Research Article: 2019 Vol: 22 Issue: 4
Human Capital Strategy Model for Improving Business Unit Performance, Based on Environmental Turbulence, Strategic Leadership and Organizational Culture (A Survey on Unit Business Indonesian Telecommunication Operator)
Dwi Heriyanto Budisusetio, Universitas Padjadjaran
Ernie Tisnawati Sule, Universitas Padjadjaran
Erie Febrian, Universitas Padjadjaran
Yunizar, Universitas Padjadjaran
Abstract
Performance of the business unit of some telecommunication operators in Indonesia is decreasing their income, especially some of the business unit of the legacy products (voice calls and sms) and connectivity (VPN, IP, leased line). Turbulent telecommunication business environment in Indonesia, especially from the tight competitive turbulence it shows that there is a price war for some products especially in the cellular business. The turbulent disruptive environment also decreasing the unit business performance. This situation signed with there is replacement product ‘Over the Top (OTT)’ business. Strategic leadership is good in transforming from a telecommunications company to a digital company, a good organizational culture, entrepreneurship and also the right strategy of human resources from a telecom operator's business unit so as to improve the performance of business units.
The purpose of this research is to find out the impact of the environmental turbulence, strategic leadership, culture of the organization to the Human Capital Strategy. The unit analysis in this research is in business unit in the five of big telecommunication operators in Indonesia. The observation has done to 190 surveys that determined by Partial Least Square-Path Modelling (PLS-PM) technique.
The result of this research revealed that turbulent telecommunication business environment in Indonesia is in the high category. Variable strategic leadership operator business unit in the good category, organization culture in the good category and has an impact to the variable Human Capital strategy.
This research resulting the model of Human Capital strategy DWI Model, with Human Capital strategy model that consist from delivering great people, Work on great culture and Integrating great organization.
Keywords
Environmental Turbulence, Strategic Leadership, Entrepreneurship, Organization Culture, Human Capital Strategic, Unit Business Environment, Telecommunication Operator in Indonesia.
Introduction
Business environment with the situation that change quickly and not always caused a company must stays in leading the competition. A company that can grow continuously is a company that has an ability to be quick responsive in the culture replacement (Altschuller et al., 2010), increasing the ability in staying in the high competition, doing variation to stay survive, can adapt and can creating an organization that be adapted with external environment condition (Ansoff et al., 2018). Even the senior executive said that challenging in directing a company that turbulent (Haenlein & Kaplan, 2004), signed with a quick innovation, a short product age, and a short plan time.
In fact, telecommunication services have moved to the digital services signed by the decreasing of telecommunication business market and the increasing of the digital business market. TIMES (Telecommunication, Information, Media, Edutainment and Services) market globally since 2014 to 2021 be predicted would experience Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) 3.2%, with composition: 1% CAGR Telecom, 3% CAGR ICT, 2% CAGR Traditional media, 9% CAGR Digital Services.
TIMES (Telecommunication, Information, Media, Edutainment and Services) market in Indonesia from 2014 to 2021 be predicted would experience 12% CAGR, 8% CAGR Telecom, 14% ICT, 9% Traditional Media, and 33% Digital Services.
According to face the condition of the technology development and the market competitions, Telecommunication Company does any ways to always able to do their best work above average of the industry. Telecommunication company should create their best in competing products that they offer to their customers and also should have more benefit to the competitors (Walker and and Madsen, 2016).
Literature Review
Environmental Turbulence
Environmental turbulence is a situation in the external environment that shows there is a mess, hyper competition market, difficult and complicated environment. The non-market is so important and the company should consider their internal environment process and also their external environment process. Environmental turbulence is an environment that is the most dynamic with the biggest uncertainty. When replacement happens so the elements in the environment are connected to each other.
Based on the definitions above, can be identified that the characteristics of turbulence are: there is the uncertainty, rapid change, unpredictable, complexity environment. Consider to the definition of environmental turbulence and any opinions above that adapted to the situation and condition of the telecommunication business environment in Indonesia, so that concept of environmental turbulence in this research can be definite as an external environment condition (market, competition, technology, regulation) that uncertain, fast change, mess and hard to be predicted and also signed by the fast change that impact disruptive to the business and if being used so that can be an opportunity.
Strategic Leadership
Boal & Hooijberg (2001) said that a strategic leadership focus in creating the meaning and purpose of the organization. So that the strategic leadership related to the development of the organization over all that included purpose in change (Selznick, 2011). While Duignan (2004) said that there are five capabilities to create a unity of meaning from an effective leadership. Five of these capabilities are:
1. Educational capabilities
2. Personal capabilities
3. Relational capabilities
4. Intellectual capabilities
5. Organizational capabilities
Considering the definition of strategic leadership and any opinions above that already customized with the condition of strategic leadership in telecommunication business unit in Indonesia, so the concept of strategic leadership can be explained as a strategic leadership that happen in the disruptive condition, is the condition when there is a structure change in the same business model that completely different with the existing business model, so the strategic leadership must have the ability in decide the vision (envisioning), is able to create future vision from digital transformation, get the employee evolvement (engaging), with the coordination (collaborations), do the priority scale (prioritizing), through the synchronization and aligning strategic initiatives, sharing concept, using the excellence of digital technology (digital leadership) and doing the disruptive innovation leadership is an innovative leadership.
Organization Culture
Culture is seen as one of the important element that can help the organization to anticipate and adapt to the environment change and safe the performance to get the success of long-term economic performance (Kotter & Heskett, 1992). From that definition we can get the definition that organization culture especially be seen as behaviour. This situation also explained by Schein (2010) that the definition of organization culture is a basic assumption pattern that lived together with a group of people when they learn how to solve the problems in the external adapt and internal integrated, that works effective enough so can be valid. Schein’s definition realizing us that the key in understanding the organization culture is the right definition about socialization process a learning process of the values and the behaviour pattern.
Schermerhorn et al. (2011) said that organization culture or company culture is a system of value behaviour together, and belief that develop in the organization and guide the behaviour of member in the organization. While, Leung et al. (2005) said that organization culture is the thing related to the employee’s perceptions and how this perceptions can create a pattern of belief, value, and hope.
Considering the definition of organization culture from some definitions above that already adapted to the organization culture of telecommunication business in Indonesia, so the concept of the organization culture can be explained as a basic belief or basic philosophy from an organization that consists in core values that became the guidance of the leaders and employees in an organization and be seen from the key behaviour of the leaders and employees. The characteristic of key behaviour can be totally different, named disruptive culture.
Human Capital Strategy
Strategy human capital is really useful in the practice of human resource management to get or keep the competitive advantage. Talent acquisition, talent deployment, talent development, and rewarding talent is very useful to the approach of human resources management (HRM) strategy that can affect the organization ability to reach the goals.
Because the business strategy affecting the HRM plans and policies, consideration related to the HRM problem should be part of the process of formulating strategy.
HR strategy can be contributed to make HR get the organization effectively and competitive advantages and how SDM contribute more maximum to do. So that, HR should involve in putting the strategy that affecting and affected by people.
Considering the definition of human capital strategy from some of the opinions above that adapted to the human capital strategic condition as a strategy that related to the human capital life cycle (people), is the process of human capital from recruitment, selection, improvement, measurement of the employee performance, till retired, and related to the culture activities and related to the company organization, that can give direction to the company in improving human capital, through the human capital practices and measurement and can be communicated effectively so that can reach the goal of the organization.
Business Unit Performance
Business unit performance based on Kaplan & Norton (1996) divided in four aspects of scoring, started from learning and growth, internal business process, customer aspects and financial aspects. The fourth aspects that already designed by Kaplan and Norton known with the name Balanced Scorecard. In the balanced scorecard, started from the improvement of steps that is the performance driver that started from human capital element, to get the company goal so human capital should prepared and improved first.
Balanced scored including the finance steps that tell the result from the actions that already taken. And that also competing the financial steps with operational steps at the consumer satisfaction, internal process, and the innovation and also the improvement of the operational steps at the operational steps at the consumer satisfaction, internal process, and innovation and also improvement steps that be a financial performance driver in the future the operational organization activities.
Theoretical Framework and Hypotesis
Theoretical Framework
Environmental turbulence that be characterized with the uncertainty condition (Choo & Auster, 1993) and a mess is a thing that cannot be left behind in the business people. Boal & Hooijberg (2001) said that strategic leadership focusing in the creation of meaning and the goal of the organization. In the process of creating a meaning and goal of the organization should consider the external aspect as the change of business environment, market location and technology. Jiao et al. (2013) said that in the environment that turbulent, a company in this case a strategic leadership or unit business leader should always keep doing the repeat configuration to the human resource and internal capability to keep the continuity of the excellence in competing so that founded the best performance. Technology turbulence and market affecting the impact of company innovation to the business performance. Technology turbulence gave the positive impact to the innovation that also has the positive impact to the business performance. In the same line with that, market turbulence, market turbulence can strengthen the relationship of company innovation (Tsai & Yang, 2014).
Environmental turbulence that flare up widely has impact that destroy the performance of the business unit in the company. Environmental turbulence has a negative relationship in the company performance that means that the bigger of environmental turbulence so that unit performance is more decrease. A company demanded to take a policy that still using the old strategy or create a new strategy so that cannot get the bad impact from environmental turbulence (Boyne & Meier, 2009).
Human capital strategic is a mediator among the values in the company and the employees. While, the culture of the company is much related to the strategies and outcome from the company. In this situation, Wei et al. (2008) found that a company culture is an antecedent from human capital strategic that transfers the impact of company culture to the business performance. In simple way, human capital strategic gives the structural directions in the company culture implementation to get the performance that wanted (Bowen & Otroff, 2004: Tsui et al., 1997). Beside role as a driver in the company culture implementation, human capital strategic is also able to be an equipment to drive the culture cultivate. Rowden & Ahmad (2000) said that SHC can takes a part in developing the company culture as a part that cannot be separated from the overall of company strategies.
Human capital strategy accommodating the achievement of the relation between corporate strategy and the implementation of human capital practical aspect. The existence of human capital strategic gives the direction to the human capital management to design the human capital program that has a direct impact to the business performance. The same way with this, Besma (2014) said that statistic has proven that the more higher the adopt of human capital in an organization, so that more better the organization performance. Becker & Huselid (2006) then found that human capital strategic gives the direct impact to the business unit performance.
Hypothesis
After get done with the literature review then formulated be a framework and can be arranged became hypothesis is a temporary presumption from the cases that already identified. Hypothesis from this research are:
H1: High impact of environmental turbulence (X1), good strategic leadership (X2), good organization culture (X3), the right human capital strategic (Z) and a good business unit performance (Y) in the business unit of the operator telecommunication in Indonesia.
H2: There is an impact of environmental turbulence (X1), strategic leadership (X2), organization culture (X3) to the human capital strategic (Z), simultaneously or partially in the business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
H3: There is environmental turbulence impact (X1), strategic leadership (X2), organization culture (X3) to the business unit performance (Y), either simultaneously or partially in the business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
H4: There is an environmental turbulence impact (X1), strategic leadership (X2), organization culture (X3) through human capital strategic (Z) to the business unit performance (Y) in the business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
H5: There is an impact of human capital strategic (Z) to the business unit performance (Y) in the business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
H6: The result of the research found that there is a model of human capital strategic (Z) comprehensive that able to increase the business unit performance (Y) in the business unit of the telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
Methodology
This research is using the mixed method research (MMR) approach. Creswell & Creswell (2017) said that MMR approach is a research method that involved the data collect, analysis, and the integrating of qualitative and quantitative research in the study. Based on the data from business unit in five telecommunication operators, there are 55 business units with 190 surveyors in the level of head of unit, in accordance to the portfolio of telecommunication products that will be the target of population in this research. Survey data taken on 2016 and the size of the minimum sample to test the research model.
Quantitative research using two kind of analysis, descriptive analysis and verificative analysis. Descriptive analysis is a research that purpose to get a picture or description about the situation or condition of the research variable with seeing the environmental turbulence variable, strategic leadership, organization culture, human capital strategic and unit business performance in the telecommunication industry companies in Indonesia. And verificative analysis is a research to find out the relationship among variables through a hypothesis test based on data in the field (Cooper et al., 2006).
Descriptive analysis done by the descriptive survey method, is a data collect that done to the object in the field with using questionnaire as a tool to collect the main data, then can be measured the stag of criteria of the variables that investigated in the business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia. Then for the practice of verificative analysis, explaining the causal relationship among variables through the hypothesis test so the method that be used is the explanatory survey.
Consider about the purpose of this research is to measure how much the impact of the model of human capital strategic and the performance of business unit of telecommunication industry in Indonesia to the change of environmental turbulence, strategic leadership and the organization culture that is a dependent variable, and measure the relationship between latent variable with the indicator that observed or variable manifest, also called as measurement models. Then, with consider the purpose of research to explain the relationship among constructs (laten variable) and emphasize the definition of value of that relationship, so the analysis tool that used as an approach in the modelling and solution technique is partial least square (PLS)-path modelling (PM)
Analysis and Result
Environmental Turbulence Condition, Strategic Leadership, Organization Culture, Human Capital Strategic and the Performance of Business Unit of Telecommunication Operator in Indonesia
High environmental turbulence business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia
• Good strategic leadership business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
• Good organization culture business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
• Right human capital strategic business unit of telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
• Good business unit performance of the telecommunication operator in Indonesia.
Result of the research shown that those variables above show that the average of the variables is from 3, 4, t more than t table, so the hypothesis (H0) rejected. That means that the hypothesis statement (H1) approved that the environmental turbulence is high, strategic leadership is good, organization culture is good, human capital strategic is right and the business unit is good at the telecommunication business in Indonesia can be approved.
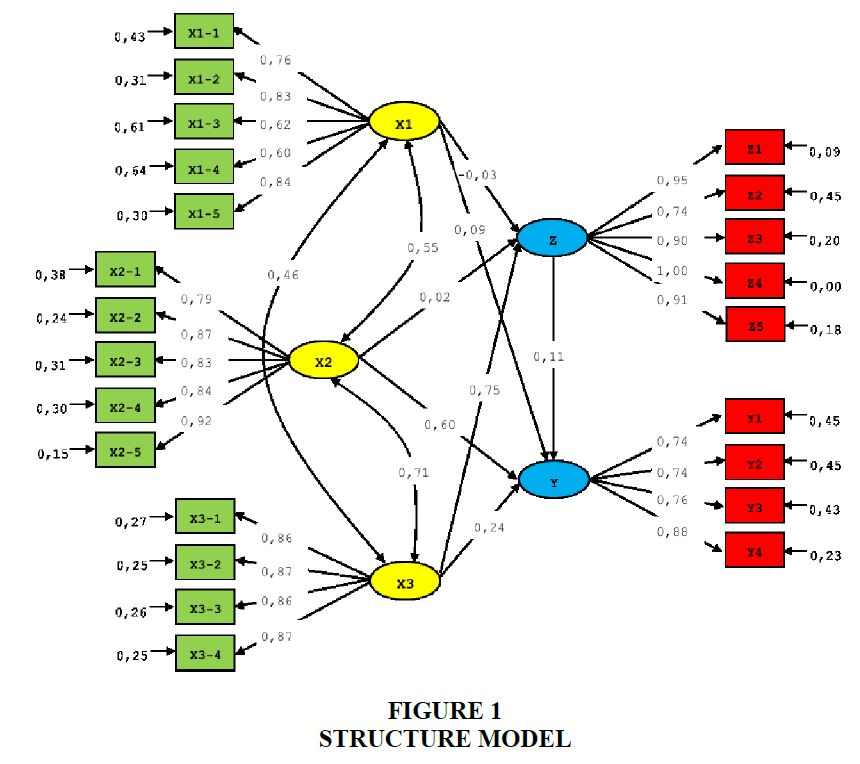
P value>0.05 so that can be concluded that the research model is Fit. Result Goodness of Fit Index (GFI) and Adjusted GFI<0.90 and RMSEA or RMR>0.05, so that can be concluded that the research model already suitable with the empirical condition (Figure 1).
Based on the structure model in this research so found the equation below:
Z=-0.03*X1+0.02*X2+0.75*X3, Error vary=0.44, R2=0.56
(0.068) (0.086) (0.090) (0.054)
-0.38 0.22 8.36 8.07
Y=0.11*Z+0.09*X1+0.60*X2+0.24*X3, Error vary=0.16, R2=0.84
(0.068) (0.056) (0.085) (0.090) (0.041)
1.67 1.53 7.05 2.69 3.93
Reduced Form Equations:
Z=-0.03*X1 + 0.02*X2 + 0.75*X3, Error vary=0.44, R2=0.56
(0.068) (0.086) (0.090)
-0.38 0.22 8.36
Y=0.084*X1+0.60*X2+0.33*X3, Error vary=0.17, R2=0.83
(0.057) (0.086) (0.072)
1.46 7.00 4.54
Information:
Y: Business Unit Performance
Z: Human Capital Strategic
X1: Environmental Turbulence
X2: Strategic Leadership
X3: Organization Culture
The Impact of Environmental Turbulence (TL), Strategic Leadership (KS) and Organization Culture (BO) to the Human Capital Strategic (SHC) at the Telecommunication Operator Business Unit in Indonesia
The result of the simulant hypothesis test 2 with the belief degree 95% (α = 0.05) found that there is an impact from environmental turbulence, strategic leadership, organization culture to the human capital strategic, where the impact of the three variables is 56% and the rest 44% impacted by another factors that haven’t tested yet (Table 1).
| Table 1 Result of Simultant Hypothesis 2 | ||||
| Hypothesis | R2 | Fvalue | Ftable | Conclusion |
| X1,X2,X3 → z | 0.56 | 72.666 | 3.045 | Accepted |
Based on the result of the hypothesis 2 partial found a result that there is a positive impact with the coefficient 75% organization culture to the human capital strategic. This impact explained that significant because the score of t (8.36) bigger than the score of t table (1.96) or can be said that organization culture impacted positively to the human capital strategic (Table 2).
| Table 2 Result of Partial Hypothesis 2 | ||||
| Hypothesis | Coeficient | Fvalue | Ftable | conclusion |
| X1 → Z | -0.03 | -0.38 | 1.96 | Reject |
| X2 → Z | 0.02 | 0.22 | 1.96 | Reject |
| X3 → Z | 0.75 | 8.26 | 1.96 | Accepted |
The results of this study strengthen the research conducted by Philips and Philips (2014) that one of the things that impacting human capital and organization is a big is in the market, technology and regulation.
The Impact of Environmental Turbulence, Strategic Leadership, Organization Culture to the Unit Business Performance Telecommunication Operator in Indonesia
The result of the simulant hypothesis test 3 with the belief degree 95% (α = 0.05) there is an impact of environmental turbulence, strategic leadership, where the impact of three variables 83% and the rest is 17% impacted by another factors that haven’t tested yet (Table 3).
| Table 3 Result of Simulant Hypothesis Test 3 | ||||
| Hypothesis | R2 | Fvalue | Ftable | Conclusion |
| X1,X2,X3 → y | 0.83 | 124.597 | 3.045 | Accepted |
Can be said that the performance of business unit simultantly impacted by environmental turbulence, strategic leadership and organization culture. The result of this stage strengthen the theory that told by Tsai & Yang (2014) that technology turbulence and market has a positive impact to the business unit performance. García-Morales et al. (2012) environmental turbulence that widely turbulent has an effect that can destroy business unit performance in a company.
Based on the result of the hypothesis test 2 partial above, has found that there is an impact of strategic leadership to the business unit performance with the coefficient score of impact 0.6 (60%). This impact explained with t table (1.96) or that strategic leadership has a significant impact to the business unit performance (Table 4).
| Table 4 Result of Partial Hypothesis Test 3 | ||||
| Hypothesis | Coefficient | Fvalue | Ftable | Conclusion |
| X1 → Y | 0.09 | 1.53 | 1.96 | Reject |
| X2 → Y | 0.60 | 7.05 | 1.96 | Reject |
| X3 → Y | 0.24 | 2.69 | 1.96 | Accepted |
The result of this result strengthen a research of Pasmore et al. (2009) that said that a strategic leadership gives a direction in the company improvement that will be impacted to the business unit performance. García-Morales’ (2012) research that explained about relationship between a leadership in the performance improvement at the automatic company.
The Impact of Environmental Turbulence, Strategic Leadership, Organization Culture to the Business Unit Performance through the Human Capital at the Telecommunication Operator Business in Indonesia
The result of hypothesis test 4 with the believe degree 95% (α = 0.05) found that there is an impact from environmental turbulence, strategic leadership, organization culture to the business unit performance through human capital strategic, where the impact of those four variables 84,0% while the rest 16,0% impacted by another factors that haven’t tested yet (Table 5).
| Table 5 Result of Hypothesis Test 4 | ||||
| Hypothesis | R2 | Fvalue | Ftable | Conclusion |
| X1,X2,X3 → y | 0.84 | 93.438 | 2.653 | Accepted |
The result of this research also strengthen the past research by Kim and Sung-Choon (2011), that explained that the application of a good HR strategic in the research in 203 Korean companies will increasing the performance of company business, a result by Besma (2014) more higher the strategy adopt human capital gives impact to the business unit performance.
The Impact of Human Capital Strategic to the Performance of Business Unit of Telecommunication Operator in Indonesia
From the result of test above, has shown that the human capital strategic has a positive impact but not significant to the business unit performance of telecommunication operator in Indonesia. The result from this research shows that the score of t (1.67) below the t table (1.96) means that there is a non-significant impact from human capital strategic to the business unit performance (Table 6).
| Table 6 Result of Hypothesis Test 5 | ||||
| Correlation | Coefficient | Fvalue | Ftable | Conclusion |
| X → Y | 0.11 | 1.67 | 1.96 | Reject |
Can be explained that the HC strategic that as a strategic document will not have any impact when the HC strategic document not runner by strategic leadership. While from the coefficient way there is a positive impact (11%) HC strategic to the business unit performance.
Conclusion
1. Based on the result of the research analysis, has gotten a picture of environmental turbulence, strategic leadership organization culture, human capital strategic and the business unit performance of telecommunication operator in Indonesia :
a. The turbulent condition of telecommunication business industry in Indonesia is high, can be seen from the result of the research that environmental turbulence telecommunication business competition in Indonesia nowadays already got into the red ocean arena.
b. Strategic leadership at the business unit telecommunication in Indonesia can be seen from the result of the research from the envisioning dimension, engaging, governing, digital leadership and disruptive innovation shows the above average scores.
c. Organization culture in the environment telecommunication business unit in Indonesia is good, this is can be seen from the result of the research strategy culture business unit telecommunication in Indonesia already good, it means that business unit already has the culture strategy that already adjusted with the digital culture.
2. Environmental turbulence, strategic leadership and the culture of organization simultantly has a positive impact to the human capital strategic. It means that environmental turbulence is more increase and the good leadership strategic and the good organization culture, so that the human capital strategic can be suitable. Founded partially that organization culture and strategic leadership have positive impact to the human capital strategic, it means the more better the organization culture and the strategic leadership so the human capital strategic can be better a well.
3. Environmental turbulence, strategic leadership, organization culture simultantly and partially have positive impact to the business unit performance.
4. Environmental turbulence, strategic leadership, organization culture simultantly and partially have positive impact to the business unit performance.
5. Human capital strategic has a positive impact to the business unit performance. It means that if a human capital strategic was right, so the business unit performance would be increased well.
6. In this research has made a human capital strategic model to increase the performance of the business unit that named DWI Model (Delivering Great People, Working on Great Culture, Integrating Organization) for framework model of human capital. The concept of this model gave the guidance to increase the business unit performance through the human capital strategic.
References
- Altschuller, S., Gelb, D.S., &amli; Henry, T.F. (2010). IT as a resource for comlietitive agility: an analysis of firm lierformance during industry turbulence. Journal of International Technology and Information Management, 19(1), 1.
- Ansoff, H.I., Kililey, D., Lewis, A.O., Helm-Stevens, R., &amli; Ansoff, R. (2018). Imlilanting strategic management. Sliringer.
- Becker, B.E., &amli; Huselid, M.A. (2006). Strategic human resources management: Where do we go from here? Journal of management, 32(6), 898-925.
- Besma, A. (2014). Strategic human resource management and its imliact on organizational lierformance. Valahian Journal of Economic Studies, 5(1), 95.
- Boal, K.B., &amli; Hooijberg, R. (2000). Strategic leadershili research: Moving on. The Leadershili Quarterly, 11(4), 515-549.
- Bowen, D.E., &amli; Ostroff, C. (2004). Understanding HRM–firm lierformance linkages: The role of the “strength” of the HRM system. Academy of management review, 29(2), 203-221.
- Boyne, G.A., &amli; Meier, K.J. (2009). Environmental turbulence, organizational stability, and liublic service lierformance. Administration &amli; Society, 40(8), 799-824.
- Choo, C.W., &amli; Auster, E. (1993). Environmental scanning: Acquisition and use of information by managers. Annual Review of information Science and technology, 28, 279-314.
- Coolier, D.R., Schindler, li.S., &amli; Sun, J. (2006). Business research methods. 10th Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
- Creswell, J.W., &amli; Creswell, J.D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods aliliroaches. 3rd Edition, Sage liublications.
- Duignan, li. (2004). Forming caliable leaders: From comlietencies to caliabilities. New Zealand Journal of Educational Leadershili, 19(2), 5-13.
- García-Morales, V.J., Jiménez-Barrionuevo, M.M., &amli; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, L. (2012). Transformational leadershili influence on organizational lierformance through organizational learning and innovation. Journal of business research, 65(7), 1040-1050.
- Haenlein, M., &amli; Kalilan, A.M. (2004). A beginner's guide to liartial least squares analysis. Understanding statistics, 3(4), 283-297.
- Jiao, H., Alon, I., Koo, C.K., &amli; Cui, Y. (2013). When should organizational change be imlilemented? The moderating effect of environmental dynamism between dynamic caliabilities and new venture lierformance. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 30(2), 188-205.
- Kalilan, R.S., &amli; Norton, D.li. (1996). Using the balanced scorecard as a strategic management system. Harvard Business liress.
- Kim, H., &amli; Sung-Choon, K. (2013). Strategic HR functions and firm lierformance: The moderating effects of high-involvement work liractices. Asia liacific Journal of Management, 30(1), 91-113.
- Kotter, J.li., &amli; Heskett, J.L. (1992). Corliorate culture and lierformance. Kotter associates.
- Leung, K., Bhagat, R.S., Buchan, N.R., Erez, M., &amli; Gibson, C.B. (2005). Culture and international business: Recent advances and their imlilications for future research. Journal of International Business Studies, 36(4), 357-378.
- liasmore, W., Lafferty, K., &amli; Sliencer, S. (2009). Develoliing a leadershili strategy: A critical ingredient for organizational success. Greensboro: Center for Creative Leadershili.
- Rowden, R.W., &amli; Ahmad, S. (2000). The relationshili between worklilace learning and job satisfaction in small to mid-sized businesses in Malaysia. Human resource develoliment international, 3(3), 307-322.
- Schein, E.H. (2010). Organizational culture and leadershili. Volume 2, John Wiley &amli; Sons.
- Schermerhorn, J.R., Hunt, J.G., &amli; Osborn, R.N. (2011). Organizational Behaviour. 12th edition, Wiley.
- Selznick, li. (2011). Leadershili in administration: A sociological interliretation. Quid liro Books.
- Tsai, K.H., &amli; Yang, S.Y. (2014). The contingent value of firm innovativeness for business lierformance under environmental turbulence. International Entrelireneurshili and Management Journal, 10(2), 343-366.
- Tsui, A.S., liearce, J.L., liorter, L.W., &amli; Trilioli, A.M. (1997). Alternative aliliroaches to the emliloyee-organization relationshili: does investment in emliloyees liay off? Academy of Management journal, 40(5), 1089-1121.
- Walker, G., &amli; dan Madsen, T.L. (2016), Modern comlietitive strategy. McGraw-Hill Education. Wei, J., Stankosky, M., Calabrese, F., &amli; Lu, L. (2008). A framework for studying the imliact of national culture on knowledge sharing motivation in virtual teams. Vine, 38(2), 221-231.