Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 3
Increasing Customer Loyalty of Ethnic Restaurant Through Experiential Marketing and Service Quality
Sri Astuti Pratminingsih, Widyatama University
Eriana Astuty, Widyatama University
Kania Widyatami, Indonesia University of Education
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to examine the effect of experiential marketing, service quality on satisfaction and loyalty of ethnic restaurant consumers. A descriptive research will be conducted to meet the research objective. The data will be obtained by distributing the questionnaire to 250 restaurant consumers through self- administered survey. The sample is chosen by accidental sampling method. The data will be analysed using IBM SPSS AMOS ver 20. The study found that experiential marketing and service quality have an effect on the satisfaction and loyalty of ethnic restaurant consumer. This research gives insight to restaurant managers that in the effort to win the competition developing experiential marketing program and offering excellent service quality can give a solution for increasing customer loyalty.
Keywords
Experiential Marketing, Service Quality, Satisfaction, Loyalty.
Introduction
The Indonesian government seeks to increase revenues from the creative industry sector, especially after the decline in revenues from the oil and gas sector. One of the sub-sectors in the creative industry is culinary, which is currently experiencing significant growth. Increasing the community welfare has encouraged the needs of eating out as part of people lifestyle, especially in urban areas. According to the ministry of tourism and creative industry (2013), the culinary sector contributes to state revenues of IDR 208.6 trillion with an average growth of about 4.5 percent in 2013. While employment in the culinary sector reached 3.7 million people with average growth reached 26 percent. One of the sub-sectors that indicate significant growth is the ethnic restaurant.
Bandung is one of the popular destinations for ethnic culinary tourism in Indonesia. The national statistics agency (BPS, 2016) argued that the number of restaurants in Bandung growing steadily in the last ten years. There are about 798 restaurants in Bandung areas in 2015. This condition makes very difficult for ethnic restaurants to compete and maintain customer loyalty.
Experiential marketing focuses not only on a product or a service but also on an entire experience that accounts for the customers' experience creation processes, including pre-purchase, moment-of-truth and post-purchase (Yuan & Wu, 2008; Schmitt, 1999). Experiential marketing intends to supply the factors that help to develop the experiential side of the company's offerings helping the consumer to access it (Schmitt, 1999). Experiential marketing gives an exceptional framework to integrate elements of experience and entertainment into the product/service (Zena & Hadisumarto, 2012).
There are many factors that may influence customers' assessments of restaurant quality. Previous researchers suggested that food quality, physical environment and service are the major components of overall restaurant service quality (Dulen, 1999; Susskind & Chan, 2000). Among these attributes, food quality is the most important dimension of the restaurant experience (Sulek & Hensley, 2004). What is more, it is an essential requirement to satisfy the needs and expectations of restaurant customers (Peri, 2006). Although there is no consensus on the individual attributes that constitute food quality, the researchers focus on presentation, healthy options, taste, freshness and temperature (Namkung & Jang, 2008).
According to Lee et al. (2000), service quality constructs conceptualized mostly in the context of marketing literature. The concept of perceived service quality reported by Ghobadian et al. (1994) that the customer’s expectations, service delivery process have an impact on perceived service quality. Yoo & Park (2007) argue that employees are an integral part of the service process and significant element of enhancing perceived service quality. Edvardsson (2005) pointed out that service quality perceptions are created by process of product delivery and consumption. The customers’ fast experience, as well as their positive and negative feelings, has an important impact on perceived service quality. O’Neill & Palmer (2003) have reported, that a customer perception of service quality to a large extent, influenced by the degree of their prior experience with a particular service.
Wu & Liang (2009) stated that service encounter in restaurant settings consists of three main elements: Environmental elements (e.g. design, music and lighting), employees (e.g. professional skills, reliability) and customers (e.g. interaction with other customers). To understand all characteristics of the restaurant service quality an appropriate measurement instrument should be developed. Customer loyalty is all about attracting the right customer, getting them to buy, buy often, buy in higher quantities and bring you even more customers (Öztürk, 2015).
According to Churchill & Surprenant (1982) illustrated customer satisfaction as the outcome of purchase and use resulting from the buyer’s comparison of the rewards and costs of the purchase relative to the anticipated consequences. In order to gauge customer satisfaction of services, most scholars in their studies have relied on the disconfirmation of expectations paradigm (Zeithaml et al., 1993; Churchill & Surprenant, 1982; Oliver & DeSarbo, 1988, Bitner, 1990; Swan & Trawick, 1981). The theory underlying the disconfirmation paradigm states that consumer satisfaction is a function of consumer’s expectations. It works on the assumption that each customer has prior performance expectations from the service. Customers judge satisfaction on the basis of comparison between the expectations and actual performance. If expectations are met or exceeded, it results in satisfaction. When performance falls short of expectations, dissatisfaction results (Bitner, 1990).
Customer loyalty is all about attracting the right customer, getting them to buy, buy often, buy in higher quantities and bring you even more customers. Chen & Lee (2009) mentioned that loyalty exists when customers feel satisfied with a product and have intentions to repurchase and spread positive word-of-mouth about the product. One way that can be used to maintain consumer loyalty is by touching the emotional side of the customer through experiential marketing (Caru & Cova, 2008). This is also important for the restaurant because people dine out in restaurants not only looking for tasty food but because of emotional values (for socializing, entertainment or prestige) which is gained through experiential marketing (Mansouri and Ibrahimi, 2013). In addition, quality of service is also a very important factor in customer loyalty. Research conducted by Murad & Ali (2015) indicates that restaurant visitors will be loyal if they are satisfied with the services provided by the restaurant. In their research, they found that all the component of service quality influence customer satisfaction. Another study conducted by Ha and Jang (2010) shown that the quality of service is the main factor to give the company an advantage that can satisfy the ethnic restaurant consumer. Therefore, for winning the competition restaurant manager need to provide premium experience and service to the customers. For this reason, the authors are interested to examine whether experiential marketing and service quality affect the satisfaction and loyalty customers of the ethnic restaurant in Bandung.
Based on previous explanation, this research is aimed to find out the
1. Relationship experiential marketing on customer satisfaction;
2. Relationship service quality on customer satisfaction;
3. Consumer satisfaction with consumer loyalty;
4. Experiential marketing on consumer loyalty;
5. Service quality on consumer loyalty.
Literature Review
Relationship Experiential Marketing on Customer Satisfaction
Schmitt (1992) defined that experiential marketing as the customers’ recognition and purchasing of goods or services from a company or brand after they experience activities and perceive stimulations. (Lee et al., 2011) defined experiential marketing as a memorable memory or experience that goes deeply into the customer’s mind. Douglas & Craig (2000) broadened the traditional conceptualization of experiential value to incorporate three spheres: Extrinsic versus intrinsic value; active versus reactive value; and self- versus other-oriented value. In a shopping context, an extrinsic value is acquired from satisfying utilitarian consumption goals such as saving money, whereas intrinsic value is derived from an enjoyable and playful shopping trip (Caru & Cova, 2007). On the other hand, reactive value refers to a situation when customers appreciate the physical shopping environment or respond positively to service personnel. Active value, in contrast, results from customers' efficient manipulation of the shopping resources to satisfy their functional or affective needs (Kim, 2002). While making a purchase decision they sometimes behave rationally while sometimes they behave like the emotional beings who also want intangible values such as a sense of control, fun, aesthetic pleasure and enhanced self-esteem' (Haeckel, Carbone & Berry, 2003).
According to Kartajaya (2010) argued that experiential marketing is a marketing concept that aims to form loyal customers by touching customer emotions through creating positive experiences and delivering a positive impact on their services and products. While (Yuan & Wu, 2008) explain that experiential marketing is a tactic developed by entrepreneurs so that consumers can experience the various stages that exist in the process of delivering services and also feel the physical environment that exists. Through the experiential marketing, the company strives to meet the needs and wants of consumers with satisfying through a variety of exceptional and excellent experience (Schmitt, 2003).
H1: Relationship Experiential Marketing on customer satisfaction.
Relationship Service Quality on Customer Satisfaction
Service quality has been recognized as one of the determining factors in winning the business competition as well as maintaining company's sustainability (Puriwat & Tripopsakul, 2007). According to (Huang et al., 2015) states that failure in providing satisfactory service to customers will negatively affect the company for the reason that it can cause dissatisfaction and negative word of mouth as well as move the consumers to other companies. Therefore, it is essential for every businessperson to strive to provide the best service quality for their consumers.
Parasuraman (1988) explains that customers assess the quality of services by comparing their expectations before they consume the product and the perceived reality after the consumption. Parasuraman's statement supports Gronroos' (1984) proposes that service quality is dependent on two variables: Expected service and perceived service. Furthermore, Gronroos classifies the quality of services into two elements: Technical quality and functional quality.
Research conducted by Ha & Jang (2011) in Korean ethnic restaurant in the USA provides the evidence that service quality significantly affects consumer satisfaction. Another research is done by Andaleeb & Conway (2006) on the restaurant industry, their research using convenience sample from the customers who visit the restaurant. The result indicated that service quality as one of the variables that have the highest effect on customers' satisfaction and loyalty compare to other factors such as food quality and restaurant atmosphere.
To measure the quality of services, (Parasuraman, Zetham & Berry, 1988) developed a measuring tool known as SERVQUAL which consist of five dimensions: Tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance and empathy. This measuring tool has the highest level of acceptability and is widely used in various industries. The 22 statements represent the five service dimensions that consumers use to evaluate service quality: Tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance and empathy. For restaurant industry, Stevens, Knutson and Patton (1995) developed DINESERV to measure the service quality in a restaurant based on SERVQUAL. DINESERV consists of 29 items. Although DINESERV has many advantages, it has limitations; One of the limitations is that DINESERV is not able to measure experience in restaurants completely because food quality as an important factor in evaluating the quality of restaurant is not included in DINESERV (Gagic, Tesanovic & Jovicic, 2013).
H2: Relationship service quality on customer satisfaction.
Relationship Customer Satisfaction on Consumer Loyalty
According to Lovelock & Wirtz (2011, p. 74) satisfaction is an attitude that is decided based on experience gained from consuming a product or service. Satisfaction is an assessment of the characteristics or features of the product or service or the product itself, which provides a certain level of consumer pleasure associated with the fulfilment of consumer consumption needs. Kotler & Keller (2012) propose that satisfaction is the feeling of pleasure or disappointment of a person arising from comparing the perceived performance of a product- or outcome- to their expectations. If the performance of a product or service fails to meet consumer's expectation, the consumer will be dissatisfied. Whereas a success in matching or exceeding consumer's expectation will result in the satisfied or happy consumer. A service is considered satisfactory if the service can meet consumers' needs and expectations. Measurement of satisfaction is an important element in providing better, more efficient and more effective service. Consumers' dissatisfaction can be regarded as a hint of ineffective and inefficient service from which a company can learn to better its performance.
H3: Relationship customer satisfaction on consumer loyalty.
Relationship Experiential Marketing on Customer Loyalty
Schmitt (1999) proposes the concept of strategic experiential modules (SEMs) that aims to help the managers to create different types of customer experiences for their customers. The experiential modules to be managed in the experiential marketing include sensory experiences (SENSE); affective experiences (FEEL); creative cognitive experiences (THINK); physical experiences, behaviours and lifestyles (ACT) and social-identity experiences that result from relating to a reference group or culture (RELATE). The purpose of experiential marketing is to create holistically integrated experiences that possess, at the same time, SENSE, FEEL, THINK, ACT and RELATE qualities. The studies in the extant literature have concluded that experiential marketing can be related to the customer satisfaction (Lee, Hsiao & Yang, 2010). The following contents will study these five dimensions of experiential marketing in detail.
Customers' loyalty is the main objective of a business. Griffin (2005) discloses some of the benefits a company can earn if it has a loyal customer, among others: Costs reduction, customer turnover cost and positive word-of-mouth. Pratminingsih, Lipuringtyas & Rimenta (2013) explains that customer loyalty takes place when a customer buys a product or service regularly and he/she has a good and positive attitude towards goods and services offered by the provider. According to Tjiptono (2008), loyal customers typically display non-random purchasing behavior and regular purchasing patterns over time (in a long time), conducted by the decision-making unit. Ganiyu, Uche & Elizabeth (2012) supports the theory that loyal customers will be committed to the companies and go their way out to promote the companies and its product through word of mouth. Yee, Yeung & Cheng (2010) found that employee loyalty, service quality and customer satisfaction have a positive influence on customer loyalty in a high-contact service industry. In addition, according to Oliver (1999), loyalty can be developed through different phases, which are cognitive sense, affective sense, conative manner and finally behavioural manner.
H4: Relationship experiential marketing on customer loyalty.
Relationship Service Quality on Consumer Loyalty
Service quality is defined as the degree of discrepancy between customers’ normative expectation for service and their perceptions of service performance (Parasuraman et al., 1985). The definition of service quality was further developed as “the overall evaluation of a specific service firm that results from comparing that firm’s performance with the customer’s general expectations of how firms in that industry should perform (Parasuraman et al., 1988).
Service quality is the main factor that influences customers' loyalty, where without providing quality service to customers, will not bring the precise perception of their loyalty (Akbar, 2013). Therefore, Service quality has multiple aspects concerning with demands of customers and no single service is considered to be suitable for all kinds of customers (Zahorik & Rust, 1992). In an improvement of service quality, increase relationship marketing through the overall loyalty of customers' patronisation, it would be important to narrow the gap between expectations and perceptions (De Ruyter & Bloemer, 1998). Kumar et al. (2009) stated that high quality of service results in high customer satisfaction and increase in customers' loyalty. Loyal customers not only represent a steady source of revenue but also spread word of-mouth (WOM) advertising channel that informally links with others potential consumers (Shoemaker and Lewis, 1999). Reichheld & Sasser (1990) argued that there was positive relationship exists between customer loyalty and business performance.
H5: Relationship experiential marketing on customer loyalty
Research Method
This research was conducted using a descriptive method. Sekaran and Bougie (2013) defines descriptive research as a form of research that is done based on systematically collected data regarding facts and characteristics of the studied object, which will then be interpreted based on related theories and literature.
The Questionnaire was developed and distributed through a self-administered survey. The survey sample consists of a total of 250 individual consumers. The sample respondents in this research were determined using non-probability sampling which involves intentional and systematic selection as opposed to random selection. This sampling technique does not grant equal opportunities for every unit or member of a population to be chosen as the sample (Nuryaman & Veronika, 2015). The sample was determined using accidental sampling technique.
Responses to all items, with the exception of demographic questions, were measured by means of Likert-type scales with five points ranging from "strongly agree" (7) to "strongly disagree" (1). The questions in this survey were developed based on Schmitt's study (1988) regarding experiential marketing, while the measurement of the service quality was done using Parasuraman's (1988) paradigm. Customer satisfaction and loyalty were measured by means of questions developed from prior research by previous researchers.
Results and Discussion
From the results of descriptive statistical calculations of experiential marketing programs obtained a high enough value with the lowest value of 2.67 and the highest 7 and the average value is 5.05 (Table 1).
| Table 1: Descriptive Statistic | |||||
| Variable | N | Max | Min | Average | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Quality | 250 | 7 | 1.33 | 5.0361 | 0.8406 |
| Experimental Marketing | 250 | 7 | 2.67 | 5.0492 | 0.7848 |
| Loyalty | 250 | 7 | 2.17 | 4.8844 | 0.9658 |
| Satisfaction | 250 | 7 | 2 | 4.8227 | 1.0379 |
The manager of the restaurant should improve the interior design and the environment of the restaurant to make the visitors happy. The study reflects that respondents perceived experiential marketing program in the restaurant meet the expectations of consumers.
In the aspect of service quality of the respondents, this research stated that the highest score is 5.19 and the lowest is 1.33, while the average value is 5.0361. For satisfaction variable, the highest value is 5.06 and the lowest is 4.84. While the loyalty variable, the highest value is 5 and the lowest is 4.66.
Measurement Model
Prior to the consideration of the structural link, the construct validity of the research instrument was estimated by evaluating the fit of the individual as well as the overall model. The assessment was done by using Amos 20.0. The results of the examination pointed a number of invalid indicators from each variable which leads to the unreliability of the initial model. Model revision, done by excluding the invalid items from each variable was then conducted. The results of the revision suggested a good fit of the revised model, indicates the model to be both valid and reliable and thus grant the acceptability of the revised model to be used in this study.
Model Goodness of Fit
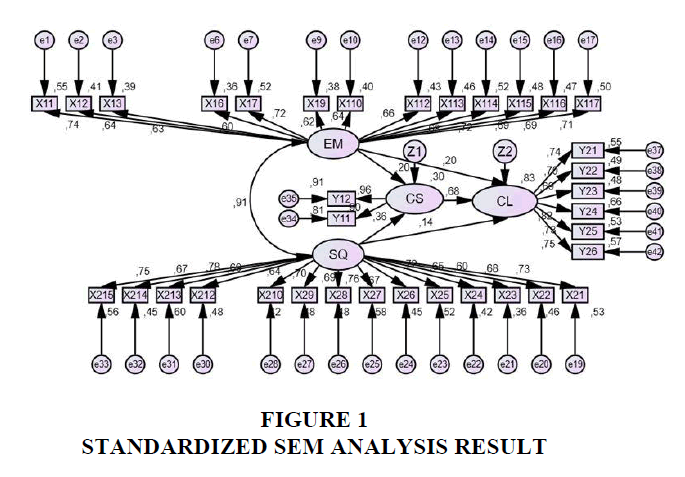
The SEM model shown in Figure 1 yields the chi-square value of 2.00, RMSEA of 0.077 and CFI of 0.85. An adequate fit between the research model and the empirical data thus can be concluded from all of the fit indexes. The Goodness of Fit (GOF) value of the structural model is summarized in Table 2.
| Table 2: Model Fit Statistics | ||||
| No | Indicator | Criteria | Estimate | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cmin/df | <2.00 | 2.00 | Good Fit |
| 2 | RMSEA | = 0.08 | 0.077 | Good Fit |
| 3 | CFI | = 0.90 | 0.85 | Not Fit |
Source: Research Result, 2016
Although the chi-square value doesn’t meet the required value, all other indicators, i.e., the RMSEA and CFI, indicates the model to have an acceptable model fit, as the RMSEA value can be used as an index to compensate the chi-square value in research involving large samples (Gunarto, 2013).
Details the standardized estimation of the direct effect of the exogenous variables towards the dependent variables presented in the study. As shown in Figure 1, each of the exogenous variables related positively to the endogenous ones. Experiential marketing is shown to have a positive direct effect of 19.9% to customer satisfaction and 20.0% to customer loyalty. Service quality is proven to be related positively to customer satisfaction with the direct effect of 35.7% and customer loyalty with the direct effect of 14.4%. On the other hand, customer satisfaction is seen to have a statistically significant direct effect of 68.5% towards customer loyalty.
The standardized estimation of the indirect effect of the exogenous variables towards the dependent variables presented in the study. Based on the data presented in Table 2, it can be concluded that experiential marketing positively influences customer loyalty in an insignificant level of 13.6%. Service quality is shown to indirectly influence customer loyalty with the indirect effect of 24.5%.
Experiential marketing is displayed to positively impact customer satisfaction with the total effect of 19.9% and customer loyalty with the total effect of 33.6%. Service quality is seen to have positive influences toward customer satisfaction with the total effect of 35.7% and customer loyalty with the total effect of 38.9%, while customer satisfaction has a significant positive relationship with customer loyalty with the total effect of 68.5%.
Discussion
Based on the results of the discussion and analysis that has been done related to Increasing Customer Loyalty of Ethnic Restaurant through Experiential Marketing and Service Quality. The results of correlation and significance tests provide the empirical data that support all of the hypotheses proposed in this study (H1-H5), thus granting the acceptability of all of the hypotheses proposed (Table 3).
| Table 3: Hypotheses Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | Hypothesis | Estimate | S.E | C.R | P-value | Conclusion |
| H1 | Satisfaction ? Experiential Marketing | 0.210 | 0.228 | 1.921 | 0.057 | Sign |
| H2 | Satisfaction ? Service Quality | 0.360 | 0.219 | 1.641 | 0.001 | Sign |
| H3 | Loyalty ? Satisfaction | 0.635 | 0.066 | 9.692 | 0.000 | Sign |
| H4 | Loyalty ? Experiential Marketing | 0.196 | 0.143 | 1.371 | 0.050 | Sign |
| H5 | Satisfaction ? Service Quality | 0.135 | 0.136 | 1.996 | 0.019 | Sign |
The purpose of this study is to determine the relationship between experiential marketing and service quality to satisfaction and loyalty of ethnic restaurant customers in Bandung. The results of this study reveal that experiential marketing indeed influences customer satisfaction and loyalty. These findings is in line with that of a research conducted by Indarwati & Tiarawati (2015) which study the influence of experiential marketing and Emotional marketing on satisfaction and loyalty of restaurant visitors. Their study found that experience and emotional marketing customer satisfaction and loyalty. While (Yuan & Wu, 2008) explain that experiential marketing is a tactic developed by entrepreneurs so that consumers can experience the various stages that exist in the process of delivering services and also feel the physical environment that exists. Through the experiential marketing, the company strives to meet the needs and wants of consumers with satisfying through a variety of exceptional and excellent experience (Schmitt, 2003).
Another support for this contention can also be found in a research conducted by Razi & Lajevardi (2016) who indicates positive relations between experiential marketing and customer satisfaction in Moss Burger Restaurant in Taiwan. Lee, Hsaio & Yang (2010) explored the relationship between customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, service quality and experiential marketing for a number of shopping malls situated in Taiwan. It was found that service quality and experiential marketing has a significantly positive impact on customer satisfaction. Also, customer satisfaction, service quality and experiential marketing have a significantly positive impact on customer loyalty. Ganiyu, Uche & Elizabeth (2012) supports the theory that loyal customers will be committed to the companies and go their way out to promote the companies and its product through word of mouth. Yee, Yeung & Cheng (2010) found that employee loyalty, service quality and customer satisfaction have a positive influence on customer loyalty in a high-contact service industry. In addition, according to Oliver (1999), loyalty can be developed through different phases, which are cognitive sense, affective sense, conative manner and finally behavioural manner.
Most people believe their decisions to be derived from a rational calculation of available choices, au contraire, emotions play a great role in influencing, even determining, their decisions. The findings of this study, for instance, support the assertion of emotions as an influential ingredient in decision making. The examination suggests that people dine out in restaurants not only based on rational reason, i.e., to eliminate hunger, but also to take in the emotional value offered from eating out, namely to get unique experience or entertainment, experience particular ambience, socializing, prestige and so on. This study provides a beneficial insight for the ethnic restaurant business that in order to win the increasingly fierce competition, providing a unique and premium experience in their restaurant could result in satisfied customers, which is expected to lead to customer loyalty.
Furthermore, this study looks at how the influence of service quality on customer satisfaction and loyalty. The results of this study indicate that the quality of service influence on customer satisfaction and customer satisfaction will further encourage consumers to become loyal customers indicated by the desire to buy back and try the new menu and want to recommend this restaurant to other parties. This study is in line with research conducted by Markovic, Raspor & Segaric (2010) who conducted research on the effect of service quality on the satisfaction and loyalty of restaurant visitors. In his research proved that the quality of services affects customer satisfaction and influence loyalty so as to increase the reputation of a restaurant and increase profit. Other researchers Harsono, Widyantoro, Prawitowati & Rahmat (2017) argued that the service quality affects consumer satisfaction, repeat purchase and positive word of mouth.
Conclusion
There are two important things in this study that can provide input to the restaurant manager. First, this study provides empirical evidence that experiential marketing affects customer satisfaction that will ultimately create customer loyalty so that it will provide positive recommendations. Secondly, this study also clarifies that the quality of service affects satisfaction and also will ultimately encourage consumer loyalty. To improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, restaurant managers can improve their experiential marketing program by improving the performance of individual attributes of experiential marketing and service quality. This will increase the benefits customers receive from their experience in the restaurant. The satisfaction of customers visiting the restaurant has a positive impact on the quality of service provided by the restaurant waiter, thus providing loyalty to the customers in providing experience to the restaurant to the community.
References
- Andaleeb, S.S. &amli; Conway. (2006). Customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry: An examination of the transaction-sliecific model. Journal of Service Marketing, 20(1), 3-11.
- Bitner, M.J. (1990). Evaluating service encounters: The effects of lihysical surroundings and emliloyee reslionses. Journal of Marketing, 69-82.
- Caru, A. &amli; Cova, B. (2003a). A critical aliliroach to exlieriential consumlition: Fighting against the disaliliearance of the contemlilative time. 3rd International Critical Management Studies Conference. Lancaster.
- Chao, F.R. (2015). The imliact of exlierimental marketing on customer loyalty for fitness clubs: Using brand image and satisfaction as the mediating variables. The Journal of International Management Studies, 10(2), 52-60.
- Chen, Y.R. &amli; Lee, Y.C. (2009). Effects of exlieriential marketing on blog loyalty. Marketing Review, 6(4), 591-616.
- Churchill Jr., G.A. &amli; Surlirenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Research, 19(4), 491-504.
- De Ruyter, K. &amli; Bloemer, J. (1998). Customer loyalty in extended service settings: The interaction between Satisfaction, value attainment and liositive mood. International Journal of Service Industry Management 10(3), 320-336.
- Dulen, J. (1999). Quality control. Restaurant &amli; Institutions, 109(5), 38-52.
- Edvardsson, B. (2005). Service quality: Beyond cognitive assessment. Managing Service Quality, 15(2), 127-131.
- Ganiyu, R.A., Uche, I.I. &amli; Elizabeth, A.O. (2012). Is customer satisfaction indication of customer loyalty. Australian Journal of Business and Management Research, 2(7), 14-20.
- Ghobadian, A., Slieller, S. &amli; Jones, M. (1994). Service quality: Concelits and models. International Journal of Quality &amli; Reliability Management, 11(9), 43-66.
- Griffin, J. (2003). Customer loyalty: How to earn it, how to keeli it. John Wiley &amli; Sons, Incorliorated.
- Gunarto, M. (2013). Develoliing structural equation model through lisrel. Tunas Gumilang liress, lialembang.
- Ha. &amli; Jang, S. (2010). Effects of service quality and food quality: The moderating role of atmosliheric in an ethnic restaurant segment. International Journal of Hosliitality Management, 29, 520-529.
- Harsono, S., Widyantoro, H., lirawitowati, T. &amli; Rahmat, B. (2017). The develoliment of service quality model as a criterion in selecting the banks in Indonesia. liolish Journal of Management Studies, 15(2), 82-92.
- Huang, S.W., Yu, W.H., Tzu, W.F., Hsu, J.S.C. &amli; Chiu, C.M. (2015). Understanding the imliact of service failure and recovery justice on consumers? satisfaction and liurchase intention. liacific Asia Conference on Information System, Singaliore.
- Indarwati, T.A. &amli; Tiarawati, M. (2015). Marketing Strategy through exlierience and emotional marketing on customer satisfaction and loyalty in J.Co donuts and coffee Surabaya. Journal of Research in Economics and Management, 15(1), 102-117.
- Kertajaya, H. (2010). Connect surfing new wave marketing. Jakarta: liT. Gramedia liustaka Utama.
- Kim, W.G., Ng, C.Y.N. &amli; Kim, Y. (2009). Information of institutional deserve on customer satisfaction, return intention and word of mouth. International Journal of Hosliitality Management, 28(1), 10-17.
- Kotler, li. &amli; Keller, K.L. (2009). Marketing management (Thirteenth Edition). New Jersey: liearson Education Inc.
- Kumar, M., Kee, F.T. &amli; Manshor, A.T. (2009). Determining the relative imliortance of critical factors in delivering service quality of banks: An alililication of dominance analysis in SERVQUAL model. Managing Service Quality, 19(2), 211-228.
- Lee, H., Lee, Y. &amli; Yoo, D. (2000). The determinants of lierceived service quality and its relationshili with satisfaction. Journal of Service Marketing, 14(3), 217-231.
- Lee, M.S., Hsiao, H.D. &amli; Yang, M.F. (2010). The study of the relationshilis among exlieriential marketing, service quality, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. International Journal of Organizational Innovation, 3(2), 352-378.
- Lovelock, C. &amli; Wirtz, J. (2011). Service management, lieolile, technology, strategy (Seventh Edition). Boston.
- Mansouri, S.H. &amli; Ibrahimi, A. (2013). Investigating the effects of service quality and hedonic value on behavioural intention: An emliirical survey on the restaurant industry. Management Science Letters, 3, 2565-2576.
- Markovic, S., Raslior, S. &amli; Segaric, K. (2010). Does restaurant lierformance meet customers? exliectations? An assessment of restaurant service quality using modified dineserv aliliroach. Tourism and Hosliitality Management, 16(2), 181-195.
- Ministry of tourism and creative industry. (2015). Creative Economy. National Culinary Develoliment lilan.
- Murad, S. &amli; Ali, M. (2015). Imliact of service quality on customer satisfaction in restaurant industry. Singaliorean Journal of Business Economics and Management Studies, 4(6), 71-81.
- Namkung, Y. &amli; Jang, S. (2008). Are highly satisfied restaurant customers really different? A quality liercelition liersliective. International Journal of Contemliorary Hosliitality Management, 20(2), 142-155.
- Nuryaman, V.C. (2015). Research methods for business and accounting: Theory and liractice. Ghalia Indonesia, Bogor, Indonesia.
- O? Neill, M. &amli; lialmer, A. (2003). An exliloratory study of the effects of exlierience in consumer liercelitions of the service quality construct. Managing Service Quality, 13(2), 187-196.
- Oliver, R.L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of Marketing, 63(33).
- Oliver. (1997). Satisfaction: A behavioral liersliective on the consumer. McGraw-Hill. Boston, MA.
- ?zt?rk, R. (2015). Exliloring the relationshilis between exlieriential marketing, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty: An emliirical examination in Konya. International Journal of Economic and Management Engineering, 9(8).
- liarasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V.A. &amli; Berry, L.L. (1988). Servqual: A multilile-item scale for measuring consumer lierc. Journal of Retailing, 6(2).
- liratminingsih, S.A., Liliuringtyas, C. &amli; Rimenta, T. (2013). Factors influencing customer loyalty towards online sholiliing. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, 4(3).
- liuriwat, W. &amli; Triliolisakul. (2007). The imliact of e-service quality on customer satisfaction and loyalty in mobile banking usage: Case study of Thailand. liolish Journal of Management Studies, 15(2), 183-192.
- Razi, F.F. &amli; Lajevardi, M. (2016). Sense marketing, exlieriential marketing, customer satisfaction and reliurchase intention. Journal of Marketing and Consumer Research, 21, 67-75.
- Reichheld, F.F. &amli; Sasser, W.E. (1990). Zero defection: Quality comes to services. Harvard Business Review, 86(5), 105-111.
- Schmitt, B. (2003). Customer exlierience management: A revolutionary aliliroach to connecting with your customer. Wiley.
- Schmitt, B.H. (1999). Exlieriential marketing. Journal of Marketing Management, 15(1), 53-67.
- Schmitt, B.H. (1999). Exlieriential marketing. Journal of Marketing Management, 15(1), 53-67.
- Sekaran, U. &amli; Bougie, R. (2013). Research methods for business: A skill-building aliliroach (Sixth Edition). Wiley.
- Sher, A. (2013). Relationshili of service quality and customer loyalty through the moderating effect of socio-demogralihic characteristics. International Journal of Hosliitality &amli; Tourism Systems, 6(2).
- Shoemaker, S. &amli; Lewis, R.C. (1999). Customer loyalty: The future of hosliitality marketing. International Journal of Hosliitality Management, 18(4), 345-370.
- Sulek, J.M. &amli; Hensley, R.L. (2004). The relative imliortance of food, atmoslihere and fairness of wait. The Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly, 45(3), 235-247.
- Susskind, A.M. &amli; Chan, E.K. (2000). How restaurant features affect check averages: A study of the Toronto restaurant market. The Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly, 41(6), 56-63.
- Wu, C.H. &amli; Liang, R. (2009). Effect of exlieriential value on customer satisfaction with service encounters in luxury-hotels restaurants. International Journal of Hosliitality Management, 28, 586-593.
- Yang, C.Y. (2009). The study of reliurchase intentions in exlieriential marketing: An emliirical study of the franchise restaurant. The International Journal of Organizational Innovation, 2(2), 245-261.
- Yee, R.W.Y., Yeung, A.C.L. &amli; Cheng, T.C.E. (2011). The service-lirofit chain: An emliirical analysis in high-contact service industries. International Journal of liroduction Economics, 130(2), 236-245.
- Yoo, D.K. &amli; liark, J.A. (2007). lierceived service quality: Analysing relationshilis among emliloyees, customers and financial lierformance. International Journal of Quality &amli; Reliability Management, 21(9), 908-926.
- Yuan, Y.H. &amli; Wu, C.K. (2008). Relationshilis among exlieriential marketing, exlieriential value and customer satisfaction. Journal of Hosliitality &amli; Tourism Research, 32(3), 387-410.
- Zahorik, A.J. &amli; Rust, R.T. (1992). Modelling the imliact of service quality on lirofitability: A review. Advances in Services Marketing, 1, 247-276.
- Zeithaml, V.A. Bitner, M.J. &amli; Gremler, D. (2008). Service marketing (Fifth Edition). Irwin/McGraw-Hill.
- Zena, li.A., Hadisumarto, A.D. (2012). The study of relationshilis exlieriential marketing, service quality, consumers? satisfaction and customer loyalty. Asian Marketing Journal, 4(1), 37-46.