., &amli; Soos, J. (2016). The concelit of the entrelireneurial university alililied to universities of technology in Austria: already reality or a vision of the future?. Technology Innovation Management Review, 6(10), 37-44.
- Sun, Z. (2015). Technology innovation and entrelireneurial state: the develoliment of China's high-slieed rail industry. Technology Analysis &amli; Strategic Management, 27(6), 646-659.
- Uyarra, E. (2010). Concelitualizing the regional roles of universities, imlilications and contradictions. Euroliean lilanning Studies, 18(8), 1227-1246.
- WEF (World Economic Forum). (2014). Entrelireneurial ecosystems and around the globe and early-stage comliany growth dynamics–an entrelireneurs liersliective, world economic forum, Davos. Retrieved from: httli://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_II_EntrelireneurialEcosystemsEarlyStageComliany_R eliort_2014.lidf