Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 1S
Evaluating the Performance Accounting and Financial Studies of Primary School Principals According to the Standards of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Ekhlas Zaki Faraj, The Center of Research and Educational studies
Citation Information: Faraj, E.Z. (2022). Evaluating the performance accounting and financial studies of primary school principals according to the standards of total quality management (tqm). Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 26(S1), 1-17.
Abstract
TQM is one of the most important administrative concepts because it is a comprehensive philosophy and business style enables the organization to achieve competitive advantage that helps it survive and sustain successive environmental changes. The aim of the research is to evaluate the administrative competencies that the principals of primary schools have in accordance with the standards of Total Quality Management using the criteria of comprehensive management according to following axes administrative communication decision making planning and organizing human relations time management assessment, knowledge innovation. As the problem of research in the question about the administrative competencies of primary schools principals which are consistent with (TQM) standards. To achieve the objective of researcher used the analytical descriptive method, so that the researcher set a questionnaire for this purpose includes (48) questions on seven axes. The research reached a set of conclusions and recommendations.
Keywords
Management, Accounting, Finance, Total Quality, School Principals.
Introduction
The end of the last century witnessed vigorous efforts to advance the educational process from the beginning of the educational ladder represented by kindergartens until the end of the university stage and beyond. These efforts also extended to include all elements of the educational process, starting with the school building, the curriculum and its development, the teacher and his preparation, and the school administration and its modernization.
Therefore, the starting point in trying to reform any educational system should be its evaluation that reveals its reality without exaggeration or underestimation, and clarifies the elements of its strength and weakness, and surrounds all aspects of the educational process from the teacher, learner, school administration, activities and others, which contributes to supporting the course of the educational process.
Performance evaluation has witnessed a clear transformation in its concepts and fields, as it moved from a limited scope that revolves around evaluating students in one or more aspects of their development to a movement of comprehensive review and accountability of educational systems aimed at ensuring that they achieve their goals. Thus, the convergence between the comprehensive evaluation processes and the total quality management processes was achieved in these educational organizations, so these organizations must build a culture of quality to improve the performance of managers, teachers and all workers, because they are the core value of the work of any educational organization.
The research consisted of four chapters, the first section dealt with the research methodology, while the second chapter dealt with previous studies, while the third chapter included total quality management, while the fourth chapter was devoted to presenting and analyzing the results, and the sixth chapter included the most important conclusions and recommendations.
First: Research problem
Primary school principals at the present time face great challenges, which require that they be educational leaders in their schools, with high performance skills and competencies, and this entails the application of new models to improve performance. In addition to the traditional problems that schools suffer from, there are unconventional challenges, including high repetition rates, dropouts, overcrowded classes, and double shifts, as well as other difficulties, including poor training and frequent changes to the curriculum, which require principals to address them in unconventional methods, otherwise he will face many major problems in his management. Therefore, the research problem stems from the following question:
What are the administrative competencies possessed by primary school principals that are compatible with the standards of total quality management?
Second: Importance of Research
The importance of the research gains the following:
1. Our schools need effective educational leaders who contribute efficiently and competently in facing challenges and problems.
2. The need to shift from the traditional style of management to more modern and flexible management styles in educational institutions, as the traditional style is no longer suitable for these organizations, and perhaps adopting total quality management helps in improving and developing administrative and educational performance in these organizations.
3. The high level of waste represented in repetition and dropout rates, the decrease in graduation rates, and the weakness in the efficiency of graduates, which calls for adopting new models in management.
4. The urgent need of the Ministry of Education (1977) for research that contributes to developing and improving performance.
Third: the Purpose of the Research
Evaluating the performance of primary school principals according to the standards of total quality management.
Fourth: The Limits of Research
The current research is limited to the administrative educational supervisors of primary schools in the general directorates of education in all governorates of Iraq except for the Kurdistan region for the academic year 2018-2019.
Fifth: Search Terms
1. Evaluation: an organized process of collecting and analyzing information to determine the extent to which educational goals are achieved by learners and to make decisions about them. This concept implies the need to formulate cognitive, skill and emotional goals as a first step in the education process because it is an intentional and purposeful process (Chalabi, 2005).
2. Performance: Performance is the amount of work completed within one hour, taking into account quality. So, performance is a behavior in which the individual contributes in expressing his contributions to achieving the organization’s goals, provided that this behavior is supported and reinforced by the organization’s management and in a manner that guarantees quality and quality through training (Sheen, 2006).
3. School Principal: Each person who leads, coordinates and directs the work of others on an ongoing basis to achieve the desired goals (Ministry, 1977).
4. He was also known as an educational leader whose mission is to coordinate all efforts and provide facilities and capabilities to achieve the goals of his school that stem from the goals of his community, and this task imposes on the principal various roles that he should play in order to achieve this" (Zahran, 1991).
The researcher can identify the most important roles of the school principal:
A. Planning, organizing, directing, motivating and following-up employees (teachers and administrators), as well as investing the available material resources in achieving educational goals.
B. The success or failure of the school depends largely on the ability and personality of the principal.
1- Total Quality Management: A system that includes a set of integrated intellectual philosophies, statistical tools and administrative processes used to achieve the goals and raise the level of satisfaction with the educational product, through continuous improvement of the school’s performance with the active participation of all for the benefit of the student, and thus improving the quality of life in the community (Sheen, 2006).
2- The procedural definition of total quality management: a comprehensive management philosophy for managing the organization more quickly and flexibly, as it contributes to making it a solid system, seeking to gain the trust of the beneficiary of the educational service, and also contributing to creating an environment that allows employees to participate in planning and implementing continuous improvement methods.
The concept of total quality management in education
Total quality in educational organizations is a synergy of efforts and an investment of the various energies of administrators and educators, and teamwork to improve educational performance (Diab, 1997). Some also defined it as achieving the expectations and desires of the beneficiaries through the union of the efforts of the workers in the educational organization to achieve the goals (Field, 1995).
While (Egbert, 1990) stated that total quality in the field of education means efficiency, and (Al-Mahdi, 1997) mentioned that it is effectiveness. Some also indicated that total quality includes both efficiency and effectiveness, and this means that efficiency is the optimal use of available educational inputs in order to obtain distinct educational outcomes, or to obtain the optimal amount of educational outputs using the lowest amount of educational inputs (the lowest possible cost), and this One of the pillars on which total quality management is based, as well as achieving the required specifications in the best ways and at the lowest costs. And if effectiveness in its simplest sense means achieving the goals, or the required outputs, it represents an important basis for total quality as well, but it goes beyond that, as continuous improvement in the various stages of work and in the goals of the organization is one of the most important foundations of quality (Ashiba, 2000).
Total quality in the field of education means the ability of the educational organization to provide a service with a high level of quality and excellence through which it can meet the needs and desires of the beneficiaries (students, parents, society, and others), in a manner consistent with their expectations, and to achieve their satisfaction. This is achieved through pre- established standards for evaluating outputs, and achieving quality and excellence in them (Al- Saud, 2002).
It is clear from what was mentioned above the focus on efficiency and effectiveness only as if they are the content that includes total quality management and that the use of the two terms can be an alternative to total quality management, and despite their importance, quality is broader and more comprehensive.
As it is a comprehensive management philosophy based on a number of administrative concepts (efficiency and effectiveness within them, but not all) based on creative administrative methods and technical skills in order to improve performance and continuous development (Al-Khatib, 2007). Based on the foregoing, quality in education from the perspective of total quality management can be summarized:
1. Excellence and perfection should be achieved and measured.
2. Striving to provide the best service to the beneficiaries in order to achieve their satisfaction.
3. Seeking the happiness of the beneficiaries, as well as their satisfaction
4. Attention to everything, focusing on details, in order to reach perfection
Linked to the expectations of (the beneficiaries) in terms of:
1. Accuracy and perfection
2. Outstanding performance.
3. Providing the good or service at the appropriate time that the beneficiary desires.
4. Providing the good or service at an appropriate cost.
An indicator of a number of aspects, the most important of which are the following:
1. The service is free from defects or errors
2. Outstanding process design
3. Effective supervision of all aspects of the educational process
4. The work is free from overlap and duplication
5. Low cost compared to the level of quality desired by the customer
6. Excellence in planning, organizing and investing time
7. Effective use of human and material resources
8. Wastage is reduced to the lowest level
9. Speed in performance
Evaluating the success of the educational organization (the school) in all its aspects, as it can, through quality, know if it has performed what it planned to provide according to the wishes of the beneficiaries. Recognizing the extent to which it has achieved the objectives, as achieving the beneficiaries’ satisfaction with the service means that the total quality management has achieved its objectives (Akili, 2009).
The concept of quality management, total management in education, is determined by three main factors:
1. Philosophy: It is based in essence that the student or the student is not originally the educational product or service, but the product is what the student or student acquires in education of knowledge, skills, and moral and aesthetic values that work on his self-development in aspects related to knowledge, skills, experiences and educational principles (Al-Bakr, 2001).
2. Objective: The educational product or service should reach all beneficiaries with the highest possible level of quality, and conform to the standards set for it.
3. Process: Paying attention to the feedback from parents, students, students and community members to determine the level of the educational product or service, and using trained workers to take these opinions into consideration to develop them to the satisfaction of the beneficiaries ( Herman, 1994).
Requirements for the Application of Total Quality in Education
The application of total quality management needs to provide a number of requirements, including:
1. Supporting senior management: The implementation of total quality management is a long-term strategic decision, which needs to determine how and when to reach it. It also needs the higher management's conviction of its necessity, and the provision of material and moral support to it.
2. Good selection of school principals: The selection process for school principals should be based on professional and ethical grounds. As the school principal's competencies, skills and attitudes depend on the implementation and application of this modern administrative approach.
3. Continuing training of school principals: The right choice of school principals does not mean that they will succeed, but rather that they can succeed. In order to ensure their success, it is necessary to provide them with a lot of information and skills that enable them to apply this management approach effectively, and this can only come through training, which should be continuous (Odeh & Khalili, 1988).
4. Preface before application: Those responsible for the application of total quality management should instill in school employees the conviction of it before applying it. Acceptance with conviction enhances confidence in this methodology, facilitating the application process, and the commitment of employees to it (Al-Saud, 2002).
First, the Research Community
The research community is limited to evaluating the performance of primary school principals from the point of view of administrative educational supervisors in all governorates in Table 1.
| Table 1 Research Community | ||
| S | Directorate General of Education in the province of | The number of administrative educational supervisors |
| 1 | Nineveh | 24 |
| 4 | Salahuddin | 37 |
| 7 | Kirkuk | 24 |
| 2 | Diyala | 73 |
| 5 | Baghdad-Rusafa | 71 |
| 6 | Baghdad-Rusafa2 | 54 |
| 3 | Baghdad-Rusafa3 | 72 |
| 8 | Baghdad-Karkh 1 | 48 |
| 9 | Baghdad-Karkh 2 | 28 |
| 14 | Baghdad-Karkh 3 | 72 |
| 11 | Anbar | 64 |
| 14 | Babylon | 67 |
| 17 | Holy Karbala | 43 |
| 12 | Najaf | 72 |
| 15 | Qadisiyah | 29 |
| 16 | Double | 18 |
| 13 | Wasit | 26 |
| 18 | Dhi Qar | 24 |
| 19 | Maysan | 74 |
| 44 | Basra | 79 |
| Total | 845 | |
Second: the Research Sample
After defining the research community, a group of (825) administrative educational supervisors were selected in the general directorates of education for the governorates of Iraq, except for the Kurdistan region. After distributing the questionnaire, all questionnaires were retrieved and a sample was adopted for research.
Third: the Search Tool
Due to the suitability of the descriptive approach to the research problem, and since the questionnaire is one of the tools used in this approach, which can achieve the objectives of the research, the questionnaire was adopted as a tool for this purpose.
Fourth: Tool Building Procedures
For the purpose of evaluating the performance of primary school principals, a survey questionnaire and a closed questionnaire were prepared and the following steps were followed:
Reconnaissance Survey
The exploratory questionnaire (extension 1) is one of the important means in educational, administrative and psychological research because it enables the researcher to collect a lot of information about the thinking and behavior of the sample in an economic and quick way (Van Dalen, 1984). Accordingly, an exploratory questionnaire was prepared representing (11.2) of the educational supervisors in the General Directorates of Education in all the governorates of Iraq. The total number of the survey sample included in the research was (160) educational supervisors for the purpose of polling their opinions, which included basic aspects of evaluating the performance of school principals.
Closed Resolution
After distributing the open questionnaire to the sample members, a closed questionnaire was prepared that included seven basic axes to evaluate the performance of primary school principals for the purpose of identifying the most important strengths and weaknesses, namely (administrative communication, decision-making, planning and organization, human relations, time management, evaluation, knowledge renewal) Annex 2) These themes included a varying number of paragraphs, as shown in Table 2.
| Table 2 Resolution Axes and Number of Paragraphs | ||
| Number Of Paragraphs | Domain name | S |
| 6 | Administrative contact | 1 |
| 6 | Make decision | 2 |
| 6 | Planning and Organizing | 3 |
| 8 | Human relationships | 4 |
| 8 | time management | 5 |
| 8 | Calendar | 6 |
| 6 | cognitive renewal | 7 |
Fifthly: the Validity of the Tool
There are several methods and methods for finding honesty. In finding the validity of the questionnaire, the researcher relied on the apparent honesty by presenting the tool to a sample of specialized arbitrators to ensure the validity of the questionnaire’s paragraphs and to provide observations about it paragraphs. Under the opinions and suggestions of the arbitrators, some paragraphs were amended.
Sixth: the Stability of the Tool
Reliability means acquiescence, stability, and predictability of the scale in what provides us with information about the opinions of the sample members. The tool must give the same results if it is applied to the same individuals twice and in similar circumstances. On a sample of educational supervisors, this method is one of the common methods used and spread, especially in research and human studies, where the questionnaire was distributed to a random sample of the study population consisting of (50) educational supervisors, and after (15) days the questionnaire was redistributed to the same sample, and it was found That there is a correlation between the first and second applications amounted to (0.78), and this indicates that the tool is characterized by stability, as the acceptable percentage in such research is (70%) and above (Awda, 1988, 166).
Seventh: Statistical Means
For the purpose of analyzing the sample responses to the research tools, the following statistical methods were applied, with the help of the statistical program (SPSS).
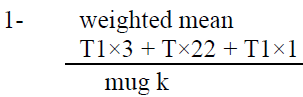
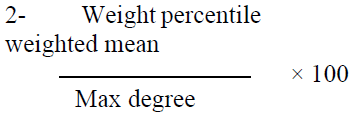
View and Analyze Results
This chapter aims to present, evaluate and analyze data based on the answers of the research sample to obtain a real and clear view of the performance reality of primary school principals, as well as to identify the most influential axes to give them priority when providing solutions. The following is an analysis of the answers according to the main themes:
First: Administrative Communication
This axis consists of (6) paragraphs, and it is one of the important axes. Without effective communication skills, the director loses the ability to communicate with teachers and solve problems. From analyzing the answers, the paragraph (delegating some powers to members of the teaching staff) obtained a weighted average of (2.5) and a weight percentile (71). and came in the first place, while the paragraph (chooses the good administrative method in communicating information to members of the teaching staff) ranked second, as it obtained a weighted mean (2.12) and a weight percentile (66.3), either in the third place, the paragraph (keeps to be The orders and directives issued by him are clear) with a weighted average (1.88) and a percentage weight (58.6), while the fourth paragraph (has the ability to persuade and build bridges of trust between him and members of the teaching staff) was ranked with a weighted average (1.33) and a percentage weight (59.6), while the The paragraph (always reconsidering the procedures used in the communication process) ranked fifth with a weighted mean (1.18) and a percentage weight (52.2), and finally came in the last place the paragraph (investing the results of the feedback in the development of administrative communication processes) with a weighted average (1.04) and a percentage weight (46), as shown in Table 3.
| Table 3 The Paragraphs of the Administrative Communication Field are Arranged In Descending Order According to their Weighted means and Percentage weights | ||||
| weight percentile | weighted mean | Paragraphs | Paragraph no. | S |
| 71 | 2.5 | Delegates some powers to members of the teaching staff | 1 | 1 |
| 66.3 | 2.12 | Chooses the appropriate administrative method in communicating information to members of the teaching staff |
6 | 2 |
| 58.6 | 1.88 | He makes sure that the orders and directions issued by him are clear |
2 | 3 |
| 59.6 | 1.33 | He has the ability to persuade and build bridges of trust .between him and the members of the teaching staff |
3 | 4 |
| 52.5 | 1.18 | Always review the procedures followed in the .communication process |
4 | 5 |
| 46 | 1.04 | Invests feedback results in developing management .communication Paragraph No |
5 | 6 |
Second: Making a Decision
The decision-making axis consists of (8) paragraphs, and this axis is one of the main axes that are no less important than the other axes, as the director’s ability to make a decision plays an important and effective role in the teachers’ performance of their educational and scientific role efficiently and effectively, either with regard to measuring the degree of severity and weight percentage. For the sample answers, the table 4 shows the sequence of the paragraphs in terms of their importance, as the first rank was occupied by a paragraph (takes responsibility for the decision he takes) with a weighted mean (2.5) and a weight percentile (76.25), either in the second place came the paragraph (be careful not to retreat when making the decision) With a weighted mean of (2.3) and a weight percentile of (71), while the paragraph (balances between firmness and flexibility in decision-making) came in third place with a weighted mean of (2.07) and a weight percentile of (66.75), while the two paragraphs came (involve members of the educational staff with him in decision-making). If necessary) and (take the appropriate decision at the right time) ranked fourth as they obtained a weighted mean (1.8) and weight percentile (61). among those affected by the decision and gain their support) with a weighted mean of (1.6) and weight percent And (60), either the last rank was given to the paragraph (deals with time and situation with a holistic view in decision-making), with a weighted mean (1.3), and a weight percentile (46).
| Table 4 The Decision-Making Items are Arranged in Descending Order According to Their Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | ||||
| Weight percentile | Weighted mean | Paragraphs | Paragraph no. | S |
| 76.25 | 2.5 | He takes responsibility for the decision he makes | 6 | 1 |
| 71 | 2.3 | He is careful not to back down when making a decision | 3 | 2 |
| 66.75 | 2.07 | Balances firmness and flexibility in decision- making |
5 | 3 |
| 61 | 1.8 | Involve members of the teaching staff with him in decision-making, if necessary |
4 | 4 |
| 61 | 1.8 | Take the right decision at the right time | 2 | 5 |
| 60 | 1.6 | Familiar with the concept of decision-making and the specifications of good administrative decision |
1 | 6 |
| 60 | 1.6 | Confirms the conviction of those affected by the decision and gains their support |
7 | 7 |
| 46 | 1.03 | Deals with time and situation with a holistic view in decision-making | 4 | 8 |
Third: Planning and Organizing
Planning and good organization play a major role in the success achieved by the school in its tasks. This axis consists of (9) paragraphs. Table (5) shows that the first rank was occupied by the paragraph (depends on some members of the educational staff who are competent in carrying out administrative work) in the first place with a weighted average of (2.5) and a percentage weight (76.2), and the second rank was obtained by the paragraph (knowledge of the new variables that took place in society and ways of translating their requirements into reality), a weighted mean (2.32) and a percentage weight (71), while the paragraph (works to make its planning for school work flexible) got the second rank. According to the probabilities of changes in society) on a weighted mean (2.23) and a percentage weight (66.3), while the two paragraphs got weighted means and close percentage weights, namely (preparing comprehensive and detailed plans) and (familiarizing with the public and private educational policy in the primary stage), with two weighted means (2.21) and (2.14) and weight percentile (62.8), (61.3), respectively, and they came in third place. As for the fourth place, the two paragraphs (informing the general and specific educational philosophy in the primary school) and (working to provide students with the skills of scientific thinking and creative thinking) came with a weighted average of (1.89), (1.88), and two percentile weights (59.6), (58.2), while The weighted averages for the two paragraphs (it adopts educational renewal formulas for the development of the primary school) and (works to educate the members of the educational staff to anticipate the future and its challenges) reached (1.08), (1.01), and two percentile weights (51.8), (50.2), occupying the last rank, and as shown in Table 5.
| Table 5 The Paragraphs of the Planning and Organization Axis are Arranged In Descending Order According to Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | ||||
| S | Paragraph no | Paragras | Weighted mean | Weight percentile |
| 1 | 6 | It relies on some qualified faculty members to carry out administrative work |
2.5 | 76.2 |
| 2 | 4 | Familiar with the new changes that have taken place in society and ways to translate their requirements into reality |
2.32 | 71 |
| 3 | 5 | He works to make his school work planning flexible according to the possibilities of change in society |
2.23 | 66.3 |
| 4 | 1 | Prepares comprehensive and detailed plans |
2.21 | 62.8 |
| 5 | 3 | Familiar with public and private educational policy at the primary level |
2.14 | 61.3 |
| 6 | 2 | Familiar with general and special educational philosophy in elementary school |
1.89 | 59.2 |
| 7 | 7 | It works to provide students with the skills of scientific thinking and creative thinking |
1.88 | 58.6 |
| 8 | 9 | Adopts educational renewal formulas for the development of the primary school |
1.08 | 51.8 |
| 9 | 8 | It educates faculty members about the future and its challenges | 1.01 | 50.2 |
Fourth: Human Relations
The human relations axis includes (8) paragraphs, which came at the forefront of the paragraphs in terms of importance, a paragraph (that achieves justice in dealing with students and teachers), as it obtained a weighted mean (2.32) and a percentage weight (78). Either the paragraphs (works to spread the team spirit in order to implement the educational tasks on time) and (works to create a healthy educational climate inside the school) and (knows the principles of human relations and realizes their importance and works in them) and (develops positive relations between members of the educational staff) and (He devotes part of his time to strengthening social relations with civil society organizations) came in second place, as it obtained weighted averages that ranged between (2.21-2.10) and percentage weights that varied between (74-70), while the paragraph came (cooperates with parents to solve problems Their educational children) ranked third with a weighted mean (1.88) and weight percentile (65), while the last rank was occupied by the paragraph (works to educate parents of students and activate their contribution to the success of parent-teacher councils) with a weighted mean (1.08) and a percentage weight (51) in Table 6.
| Table 6 Paragraphs of the Field of Human Relations are Arranged in Descending Order According to Their Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | ||||
| Weight percentile | Weighted mean | Paragraphs | Paragraph no | S |
| 78 | 2.32 | He achieves justice in his dealings with students and teachers |
4 | 1 |
| 74 | 2.21 | Works to spread team spirit in order to carry out educational tasks on time |
6 | 2 |
| 73 | 2.20 | Creates a healthy educational climate within the school | 8 | 3 |
| 72 | 2.19 | He knows the principles of human relations and understands their importance and works with them |
1 | 4 |
| 71 | 2.15 | Develops positive relationships between faculty members |
7 | 5 |
| 70 | 2.10 | He devotes part of his time to strengthening social relations with civil society organizations |
2 | 6 |
| 65 | 1.88 | Cooperating with parents to solve their children's educational problems |
5 | 7 |
| 51 | 1.08 | It works to educate parents of students and activate their contribution to the success of parent-teacher councils |
3 | 8 |
Fifth: Time Management
Time is the most wasted element and the least investment. This axis contained (8) paragraphs that ranked first, the paragraphs (estimates the importance of time in every work he does), (allocates sufficient time to follow up on personnel affairs) and (stays away from problems that lead to wasting time) in terms of importance because it obtains close weighted circles, as it obtained mean (2.52 - 2.50 - 2.49) and percentage weights (67.6 - 66 - 65), but in the second place, the two paragraphs (setting the dates of meetings and various meetings in the school) and (designing the weekly lesson schedule to ensure the optimal investment of time) were missed. With a weighted average of (1.92-1.90) and two percentage weights (60-59), while the third item (time is invested in managing the various activities in the school) came in the third place with a weighted mean (1.87) and a percentage weight (56), while the paragraph (time is invested in Management of various activities in the school) ranked fourth with a weighted mean (1.87) and weight percentile (56), and the penultimate rank occupied the paragraph (preparing a list of the tasks to be completed daily), its weighted mean (1.73) and its weight percentile (54), either in the last rank came Paragraph (sets appropriate times for school activities and activities) with a weighted mean of (1.09) and a weight percentile (4 .). 5), as shown in Table 7.
| Table 7 The Paragraphs of the Time Management Axis are Arranged in Descending Order According to Their Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | ||||
| Weight percentile | Weighted mean | Paragraph | Paragraph no | S |
| 76.6 | 2.52 | He appreciates the importance of time in everything he does |
1 | 1 |
| 66 | 2.50 | Allocate sufficient time to monitor personnel affairs |
6 | 2 |
| 65 | 2.49 | Avoid problems that waste time | 8 | 3 |
| 60 | 1.92 | He sets the dates for various meetings and meetings in the school |
4 | 4 |
| 59 | 1.90 | The weekly lesson schedule is designed to ensure the optimal investment of time |
3 | 5 |
| 56 | 1.87 | He invests time in managing various activities in the school |
5 | 6 |
| 54 | 1.73 | He prepares a list of tasks to be completed daily | 2 | 7 |
| 45 | 1.09 | Determine appropriate times for school events and activities |
7 | 8 |
Sixth: The Calendar
Table 8 shows the opinions of the total sample members, as it came at the forefront of the paragraphs, the importance of the paragraph (taking into account the public interest before personal interests when evaluating school tasks) ranked first, as it obtained a weighted mean of (2.36) and a percentage weight (79), and the two paragraphs (implementation continues School plans and lesson plans provided by teachers) and (using self-evaluation methods for members of the teaching staff) on two weighted averages (2.33) and (2.31) and weight percentiles (77) and (76) in the second place, and in the third place came the paragraphs (reveals the deficiencies and deviation in performance and analyzes the causes) and (adopts objective criteria in evaluating teachers and the educational process) and (sees exam questions and discusses teachers with them) and (keeps to follow up on the information required of him from higher authorities) with weighted circles (2.21-2.18-2.15-2.10) And a percentage weight of (73, 72, 71, 70), while the paragraph (contributes to the development of evaluation systems, exams and school tests) ranked last with a weighted mean of (1.89) and a percentage weight (66).
| Table 8 The Paragraphs of the Calendar Field are Arranged in Descending Order by Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | ||||
| Weight percentile | Weighted mean | Paragraph | Paragraph no | S |
| 79 | 2.36 | He takes the public interest before personal interests when evaluating school assignments |
5 | 1 |
| 77 | 2.33 | Follows up on the implementation of school plans and lesson plans provided by teachers | 1 | 2 |
| 76 | 2.31 | Uses self-evaluation methods for faculty members |
2 | 3 |
| 73 | 2.21 | It detects glitches and deviation in performance and analyzes the causes |
6 | 4 |
| 72 | 2.18 | It adopts objective criteria in evaluating teachers and the educational process | 3 | 5 |
| 71 | 2.15 | He looks at the exam questions and discusses them with teachers | 4 | 6 |
| 70 | 2.10 | He is keen to follow up on the information required of him from the higher authorities |
7 | 7 |
| 66 | 2.89 | Contributes to the development of evaluation systems, exams and school tests |
8 | 8 |
Seventh: Cognitive Renewal
Table 9 of the respondents’ answers shows that the paragraph (visiting teachers in the classroom during teaching and providing educational and scientific guidance) got the first rank with a weighted mean of (2.28) and weight percentile (76), and in the second place the two paragraphs (keen to feed the school library) In modern accessible references and periodicals) and (in-service training is seen as a right and duty for members of the educational staff) on a degree of severity (2.08) and a weight percentage of (69), while the paragraph (is keen to benefit from the opinions of educational supervisors towards the development of competencies of members of the educational staff) ranked The third is with a degree of severity (2.04) and a weight percentile (67), and in the fourth and last place are the two paragraphs (encouraging teachers to contribute to conferences, seminars, and scientific and educational activities) and (it adopts modern technologies, training methods and self-learning) with a degree of severity (1.66- 1.64) and a percentage weight (55-54).
| Table 9 Paragraphs of the Cognitive Renewal Domain are Arranged in Descending Order by Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | ||||
| Weight percentile | Weighted mean | Paragraph | Paragraph no | S |
| 76 | 2.28 | He visits teachers in classes while teaching and provides educational and scientific guidance |
5 | 1 |
| 69 | 2.08 | It is keen to feed the school library with modern, accessible references and periodicals |
6 | 2 |
| 69 | 2.08 | In-service training is seen as a right and a duty for faculty members |
1 | 3 |
| 67 | 2.04 | He is keen to benefit from the opinions of educational supervisors towards developing the competencies of members of the educational staff | 4 | 4 |
| 55 | 1.66 | Encourages teachers to participate in conferences, seminars, and scientific and educational activities | 3 | 5 |
| 54 | 1.64 | Adopts modern technologies, training methods and self-learning | 2 | 6 |
It is noted that the administrative communication axis ranked first with a weighted mean (4.130) and weight percentile (82.60), while the decision-making axis ranked second with a weighted mean (4.121) and weight percentile (82.42). While the axes of planning, organization and human relations ranked third with a mean (4.074) and a weight percentage (81.48). The time management axis ranked fourth with a weighted mean (4.044) and a weight percentile (80.88). The assessment axis came in the sixth rank with a weighted mean (3.967) and a weight percentage (80.08), and the field of cognitive renewal came in the seventh and last rank with a weighted mean (3.938) and a percentage weight (78.76) in Table 10.
| Table 10 Instrument Fields Arranged in Descending Order by Weighted Means and Percentage Weights | |||
| Weight percentile | Weighted mean | Field | S |
| 82.60 | 4.130 | Administrative contact | 1 |
| 82.42 | 4.121 | Make decision | 2 |
| 81.48 | 4.074 | Planning and organizing | 3 |
| 81.48 | 4.074 | Human relations | 4 |
| 80.88 | 4.044 | Time management | 5 |
| 80.08 | 3.967 | Calendar | 6 |
| 78.76 | 3.938 | Cognitive renewal | 7 |
Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusions
1. The responsibility of the school principal is no longer confined to precisely, but extends to managing the teaching and learning process, organizing, directing and evaluating it, in addition to his responsibility for the quality of the school’s outputs .
2. His lack of many decision-making powers that help in achieving quality, as school principals do not have the method of self-management, but rather carry out the tasks assigned to them.
3. Lack of awareness of the educational total quality management standards and his ability to comprehend their concepts.
4. The lack of systems that work to achieve regular and periodic preventive control over operations at all stages, and this is something that indicates that operations are managed in a traditional way, far from standards of quality and perfection.
5. Weak standards for evaluating teachers’ performance, as well as the lack of mechanisms to ensure the efficiency of the administrative organization in general.
6. The weakness of the training methods used in training managers, which are commensurate with the standards of total quality management
7. Many managers neglect the feedback, because one of the most important ingredients for the success of modern management is to measure the possible reactions to decisions and actions to correct them.
Recommendations
1. Updating the mechanisms of administrative work by using new concepts in school management, such as total quality management, to meet the requirements of global scientific and technological changes and keep pace with the new changes in Iraqi society.
2. Adopting a set of objective procedures when interviewing and testing school principals to ensure the availability of the necessary administrative and educational competencies when selecting them.
3. Providing school principals with a set of administrative and educational experiences before and after assuming his duties as a school principal, through effective training programs to which the principal is subjected periodically.
4. Paying attention to the scientific content of the training courses by making use of contemporary educational trends in educational administration.
5. Giving principals more powers to help them run their schools efficiently and effectively, so that they feel loyalty and belonging to the school community.
6. Introducing a new reward and incentive system to honor principals who achieve high success rates in their schools or who provide innovative educational methods that prove their effectiveness.
7. The need to change the concept of control and evaluation from the traditional concept that includes trapping mistakes in order to hold those responsible accountable and punish them to the concept of providing appropriate assistance to solve problems and treat deviations.
8. Strengthening the relationship between the school and the external community (community partnership) by holding seminars and meetings with parents of students, civil society organizations, and local and municipal councils to participate in developing the school's performance.
9. Introducing the Department of Educational Administration in the Colleges of Basic Education, as educational administration has become a stand-alone science with its theories, principles and laws.
References
Al-Khatib, M. (2007). Introduction to the Application of Total Quality Standards and Systems in Educational Institutions, Hammad Institution for University Studies for Publishing and Distribution, Jordan - Irbid.
Al-Saud, R. (1994). School Effectiveness in American Educational Thought: An Introduction to the Right and Development of Education in the Arab School, Dirasat Journal, University of Jordan, 21(1).
Ashiba, F.D. (2000). Total Quality and the Possibility of Its Application in Egyptian University Education: An Analytical Study, Journal of the Association of Arab Universities, (3).
Chalabi, S.S. (2005). The Basics of Building Psychological and Educational Tests and Measures, Aladdin Foundation for Printing and Distribution, Damascus, Syria.
Egbert, D.W. (1990). A Macro- Analysis of Quality Assessment in Higher Education, Higher Education, 19(1). Field, D.B. (1995). Quality Control, translated by Sorour Ali Sorour, Cairo, Academic Library.
Herman, J.J. (1994). Educational quality management: Catalyst for integrated change. PA: Economic publishing company.
Ministry of Education. (1977). Ministry of Education, Press No. 2, Baghdad, Iraq.
Sheen, N. (2006). Strategic performance, entrance to competitive advantage, Faculty of Economics and Management Sciences, University of Biskra.