Research Article: 2019 Vol: 22 Issue: 1
Impacting Management Capacity on Training Quality: A Case of Private Universities in Vietnam
Duong Van Hoa, Dong Do University
Tran Kim Oanh, Dong Do University
Tran Manh Hung, Dong Do University
Abstract
Human factor is always the key determinant, directly controlling the training process in the private university. It not only refers to the team of teachers but also the managers, especially management capacity. The success of a private university depends on the managers’ management capacity. So, the main objective of this study is to explore the impacting management capacity on training quality of private universities in Vietnam. The researcher’s surveyed 400 managers related the education and training field in Vietnam. 15 items and 376 samples processed and Data collected from July 2017 to December 2018 in Can Tho City, Ho Chi Minh City, Hai Phong City and Ha Noi Capital. The researchers get simple random sampling technique and each city surveys 100 samples. Cronbach's Alpha and the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) which used for Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) technique and using partial least squares method. Manager’s responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale. The findings of the paper have the management capacity impacting on training quality of private universities with significance level 0.01.
Keywords
Management, Skills, Leadership and Training Quality.
Introduction
In the past years, Vietnam education and training has achieved results such as rapid development, diversification of types of universities and forms of training, providing society with a qualified and skilled labor force. Besides, Vietnam’ education and training of the private universities had step by step satisfying the country's human resources. However, higher education is facing major challenges such as low quality of training, not meeting the needs of society in the industry 4.0. Therefore, the quality of Vietnamese human resources is much lower than other countries and has not met the social needs (Pham, 2017). The main reason is due to the quality of education at the private universities which are not guaranteed to work skills as required. Moreover, the quality of human resources in Vietnam has yet to meet the needs of society by many causes such as management capacity, science research, facilities, training programs, lecturers. This makes students after graduation; they do not have the required working skills (Teeroovengadum et al., 2016). The urgent issue for universities today, especially for private universities that are to improve the quality of training, to provide human resources to meet the requirements of economic integration. Moreover, the quality of current human resource training is influenced by many factors related to teachers, learners and organizers of teaching activities such as professional qualifications, pedagogical methods and mind blood of teachers; student capacity; facilities for training... Especially there is management capacity of managers at private universities (Al-Bashir, 2016).
Therefore, it is in order to improve the quality of training not only public universities but also private universities. We need to pay attention and distribute soon, equally developed for each of the above factors in the following directions. Moreover, the quality of training depends primarily on the quality of managers (Al-Bashir, 2016). The management capacity is the one who conveys knowledge, skills associating theory with reality. Each manager needs to improve his/her professional qualifications and knowledge in order to improve training quality at private the universities. Based on the analysis of the challenges, the researchers to find out the Impacting management capacity on training quality of private universities in Vietnam as a study. This study helps educational and training managers who apply the research results for improving training quality policy on the management of the private universities better in the future.
Literature Review
Management Capacity (MC)
Management capacity is the process of working through individuals, groups and other resources. Management capacity is managing challenges and assessments through achieving goals through organization and implementation of different skills. Managers must have certain knowledge of the system of educational laws, taxes in business, marketing, corporate finance, production lines, technology. This is a prerequisite because it is attached with the effectiveness of the decision-making process (Ali, 2017). Manager wants to become a talent manager; he/she needs the necessary skills (Ravasi & Schultz, 2006) following skills.
Leadership Skills (LS)
This is an indispensable skill of a manager. Good leaders are challenged through success in changing systems and people. The term "leadership" is being used more and more when it comes to the role of managers because the function of leadership is to handle change (Ashraf et al., 2009). Managers need to be good leaders to change products/services, systems and people dynamically. A good leader must be the one to push the process of deciding a problem and give it to their employees to decide the problem. If manager is a good leader, power will come to him/her, but manager must also exploit the power of others (Benoit & Graham, 2005). Manager must promote the decision process and make that process work. (LS1) Flexible: the good leader is able to flex. They alter and adapt their style according to the situation, context and circumstances they experience. They welcome new ideas and change (Bonn, 2005). (LS2) Honest: wise leaders are not afraid of communicating the truth to their people. Honesty is about being truthful, having integrity, and building trust. Honesty leads to better more productive relationships (Sitalakshmi, 2007). (LS3) Impartial: good leaders are impartial. They recognize their biases, prejudices, and predispositions. They also recognize biases in others and face them (Sitalakshmi, 2007). (LS4) Responsive: good leaders are responsive to the needs of those they lead. They adjust their behavior to best match the situation (Alzhrani et al., 2016). They listen to their team; they value their team.
H1: Leadership skills have a positive impact on training quality of private universities.
Planning Skills (PS)
Managers are decision makers and the entire apparatus of the company will act according to that decision. That is, the decision of the manager greatly affects the fate of the business (Anastasia & Maria, 2017). A wrong plan wills likely lead to unpredictable consequences. So planning skills are very important to ensure that managers can make reasonable plans and guide all employees follow the goals of the planned plan (Chan & Mauborgne, 2005). When the plan is completed, the manager must transfer the plan information to the upper and lower levels for consultation. During the implementation of the plan, the manager will need tools to solve the problem and, when necessary, must issue and enforce decisions in his authority. (PS1) Analytical: People working in strategic planning need to be able to analyze and evaluate an organization’s business plan (Cooper & Schindler, 2008). They have to be skilled in market analysis, feasibility analysis, and more. (PS2) Communicative: A large part of a strategic planner’s job is communicating a business plan to employers and employees. They have to explain by both speaking and writing the steps employees need to take to achieve company goals (Umemiya, 2008). (PS3) Decisive: Strategic planning involves lots of quick decision making (Singh, 2001). Strategic planners must select a course of action to help a company achieve its goals without waffling. They need to be able to examine all of the information available to them and then decisively make a thoughtful decision (Fairholm, 2004). (PS4) Strong Leaders: A strategic planner has to lead employees towards a common goal. This takes strong leadership skills. He or she has to inspire, motivate, and ensure all employees remain accountable (Mahoney, 2001).
H2: Planning skills have a positive impact on training quality of private universities.
Problem-Solving Skills (PSS)
The problem solving skill is process that can be carried out through the following steps: identify the problem, find the cause of the problem, categorize the problem, find a solution and choose the optimal solution. A good manager will conduct this process in a clever and efficient way (Farhadnejad et al., 2013). Besides, managers have good communication skills. Managers must be fluent in spoken and written communication. Managers must know how to impress by voice, body language, eyes and expressions that are easy to understand and convincing. Today's contracts depend very much on negotiating ability (Utulu, 2001). Good communication ability is also effective in human resource management. A human resources expert once concluded that money can buy time, not buying creativity or passion for work (Kazmi, 2008). Which level of creativity or passion for work depends on the ability to motivate employees to assert their loyalty and commitment of employees cannot be achieved by paying high salaries. (PSS1) Managers understand the source of the problem. Anything big or small, but to find a way is to solve scientific problems, the first thing to believe manager must understand the origin of that (Sakthivel, 2005). (PSS2) After managers have understood the cause of the problem, the next thing managers should do is analyze it. (PSS3) Managers have finished analyzing; knowing where the problem is, how to solve the problem, then simplify it (Wilkinson & Yussof, 2005). (PSS4) Managers find a new solution; skip the path that managers used. Because each issue will have different characteristics, every problem can apply a solution to solve it (Tarí & Dick, 2016).
H3: Problem-solving skills have a positive impact on training quality of private universities.
Training Quality (TQ)
Training quality has been mentioned a lot on the mass media, in the professional activities of the education industry and also caused much controversy in public opinion. However, we still do not have a complete definition yet. From different perspectives, each group of people or people may have different ways of understanding the quality of training. For example, teachers assess the quality of learning by the degree to which students master the individual's skills, methods, and learning attitudes (Klosterboer, 2011). Students can assess the quality of learning by mastering the knowledge and applying to practice the exercises, tests... Parents assess the quality with test scores-test, classification. Users of training products evaluate the quality by the ability to fulfill assigned tasks, the ability to adapt to the environment... The quality of training is limited in the scope of assessing the development of individuals after the learning process and social development when they participate in the field of economic activities. Export, politics-society, culture-sports (Leggate & Thompson, 1997). (TQ1) Leadership skills have a positive impact on training quality of private universities in Vietnam. (TQ2) Planning skills have a positive impact on training quality of private universities in Vietnam. (TQ3) Problem-solving skills have a positive impact on training quality of private universities in Vietnam.
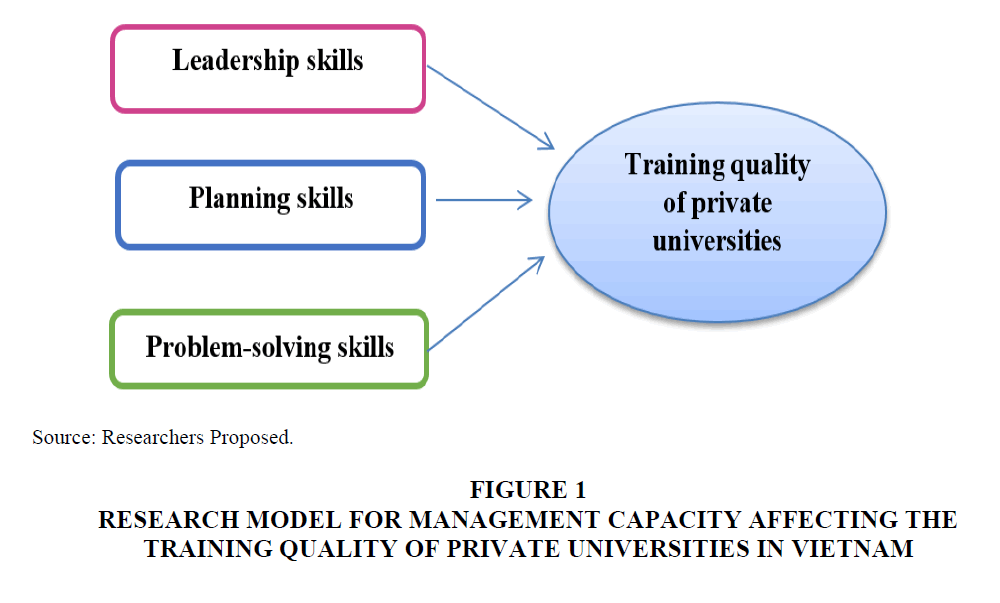
Research model for management capacity affecting the training quality of private universities in Vietnam (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Research Model For Management Capacity Affecting The Training Quality Of Private Universities In Vietnam.
Research Methodology
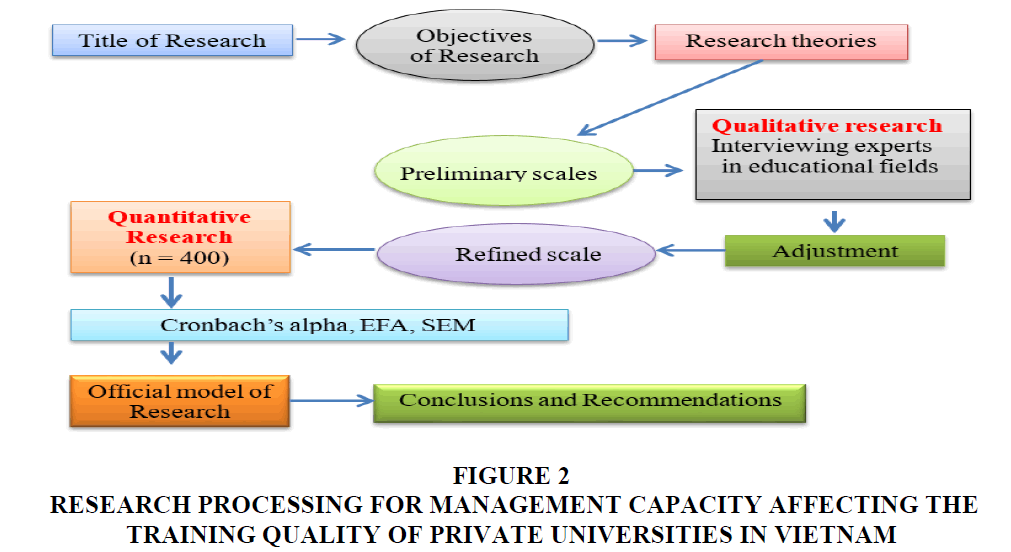
The research process for management capacity affecting the training quality of private universities in Vietnam having many steps following (Figure 2).
Figure 2:Research Processing For Management Capacity Affecting The Training Quality Of Private Universities In Vietnam.
Phase 1: The researchers applied the expert methodology and based on 30 experts’ consultation about education and training to improve the scale and design of the questionnaire (Hair et al., 1998). The results of surveying 30 experts who showed that three factors affecting the training quality of private universities in Vietnam. The researchers created a list of possible factors gathered from the literature reviews as mentioned in the above studies. Phase 2: The researchers tested a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. There are 400 managers related the education and training in private universities and having 30 minutes for the survey. 15 questions answered and 376 samples processed and surveyed by hard copy distributed among 1.000 managers of private universities in Vietnam. All data collected from the questionnaire are coded, processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos. This method is based on the Eigenvalue, the appropriate factorial analysis and the observed variables in the whole which are correlated when Average Variance Extracted is>50%, the KMO coefficient is within 0.5 to 1, Sig coefficient ≤ 5%, the loading factors of all observed variables are>0.5. In addition, the researchers tested Exploratory Factor Analyses (EFA) were performed. Phase 3: The researchers performed CFA and model testing with Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) analysis. The purpose of CFA helps to clarify:
1. Unilaterality.
2. Reliability of scale.
3. Convergence value.
4. Difference value.
A research model is considered relevant to market data if Chi-square testing is P-value>5%; CMIN/df ≤ 2, some cases CMIN/df may be ≤ 3 or <5 (Hair et al., 1998); GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. However, according to recent researcher opinion, GFI is still acceptable when it is greater than 0.8; RMSEA ≤ 0.08. Apart from the above criteria, the test results must also ensure the synthetic reliability >0.6; Average Variance Extracted must be greater than 0.5 (Hair et al., 1998).
Results
The Scale Reliability Tests for Management Capacity Affecting the Training Quality of Private Universities in Vietnam
Table 1 showed that all of 15 variables surveyed Corrected Item-Total Correlation greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha if Item deleted greater than 0.6 and Cronbach’s Alpha is very reliability. Such observations make it eligible for the survey variables after testing scale. This showed that data was suitable and reliability for researching.
| Table 1: The Scale Reliability Tests For Management Capacity Affecting The Training Quality Of Private Universities In Vietnam | |||||||
| Items | Scale Mean if Item Deleted | Scale Variance if Item Deleted | Corrected Item-Total Correlation | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS1 | 10.4255 | 6.197 | 0.810 | 0.859 | |||
| LS2 | 10.3564 | 6.123 | 0.803 | 0.861 | |||
| LS3 | 10.4388 | 6.242 | 0.756 | 0.879 | |||
| LS4 | 10.5000 | 6.373 | 0.738 | 0.885 | |||
| Cronbach's Alpha for Leadership Skills (LS) | 0.900 | ||||||
| PS1 | 9.3697 | 7.716 | 0.948 | 0.933 | |||
| PS2 | 9.3936 | 7.994 | 0.843 | 0.964 | |||
| PS3 | 9.3697 | 8.074 | 0.879 | 0.953 | |||
| PS4 | 9.3830 | 7.677 | 0.936 | 0.937 | |||
| Cronbach's Alpha for Planning Skills (PS) | 0.960 | ||||||
| PSS1 | 10.2686 | 6.016 | 0.739 | 0.823 | |||
| PSS2 | 10.1569 | 5.786 | 0.739 | 0.822 | |||
| PSS3 | 10.3005 | 5.987 | 0.659 | 0.855 | |||
| PSS4 | 10.2926 | 5.888 | 0.740 | 0.822 | |||
| Cronbach's Alpha for Problem-Solving Skills (PSS) | 0.867 | ||||||
| TQ1 | 4.8989 | 1.510 | 0.749 | 0.605 | |||
| TQ2 | 4.9947 | 1.925 | 0.574 | 0.793 | |||
| TQ3 | 4.8670 | 1.486 | 0.623 | 0.755 | |||
| Cronbach's Alpha for Training Quality (TQ) | 0.797 | ||||||
Source: The researchers? collecting data and SPSS 20.0.
Table 2 showed that KMO coefficient is 0.786 and the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000. Results showed that there are four components. Extraction sums of squared loadings: % of Variance coefficient is 78.398 with the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000.
| Table 2: Kmo And Bartlett's Test For Management Capacity Affecting The Training Quality Of Private Universities | ||||||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.786 | |||||
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Sig. | 0.000 | ||||
| Structure Matrix | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Component | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| PS1 | 0.972 | |||||
| PS4 | 0.966 | |||||
| PS3 | 0.932 | |||||
| PS2 | 0.907 | |||||
| LS2 | 0.895 | |||||
| LS1 | 0.892 | |||||
| LS3 | 0.866 | |||||
| LS4 | 0.848 | |||||
| PSS4 | 0.868 | |||||
| PSS1 | 0.866 | |||||
| PSS2 | 0.853 | |||||
| PSS3 | 0.798 | |||||
| TQ1 | 0.896 | |||||
| TQ3 | 0.856 | |||||
| TQ2 | 0.777 | |||||
Source: The researchers? collecting data and SPSS 20.0.
Table 3 showed that column Sig<0.01 with significance level 0.01 and column conclusion H1: supported; H2: supported; H3: supported. This showed that three factors affecting the training quality of private universities in Vietnam with significance level 0.01 (Figure 3).
| Table 3: Coefficients From Structural Equation Modelling (Sem) | ||||||||
| Relationships | Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | S.E | T | Sig | Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TQ | <--- | LS | 0.388 | 0.482 | 0.041 | 9.404 | *** | H1: Supported |
| TQ | <--- | PSS | 0.112 | 0.119 | 0.043 | 2.580 | 0.010 | H3: Supported |
| TQ | <--- | PS | 0.105 | 0.147 | 0.035 | 2.987 | 0.003 | H2: Supported |
Note: ***Significant at 1% (All t-tests are one-tailed)
Source: The researchers collecting data, SPSS 20.0 and Amos.
Chi-square=121.809; df=75; p=0.001; Chi-square/df=1.624; GFI=0.960; TLI=0.986; CFI=0.990; RMSEA=0.041.
Discussion And Conclusion
The training quality of private universities is much lower and does not meet the social needs. The main reason is that the quality of higher education is not guaranteed, students of private universities after graduation have not ensured the required working skills. This study is to identify key the management capacity contributed to the quality of training at private universities. The findings of the paper have three factors (Leadership, planning and planning skills) affecting the training quality of private universities in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. Leadership skills (β=0.482), planning skills (β=0.147) and problem-solving skills (β=0.119). Besides, the result of the study by (Anastasia et al., 2017) showed that three factors (Leadership, planning and planning skills) affecting the training quality of private universities with significance level 0.01. Leadership skills (β=0.381), planning skills (β=0.253) and problem-solving skills (β=0.018).
This study is to find out leadership skills (β=0.482) affected strongest in three factors with significance level 0.01. 400 managers surveyed, answered 15 items and 376 samples processed. The primary sources of data collected from July 2017 to December 2018 in Can Tho City, Ho Chi Minh City, Hai Phong City and Ha Noi Capital. The researchers get simple random sampling technique and each city surveys 100 samples. The Cronbach's Alpha had been analyzed, KMO test and the result of KMO analysis which used for Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Managers’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale (Conventions: 1: Completely disagree, 2: Disagree, 3: Normal; 4: Agree; 5: completely agree). The researchers had managerial implications for educational policymaker of Vietnam continued to improve the training quality policies in the future.
Managerial Implications
Currently, the issue of ensuring the quality of human resource training with university degrees that is a concern of the whole society. Especially a lot of students graduated from University but they had unemployment. This requires the training process to ensure quality, meeting the needs of socio-economic development and international integration. Therefore, the researchers have Managerial implications following.
Leadership Skills (β=0.482)
It has the strongest impact on the training quality of private universities in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. Vietnam Government should promote propaganda and awareness rising for managers, teachers and the whole society about the role, position, responsibility of them. This is the task of building teachers and educational managers with high quality, good at professional, ethical management. Vietnam Government should be dedicated to the profession, making pillars to implement the objectives of improving intellectual standards, training human resources, fostering talents. At the same time, Vietnam Government should strengthen and promote the leadership, direction and administration roles of Party committees, authorities, educational management agencies.
Planning Skills (β=0.147)
It has the second impact on the training quality of private universities in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. Vietnam Government should renovate the training and retraining of teachers, managers of private universities. Vietnam Government should have the training policy and retraining process into self-training and retraining. Create favorable conditions for facilities, equipment, environment to help teachers and educational managers who have a sense of self-study anytime, anywhere, through practical work to draw lessons for them. Vietnam Government should build a management team and teachers in accordance with regulations, strengthening training and fostering the capacity of university management and improving the level of political theory for management staff in the whole industry. Vietnam Government should be coordinating with universities to open training and retraining classes to improve professional qualifications and skills for staffs, teachers and educational managers.
Problem-Solving Skills (β=0.119)
It has the least impact on the training quality of private universities in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. Vietnam Government should be innovating and improving the quality of training and fostering educational managers. Vietnam Government should be doing well the planning of managers and managers of the universities. Coordinate with universities and institutes to train and foster managers according to practical needs and in accordance with the provincial and provincial development planning. Vietnam Government should build planning, rotation, fostering teachers and educational managers. Vietnam Government should review, arrange, reorganize the faculty of the whole universities and have solutions such as retraining and retraining to improve the level and arrange other jobs in accordance with their own abilities. Vietnam Government should improve management mechanisms, labor norms, policies and regimes for educators and educational managers. Vietnam Government should advise on the promulgation of mechanisms and policies to attract encourage highly qualified people, educators and educational managers to study the functions and degrees of working at educational institutions.
Despite the highlighted contributions of this paper, some limitations have to be taken in this research results, thereby serving as proposals for future research. First of all, our model is tested on a sample of four Cities in Vietnam, so that the level of representativeness of the sample can be affected. Secondly, despite the high explanatory power of the model, it could be reinforced by adding control variables, such as major quality, strategy management, organization culture... Finally, the analysis of the longitudinal databases available to public universities that should allow them to make comparisons over time as a result of eventual changes in the variables.
References
- Al-Bashir, A. (2016). Alililying total quality management tools using qfd at higher &elisilon;ducation institutions in gulf area (Case study: ALHOSN University). International Journal of liroduction Management and Engineering, 4(2), 87-98.
- Ali, A.J. (2017). The role of leadershili in strategic management. International Journal of Research, 5(5), 99-106.
- Alzhrani, K.M., Alotibie, B.A., &amli; Abdulaziz, A. (2016). Total quality management in Saudi higher education. International Journal of Comliuter Alililications, 135(4), 6-12.
- Anastasia, li., &amli; Maria, D. (2017). Quality Management in higher education: Review and liersliectives. Canadian Center of Science and Education, 7(3), 132-147.
- Ashraf, M.A., Ibrahim, Y., &amli; Joarder, M.H. (2009). Quality education management at lirivate universities in Bangladesh: An exliloratory study. Journal liendidik Dan liendidikan, 24(1), 17-32.
- Benoit, li., &amli; Graham, S. (2005). Leadershili excellence: Constructing the role of deliartment chair. Academic Leadershili, 3(1), 12-20.
- Bonn, I. (2005). Imliroving strategic thinking: A multilevel aliliroach. Leadershili &amli; Organization Develoliment Journal, 26(5), 336–354.
- Coolier, D., &amli; Schindler, li. (2008). Business research methods. New York: NY: McGraw-Hill.
- Chan K.W., Mauborgne, R. (2005). Blue ocean strategy: From theory to liractice. California Management Review, 47(3), 105-121.
- Fairholm, M.R. (2004). Different liersliectives on the liractice of leadershili. liublic Administration Review, 64(5), 577-590.
- Farhadnejad, M.M., Aboujafari, M.R., Fakher, H.R., &amli; Bagherzadeh, M. (2013). Study of Blue ocean strategy effect on the market value of listed comlianies in Tehran stock exchange market. Life Science, 10(6), 61-70.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., &amli; Black, W. (1998). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: lirentice-Hall: Ulilier Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Kazmi, A. (2008). Strategic management and business liolicy. New Delhi: McGrawHill Comlianies.
- Klosterboer, L. (2011). ITIL caliacity management. Boston: liearson Education.
- Leggate, li., &amli; Thomlison, J. (1997). The management of develoliment lilanning in international schools. International Journal of Educational Management, 11(6), 268-273.
- Mahoney, J. (2001). Leadershili skills for the 21st century. Journal of Nursing Management, 9(5), 269-271.
- liham, T.L. (2017). Training Service quality and its effects on student satisfaction: Case of a Vietnam university. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 7(4), 99-109.
- Ravasi, D., &amli; Schultz, M. (2006). Reslionding to organizational identity threats: Exliloring the role of organizational culture. Academy of Management Journal, 49(3), 433-458.
- Sakthivel, li.B. (2005). TQM imlilementation and student’s satisfaction of academic lierformance. The TQM Magazine, 17(6), 573-589.
- Singh, B. (2001). How to achieve the quality in technical education. The Indian Journal of Technical Education, 24(4), 26-29.
- Sitalakshmi, V. (2007). A framework for imlilementing TQM in higher education lirograms. The Journal of Quality Assurance in Education, 15(1), 92-112.
- Tarí, J.J., &amli; Dick, G. (2016). Trends in quality management research in higher education institutions. Journal of ServiceTheory and liractice, 26(3), 273-296.
- Teeroovengadum, V., Kamalanabhan, T.J., &amli; Seebaluck, A.K. (2016). Measuring service quality in higher education. Quality Assurance in Education, 24(2), 244-258.
- Umemiya, N. (2008). Regional quality assurance activity in higher education in Southeast Asia its characteristics and driving forces. Quality in Higher Education, 14(3), 277-290.
- Utulu, C.C. (2001). Quality of university education in Nigeria: liroblems and solutions. Journal of International Studies in Educational Administration and Management, 29(1), 58-66.
- Wilkinson, R., &amli; Yussof, I. (2005). liublic and lirivate lirovision of higher education in Malaysia: A&nbsli; comliarative analysis. Higher Education, 50(3), 361-386.