Research Article: 2023 Vol: 26 Issue: 6S
How the Quality of Accounting Information System Impact on Accounting Information Quality Research on Higher Education in Bandung
Citation Information: Meiryani. (2023). How the quality of accounting information system impact on accounting information quality research on higher education in bandung. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 26(S6), 1-9.
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine how much influence the quality of accounting information systems on Accounting Information Quality in Higher Education in the city of Bandung-Indonesia. This study was conducted based on the facts on the research findings that indicate to the present system accounting information on the various organizational units not integrate well, yet safe to use, difficult to use, difficult to access, not flexible and efficient, and they often had problems/errors. Such conditions lead to dissatisfied users and applications the system is not used in the organization's activities. Furthermore, the condition of accounting information on the various organizational units in Indonesian not much different and it can be said not quality because accounting information cannot be presented timely, accurate and relevant, is not presented in full, it is not safe to use, difficult to access, the presentation did not follow the standards / guidelines and less can be understood by the various users. The method used is descriptive and explanatory research, with the number of samples used in this study was 37 Universities. Statistical testing using structural equation modeling (SEM) based component or a variance known as Partial Least Square (PLS) and test the hypothesis by using SPSS 2.0 for Microsoft Windows. The results showed the quality of accounting information systems significant positive effect on quality of accounting information on Higher Education in the city of Bandung, Indonesia.
Keywords
The Quality of Accounting Information Systems, Universities in Bandung Indonesia.
Introduction
Until now, quality accounting information systems cannot be fully applied to various types of companies in Indonesia. Not quality accounting information as yet integrated information system, accounting information system is still not safe to use, they found the inaccurate recording transactions, in addition to these conditions is still accounting information systems are inflexible and inefficient. The findings of fact stated by: Edward (2014); Sigit (2015); Primary (2015).
Accounting Information System is a collection (integration) of the subsystems/ components both physical and nonphysical interconnected and cooperate with each other in harmony to process transaction data related to financial problems into financial information Azhar (2013) , The integration of different components/sub-systems in Accounting Information Systems can fulfill three main business functions within an organization, namely: 1) AIS function in the collection and storage of data integreted with a variety of activities, resources, and employees in an organization, 2) AIS function in transforming data into information that can be used by management in planning, executing, controlling and evaluating a variety of activities, resources and employees of the company, 3) provides adequate control for save property and its data (Romney & Steinbart, 2015).
Accounting Information Systems produce accounting information (Bockholdt, 1999). Accounting Information Systems built with the main purpose to process financial data into the accounting information (Azhar, 2013).The system accounting information is designed to change the financial data with the aim to produce financial information that can be used as a basis for decision making (Bodnar & Hapwood, 2014). Accounting information systems provide added value to an organization by providing accounting information is accurate and timely (Romney & Steinbart, 2006).
Information is a powerful force for an organization (Baltzan, 2014). Information is an important resource for an organization (Bodnar & Hapwood, 2014). Information in all parts of the organization. The quality of information generated in an organization will affect every decision taken by the management or by the perpetrators of the organization (Azhar, 2013). Quality information is information useful in the decision making process (Gelinas & Dull, 2008). Furthermore Richardson (2014) state to be used in making decisions, the information generated from the accounting information system must have the properties/relevant and reliable. Marakas & O'Brien (2014) states the quality of accounting information can be described using the time dimension (information technology), content (content) and the format/form (form). That the quality of information can be explained by: time Dimension, Location Dimension and Dimension Form. Furthermore Gorla et al. (2010) classifies the quality dimensions of information into two groups: the content dimensions (content information) and Form dimension (format information). This study aims to reexamine how much SIA quality affects the quality of accounting information is carried out at universities in Bandung.
Literature Review
Accounting Information System
Accounting information system to record and process the transaction data is communication the financial and accounting information that can be used in decision making (Kieso et al., 2016). According to Romney & Steinbart (2015) accounting information system is a system that collect, record, store and process the data to produce information used in the decision-making process. Furthermore, Marakas & O'Brien (2014) states accounting information system is an information system that records and reporting the activities of business transactions and the flow of money/funds in an organization to further produced financial statements.
DeLone & Mclean (1992) uses the term success/effectiveness to demonstrate the quality of information systems. Anderson (2000) states quality information system is measured by the ability to provide information needed by the information systems manager at the time and Appropriate Appropriate. Furthermore, According to Deghanzade et al. (2011) the effectiveness of accounting information system is a condition of user satisfaction information in getting the desired information. In line with previous opinion in Azhar (2013) states Effectiveness of Information Systems is a condition of availability of information in decision making in accordance with the needed. Based on the various statements can be said that the quality / success / effectiveness of the accounting information system is a condition of satisfaction of users of information systems in accordance with the information that is needed in the decisionmaking process.
The quality of accounting information system according to Stair & Reynolds (2012) is the satisfaction of users of information systems and the valuable information generated. Furthermore Kieso et al. (2016) states the efficiency and effectiveness of the accounting information system refers to the principles of certain basic consisting of: cost-effectiveness, usefulness (efficiency) and flexible (Kieso et al., 2016). Seddon & Yip (1992) developed a model of the effectiveness of information systems by using five (5) dimensions: system quality, information quality perception of the level of use, user satisfaction and use of information systems. Baltzan (2015) to measure the quality of accounting information systems in viewpoint: usability, user satisfaction, the rate of change (flexibility), and finance (financial). In a deeper study Stair & Reynolds (2012) states the size of an effective information system is the condition of User Satisfaction (user satisfaction) systems as well as the condition of a system that can receive and use (system use) by an organization. Furthermore Bockholdt (1999) states that the accounting information system of quality if the achievement of objectives in generating accurate and timely, sensible use of time in its development (efficient), meet the needs of the organization and giving satisfaction to the users. In this study the quality of accounting information systems are limited to the dimensions of the use of information systems and user satisfaction system to the desired information.
Quality of Accounting Information
Information by Romney & Steinbart (2015) is the Data that has been organized and processed to give meaning to the user. Users need the information to the make decisions or improve the decision making process. Gelinas & Dull (2008) describes the notion of information as follows: Information is the data is presented in a form that is useful in decision making activities. In line with various previous opinions Kenneth & Jane (2014) states the information is the data that has been shaped into something that has meaning and useful for users. Likewise with the views Expressed by Azhar (2013) The information is the result of the data processing that Gives meaning and benefits for the user. Based on various definition that has been presented, it can be concluded that the information is the data that has been processed that has meaning and useful for a variety of users.
Valuable information/quality and can be used in decision making should have the characteristics/traits of certain (Stair & Reynolds, 2012). A high quality product information information own characteristics, attributes or quality that makes information more valuable to those who use (Marakas & O'Brien, 2014). Quality information is the right information (relevant) for use (Eppler, 2013). Gelinas & Dull (2008) measures the quality information through the information available in a timely and correct information/accurate (integrity). Hall (2011) states quality information must have the properties/attributes are relevant, accurate, complete, Concise, and timely. Furthermore, Romney & Steinbart (2015) states that information useful characteristics/quality are: relevant, reliable, complete, timely, easily understood, easily accessible, and can be verified. Valuable information/quality According to Stair & Reynolds (2012) must have the characteristics: easily accessible, accurate/precise, complete, economical, flexible, relevant, reliable, safe, simple, and available timely, and verifiable.
Framework and Hypotheses
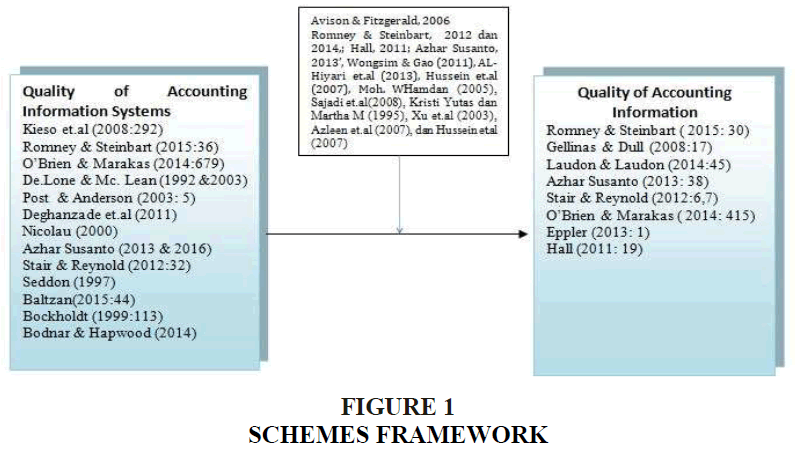
Information systems within an organization to function in processing and providing information that can be used in the process of making decisions information systems produce high quality information that can be used a variety of users to be Able to do a variety of tasks more Effectively and efficiently (Hall, 2011). Accounting information system is built with the main purpose to process the data into accounting accounting information needed by a wide range of users to reduce risk when making decisions (Azhar, 2013). An accounting information system can improve the decision making process by providing information to provide accurate and timely (Romney & Steinbart, 2012). Results of research conducted by previous Researchers Showed consistently empirical evidence that the quality of accounting information systems Affect the quality of accounting information on the various organizational units worldwide. Research conducted by Wongsim & Gao (2011), AL-Hiyari et al. (2013), Hussein et al. (2007), Hamdan (2012), Sajadi et al. (2008); Azleen et al. (2007), and Hussein et al. (2007) Provides empirical evidence there is a significant positive effect between the quality of accounting information system on the quality of accounting information Figure 1.
Research Methodology
This research method using descriptive and explanatory research. The study population as many public and private universities in Bandung as many as 60 universities with a sample of 37 universities selected by probability sampling methods. Validity Test performed to Determine the feasibility of variable and reliability tests to measure the reliability of the measured object. Descriptive analysis of data was done by using a score Categorization inter quartile range (Cooper & Schindler, 2006). Analysis of verification are used structural equation modeling (SEM) based component or a variance known as Partial Least Square (PLS).
Results
Testing the validity and reliability
All measure to the variable quality of the information system Accounting and Accounting Information Quality variable declared invalid Because value tcount> 0:30 so it can be concluded that the measuring tools such as questionnaires statement has had a good level of validity (appendix). Based on research data reliability test results good for two variables (quality of accounting information systems and quality of accounting information) indicates that tcount more value of greater than 0.7 can be concluded the statement questionnaire as a measure of the variables used are reliable (Recapitulation in the annex).
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation model for the effect of Accounting Information System Quality Information Quality on calculated using SEM approach Partial Least Square (PLS) as follows:
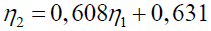
Testing Measurement Model (outer model)
Convergent validity: The results based on Table 1, show dimension user satisfaction and system usage has been appropriately used as a model for the measurement of the variable quality of accounting information system.
| Table 1 Measurement Model Accounting Information Systems Quality Variable | |||
| Manifesto variable | Loading Factor | measurement Model | thitung |
| User satisfaction (X1) | 0,916 | Y1= 0,916 Y+ 0,162 | 49,807 |
| System Usage (X2) | 0,942 | Y2= 0,942 Y+ 0,112 | 65,868 |
Furthermore, based on Table 2, it can be concluded all eight indicators used was appropriate to represent the dimensions of the measurement model variable quality of accounting information systems (Values tcount more than 1.96).
| Table 2 The Measurement Indicator of Dimensional Models The Variable Quality of Accounting Information Systems | |||
| Manifesto variable | Loading Factor | measurement Model | thitung |
| X1.1 <- X1 | 0,7679 | Y11= 0,7679 X1+ 0,410 | 13,1839 |
| X1.2 <- X1 | 0,7707 | Y12= 0,7707 X1+ 0,406 | 11,5414 |
| X1.3 <-X1 | 0,7990 | Y13= 0,7990 X1+ 0,362 | 14,3516 |
| X1.4 <- X1 | 0,7008 | Y14= 0,7008X1+ 0,509 | 12,3391 |
| X2.1 <- X2 | 0,8422 | Y21= 0,8422X2+ 0,291 | 17,9928 |
| X2.2 <- X2 | 0,8164 | Y22= 0,8164X2+ 0,333 | 14,6540 |
| X2.3 <- X2 | 0,7895 | Y23= 0,7895X2+ 0,377 | 10,5291 |
| X2.4 <- X2 | 0,7545 | Y24= 0,7545X2+ 0,431 | 11,2357 |
Based on Table 3 show dimension time, content, location and form and usage system has been appropriately used as a model for the measurement of the variable quality of accounting information (see Table 3 loading factor value of more than 0.6).
| Table 3 Measurement Model Variables Accounting Information Quality | |||
| Manifesto variable | Loading Factor | measurement Model | thitung |
| Time Dimension (Y1) | 0,922 | Y1= 0,922 Y+ 0,150 | 35,198 |
| Content Dimension (Y2) | 0,907 | Y2= 0,907 Y+ 0,177 | 30,506 |
| Location Dimension (Y3) | 0,848 | Y3= 0,848 Y+ 0,280 | 20,635 |
| Form Dimension (Y4) | 0,818 | Y4= 0,818 Y+ 0,330 | 14,992 |
Furthermore, based on Table 4, it can be seen indicators, timelines, time period, accuracy, relevance, completeness, accessibility, security, clarity, and presentation exactly represent the dimensions of the measurement model variable quality of accounting information systems ( t values more than 1.96 ).
| Table 4 Measurement Models to the Dimensions Indicators Accounting Information Quality Variable | |||
| Manifesto variable | Loading Factor | measurement Model | thitung |
| Y.1.1 <- Y1 | 0,897 | Y11= 0,897 Z1+ 0,196 | 35,162 |
| Y.1.2 <- Y1 | 0,878 | Y12= 0,878 Z1+ 0,229 | 16,683 |
| Y.2.1 <- Y2 | 0,881 | Y21= 0,881 Z2 + 0,224 | 34,423 |
| Y.2.2 <- Y2 | 0,821 | Y22= 0,821 Z2+ 0,325 | 8,176 |
| Y.2.3 <- Y2 | 0,682 | Y23= 0,682 Z2+ 0,534 | 7,844 |
| Y.3.1 <- Y3 | 0,789 | Y31= 0,789 Z3+ 0,378 | 13,126 |
| Y.3.2 <- Y3 | 0,884 | Y32= 0,884 Z3+ 0,218 | 28,718 |
| Y.4.1 <- Y4 | 0,894 | Y41= 0,894Z4+ 0,201 | 20,640 |
| Y.4.2 <- Y4 | 0,905 | Y42= 0,905Z4+ 0,181 | 20,640 |
Discriminan validity
Discriminant validity results Table 5, shows the construct has met the minimum value for AVE good construct more than 0.5.
| Table 5 Value Average Variance Extracted (AVE) Latent Variables | |
| Variabel laten | AVE |
| Quality of Accounting Information Systems | 0,5236 |
| User satisfaction (X1) | 0,5783 |
| System Usage (X2) | 0,6421 |
| Quality of Accounting Information | 0,5556 |
| Time Dimension (Y1) | 0,7876 |
| Content Dimension (Y2) | 0,6388 |
| Location Dimension (Y3) | 0,7019 |
| Form Dimension (Y4) | 0,8093 |
Composite Reliability
Based on Table 6 it can be concluded that all constructs reliably meet the criteria (composite value reliability above 0.70). This means that the latent variable quality of accounting information system (X) and the Quality of Accounting Information latent variable (Y) have consistently high.
| Table 6 Latent Variable Value Composite Reliability | |
| Variabel laten | Composite Reliability |
| Quality of Accounting Information Systems (X) | 0,8974 |
| User satisfaction (X1) | 0,8455 |
| System Usage (X2) | 0,8775 |
| Quality of Accounting Information (Y) | 0,9176 |
| Time Dimension (X1) | 0,8812 |
| Content Dimension (X2) | 0,8400 |
| Location Dimension (X3) | 0,8243 |
| Form Dimension (X4) | 0,8946 |
Hypothesis Testing
The first hypothesis testing results show that the relationship variables influence the quality of accounting information system with the quality of accounting information indicated by the path coefficient of 0.608 with tcount of 5.257. Scores t-statistic is greater than tcritical (1,960) Table 7, which means that the quality of accounting information systems affect the quality of accounting information.
| Table 7 Significance Test of Influence Effectiveness of Accounting Information Systems on the Quality of Accounting Information | |||
| Coefficient | t Path | t Critical | Conclusion |
| 0,608 | 5,257 | 1,96 | Significant |
The amount of influence the quality of accounting information system of the quality of accounting information is the amount of (0.608 × 0.608 × 100%) = 36.9%. This means that the quality of accounting information systems give 36.9% influence on the quality of accounting information if there are no other variables are considered.
Discussion of Results
Based on the results of this research are known causes of system accounting information is not quality Because it is the caused by Several factors are as follows: accounting information system available on the company yet flexible, not easy to use, difficult, to access, it is not safe , yet well-integrated and Often have error / interference (Azhar, 2016). Based on the results of research It is also known Accounting Information Quality in higher education in the city can be said to be inadequate. Results responder indicate that until now there is still a college financial reports (accounting information) is not timely, the information content of accounting incomplete accounting information is not safe to use and difficult, to access, there are presentation of accounting information roommates does not follow the standards / guidelines as well as the format less can understand it by various users. The amount of influence on the Quality of Accounting Information Systems Accounting Information Quality is 36.9% with the direction of positive relationships, meaning that with the quality of accounting information systems that will improve the quality of accounting information on the company. Hypothesis testing results showed that the quality of accounting information systems have a significant effect on the quality of accounting information. Upon the acceptance of the research hypothesis, the study reinforces the theory and the results of previous research proposed by Romney & Steinbart (2012); Hall (2011); Azhar, (2013); Wongsim & Gao (2011); AL-Hiyari et al. (2013); Hussein et al. (2007); Hamdan (2012); Sajadi et al. (2008); Azleen et al. (2007), Hussein et al. (2007).
Conclusion
The study concluded that the quality of accounting information systems Affect the quality of accounting information. Not to quality accounting information systems at universities in the city due to the accounting information system is not flexible, difficult, to use, difficult, to access, it is not safe, yet well-integrated and Often has an error / interference. Based on the research findings in mind Also the quality of accounting information on higher education in the city has not adequately because accounting information presented is not timely, incomplete, not safe to use, difficult, to access, the presentation did not follow the standards / guidelines and less can be understood by the various users.
Suggestion
Results of this study was to answer the problems noted earlier in the background of research, but there are some things that need to advise in respect of these results shows little effect among value variables studied. As for suggestions that will be presented are as follows:
Practical Aspects (Troubleshooting)
a) To anticipate the re-emergence of the same problems associated with not quality information systems Accounting, universities in Bandung recommended in order to: Increase user satisfaction (user satisfaction) and the use of accounting information systems (system usage) by designing an accounting information system that is more flexible, has a data processing that is well integrated, secure and easy to use (user friendly).
b) The availability of quality accounting information can be realized by presenting the accounting information with the content and form (format) in accordance with guidelines / applicable accounting standards.
Theoretical Aspects (science development)
The results of this study are expected to be used as a reference for further research (replicability), increased confidence in the research that has been done (precision and confidence) as well as the applicability of the results to be widely accepted (generalizability). The suggestions can be put forward for the developments of science are:
a. The researchers then expected to add to the sample in order to obtain a more optimal research results.
b. The researchers then used the research units / locations with different research used in this study thus strengthening support for the linkage theories have been put forward by experts earlier.
c. The researchers then expected to conduct research using test equipment for statistically different to the one used in this study in order to test a theoretical model that is used whether it will produce the same effect when tested using different statistical testing techniques.
References
Al-Hiyari, A., Al-Mashregy, M.H.H., Mat, N. K., & Alekam, J.E. (2013). Factors that affect accounting information system implementation and accounting information quality: A survey in University Utara Malaysia. American Journal of Economics, 3(1), 27-31.
Anderson, D.L. (2000). Management information systems: Solving business problems with information technology. McGraw-Hill, Inc..
Azhar, S. (2013). Accounting Information Systems. Lingga Jaya, Bandung.
Azhar, S.(2013). Management Information Systems (Structured Approach - Risk Development). Lingga Jaya, Bandung.
Azhar, S.. (2013). Information Technology for Business & Accounting. Lingga Jaya, Bandung.
Baltzan, P. (2014). Business Information System. 4th Edition. Mc. Graw-Hill International, USA.
Baltzan, P. (2015). Business Driven Technology. 6th edition. Mc.Graw-Hill International, USA.
Bodnar, G.H., & Hoopwood. W.S.(2014). Accounting Information Systems. Pearson Education Limited, USA.
Cooper, D.R., & Schindler, P.S. (2014). Business Research Method. Twelfth Edition. Singapore: Mc. GrawHill.
DeLone, W.H., & McLean, E.R. (1992). Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Information Systems Research, 3(1), 60-95.
Edward, S. (2014). Lion Air Ready to Bring Airport Tax in Ticket.
Eppler, M. (2013). Managing Information Quality. Springer Berlin Heidelberg Germany.
Gelinas, U.J., & Dull. R.B. (2008). Accounting Information System. Seventh Edition. Canada: Thomson South-Western a part of The Thomson Corporation
Hall, J. A. (2011). Accounting Information System. Seventh edition. South Western Cengage Learning, USA.
Hamdan, M.W. (2012). The impact of accounting information systems (AIS) development life cycle on its effectiveness and critical success factors. European Scientific Journal, 8(6), 19-32.
Hussein, R., Shahriza Abdul Karim, N., & Hasan Selamat, M. (2007). The impact of technological factors on information systems success in the electronic‐government context. Business Process Management Journal, 13(5), 613-627.
Kenneth C.L.N., & Jane P.L. (2014). Management Information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm Thirteenth Edition.
Kieso, D.E., Weygandt, J. J., & Warfield, T. D. (2016). Intermediate accounting. John Wiley & Sons.
Marakas, G.M., & O'Brien, J.A. (2013). Introduction to information systems . 624.
Primary, D.P. (2015). Information System in Indonesia Not Safe.
Richardson, A. (2014). Accounting Information System. Mc.Graw-Hill International, USA.
Romney, M.B., & Steinbart, P.J. (2015). Accounting Information Systems, Thirteenth Edition. Pearson Education, USA.
Romney, M.B., & Steinbart, P.J. (2006). Accounting Information Systems, Tenth Edition. Pearson Education, USA.
Romney, M.B., & Steinbart, P.J. (2012). Accounting Information Systems, Twelfth Edition. Pearson Education, USA.
Sajady, H., Dastgir, M., & Hashem Nejad, H. (2008). Evaluation of the effectiveness of accounting information systems. International Journal of Information Science and Management (IJISM), 6(2), 49-59.
Seddon, P., & Yip, S.K. (1992). An empirical evaluation of user information satisfaction (UIS) measures for use with general ledger accounting software. Journal of Information Systems, 6(1).
Sigit, H. (2015). Minister of Religion Want entire Satker Integrated Information System.
Stair, R.M & Reynolds, G. (2012). Fundamentals of Information Systems.Sixth edition. Cengage Learning, USA.
Wongsim, M., & Gao, J. (2011). Exploring information quality in accounting information systems adoption. Communications of the IBIMA.
Received: 17-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. AJEE-23-13498; Editor assigned: 19- Apr -2023, Pre QC No. AJEE-23-13498(PQ); Reviewed: 03- May-2023, QC No. AJEE-23-13498; Revised: 25-Jul-2023, Manuscript No. AJEE-23-13498(R);Published: 01-Aug-2023