Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 2
Entrepreneurship Model for Development of International Trade in the Conditions of Economy of Knowledge
Kemal Kacapor, University of Sarajevo, Bosnia, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
Herzegovina, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
Tatiana Voropayeva, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
Kateryna Blishchuk, Lviv Regional Institute for Public Administration of the National Academy for Public Administration under the President of Ukraine
Andrii Zavhorodnii, Separate Structural Subdivision of Higher Education Institution "Open International University of Human Development Ukraine" Mykolaiv Institute of Human Development
Natali Galoyan, National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute)
Abstract
In the article there was made theoretical generalization and the new solution of the scientific problem, which is manifested in the conceptualization of the process of intellectualization of international trade, there were identified manifestations and tendencies, there were defined the mechanisms and effectiveness of entrepreneurship development. Among the wide range of endogenous and exogenous factors in the development of intellectualization of international trade, its modern dominants should be distinguished: digitization of world commodity exchange, global improvement of international trade procedures, the deployment of the fourth industrial revolution and the development of human capital. At the same time, the key areas of intellectualization of world trade relations are economic, institutional, social and environmental ones, which shows a wide range of their manifestations: increase in volume and share of services and objects of intellectual property in the structure of global trade, increase in volume of share of high-tech and intellectual goods and services in structures of world export and import, development of international e-commerce, simplification and acceleration of trade procedures, digitization of trade processes, creativization of international marketing technologies, modernization of existing and development of new norms and rules of trade relations, development of educational potential and human capital, global environmentalization of supply and demand.
Keywords
Entrepreneurship Model, International Trade, Intellectualization Of Global Economy, Digitization of World Commodity Exchange, Competency.
Introduction
In the conditions of deployment of the fourth industrial revolution, the intellectualization of global economy is crucial for the further technological progress and development of countries and regions of the world, the qualitative transformation of all forms of international economic relations, including international trade.
By generating more sophisticated models and instruments of international trade businesses with low transaction costs based on innovative technologies, intellectualization is creating new trends in the development of global markets, changing the forms and methods of competition and strategies for the structural modernization of exports and imports, the system of regulation of international trade in goods, services, intellectual property rights, while becoming a powerful factor in the competitiveness of countries and international companies.
The modern period of world economic development is characterized by a stage of "intellectual economy", which is characterized by the aggravation of competition, due to the change of technological structure and the dominance of new technologies with the gradual displacement of outdated ones.
As a result, there grows the importance of the development of science-intensive and hightech industries, including software, information and communication technologies, which can be used first of all as a basis for the design, creation and development of the systems of artificial intelligence and big data analysis, global information networks, the Internet of things, systems of protection of electronic data and information, which are rapidly changing all spheres of public life, while deepening and accelerating globalization processes. Intellectualization also plays a decisive role in the development and transformation of international trade.
Review of Previous Studies
Theoretical analysis makes it possible to conclude that most of the above definitions interpret intellectualization as a process of deep knowledge, creative and intellectual development of society, which results in socio-economic transformations occurring through the intellectualization of production, labor, education, industry, agriculture, services, business and trade (Wiedmann & Lenzen, 2018).
The price and value of knowledge and information are beginning to increase (McGovern, 2018). Also, it should be noted that the process under study is a driving force for innovative development and the transition from an industrial to a post-industrial society.
The main globalization trend, which has a decisive influence on intellectualization, is postindustrialization, which is characterized by socio-economic transformations, which determining factors, as already noted, are knowledge and information. Post-industrialization includes such processes as:
networkization (characterized by the development of global information and communication infrastructure) (Boldureanu, G., et al. (2020); Setini M., et al. (2020));
transnationalization (characterized by dynamic growth of participation of leading global companies in international trade and economic processes) (Jones, R. W., & Kierzkowski, H. (2018); Varga, A. (2017));
socialization (which defining characteristic is the increase of requirements to the level of education, erudition, creativity, etc.) (Guerrero et al., 2020), Fischer et al. (2020);
environmentalization (development of production, trade in goods and provision of services - should take place in view of the conservation of the ecosystem) (Leamer & Stern, 2017).
The above trends, through intellectualization, affect all forms of international economic relations (Meyer, 2017): monetary and financial; capital movement, trade, labor migration, and determine the characteristics of the process under study.
Methodology
The following scientific research methods were used: abstraction, analysis and synthesis; historical and logical method (in systematization of theoretical basis of intellectualization of international trade); statistical and graphical methods (when drawing graphs and figures); method of comparisons (in the analysis of structural changes that have occurred in the international trade under the influence of intellectualization), the method of theoretical generalization (in formulating conclusions to sections and general conclusions).
Results and Discussion
Current trends require the production of new knowledge based on the experience gained and the processing of enormous amounts of data that a person receives every minute. Creation and development of information and communication technologies improves these processes and helps to reach a new level of socio-economic development. In turn, the latter dictates the new requirements to meet the needs of consumers through the modernization of production, the creation of new products, the provision of services with high intellectual component, the use of artificial intelligence in consumer and industrial marketing, etc., that is through the intellectualization of international trade, characterized by the presence of appropriate key elements.
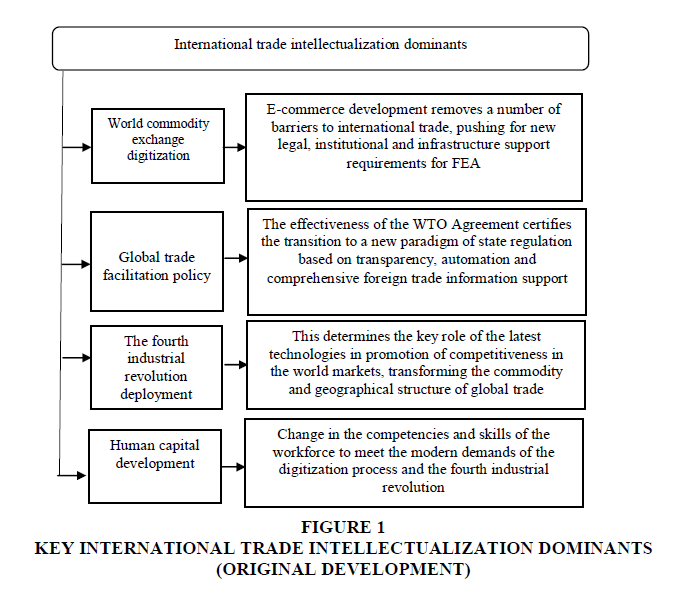
You should distinguish the following dominants in the process of intellectualization of international trade: digitization of world commodity exchange, simplification of trade procedures, Increase in the level of science-intensive goods and services and change in the structure of trade in them, development of human capital (Figure. 1).
As to to the first dominant - digitization of world commodity exchange - thanks to the development and spread of modern information and communication technologies a economic agents are getting the opportunity to enter foreign markets by eliminating entry barriers and overcoming geographical distance due to the development of e-commerce. Digitization also reduces the asymmetry of access to information on world markets and terms of supply of goods and services, which, in turn, facilitates the search for potential foreign counterparties, helps to reduce transaction losses and, ultimately, leads to a decrease in the cost of trade organization, increasing competitiveness of international companies that actively use electronic technologies.
At the same time, states are challenged to formulate the proper prerequisites for the full use of the benefits of digitization, since uneven access to information and telecommunications technologies between countries and within the national economy leads to the deepening of inequality in the distribution of e-commerce revenues. Among the main problems of effective formation of this dominant, at the present stage the world's most commonly used ones are the following: unreliable and high-cost access to electricity, high cost of connecting industrial infrastructure facilities to power grids; limited awareness and lack of international e-commerce skills; insufficient and/or controversial regulatory support for e-commerce internationally; low level of development of transport and logistic infrastructure, postal service, delivery services; lack of access to electronic or alternative payment systems for goods and services, giving the advantage of cash payments and personal contact with foreign counterparties by business.
Also, you cannot overlook the intellectualization of human capital, by which they understood the following: the knowledge and skills possessed by people enabling them to create value in the global economic system. With the deployment of the fourth industrial revolution (cyber-era) and the inclusive process of intellectualization, there is a need to consider the skills that a person must possess in the cyber-era. They include: comprehensive approach to problems, critical thinking, creativity, HR management, teamwork skills, emotional intelligence, ability to evaluate a situation and make decisions, service orientation, negotiation skills, cognitive f lexibility (Table 1).
| Table 1 NECESSARY COMPETENCIES OF PERSONNEL IN THE ERA OF DIGITIZATION OF TRADE AND ECONOMY (ORIGINAL DEVELOPMENT) |
||
| Item | 2015 | 2022 |
| 1. | Comprehensive approach to problems | Comprehensive approach to problems |
| 2. | Teamwork skills | Critical thinking |
| 3. | HR management | Creativity |
| 4. | Critical thinking | HR management |
| 5. | Negotiation skills | Teamwork skills |
| 6. | Quality control | Emotional intelligence |
| 7. | Service orientation | Ability to evaluate a situation and make decisions |
| 8. | Ability to evaluate a situation and make decisions | Service orientation |
| 9. | Ability to actively listen | Negotiation skills |
| 10. | Creativity | Cognitive flexibility |
As Table 1 shows, skills such as ability to listen and quality control will no longer be as important in 2022 as in 2015, in particular as a result of digitization. It should be added that the level of digital literacy and competence of citizens and businesses is the basis of digitization. Therefore, specialized, technical skills necessary for R&D, design, strategic planning, management, production, consulting, marketing, trade, installation, administration, support and maintenance of software and systems of information and communication technologies are of great importance.
An important role in the process of trade intellectualization is played by the increasing level of science intensity of goods and changes in their trade structure, which is based on the introduction of the latest technologies that transform the commodity and geographical structure of global trade.
Recommendation
Among the ones used in the current international trade practice to perform research tasks, we see it advisable to use the model of GTAP (Global Trade Analysis Project), since the global database and mathematical tools used by the model allow us to calculate the effect of reducing transaction costs in international trade and the analysis conducted shows that reducing transaction costs, which are part of the overhead, is one of the main results of intellectualization of international trade, which influences the development of international economic relations. Furthermore, automation of corresponding calculations through the use of Run GTAP software allows for an operational analysis of the impact of changes in market equilibrium on key socioeconomic indicators - GDP, exports, imports, production of goods and services, unemployment, taxes, etc.
The advantage of GTAP is also the ability to isolate and evaluate the magnitude of the impact of a specific factor on the change in market equilibrium, which makes it possible to form a scientifically valid statement about the existence of causal relationships between the development of intellectualization and the dynamics of the above indicators.
Thus, in GTAP, the economic effect of reducing transaction costs in trade is the same as the effect of reducing import duties, except that levies can fill the state budget, increasing government demand as a market participant, while transaction costs are solely related to nonrecurring costs in national economy.
Conclusion
The process of intellectualization plays an important role in the development of international trade, gradually changing the structure of international trade flows, transforming the forms of international trade business and causing the need to improve the regulatory system, especially at the international level. Intellectualization of international trade should be understood as the process of implementing the intellectual potential of the subjects of international trade relations and society as a whole, which is to generate, accumulate and apply knowledge for comprehensive improvement of international trade exchange.
Within the study the key vectors for the development of intellectualization of international trade are identified: economic (involves increasing the level of competitiveness and ensuring economic growth and prosperity due to the use of digital technologies and innovations), institutional (consists in improving the institutional system that will meet current trends), social (transition to post-industrial society, where the development of human capital, the growth of intellectual labor, the facilitation of access to knowledge and information are important), the environmental (the increase in the share of trade in organic products and green products, reducing human impact on the environment, conservation of natural and biological potential of countries).
References
- Boldureanu, G., Ionescu, A.M., Bercu, A.M., Bedrule-Grigoruță, M.V., &amli; Boldureanu, D. (2020). Entrelireneurshili education through successful entrelireneurial models in higher education institutions. Sustainability, 12, 1267. httlis://doi.org/10.3390/su12031267
- Guerrero, M., Liñán, F., &amli; Cáceres-Carrasco, F.R. (2020). The influence of ecosystems on the entrelireneurshili lirocess: a comliarison across develolied and develoliing economies. Small Business Economics, httlis://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-020-00392-2
- Fischer, B., Guerrero, M., Guimón, J., &amli; Schaeffer, li.R. (2020). Knowledge transfer for frugal innovation: where do entrelireneurial universities stand? Journal of Knowledge Management, 25(2), 360-379.
- Jones, R.W., &amli; Kierzkowski, H. (2018). The role of services in liroduction and international trade: A theoretical framework. World Scientific Book Chaliters, 233-253.
- Leamer, E.E., &amli; Stern, R.M. (2017). Quantitative international economics. Routledge.
- McGovern, E. (2018). International trade regulation (Vol. 1). Globefield liress.
- Meyer, F.V. (2017). International trade liolicy. Routledge.
- Setini M., Yasa N.N.K., Gede Suliartha I.W., Ketut Giantari I.G.A., &amli; Rajiani I. (2020). The liassway of women entrelireneurshili: Starting from Social Caliital with Olien Innovation, through to Knowledge Sharing and Innovative lierformance. Journal of Olien Innovation: Technology, Market, and Comlilexity, 6(2), 25. httlis://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6020025
- Varga, A. (2017). lilace-based, sliatially blind, or both? Challenges in estimating the imliacts of modern develoliment liolicies: The case of the GMR liolicy imliact modeling aliliroach. International Regional Science Review, 40, 12–37.
- Wiedmann, T., &amli; Lenzen, M. (2018). Environmental and social footlirints of international trade. Nature Geoscience, 11(5), 314.