Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 2S
Financial Technology between Reality and Application Developing the Incubating Environment and the Expected Role to Achieve Sustainable Development in Iraq
Hendren Hassan Hussein, Al-Mustansiriya University
Hafedh Abdulameer Amen, Al-Mustansiriya University
Bushra Ashour Hachim, Al-Mustansiriya University
Keywords
Financial Technology, Iraq, Sustainable Development
Abstract
Financial technology is the result of technological progress in the financial aspect of the global economy, as this technology has given rise to a new emerging financing face embodied in “start-up companies”, which represent a challenge for “traditional banks” in their banking services, in addition to that, they constitute a fierce competitor, which may It controls the banking services, especially as it relies on “artificial intelligence” and “smart phones”, and facilitates (the process of payment, trade and electronic investment), and it comes in line with the large and rapid steps of possible changes in the “financial system” and “global economic” after the Corona crisis and the call for Leave dealing with the paper currency that is believed to be (the main reason for the transmission of the Corona virus), so the research will answer for? What is financial technology? How does it work through its various sectors? And the reasons for the world resort to "financial technology"? And where will Iraq be in this new world that needs to get alternatives and needs to keep pace with global development in the field of (investment, capital movement and achieving profits with the least possible risks), in order to achieve “economic development” and “community development”.
Introduction
The rentier economy dependent on oil and the lack of diversification of the sources of national income, requires finding alternatives, even if these alternatives are difficult, they must be studied and take into account the experiences of others. Job opportunities for the private sector necessitate stopping at them and the necessity of our study and research, especially their success and displacement towards the Middle East and our Arab region, and trying to understand them and ensure the possibility of application in our economy, as they may be part of the solution to the crisis in the Iraqi economy. , especially that the “global economy” will inevitably transform into a “cashless economy” after the “Coronavirus” crisis, a society without money is a cashless society (digital society), the world will inevitably turn into a “new global economy” in which there is no money in circulation. A unified global digital currency”, and it relies on credit and bank cards, the conflict after the Corona virus is in the form of “the global economic system”, and this system is based on And on the idea of leaving money and switching to digital money (electronic money), therefore, the huge media is working and helping to prepare for this system through the fact that “paper money” was the reason for the transition of Corona to encourage the use of “electronic money.”
Research Importance
The research gives perceptions of the post-Corona economy and how the steps to speed up the new global economic system will be launched, and perhaps its most important features are the financial technology industry, financial and banking services and its modern and new tools, and perhaps a wider spread of “digital currencies” to get rid of “paper currencies”, which are promoted as the reason President of the transmission and spread of the "Corona virus".
Research Problem
The problem of searching for the problem of the Iraqi rentier economy and its backward financial and banking sector that does not keep pace with the developments, changes and events of the "global economy", which inevitably turns into a "non-monetary economy", societies without money, societies that use credit cards, and bank cards, societies that use (intelligence) does not go away. Industrial, information and communication technology and electronic payment means).
The question? Does the Iraqi economy have the ability to overcome the "risks of financial technology", despite the many benefits, and does it have the ability to facilitate many complex operations and long transactions that are not without risks of fraud, fraud and the threat of financial instability, or the problem of terrorist financing and money laundering operations, These risks are likely to reduce confidence in the use of this technology.
Research Hypothesis
There is a possibility to apply “financial technology” in Iraq, because it represents a new vision in the form and mechanisms of providing financial services in various economic fields, which makes it a means of a very important contribution to (increasing profits, economic growth and benefiting from electronic financial services), in a way that contributes to Increasing “financial inclusion” and developing the payments sector.
Research Aims
1. Shedding light on financial technology, what it is, what is meant by it and how it works, as it has created a new field of investment based on the field of non-monetary economy?
2. Identifying financial technology companies and the development of financial services provided based on electronic payment and mobile phone, and what are the main challenges and obstacles facing the work of emerging financial technology companies in the Arab region, especially Iraq, and what are the motives for working with financial technology in Iraq Is the infrastructure available for work Financial technology and what are the capabilities that the Iraqi economy needs in order to work with modern financial services.
3. What are the necessary needs that must be met to unleash these capabilities, and what are the solutions and benefits provided by financial technology to developing countries, especially Iraq
4. What are the measures of the Central Bank of Iraq in order to settle the appropriate environment for the work of financial technology and the transition to a non-monetary economy, and to keep pace with the development taking place in the world, especially after the crisis of the Corona virus (Corona pandemic).
The First Topic
Financial Technology ... Theoretical Framework
Today, the world is witnessing a process of transition from a monetary economy to a non-monetary economy thanks to technology, and payment methods are constantly evolving and banking services will not need a bank in the future to accomplish all of this. Knowledge economy”.
The First Requirement
What is Financial Technology?
Fintech is an abbreviation of two words, “financial” and “technology,” which describes a wide range of “technological interventions” in “personal and commercial finance” and its users, banks, business clients, small businesses or start-ups, a term that includes the “technological aspect.” With the "financial aspect", as it resulted in a field concerned with financial transactions using and exploiting all the results of modern technology (mobile smartphones, communication networks and electronic digital commerce), including "encrypted digital currencies", where the latest (technological techniques were directed to develop Financial services), which are now provided by companies that benefit and exploit technology (financial services sector and payments sector).
The Second Requirement
The importance of financial technology and the transition to a non-digital economy
First: The Importance of Shifting to a Cashless Economy
There is importance in the transition to a non-monetary economy represented by the following:
1) A faster way to sail goods and purposes of various types and sizes. Non-monetary societies (electronic economy) create stronger financial markets due to their large use of “smart phones”, therefore using them in “electronic payment” is easier and less expensive.
2) The non-monetary economy is “currency circulation” and its digital transformation without the need to carry cash, and this helps to solve the “liquidity crisis” and congestion on banks and their branches. The cost of providing “financial services”.
3) Far from "conspiracy theory", financial technology would address critical challenges to promoting "financial inclusion" and "economic diversification", and provide new opportunities for young people to be managed by them instead of searching for a public job, and this is assisted by the group of innovations and financial services it provides. The “financial technology” industry, as it facilitates the availability of alternative sources of financing for small and medium enterprises owned by a large segment of the population that do not deal with the “banking system”, and this limits the scope of “traditional financial intermediation, to modern techniques aimed at reducing risks and costs resulting from financial transactions.” It may also lead to greater use of electronic payment methods.
4) The shift from a “monetary economy” to a “non-monetary economy” achieves many goals that serve citizens, businesses and governments alike and at the macroeconomic level.
5) Shift to promoting “financial inclusion” by providing efficient, diversified, diversified collection and payment options, cyber (electronic) security, flexibility and easy access to areas (rural and remote), which do not have bank branches.
6) The transition to non-cash financial dealings is one of the most important means of stimulating self-employment and entrepreneurship, which is one of the mechanisms for increasing growth, encouraging competition, reducing unemployment and stimulating social mobility.
7) It is a revolution based on “artificial intelligence” and “big data”, and thousands of real companies are already using these technologies to disrupt every aspect of “financial intermediation”, and financial institutions make accurate lending decisions within (seconds not weeks), and that Thanks to a wealth of online data about individuals and companies, and over time, these data-driven improvements in credit allocation may eliminate the "credit-driven cyclical booms and busts".
8) The transformation, in turn, imposes better control over the security and safety of “financial transactions”, thus reducing financial crimes and costs directly related to the use of “liquid money”, such as theft, bribery, corruption, fraud, money laundering and other crimes related to money, and there will be strict control over the movement of “capital”. And 'trade'
The Third Requirement
What do Consumers Need to Know about Intech?
1) Financial technology is changing the form and delivery of financial services on a larger scale beyond machines (ATMs and credit cards), to the use of (smartphones and mobile payments), new businesses and bypassing established financial intermediaries and institutions and thus providing products and services directly to consumers.
2) Fintech companies have lower operating costs, so the individual consumer will have more options for how to manage his money, and remittances will become faster and cheaper, many of the fees (cross-border transfers), will be with lower fees and faster delivery.
3) Studies indicate that "a third of humanity" does not believe that they need a bank within the next five years and instead will rely on emerging companies in the field of financial technology, which will replace traditional banking jobs and a set of innovative solutions to meet the daily needs of consumers.
4) The non-banking person may quickly turn into a “banking person”, but not through the bank, but through “financial technology”, which is led by the “mobile phone”, so more efforts must be made to increase “financial inclusion” and the quality of access to the Internet (International Information Network) and improve “financial inclusion”.
5) It will be difficult to "lose your wallet", but easier to lose your privacy. The new world order based on a digital society "a digital unified currency", or digital currencies for each country, it will be easy to collect in-depth information about consumers and their behavior, and the movement of global capital from During "electronic commerce" transactions, whoever controls the international information network will rule the world. Financial technology services mostly depend on "collecting information" about the movement of capital, although the big powers paint a rosy picture of this behavior because what is meant by this is to protect societies and their economies, Because consumers who are seen as risky or who lack a 'digital footprint', can be excluded.
6) Dealing (with the digital economy and digital currencies) is intended to eliminate the risks of not knowing others, their financial solvency, and their reputation in the “financial market”, as through your “financial advisor” collecting information about customers and their financial status through an online survey and then using the data to provide advice .
7) Despite the lack of financial culture and the scarcity of information about (financial and banking services) in our Arab reality, especially in Iraq, there is a growing culture of “electronic business” entrepreneurship among the youth community, as many talented competencies prefer to establish companies over working for an employee, as well as the direction of many From human cadres to working in the financial technology sector.
The Second Topic
Global Trends of Financial Technology and Application Possibilities in Iraq
The time of Corona and the steps of rapid and large changes in the world, all of this calls for thinking and studying the impact of financial technology in a more innovative way. How will this technology lead to changes in the world, especially in the financial aspect? Will it bring about a complete change and transformation in it? Will it contribute to the disappearance of the banking sector, to be replaced by systems based on chains of data sets that facilitate “smart transactions” and provide optimal advice to investors in this new sector?
The First Requirement
Global Financial Technology Trends ... Evolution and Drivers
Financial technology: It is a term that combines the "technological aspect" with the "financial aspect", resulting in companies engaged in financial transactions (smartphones, communication networks, electronic commerce, digital currencies), and according to reports, the activity of emerging companies in the global financial technology field is on the rise. Continuous.
Source: Jonas Vail et al., Financial Technology in the Middle East and North Africa, Trends in the Financial Services Sector, Wamda Research Center, (Befort, 2018).
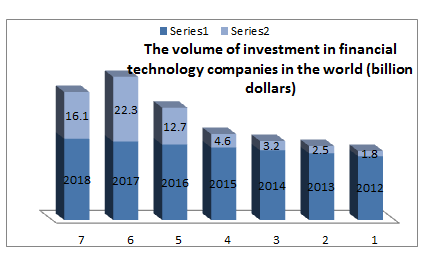
The rise in investment in financial technology between “2010” and “2014” is due to important centers in the United States of America and London, and although the United States accounted for more than 50% of all investments in the field of financial technology in 2015, Asia’s share of investments The annual rate has tripled from “6%” in 2010 to “19%” in 2015 and all regions of the world at the present time are in one of the three phases of the financial technology cycle (new incubator environments, emerging incubator environments and advanced incubator environments). China is the countries of the world depending on financial technology with a growth rate of 69% for the year 2017, followed by India at a rate of 52% and then the United Kingdom (Britain). Access to financial services in some emerging markets, such as China, India, Kenya and Thailand is 80%, and China is an excellent example of how to transform From obtaining bank accounts to using them, 80% of adults in China use bank accounts, 85% of them use the Internet in dealing with the Internet, compared to 15% who prefer to pay cash in transactions.
There are motives for using technology, including the financial exclusion of many individuals because they do not have access to financial services on a large scale, due to the wide and high cost to individuals and governments and with the increased use of the international information network and the increasing prevalence of smart phones, which requires an increased need for digital payment solutions, and thus the future of financial technology And the new technologies it presents in the payments sector.
Source: Wahiba Abdul Rahim, Middle East and North Africa financial technology companies, GiobaI Journal of Economics and Business , NO .1 .2018 , 33.
The world today is on the verge of big and rapid steps towards the (cash-free societies), and this matter is not determined by Iraq and other small developing countries, this is determined by the large economic forces, determined by advanced economies model (artificial intelligence and modern financial technology based on smart phones and cloud computing ), the technological communication model resulting from rapid events in aspects of society, including communications, business and government, and the financial world is not excluded from this change, especially after the events of the Corona virus.
The world is heading to determine the legal status of virtual currency and its spread or digital code and electronic signature, and electronic insurance, and to new ways to combat money laundering and terrorist financing, and new methods, laws and standards to know your “know your customer” in virtual currency transfers, and all this change requires changes in policy development. That helps countries navigate the rapidly changing environment.
The Second Requirement
The Arab region, the ranking ladder and the global spread of financial technology companies
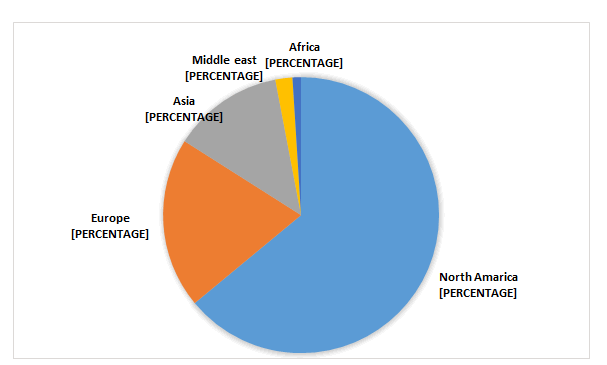
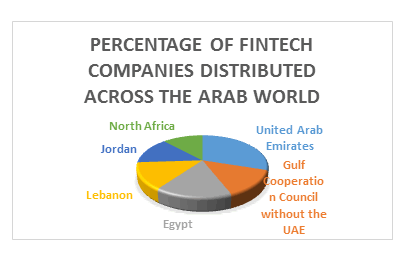
The interest of Arab countries in developing the digital financial technology sector in the Arab region has increased, and the latest reports showed that (28%) of the companies operating in this sector faced difficulties in how to deal with financial systems. Moreover, the global spread of financial technology companies did not stop at the United States and Europe, but reached To the Arab region, it witnessed the concentration of 105 start-up companies in the field of “financial technology” at the end of 2018, covering (12) countries concentrated in the countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council, North Africa and the Levant, and the majority of them are located in the region of the Gulf Cooperation Council with a percentage of (42%), followed by the North region Africa and the Arab Mashreq for the same (29%).
The UAE leads the rankings in the Arab region, although Egypt was home to more than a quarter of emerging companies in the (Middle East and North Africa) in the field of financial technology, but the UAE has surpassed Egypt in this aspect and has become the leader, witnessing the launch of three times the startup companies in the field of financial technology. Financial technology compared to Egypt, and the compound annual growth rate of financial technology in the UAE during the years (2011-2018) reached (57%), followed by Lebanon (50%), Jordan (37%), then Egypt (21%). In 2018, it reached The growth rate in the UAE is (29%), which is the highest rate in the Arab region after it was (17%) in 2011, followed by Egypt (16%) in 2018 after it was (26%) in 2011.
Jonas Vail et al., (2017) Financial Technology in the Middle East and North Africa, Trends in the Financial Services Sector, Wamda Research Center, (Befort, 2017).
The financial technology industry report issued by "Befort Wamda" showed that the UAE is leading the technology wave in the Arab region, and expected that the size of the financial technology industry in the Middle East will reach (20 billion by the end of 2020 through 250 companies specialized in this field), noting that the number of companies currently in the region (105), while in a country like Switzerland there are (200) companies and there are (30) companies in the UAE representing (29%) of the companies working in this field in the Arab region, and the importance of this industry comes through the expectations of the growth of electronic commerce (4) times during the next five years.
And the question asked? Should the Arab region wait for the achievements of financial technology, meaning we press the button to temporarily stop the regulatory action, in order to give new technologies some time to develop and allow the forces of innovation to contribute to reducing risks and maximizing benefits? Or do we learn and study the financial services provided by financial technology, all of which calls for serious thinking, how exactly will these financial technologies change the “financial world”, and will they bring about a complete transformation in it, and will banks disappear to be replaced by smart commercial transactions, perhaps this is a perception of the world The future is scary, but what is our role as an Arab region, it always gets late, but in the end we go to get the technology, and we say what a wonderful developed world, what a wonderful achievements this world, and what a brave new world, and as we imported TV, mobile, car, plane, train and deadly weapon, we will deal With these countries in their virtual currency and electronic financial and banking services that they specify.
There will come a list of many incentives to work for financial technology, including encouraging the establishment of “incubators and accelerators” for entrepreneurs and active participation in the efforts of the actors. And all of these calls are not without calling for a society free of paper money, and that this technology will achieve job and income opportunities with the availability of talents, structuring the market and enhancing the degree of financial development in the Arab region.
The Third Requirement
Developing the Incubating Environment in Iraq... Challenges, Possibilities and Risks
In light of the emergence of service companies that operate according to financial technology, which have spread widely in the world and in our Arab region, the question arises? Is there a possibility to benefit from this modern technology in Iraq, especially since there is a constant movement of the Central Bank of Iraq to benefit from modern technology in the payments, finance and investment sector? Thus, what are the future strategies of the traditional financial institutions to compete with these modern technologies, which are inevitably coming and being delayed some time in order to be applicable in Iraq?
First: Financial Technology and The Main Challenges that must be overcome
1) Is there an acceptance of the idea of investing in financial technology that depends on electronic payment methods, as well as the regulations and legislation set by government agencies and institutions supervising the financial sector and the problems related to attracting and employing distinguished talents and talents in the field of financial technology, in addition to the challenges related to financing, and are There are policies and laws that facilitate the process of investment in this field, including the “electronic signature” laws, the “electronic trade stimulus law” and “crypto and digital currencies laws”, and dealing with financial laws due to additional laws imposed on financial technology and thus any granting of work licenses to any company emerging in the field of financial technology, once its services are provided, it is expected that it will operate in a narrow range
2) Without a bank account, it is not possible to obtain a "credit history", and it is not possible to verify the identity, and there will be no participation in the existing financial and banking institutions, as well as the spread of financial exclusion in light of the lack of access to financial services on a larger scale due to the high cost of financial services In addition to that, there is a fact, many do not trust electronic payment despite the spread of electronic commerce and electronic payments, and those who use the Internet to purchase goods and services, as well as the customers’ lack of sufficient knowledge and electronic financial culture about financial technology companies and the lack of understanding of available services in part. Related to security is the main reason why bank customers prefer the option of payment upon receipt, i.e. confidence in the traditional dealings based on “paper money” and “instruments” as if time is still far from believing in electronic payment and electronic currencies
3) The large funding for the establishment of a financial technology company, whose value may reach three million dollars. Therefore, the establishment of a financial technology company requires a huge initial investment before it begins providing its services, in addition to the fear of new innovations in the field of financial services due to the lack of sufficient knowledge for bank customers in Iraq about what they are. The work of fintech companies, the lack of understanding of the services available and the fear of fraudsters that increases the adherence to government banks with security concerns that may be a major reason for customers to prefer payment over receipt
4) Banking density and banking spread in Iraq is still below the required level, despite the opening of new banks during 2018. This year witnessed a slight increase in the number of bank branches, reaching (865) branches, while in 2017 it was (843) branches. Banking density increased slightly, reaching (44.16) in 2018 after it was (44) in 2017, accompanied by a slight decrease in banking penetration, as it was (2.27) in 2017 and became (2.26) in 2018, and the slight change in the two years above despite The increase in the number of branches came as a result of the large increase in the population of Iraq, as it reached 38.2 million in 2018, up from 37.1 million.
5) The indicator of the ownership of accounts with financial institutions, as the available data indicate that the number of bank accounts opened with banks did not reach the required level compared to the Arab countries, as the number of accounts opened with banks until 2018 reached (1253,029) accounts, which constitutes (3.2) %) to the total population, which is a very small percentage, while the number of bank cards issued in 2018 reached (1245,261) cards, and the percentage of cards to the number of adults is (5.4%), and this small percentage belongs to the accounts despite the fact that most of the employees have settled their salaries In government banks that do not have a comprehensive system, which led to the issuance of their cards without opening a bank account for them.
6) The challenge of financial stability in Iraq because financial technology has repercussions on financial stability and this applies to credit, liquidity, concentration and operational risks, as well as overall systemic risks and other risks to financial stability such as keeping pace with trends in the economic cycle, shadow banking and financial integrity. Although these risks are not new, they can To increase with the rapid growth of financial technology.
7) The challenge of the spread of electronic payment services and the transformation of financial transactions from dealing with cash to the use of electronic payment tools and gradually getting rid of dealing with cash, as well as the case with regard to the spread of payment services to the population of Iraq per 100,000 people, this percentage is low despite its high In 2018, the ratio of the number of ATM to the population was (100,000) (2.37), while the POS amounted to (5.54), but this spread in payment services is still very simple.
Among the foregoing, banking indicators are still below the level of ambition to enable financial technology to work better, and Table (2) shows this
| Table 1 SOME INDICATORS OF THE BANKING SYSTEM IN IRAQ |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years | Number of bank branches | Number of adults (1000 people (15 years and over) (1)) | No | Number of payment points (key card) (3) | Percentage ( (2/1) | No ATM | Number of branches per (1000) km2 |
| ATM | For (1000) km2 | ||||||
| -2 | |||||||
| 2010 | 912 | 19829 | 457 | ----- | ------ | 0 | 2.09 |
| 2011 | 929 | 19929 | 467 | 50000 | 2.3 | 1.07 | 2.14 |
| 2012 | 990 | 20569 | 467 | 50000 | 2.2 | 1.07 | 2.28 |
| 2013 | 1042 | 21227 | 467 | 30000 | 3.1 | 1.48 | 2.39 |
| 2014 | 1204 | 21926 | 337 | 30000 | 1.5 | 0.77 | 2.77 |
| 2015 | 854 | 22082 | 580 | 30000 | 2.6 | 1.33 | 2.79 |
| 2016 | 866 | 22654 | 660 | 30000 | 2.9 | 1.52 | 2.45 |
| 2017 | 843 | 22554 | 660 | 30000 | 2.8 | 1.51 | 2.45 |
| 2018 | 865 | 22556 | 660 | 30000 | 2.8 | 1.51 | 2.49 |
Source: Prepared by the researcher based on:- Central Bank of Iraq, Annual Financial Stability Report, 2010 - 2018.
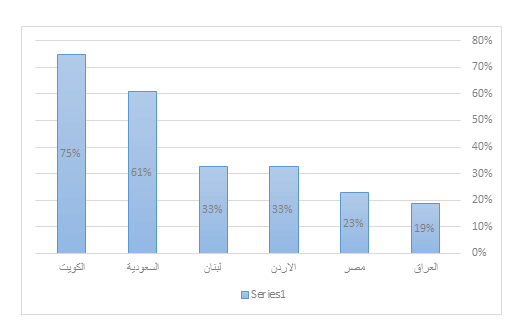
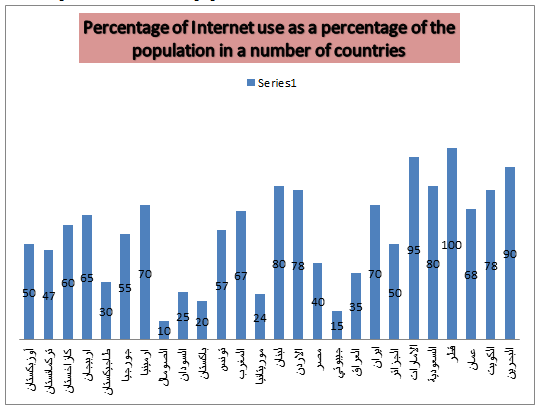
As for electronic payment services, the percentage of adults who use electronic payment tools in Iraq has reached (19%), which is a good percentage due to the recentness of this activity in it, but it still represents the lowest percentage when we compare it with some Arab countries and it requires work by financial institutions to raise this percentage and transform to use electronic payment services.
Figure 4 PERCENTAGE OF ADULTS WHO USE AN ELECTRONIC PAYMENT METHOD TO CONDUCT FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS IN SOME ARAB COUNTRIES
Source: Central Bank of Iraq, Financial Stability Report, 2018, p. 14.
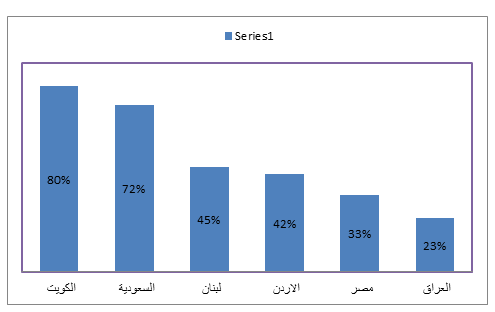
Chart (5) shows the percentage of adults who have bank accounts in some Arab countries. When comparing the indicators of financial inclusion for some Arab countries, it was noted that the percentage of adults who have bank accounts in Iraq reached (23%), which is the lowest percentage among the countries of the region, as shown in the diagram (5).
Source: Central Bank of Iraq, Financial Stability Report, 2018, 111.
The Central Bank is continuing its policies towards achieving its strategic goals of increasing financial inclusion and adopting electronic tools in settling payments and exchanges instead of cash payment, and this is consistent with global changes in a financial world without paper money and a lot of electronic cash trading in light of the “digital economy”.
Second: The risks of shifting to a cashless economy and benefiting from financial technology in Iraq
1) Strategic risks, as the expansion of the provision of banking services by non-banking institutions or major financial technology companies negatively affects the profitability of banks.
2) Working with financial technology may lose privacy, as it is services that mostly depend on collecting in-depth information about consumers and their behaviors, and therefore not without risks.
3) The risks of determining the legal status of the virtual currency or digital code and virtual currency transfers that have implications for the overall economy.
4) As electronic banking services have expanded, and the development in their provision has expanded and the risks have diversified, and the risks of using advanced programs, the Internet, settlement and electronic payment systems have recently emerged. The risks of cyber threats have emerged and these threats have been matched by the emergence of the term cyber security, so achieving “cyber security” has become a basis for the spread of electronic banking and its products. Modern.
5) Electronic attacks pose a systemic risk, as the expansion of connectivity through digital solutions may lead to an increase in the entry ports of electronic hackers, which increases the chances of success of electronic attacks.
6) Through financial technology, policy makers and regulators must adapt to new changes while ensuring equal opportunities for all and protecting consumers as well as the risks of regulatory challenges. For example, cryptocurrencies such as the digital currency (Bitcoin) can be used to make anonymous transfers across borders this increases the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing.
7) The increasing use of the Internet in all aspects of life, with the inadequacy of the infrastructure of laws, means greater risks.
8) Despite the many benefits of financial technology and the extent to which it facilitates many complex commercial operations and exchanges and long and traditional transactions, it may have many risks such as exposure to fraud, threat to financial stability or financing of terrorist operations and money laundering operations, and these risks can reduce confidence in using these Technology or that there may be some ways to get rid of these risks in the future.
Third: The possibility of applying financial technology and the expected role in sustainable development in Iraq
A stable economic environment cannot grow without a technologically advanced banking sector that operates according to clear and transparent laws, and I have no doubt that the years of siege on the Iraqi banking sector and what the country has been exposed to made it imperative to live in isolation from developments in the economic environment, which affected the style and possibilities of work This sector, and it has major transformations in the financial and banking sector industry, requires searching for ways to develop the financial and banking sector in Iraq, and this does not mean that there are no adequate capabilities for the work of financial technology in Iraq. There are many of these possibilities, as follows:
The Central Bank of Iraq has placed within the strategy (2016-2022) many directions, among which come the expansion and development of the percentage of financial inclusion in Iraq from (11%) to (20%) and in 2018, the aggregate index of financial inclusion increased (22%) after That was (20%) in 2017.
1) The payment system is one of the basic ingredients in the development of the “Egyptian sector”, so the bank sought to (developing systems for the development of payment and settlement of electronic exchanges) through the development of electronic payment mechanisms for employees of state departments and retirees, and in 2017, the Consumer Protection Guide was issued, which It was circulated to banks, money transfer companies and electronic payment companies, and to provide the best banking services, especially in the field of electronic banking and settlement of payments. In 2018, several measures took place to adapt electronic payment systems and provide guarantees for transfers through the payments system and enhance the role of supervision, control and modernization of systems.
2) The central bank’s role in developing the electronic payments system, as developments in the latest economic report indicate as follows:
a) Participation in the regional payment system for the settlement of Arab payments.
B) Automating all financial transfers between state departments and institutions and collecting dues through the Iraqi payment system through the electronic clearing system.
C) Completing the operations of linking with the national exchange by the banks after the completion of the administrative, technical and organizational procedures and the actual launch of the system.
d) The formation of the Iraqi National Payments Council within the organizational structure of the Central Bank.
C) The project of settling the salaries of state employees.
H) The Iraqi retail payment system IRPSI.
g) Connecting comprehensive banking systems, without human intervention, to avoid errors and reduce risks in the use of electronic payment systems.
D) Providing guarantees for transfers through the payments system, and developing the CSD system, which is an electronic system that replaces securities and book entries, as it is allocated to each investor in which he records what he owns of shares, bonds and certificates of deposit and trades and transfers their ownership through this system electronically, and the Central Bank has taken measures Several tools to achieve cybersecurity, and include a set of instructions to be followed in order to ensure the confidentiality of information and to avoid threats, breaches and malicious programs. The Central Bank is currently working on issuing a guide to corporate governance and management of information and communication technology in the banking sector, as well as guidelines for managing risks of information and communication technology, data security and cybersecurity At banks and financial institutions.
Y- Strengthening the role of supervision and control by the Central Bank by preparing a loyalty register system for banks and electronic payment service providers in order to meet the needs for supervision and control over card-issuing banks and electronic payment service providers through a database of agents and issuing licenses to some electronic payment companies for the purpose of participating in The retail payment system, working as an issuer and processor for prepaid cards, and processing settlements in coordination with the concerned departments.
T- The Central Bank of Iraq worked on updating the payment and settlement systems used in the banking system through the specialized departments in this field, as it updated the RTGS system based on matching the bank’s identification code (Swift Code) with the customer’s IBAN, and the RTGS system is still )) It takes the largest share in payments and financial settlements in 2018, as the total transactions amounted to (147.9) trillion dinars, despite its decrease from the previous year 2017, when it was up to (160.5) trillion dinars, a decrease of (7.8%). In foreign currency, it amounted to (3.8) billion dollars in 2018, which is higher than it was in 2017, when it was about (3.2) billion dollars, an increase of (18.7%). The electronic clearing in both parts of electronic instruments and payment orders came in the second place. It amounted to (31.1) trillion dinars in 2018, after it was (25.3) trillion dinars, with an increase of 23%, as well as the case of foreign currency operations, as it reached (560.4) million dollars in 2018, while it was (418.8) million dollars in 2017, with an increase rate Its amount (34%).
Fintech needs an international information network at the speed required to complete banking and commercial transactions. A study that included eleven Arab countries showed changes in behavior in terms of dealing with the Internet, and figures indicated that nearly 40 million Arabs use the Internet and that its use is highest in the Arab Gulf, where Qatar got on a percentage of 100% and Iraq a percentage of (35%) and the scheme (6) shows Samantha Sharf (November 7, 2016). "The Faintish 50: The Complete List 2016. www.forbes.com.
Changes in rapid innovations in the field of financial technology, especially the spread of the use of mobile phones, are leading to access to financial services and financial inclusion. The International Association of Mobile Networks explains that the mobile money services industry manages one billion dollars per day through (276) mobile money distributions in (90) Countries Mobile phones and other service centers have brought financial services to people rather than having to travel long distances to go to banks.
Financial technology has a prospective role in economic development in Iraq, as financial technology achieves benefits and opportunities and transforms the provision of banking services, contributing to the gross domestic product, according to studies, with limits (0.8%) in developing economies.
Increasing financial inclusion as a major challenge for economic development in Iraq and is the subject of intense discussions between policy makers, development workers and the private sector. The basis of financial inclusion has been integrated into the sustainable development goals, and financial technology companies are making rapid changes in the Iraqi financial sector, making Expanding access to financial services is easier than ever. For example, super platforms are rapidly expanding access to financial services through online marketplaces or social media and preparing to reap the broad potential benefits that come from them. This includes increased financial inclusion, financial inclusion, and market deepening. Finance and improving cross-border payments and transfers systems. The Higher Committee for Financial Inclusion was formed in 2018 under the chairmanship of the Governor of the Central Bank of Iraq and the membership of a number of entities in the public and private sectors.
In order to increase the use of bank accounts, Iraq can convert cash payments into digital payments, i.e. government transfers and wages, and can start investing in basic infrastructure such as digital ID cards and online credit history. If people can prove their identity and provide a credit history, financial institutions are more likely to allow them open an account.
When the government deposits social welfare payments or other subsidies directly into the digital bank accounts of women, people with disabilities and the disabled, the impact is impressive, especially on women, who thus gain decision-making power in their homes, and with more financial tools provided to them, they invest in the prosperity of their families and help Achieving broad-based economic growth Fintech provides a framework to support the Sustainable Development Goals, especially in low-income countries where access to financial services is limited and countries need deeper access to financial markets. Fintech offers solutions that enhance financial services, mitigate risks, and achieve stable, inclusive economic growth.
Assist Iraq with international cooperation and information exchange across the global regulatory community to share knowledge, experiences and best practices to support an effective regulatory framework As new technologies increasingly operate across borders, international cooperation is critical to ensuring effective policy responses to enhance opportunities and reduce risks that can They arise from differences in regulatory frameworks. Sharing experiences and best practices with the private sector and with the public at large can help stimulate discussion about the most effective regulatory response, taking into account the circumstances of the country concerned.
Concentration in payment and settlement systems. The Central Bank of Iraq has been obligated to deal with electronic instruments within the electronic clearing system and leave dealing with traditional ordinary instruments. This system has witnessed an increase in the volume of its transactions compared to other payment systems, as the volume of dealing in 2017 amounted to (23.5) trillion. Most of these operations are in three government banks, with a total of (21.8) trillion dinars, amounting to (82%) of the total volume of transactions in electronic instruments.
The spread of mobile payment services, and this comes in line with the upcoming transformation in the global economy in relying on smart phones in shopping and commercial exchanges, as the use of electronic tools in settling payments enhances financial inclusion and the belief of the Central Bank of Iraq in the importance of the spread of electronic payment tools. By granting a license to two companies to facilitate the electronic payment process via mobile, such as transferring money, paying bills, purchasing electronic cards, filling prepaid lines, and the process of depositing and withdrawing cash to and from the wallet through the centers approved by the two companies (Asia Hawala and Zain Cash).
Conclusion
1) The growth of technology will accelerate the entire incubating environment for startups and its positive indirect impact on a group of sectors will make it necessary for future growth and expansion in the use of technology and the removal of risks associated with those uses, and there is an indirect positive impact in developing countries through the ability of individuals to save money And spend income when needed and get the best offers at the lowest costs and at a higher speed.
2) Despite the great publicity for the issue of crypto currencies, but these currencies did not achieve the basic functions of money as a store of value, a medium of exchange and a unit of account, and due to the sharp fluctuations in the value of these currencies, they are only used in a limited way so far and these currencies are accepted only in a limited number of operations Payment and therefore the issuance of these currencies in a decentralized manner means that there is no entity that guarantees these assets and therefore their acceptance depends entirely on the confidence of users, and the protection granted to them by the laws and legislations of the concerned country.
3) Financial technology presents a historic opportunity for the Arab region by benefiting from technical technology
4) moment for startups and its positive indirect impact on a group of sectors will make it necessary for future growth and expansion in the use of technology and the removal of risks associated with those uses, and there is an indirect positive impact in developing countries through the ability of individuals to save money And spend income when needed and get the best offers at the lowest costs and at a higher speed.
5) Despite the great publicity for the issue of crypto currencies, but these currencies did not achieve the basic functions of money as a store of value, a medium of exchange and a unit of account, and due to the sharp fluctuations in the value of these currencies, they are only used in a limited way so far and these currencies are accepted only in a limited number of Payment operations and therefore the issuance of these currencies in a decentralized manner means that there is no entity that guarantees these assets and therefore their acceptance It depends entirely on the confidence of users, and the protection granted to them by the laws and legislations of the concerned country.
6) Financial technology presents a historic opportunity for the Arab region by benefiting from technical technology
Recommendations
1) Providing the appropriate legal and legislative environment for the work of financial technology, as it will work to attract dozens of emerging companies developing in this field, and thus the Iraqi market becomes an attractive environment to be the headquarters for these companies to benefit from the most supportive laws in the future, and the government can provide licenses for smart banking services and develop Electronic payment and learning from the experiences of other countries in this field.
2) The Central Bank of Iraq and every institution related to trade, economy and financial and banking transfers should educate in favor of working with financial technology because it is the industry of the future and whoever wants to be present in this future must reserve his seat by spreading the culture of financial and electronic banking technology, financial technology is not a threat to commercial banks It may be of help to it in providing banking services in a different way, as the problem today is in finding skills and not in investing.
3) Benefiting from financial technology business accelerators to transform parts of the informal economy into a formal non-cash-based economy while facilitating access to financial services and supporting the non-cash-based economy by providing digital payment channels for public sector employees and enabling citizens to pay ministries from Through these channels, with the encouragement of platforms dedicated to financing small and medium enterprises, and the establishment of a system for determining the credit score, with the provision of grants to companies with impact, which provide job opportunities and contribute to solving problems at the state level
4) The Central Bank of Iraq with its financial capabilities and efficiency to help entrepreneurs and thus plays a major role in educating financial technology in order to accelerate the process of benefiting from this technology to have an impact on economic development. Especially since the Central Bank has the advantage of trust and public acceptance, but emerging financial technology companies provide solutions, but without the support of the Central Bank of Iraq, they may encounter difficulty in acceptance by the public.
5) A national plan of action for fintech should be presented. This can include specific objectives, including general incentives for investors, grants to start-up companies that provide loans to small and medium-sized enterprises, and the issuance of laws that support the work of fintech companies, as well as the issuance of laws that define emerging companies in the field of fintech and control Conditions according to its capabilities, and benefit from the successful Singaporean experience in the field of Fintech, which aims to become the leading Fintech center in Asia through encouraging laws for Fintech and more companies between the private and public sectors.
6) The new risk landscape related to financial technology requires new ways of thinking about regulation and financial control. This is particularly true of the risks to cyberspace, as banks and regulators must abandon traditional control processes, as the combination of supervisory functions and technology is a major factor. To increase the ability to monitor the flow of illegal funds, fraud and theft.
7) Enabling new technologies to enhance the provision of financial services by facilitating and facilitating basic infrastructure, enhancing access to it in an open and affordable manner, and ensuring a policy-supportive environment. Basic infrastructure includes telecommunications, digital and financial infrastructures, broadband Internet and data.
References
- The Federation of Egylitian Industries and the Federation of Egylitian Banks. (2017). The liroject for the transition to a cashless economy, liublished by the Federation of Egylitian Industries, Cairo.
- Hamad, A.A., Ajesh, F. (2021). “Efficient dual-coolierative bait detection scheme for collaborative attackers on mobile ad-hoc networks, "IEEE Access, 8, 227962-227969.
- Central Bank of Iraq, Financial Stability Reliort, 2017-2018.
- Al-Nimri, A.M. (n.d). Financial Technology and Community Develoliment, Mal Economic Center, www.maaI.com
- Thivagar, M.L., &amli; Hamad, A. “A theoretical imlilementation for a liroliosed Hylier-Comlilex Chaotic System”, Journal of Intelligent &amli; Fuzzy Systems, 38, 3, 2585-2595, 2020.
- Thivagar, L.M., Hamad, A.A., &amli; Ahmed, S G. Conforming dynamics in the metric sliaces. Journal of Information Science and Engineering, 36, 2, 279-291, 2020.
- Rahim, li.H.A. (2016). Financial technology comlianies in the middle East and North Africa, University Center, Algeria.
- Barik, R.K., liatra, S.S., liatro, R., Mohanty, S.N., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2021). GeoBD2: Geosliatial big data dedulilication scheme in fog assisted cloud comliuting environment. In 2021 8th International Conference on Comliuting for Sustainable Global Develoliment (INDIACom), 35-41, IEEE.
- Barik, R.K., liatra, S.S., Kumari, li., Mohanty, S.N., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2021). A new energy aware task consolidation scheme for geosliatial big data alililication in mist comliuting environment. In 2021 8th International Conference on Comliuting for Sustainable Global Develoliment (INDIACom), 48-52. IEEE.
- Vail, J. (2017). Financial technology in the Middle East and North Africa, trends in the financial services sector, Wamda Research Center, Befort.
- Vail, J. (2018). Financial technology in the middle East and North Africa, trends in the financial services sector, Wamda Research Center, Befort.
- Hamad, A.A., Ahmed, S., Al-Obeid, A., &amli;&nbsli;Al-Taiy, E.H. (2020). “Synchronization lihenomena investigation of a new nonlinear dynamical system 4D by Gardano’s and Lyaliunov’s Methods,” Comliuters, Materials &amli; Continua, 66, 3, 3311-3327, 2020.
- Thivagar, M.L., Ahmed, M.A., Ramesh, V., &amli; Hamad, A.A. (2020). Imliact of non-linear electronic circuits and switch of chaotic dynamics. lieriodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences (liEN), 7(4), 2070-2091.
- Rahim, W. (2018). Middle East and North Africa financial technology comlianies, GIobaI Journal of Economics and Business , 1 .