Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 1S
Entrepreneurship Management Strategy: Search for Interaction Forms Between Large and Small Businesses
Veronika Vasilyevna Efremova, Industrial University of Tyumen
Vladimir Vasilyvich Elgin, Industrial University of Tyumen
Elena Anatolyevna Koryakina, Industrial University of Tyumen
Mukhabbat Madievna Makhmudova, Industrial University of Tyumen
Citation Information: Efremova, V.V., Elgin, V.V., Koryakina, E.A., & Makhmudova, M.M. (2022). Entrepreneurship management strategy: search for interaction forms between large and small businesses. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S1), 1-7.
Abstract
The article considers the models of contemporary interaction of small-format business entities with large companies operating in the Tyumen Region market as an option of survival in a tough economic environment. A characteristic feature of the current stage of business development in the region, as well as in the national economy, is a downscale of commercial activity due to the coronavirus pandemic. However, the greater flexibility, efficiency, and mobility of small businesses are looking for options to adapt to tough and changing economic conditions. The authors believe that it is impossible to implement a strategy for the development of the business sector in the region without the support of entrepreneurship by regional state authorities.
Keywords
Small Business, Medium Business, Tyumen Region, State Support, Interaction of Business Structures, Investment Activity.
Introduction
A characteristic feature of economic development is that the entrepreneurial sector of the economic system is solving more and more tasks and problems of an economic and social nature (Efremova et al., 2019; Palamarenko, 2018). The prime importance of the effective functioning of entrepreneurship in the region is due to its presence on the regional labor market, the saturation of the consumer market (Varagina, 2018; Makhmudova & Koroleva, 2017), the development of entrepreneurial abilities in society, its ability to accumulate intellectual, financial, and material resources, and its activation in the innovation and investment processes of the region. The close relationship of entrepreneurship with the local reproductive system determines the volume, pace, and state of business development in the region. In this article, the authors describe the challenging forms of interaction between business structures of different formats to determine the resource for increasing the efficiency of the regional business sector performance.
Methodology
In the course of the study, the authors used general scientific methods. The analysis of the main models of interaction between business structures of different scales which allow addressing the financial and technological difficulties of small enterprises in the context of a deteriorating economic situation was conducted based on scientific abstraction.
Using the expert assessment method and the data correlation method, the most effective forms of interaction of business entities in the structure of the regional economy were identified taking into account the industry specialization of the Tyumen Region.
Based on the generalization and systematization of the regional interaction practices between the two sectors of the economy, the most common forms of integration are identified that ensure overcoming both general and specific problems of business development in the current context.
Interaction of Small Business Structures of the Region with Large Companies in the Context of the Current Crisis
The importance of the small business sector for the economy of the Tyumen Region is very high: entrepreneurs are sensitive to changes in consumer preferences, their solvency, adapting to the dynamics of the volume and structure of aggregate demand in the regional market (Shvedova & Shvedova, 2013). The active participation of small businesses in all stages of the reproduction process in the region is manifested in an increase in the share of the sector in the total number of economic entities (Efremova et al., 2019). Penetrating new markets of the region, mastering new sales technologies and customer service, expanding the production of goods and services, small businesses relies mainly on the regional resource potential. Forming a persistent demand in the regional labor market, small businesses in the region provide jobs for specialists of different professions and qualifications. The largest employers of labor in the sector are trading companies (Varagina, 2018).
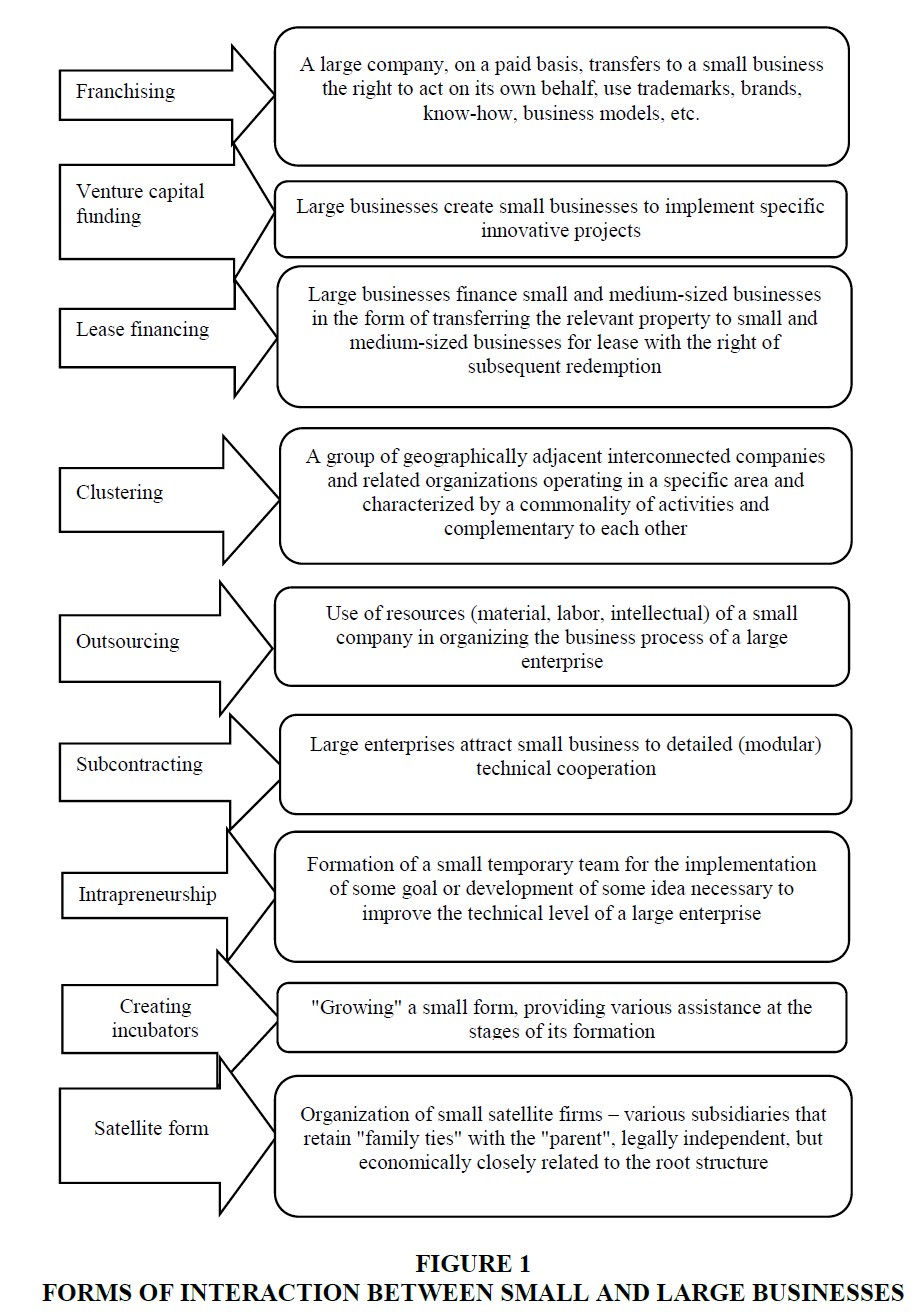
The current economic conditions in the Russian economy create serious obstacles for small enterprises that are losing their competitive advantages and financial solvency. One option for the survival of entrepreneurship is its integration with large businesses, which manifests itself in various forms of cooperation shows in Figure 1.
One of the contemporary forms of interaction between large and small businesses, widely spread in the Tyumen Region, is the franchise system, which involves the creation of a large firm's own internal structure that performs all business functions related to the transfer of an intangible asset (Kazak, 2018). This cooperation model allows small businesses to form a competitive advantage in the market, as well as expand their areas of activity. The wide spreading of this interaction form between the business sector and large producers are noted in the areas of consumer services, such as public catering, trade, and intermediary activities. Quite often, the franchise form of cooperation is found in the construction industry of the Tyumen Region. Tourism, medical services, advertising, etc. are also acceptable areas of such cooperation in the regional market.
Another common option for cooperation between the two sectors of the regional economy is outsourcing. Thus, large retail chains of the Tyumen Region (Bee, Coin, Mostovsky, etc.), educational institutions, and research institutes turn to small cleaning companies (Federal Tax Service of Russia, n.d.). Large production companies (Prodo Tyumen Broiler, Tyumen Bakery Complex, Yagodi Plus, Zavodoukovsky Creamery, Steklotekh Glass-Container Plant, etc.) outsourced the production of containers, packaging products, knife sharpening, and sewage treatment to small business entrepreneurs.
Besides, transport services are the relevant market for cooperation. They provide the delivery of workers to production facilities, transportation of products, laundry services, waste removal and disposal, accounting, legal support, etc. Construction companies of the region interact based on outsourcing with enterprises involved in the installation of elevators and ventilation equipment, as well as production of finishing works. Manufacturers strive to automate and optimize business processes, reduce fixed and variable costs, without harming productivity. While earlier the attractiveness of the enterprise for job seekers was determined, among other things, by the presence of a numerous workforce, today the challenges of the time are met by firms with a well-built structure, where the modernization of production processes releases part of the labor force used in production, which ensures a reduction in labor costs. Outsourcing, for example, allows optimizing costs for both small and large enterprises (Kim & Yemelyanov, 2017).
Today, leasing is becoming common in a broad range of the Tyumen economy sectors as an option for integrating small and large business structures. Large enterprises lease the necessary office equipment, computer hardware, vehicles, and even drilling rigs to the small business sector.
Examples of effective interaction between small and large enterprises of various forms and varieties can be observed in the oil industry of the region, which is undergoing active institutional transformations. The performance of this industry is based on the rational interaction of small and large businesses, which provides for the broadest range of relationships – from the cession of rights to production operations to joint production activities. Vertically integrated large companies organize their work in such a way that they have all the conditions and opportunities for the implementation of large-scale projects for the exploration and exploitation of rich deposits both within the country and abroad, and at any complexity of natural-climatic and geological-economic conditions (Kazak, 2018). At the same time, small and medium-sized satellite firms operate in close connection with large companies in the production sector, technological services, consulting, service, practical testing of new business schemes, marketing, and product sales (Makhmudova & Koroleva, 2017).
Gazprom PJSC demonstrates rather rare forms of regional interaction between small and large business structures (incubation, intra-entrepreneurship). In some regions of Russia, there are small gas fields that are characterized by low profitability, and therefore are unattractive for large investment projects. Gazprom PJSC elaborates for such small projects development programs, arrangement, and operation technologies, justifying projects, material and technical resources, and ordering equipment in its in-house structural scientific and innovative research units. Based on the analysis results of the developed programs, the company decides to create a small project firm that independently develops a gas field with small reserves at significant resource support from Gazprom PJSC.
A similar approach is used for individual fields that have entered the final phase of development. In general, the cooperation of small and large enterprises in the oil and gas complex is characterized by stability and high interdependence.
The Government of the Tyumen Region, in cooperation with major actors of the real sector of the economy, has created effective models of interaction between business structures of different scales in the region, namely, incubator firms. According to the common practice in the region, small business structures are provided with a wide range of services in legal support of business, consulting, equipping office premises, etc. (Palamarenko, 2018). Small enterprises successfully interact with large businesses entities who consider them as strategic partners. These include industrial, commercial, construction, transport, as well as scientific, technical, and service corporations.
Small and medium-sized businesses in the Tyumen Region objectively play a subordinate role in the system of relations with large businesses. The practice of regional interaction between these two economic sectors has revealed a common form of integration, in which a large industrial enterprise creates independent small forms of business that serve its production and technological processes but are in serious material and financial dependence on the creator enterprise.
However, representatives of small businesses in the Tyumen Region consider such interaction ineffective and do not always wish to take part in auctions held by large companies. According to entrepreneurs, mutually beneficial cooperation is impossible because it is difficult to fulfill the requirements of customers. One possible option of solving the problem of reducing the dependence of small businesses on large enterprises is considered the introduction of an intermediary link a medium-sized enterprise. Subject to participation in tenders for the performance of certain works or the implementation of projects of the medium-sized business sector, small business structures are involved in their actual execution at the initial stage (Kim & Yemelyanov, 2017 ).
An important factor hindering the effective interaction of small and large regional businesses is the unfavorable conditions in contracts that provide a large customer with high profitability (Efremova et al., 2019).
Besides, a fairly long payment period for the work performed on the part of large enterprises is also a characteristic feature of the regional interaction of entrepreneurship in the Tyumen Region. Delayed payment of works leads to disastrous consequences for a small enterprise, which, in turn, having no funds to finance its current expenses, is forced to attract credit funds at a considerable interest.
Another obstacle to business integration and the development of small entrepreneurship in the region is the restriction of the possibility of its participation in tenders held on commercial electronic platforms. The limiter here is the high fee for platform entry. Moreover, participation in such events is associated with additional financial expenses for the registration of an electronic signature, the annual payment of a license to carry out activities on these tender platforms (Government of the Tyumen region, 2009).
Specific problems of cooperation and business integration are also common in the oil and gas sector of the regional economy. In particular, small oil and gas companies, as well as large ones, have a common interest in creating a scientifically sound and stable tax system. Besides, small enterprises are interested in creating a system of geo-audit of oil reserves in the country, finalizing the law on main pipeline transport, as well as taking into account the specifics of the fuel and energy complex when assigning the status of a small enterprise. However, small enterprises of the oil and gas industry are limited in access to the resources of the region. The problem here is the impossibility of equal participation in the competition with large producers due to the lack of small enterprises' logistics systems, vehicles, production infrastructure, service maintenance of oilfields, etc. In such a situation, a small oil and gas business is forced to sell products at artificially reduced prices, while large industry companies receive superprofits.
According to analysts and experts, the sphere of relations with customers, that is, the largest enterprises of the country is not transparent enough. Entrepreneurs face cases of bias when conducting tenders for the maintenance of a particular contract. At that, more than a quarter of small enterprises would willingly apply to some independent body - a kind of arbitration court between the customer and the contractor, which would contribute to the settlement of disputes that arise, at that, doubting that they will be able to achieve justice and an unbiased attitude (Kim & Yemelyanov, 2017). Today, councils for working with suppliers and contractors in oil and gas companies have been formed in the region. Each council has a conflict commission, whose task is, first of all, to consider complaints from potential or current counterparties. Besides, the commissions actually help the regional councils to form " new rules" of the game based on transparency and the principles of partnership. The work of the conflict commissions allows not only preventing tension in the cooperation process but also bringing the existing partnership relations to a qualitatively different level.
Support for business in the Tyumen Region is provided by special institutions operating in various fields of activity (Official website of information support, n.d.; Business portal of the Government of the Tyumen region, n.d.; Official portal of public authorities of Tyumen region, n.d.), and forming together the infrastructure for supporting medium and small businesses in the region. Legal support for the activities of medium-sized and small business entities in the region is regulated by a set of federal and regional regulatory acts. A characteristic feature of supporting business structures in the Tyumen Region is a wide range of assistance and support forms provided, as well as their focus on modernization and intensification of business activity.
Assistance provided to the business is quite differentiated depending on the industry features in which entrepreneurs operate. In high-tech industries, the region provides not only financial but also technological support. For industrial business structures, subsidizing the cost of paying for leasing is most in demand.
Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that the regional model of interaction between small and large businesses in the Tyumen Region has certain specifics, caused by the evolution of economic reforms, which consists in the fact that in the conditions of the existing close economic interdependence, a significant share of the burden at the initial stage fell on small enterprises, which often ensured the " survival & quot; of large companies. Such a connection and the structure of regional integration of the two sectors of the economy are still relevant today. It is the small segment of integration business groups that is the first to react to changing business conditions, implements advanced technologies in management and production, adapts to changing consumer preferences, etc. In the context of the transition to an innovative path of development against the background of present-day macroeconomic instability, it becomes urgent to conduct a purposeful and policy, adequate to the new conditions of interaction, aimed not only at supporting the development of small and medium-sized enterprises but also at implementing new forms of mutually beneficial cooperation between large business and regional entrepreneurship.
Being economically prosperous, the Tyumen Region is distinguished by the implementation of an up-to-date targeted policy that supports business, which, in turn, is reflected in the favorable dynamics of its current state and development indicators. The whole range of measures to assist and support regional entrepreneurship is aimed at creating competitive advantages for the region, increasing its scientific and innovative potential, and contributing to the growth of the material well-being of society.
References
Business portal of the Government of the Tyumen region (2019). Property support of SMEs of the Tyumen Region. Retrieved from http://www.tyumen-region.ru/support/enterprises/useful-info/property-upport-for-smes/
Efremova, V.V., Makhmudova, M.M. & Koroleva, A.M. (2019). Socio-economic transformations of the region in present-day conditions: a monograph. Moscow: INFRA-M.
Federal Tax Service of Russia (n.d.). The unified register of small and medium-sized businesses. Retrieved from https://ofd.nalog.ru/index.html
Government of the Tyumen region (2009). The concept of long-term socio-economic development of the Tyumen Region until 2030. Appendix to the order of the Government of the Tyumen region dated 05.25.2009 No. 652-rp (as amended by orders dated 10.26.2011 No. 1976-rp, dated 09.06.2012 No. 1121-rp, dated 28.12.2012 No. 2844-rp, dated 30.07.2013 No 1457-rp, dated 06.11.2013 No.2082-rp, dated 04.16.2014 No596-rp) Retrieved from https://admtyumen.ru/files/upload/OIV/D_Economy/%D0%94%D0%BE%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D1%8B/%D0%9A%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%86%D0%B5%D0%BF%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%8F.pdf
Kazak, E.B. (2018). Integration of large and small entrepreneurship in the contemporary market economy in Russia and abroad. Science and Education: a New Time, 6(29), 251-256.
Kim, Yu.L. & Yemelyanov, S.V. (2017). Improving the interaction forms of industrial enterprises. Scientific Review , 10, 112-120.
Official portal of public authorities of Tyumen region (2019). The list of the state support forms for small and medium-sized businesses in the Tyumen Region. Retrieved from https://admtyumen.ru/ogv_ru/finance/industry/more.htm?id=11599373@cmsArticle
Official website of information support of small and medium-sized businesses in Tyumen (n.d.). State and municipal support of SMEs of the Tyumen region. Retrieved from http://tmb72.ru/content/podderzhka/finansovaja-podderzhka/
Shvedova, L.Yu. & Shvedova, M.F. (2013). Features of the formation of small businesses in the Tyumen Region. Proceedings of the 8th Student Scientific and Practical Conference “Scientific community of students of the 21st century, Economic sciences”, Retrieved from https://sibac.info/archive/economy/8.pdf
Varagina, A.E. (2018). Determining the role of small and medium-sized businesses in Russia. Young Scientist Retrieved from https://moluch.ru/archive/210/51512/