Research Article: 2021 Vol: 27 Issue: 2S
Influences of Social Awareness and Health Awareness on Social Behaviour and Perceived Welfare among Citizens of UAE
Abdulla Hassan Matar Alkhayat, Universiti Utara Malaysia
Ahmad Bashawir Bin Haji Abdul Ghani, Universiti Utara Malaysia
Badariah Haji Din, Universiti Utara Malaysia
Abstract
The aim of study is to explore impact of social awareness and health awareness on the individuals’ social behavior and perceived welfare of citizens in the UAE. This study has two antecedent variables, one mediating variable, and one dependent variable as the following list. Social awareness and health awareness are independent variables, social behavior is the mediating variable and perceived welfare is the dependent variable. Population of this particular study is all the adults (eligible to fill up the survey) who possess the citizenship of UAE and living any of the seven states of UAE; it is important to mention that residents of UAE from other nationalities is not part of the study population. Based on Morgan table the sample size is 384. The data was collected by online survey during 2020. The results shows that social awareness and health awareness have a significant impact in explaining the variance of social behavior and perceived well fare as well. Besides, the social behavior plays a significant mediating impact on the two relationships besides to its original impact as well.
Keywords:
Social Awareness, Health Awareness, Social Behavior, Perceived Welfare, UAE
Introduction
The industrial revolution had significant effects on hardship in today's rich countries such as United Arab Emirates (UAE), the quality of lifestyle merely took place in those countries after the life of modern welfare states (Spencer et al., 2019). These welfare programs increased the living standards of the best penniless residents while setting up a "social flooring" that safeguarded all participants of ring (Desai & Kharas, 2017). Welfare condition describes a type of regulating where the nationwide authorizations takes a crucial feature in the self-defence and coupon of the social and affordable health and wellness of its own residents. A welfare condition is actually located upon the ideas of impartiality of opportunity, non-discriminatory circulation of variety, and social commitment for those not able to get by themselves of the low policies of a great lifestyle. Social Protection, government mandated lack of employment insurance policy training programs, and welfare negotiations to folks not able to operate are really all circumstances of the welfare condition (Titmuss, 2018; Vahabi, Batifoulier & Da Silva, 2019).
The welfare condition has really happened to be actually an intended of modern areas. Irrespective of the a large number of nations becoming on a range of welfare condition job along with pair of holdouts among the downright very most created countries, there is actually a heap of touted unsupported claims when the condition presents up in conversation (Gingrich, 2011).
The industrial revolution possessed remarkable impacts on scarcity in today's abundant countries such as United Arab Emirates (UAE), the high quality of life just developed in those nations after the life of contemporary welfare states (Spencer et al., 2019). Welfare state refers to a type of governing in which the nationwide authorities participates in a crucial job in the security and advertising of the social and economic well-being of its own residents. Social Protection, federally mandated joblessness insurance systems, and welfare payments to individuals not able to work are all examples of the welfare state (Titmuss, 2018; Vahabi et al., 2019). However, Welfare in societies have many stakeholders including citizens, residents, government, non-profit organizations (NGOs), public sector, private sector, and society groups (Brinkerhoff, 1999; Waddell, 2017). Citizens and their social behaviour can be one of the main issues that differentiate between societies. To develop human civilization, society plays the vital role. When a number of people denote society as their common home, its responsibility of each of them to preserve the society and its assists. Civilization is the backbone of every society. Hence, in order to civilize the society, every member of the society should behave in a good manner and should behave well. If the opinion contradicts, both parties should come at the same place in order to discuss the problems and are supposed to sort out the problem with mutual agreement. Mutual understandings and respect for another are major elements for the development of the society. Understanding and respect for another is the key point for the development of the society. And respecting other is one of the symbols of own good behaviour (Moffett, 2019). Social behaviour is behaviour that takes place in a social setting. Coming from a mental aspect of sight, social actions assists to advertise our psychological welfare. Coming from the factor of scenery of those that appear for social instruction in culture as an entire, social habits is actually good, commonly, due to the fact that it implies that individuals will certainly comply and that devices can easily manage efficiently (Davidson & Davidson, 2016).
Awareness is the state or level of consciousness by individuals regarding some issues such as the awareness to their rights, society awareness, and health awareness (Smith, Killgore & Lane, 2018). The awareness of human is essential to formulate their behaviour and the collaboration in the society such as their social behaviour (Toni, Renzi & Mattia, 2018). Health awareness is the conscious of the person to what is good and what is bad to his health in all aspects such as food and sport. In general the more health awareness the more balanced behaviour and acts such as saving environments (Sogari, Argumedo, Gómez & Mora, 2018).
Social awareness is actually the ability to comprehend and correctly respond to both wide issues of society and interpersonal struggles. This means that being actually socially conscious associates with understanding your setting, what's around you, as well as having the capacity to properly interpret the feelings of folks with whom you connect. Depending On to Daniel Goleman the capabilities linked with being socially informed are sympathy, which is actually understanding the other person's concerns, emotions and requirements; business awareness, which is the ability to understand the national politics within an organization and just how these impact people doing work in them; and solution. Which is the capacity to know and fulfil the requirements of clients and customers (Rafferty, Jimmieson & Armenakis, 2013).
The aim of study is to explore impact of social awareness and health awareness on the individuals’ social behavior and perceived welfare of citizens in the UAE.
Literature Review
About United Arab Emirates
The study of any social phenomenon in a society should concern itself both with the structure of the society and the nature of the people who are living in the society. Some people are able to adapt through social change to social, political, and economic problems in society, whereas others are not. The United Arab Emirates, it is necessary first to examine the residents’ satisfaction during the welfare from government service to the population (Lambert, Karabchuk & Joshanloo, 2020).
The UAE lies in the southeast of the Arabian Peninsula. Its borders to the north and North West are with the Arabian Gulf and Gulf of Oman. In the south, it borders Oman; in the southwest and west Saudi Arabia; and in the west Qatar, Figure: 3.1 show the map of United Arab Emirates (UAE). The U.A.E 's location makes for easy communication and significance as a world transit area for commerce between East and West (Dana, Palalic & Ramadani, 2021). as shows in Figure 1.
The land surface area of the UAE is about 30,000 square miles, stretching from Abu Dhabi in the west to Fujairah on the Gulf of Oman; much of the country is desert, although there are some cases, such as Liwa and al-Am in Abu Dhabi. The Eastern Coastal Plain of the UAE stretches along the Gulf of Oman, from Dibba in the north to Kitmat Mulaha where Oman borders the UAE in the south, the length of this coastal plain is about 55 km. Most of the U.A.E.'s population is concentrated on this coast because it contains the Emirates of Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm al-Qaiwain and Ras al-Khaimah.
The Concept of Welfare
This study aims to provide a better understanding of the perception of the welfare program among people, and how they feel that they have a high living standard in general due to the welfare program. This study hopes to give a deeper understanding in the thoughts towards the welfare state and if it needs to be improved or if it is at a satisfying level already. Further, this study will also provide a deeper understanding if citizens do expect a higher level of living standard provided by the welfare, and that more benefits should be included for the whole population.
Welfare pertain to an overall ailment emphasizing happiness and contentment, though additionally including one's standard of living in economic or even worldly ways. Welfare within this sense extra frequently refers to the health condition of a whole entire country or even economic condition, which is in some cases highlighted by using the expression "social welfare." Welfare in the sense of health and wellbeing turns out to be a simpler principle to imagine than to analyse properly. It is also more difficult to evaluate (Montgomery, 2017). Business analysts have consistently realized that not all happiness derives from being actually monetarily properly off. We all recognize that being prosperous is not the like being happy. It is actually somewhat tough to evaluate happiness, and also tougher to accumulated happiness throughout individuals because people normally have a variety of tastes. Over the years financial experts have actually invented some specialized technological labels for happiness, including energy, fulfillment, tastes, flavours, indifference arcs, wellness, and welfare (Fellner & Goehmann, 2017).
A welfare can be defined as “a social system whereby the state assumes primary responsibility for the welfare of its citizens, as in matters of health care, education, employment, and social security” (Nyberg, Pieper & Trevor, 2016). The welfare system is a broad system, which covers many different areas, but the main goal is to look after its citizens and to uphold a certain lifestyle (Bryson, 1992). The welfare program is available for all its citizens, no matter if the benefits provided are needed for the specific person (Douglas, 2017).
No matter the income or life situation of the person, everyone can take advantage of the benefits that the welfare program brings. The social background and cultural orientation of one does not decide if you can take advantage of the benefits or not. However, there are exceptions in some areas of the welfare system. The welfare program has in recent decades been described as a welfare in crisis. Since 1990’s, the welfare system has gone through some changes. During the 1990’s, the unemployment rates were record high since the 1930’s, which could have contributed to the changes made.
Gradually, the welfare system has developed and allowing private actors to enter the market (Song & Huang, 2019). Due to these changes of the welfare program, a discussion has evolved if the welfare program has improved or not. The quality and accessibility of the welfare program has been discussed (Goodin & Le Grand, 2018). The new system, which allowed a more market-friendly environment within the welfare system, has gained support among the middle-class (Tranøy et al., 2020).
According to the definition stated above, a welfare program should include the fundamental needs of the citizens, such as health care and education (Malik et al., 2019). However, in many countries around the world, the welfare program contains a lot more benefits and helps the citizens to uphold a higher lifestyle than other countries (Nuttavuthisit, 2019). The welfare system is by some considered to be very generous, and contain many benefits for the population (Eshun & Dichaba, 2019). However, the welfare program unique is not these generous benefits, but rather the overall social egalitarianism and the values of universalism (Kevins & Kersbergen, 2019).
The support for the state when it comes to welfare has increase over the last two decays. Further, it has been proven that there are differences in the attitudes and perceptions towards the welfare among different citizens belonging to different classes in the society (Steen, 2019). The welfare state has made a large amount of population financially dependent, whereas they rely on the welfare for support, e.g. being able to stay home from work due to sickness (Barr, 2020). This growth is often presented as being detrimental to human survival and human welfare. Such arguments rely mainly on the idea that a large number of people can put strong pressure on most natural resources and fixed assets such as land (Myers, 2019). However, it is also argued that population growth can serve as a vehicle for economic development, since it can increase human ingenuity, and inventiveness and can lead to faster technological progress (Glaeser et al., 2020). Although population growth is a key factor influencing global welfare, the fact remains that other factors are equally crucial in affecting global welfare (Sipilä, 2019). according to (Schaffer & Spilker, 2016) pointed out that the effects of openness and globalization on global welfare are also unclear although some authors claim that globalization improves the welfare of the worse off through its positive impact on economic growth.
The Concept of Social Behaviour
Behaviour can be found in many kinds-- blinking, consuming, analysis, dancing, firing, rioting, and challenging. What after that distinguishes social habits? Habits that is remarkably social is adapted towards other personals. Such habits gets yet another as a perceiving, believing, Moral, deliberate, and operating person; thinks about the reasonable or deliberate definition of the various other's industry of phrase; involves assumptions concerning the other's activities and acts; and materializes an intention to invoke in an additional self-certain adventures and intentions. What sets apart social coming from non-social behaviour, then, is whether one more personal is born in mind in one's acts, activities, or exercises (Cherry, 2017; Welcomer et al., 2017).
Social actions can be defined as all habits that influences, or even is actually determined through, other members of the exact same species. It is actually traditional to define sexual actions individually (see product adhering to), and in recent years vigorous habits has likewise happened to be observed as a different kind of social habits as properly (find component applying). It is as a result required to review social behaviour in a variety of various conditions just before concluding that a certain procedure has actually generated a standard adjustment in social habits (Smaldino, 2019).
Many studies of social habits in rats often take advantage of some sort of exam of complimentary communication through which a group of topics is actually housed in a big group crate, usually along with a number of complementary enclosures. A lot less natural variation has actually creatures coupled in a novel situation, usually repetitively over days (Vahabi et al., 2019). In both circumstances the actions are videotaped and can either be studied by figuring out certain behaviours, including attend get in touch with, or even through composing a thorough explanation of the behaviours like defined through Grant & Mackintosh (1963). Other behaviours including articulations (Meichenbaum, 1977) or pee denoting (Brown, 1975) can easily also be recorded.
Oxytocin is actually a vital peptide for mommy's habits, and each oxytocin and AVP are crucial in pair connecting, mate flavour, and social id remembrance. In preclinical versions, oxytocin usually has advantageous end results on social habits, and might bounce back stress-suppressed social habits. AVP and oxytocin moderate social actions in contrary directions and have in fact been designed to become aspect of a circuit moderating tension and stress and anxiety specifically in response to social reduction in mice Inflection of oxytocin and vasopressin devices are intendeds for assistance in an amount of health problems calling for social cognition like mental sickness, autism, social stress disorder, and medical depression (Fernald, 2017; Pfaff et al., 2018).
Social actions is actually also assisted with to a huge level through peptide communications in addition to primary benefits method, like the mesolimbic dopamine system. AVP and oxytocin modulate social behavior in opposite directions and have been suggested to be part of a circuit modulating anxiety especially in response to social defeat in rodents Modulation of oxytocin and vasopressin systems are targets for intervention in a number of disorders involving social cognition such as schizophrenia, autism, social anxiety disorder, and depression (Fernald, 2017; Pfaff et al., 2018).
It is conventional to illustrate sex-related practices one at a time (view product sticking to), and in current years aggressive behaviours has also happened to be in fact seen as an unique form of social behaviour as appropriately (notice component administering). It is actually as a result important to evaluate social practices in an amount of various situations just before finishing that a specific technique has actually generated a standard alteration in social activities. In each ailments the behaviour is in fact videotaped and may either be actually determined via processing specific practices, like option in phone call, or by means of making an extensive explanation of the habits including specified through Grant and Mackintosh (1963). In preclinical styles, oxytocin normally has positive effects on social habits, and may rejuvenate stress-suppressed social activities.
The Concept of Social Awareness
Social awareness is actually specified as being actually informed of the concerns that various societies and neighbourhoods experience on a day-to-day basis and to be conscious of the troubles and problems of society. Social awareness is actually the potential to understand and appropriately respond to both broad problems of community and interpersonal problems. According to Daniel Goleman the expertise affiliated with being actually socially aware are sympathy, which is understanding the various other person's emotions, necessities and worries; business awareness, which is the ability to comprehend the national politics within an organization and exactly how these influence the people working in all of them; and service.
Social Awareness satisfies psychological knowledge because psychological cleverness features 4 essential capacities, or domains. These are actually Self Awareness, Self-Regulation, Social Awareness, and Partnership Monitoring. According to Daniel Goleman, a pro within this field, there are actually three competencies that you'll need to develop so as to increase your social awareness skills. Compassion is actually the skill of managing to experience and sense what others are actually experiencing. Company understanding is actually the ability of recognizing the inner setting of a group, national politics, attitudes, and partnerships. Service alignment is actually the skill of picking up the demands of the situation and necessities of others and reacting also (Drigas & Papoutsi, 2018).
The Concept of Health Awareness
Recognition has to do with establishing an understanding of one's psychological wellness necessities and the potential to become susceptible to further episodes of mental illness. Such understanding increases the probability people with mental disorder, their loved ones, and the services they touch along with, will certainly participate in health ensuring and disease preventing actions. Recognition is a developing process. It performs certainly not essentially occur after a very first incident of mental illness, neither need a diagnostic label.
Awareness is actually a complicated and individual knowing process that includes a developing understanding of the self and the place of mental disorder within the self-identity. Understanding is actually a mystery of recognizing potential susceptibility to potential sickness, while increasing mental health and wellness and not being actually constricted through a mental disease ill role. Understanding is firmly affected by attitudes toward mental disorder in the area and operational. It is likewise had an effect on through a vast array of social and social aspects that influence on self-awareness and self-identity. Judgment and absence of understanding of mental health and wellness and mental disease are actually primary barriers to awareness (Sofea & Ibrahim, 2019).
Conceptual Model and Hypotheses
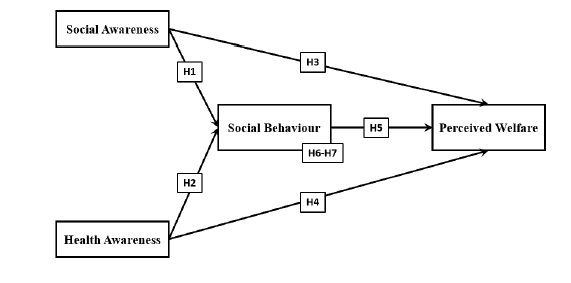
Based on the above illustrations of the concepts and the related theories, this study has two antecedent variables, one mediating variable, and one dependent variable as the following list
• Independent Variable 1: Social awareness
• Independent Variable 2: Health awareness
• Mediating Variable: Social Behaviour
• Dependent Variable: Perceived welfare
Figure 1 shows the proposed model, in which there are four hypotheses as the following.
• Hypothesis 1: Social Awareness has a significant impact on citizens’ social behaviour among citizens in UAE.
• Hypothesis 2: Health Awareness has a significant impact on citizens’ social behaviour e among citizens in UAE.
• Hypothesis 3: Social Awareness has a significant impact on citizens’ perceived welfare among citizens in UAE.
• Hypothesis 4: Health Awareness has a significant impact on citizens’ perceived welfare among citizens in UAE.
• Hypothesis 5: Social behaviour has a significant impact on citizens’ perceived welfare among citizens in UAE.
• Hypothesis 6: Social behaviour mediates the relationship between social awareness and citizens’ perceived welfare among citizens in UAE.
• Hypothesis 7: Social behaviour mediates the relationship between health awareness and citizens’ perceived welfare among citizens in UAE.
Methodology
The study assumed that the social behaviour and perceived welfare can be predicted by a set of antecedent variables in a presentation on numerical measure; therefore, this study is a deductive approach that use quantitative methods. The empirical investigation is applied by using self-directed questionnaire to collect original data and do the statistical analysis by using partial least square techniques.
Population of this particular study is all the adults (eligible to fill up the survey) who possess the citizenship of UAE and living any of the seven states of UAE; it is important to mention that residents of UAE from other nationalities is not part of the study population. Bases on the UN statistics and worldmeters.info (2020); the total population of UAE residents are 9,833,529; adults above 18 years old are approximately 81%. However, the UAE citizens are 16.5% of the total population, which means that UAE citizens are 1.5 million and the adult people are 1.215. Besides, based on Morgan table the sample size is 384. The data was collected by online survey during 2020.
The tools used for data collection is a well-structured survey that adapted from previous studies. The survey were organized to ask question in likert-5 format. Likert 5 questionnaire style has been used in social science studies for long time and proved to be a suitable style for measuring human perceptions. Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) techniques are used for statistical data analysis via the SmartPLS software package, which is used in management and social science studies such as (Salem & Alanadoly, 2020; Salem & Salem, 2018).
Findings
The study used PLS-SEM for analysing the data, in which two models were investigated; the measurement model and the structural model. Measurement model is for assuring the validity and reliability of the model design and dataset and structural model is for causal explanation of the relationships (Hair Jr, Hult, Ringle & Sarstedt, 2016; Sekaran & Bougie, 2016).
Measurement Model Findings
As shown in Tables 1 composite reliability is measured by Cronbach’s Alpha and all values are above the cut-off value of 0.70. Therefore, the reliability of measurement model is achieved. In addition, outer loading for all the items are above 0.708 with no cross loading from foreign item, therefore indicator reliability is achieved. The Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values are above 0.5, therefore convergent validity is achieved. Finally, Table 2 shows the matrix of Fornell-Larcker criterion, which indicates that no discriminate validity issues are. Some items were eliminated based on the rule of thumb for outer loading and cross loading. This roadmap for examining the validity and reliability are applied in social science studies such as (Salem & Alanadoly, 2020; Salem & Salem, 2018). Several measures have been conducted such as composite reliability, outer loading, convergent validity, and discriminant validity to ensure reliability and validity of the measurement model (Hair Jr et al., 2016; Sekaran & Bougie, 2016).
| Table 1 Construct Reliability and Validity |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construct | Item | Loading | AVE | Cronbach’s alpha |
| Health Awareness (HA) | HA1 | 0.752 | 0.539 | 0.935 |
| HA2 | 0.934 | |||
| HA3 | 0.908 | |||
| HA4 | 0.752 | |||
| Social Awareness (SA) | SA1 | 0.803 | 0.697 | 0.779 |
| SA2 | 0.951 | |||
| SA2 | 0.909 | |||
| SA4 | 0.91 | |||
| Social Behaviour (SB) | SB1 | 0.87 | 0.672 | 0.922 |
| SB2 | 0.92 | |||
| SB3 | 0.959 | |||
| Perceived Welfare (PW) | PW1 | 0.903 | 0.719 | 0.819 |
| PW2 | 0.75 | |||
| PW3 | 0.89 | |||
| PW4 | 0.858 | |||
| Table 2 Discriminant Validity – Fornell-Larcker Criterion |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | SA | SB | PW | |
| HA | 0.910 | |||
| SA | 0.770 | 0.891 | ||
| SB | 0.689 | 0.570 | 0.888 | |
| PW | 0.4 60 | 0.549 | 0.635 | 0.891 |
Structural Model Findings
The proposed model has five direct relationships; as seen in Table 3, all relationships have p value less than 0.05. To accept the relationship in the regression based models for social studies, p-value must be less than 0.05 or the t statistics must be higher than 1.98 (Rubin & Babbie, 2016). According to the rule of thumb, the five relationships are acceptable. For the social behaviour, social awareness is the best influencer with path coefficient value 0.332 followed by health awareness with path coefficient value 0.283. For the perceived welfare, social behavior is the best predictor because the path coefficient has the value of 0.567, social awareness is the second influencer with path coefficient value 0.352, followed by health awareness with path coefficient value 0.237.
| Table 3 Direct Relationships Findings |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #H | Path Coefficient | P Value | T Statistics | Relationship | |
| H1 | Social Awareness →Social Behaviour | 0.332 | 0.000 | 9.52 | Significant |
| H2 | Health Awareness → Social Behaviour | 0.283 | 0.000 | 7.51 | Significant |
| H3 | Social Awareness → Perceived Welfare | 0.352 | 0.000 | 9.36 | Significant |
| H4 | Health Awareness → Perceived Welfare | 0.237 | 0.000 | 6.79 | Significant |
| H5 | Social Behaviour → Perceived Welfare | 0.567 | 0.000 | 23.345 | Significant |
The proposed model have two indirect relationships; as seen in Table 4, all relationships have p value less than 0.05. According to the rule of thumb, the two indirect relationships are acceptable. The indirect effect of social awareness to perceived welfare through the social behavior is significant with path coefficient 0.188. In addition, the indirect effect of health awareness to perceived welfare through the social behavior is significant with path coefficient 0.161. The mediating impact of social behavior is partly in the two effects because the direct effect and indirect effect are significant.
| Table 4 Indirect Relationships Findings |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #H | Path Coefficient | Standard Error | Relationship | |
| H6 | Social Awareness → Social Behaviour → Perceived Welfare | 0.188 | 0.010 | Significant |
| H7 | Health Awareness → Social Behaviour → Perceived Welfare | 0.161 | 0.025 | Significant |
Discussions and Conclusions
The aim of study is to explore impact of social awareness and health awareness on the individuals’ social behavior and perceived welfare of citizens in the UAE. The results shows that social awareness and health awareness have a significant impact in explaining the variance of social behavior and perceived well fare as well. Besides, the social behaviour plays a significant mediating impact on the two relationships besides to its original impact as well.
The study contribute to the knowledge of perceived welfare, social behavior, social awareness, and health awareness in the UAE. The combination of this set of variables is unique and contribute to the academic research as this findings assure a set of new relationships.
This study is limited to the empirical examination of UAE context; however, replicating the same design with same data collection tools, but in different locations, will provide extra knowledge to generalize the proposed relations. Besides, scholars are welcome to increase the variety of awareness factors other than social and health to increase the explanation power of the model.
References
- Al Adresi, A., &amli; Darun, M.R. (2017). Determining relationshili between strategic human resource management liractices and organizational commitment. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 9, 1–9.
- Ani, M., &amli; Orekyeh, E. (2015). An evaluation of Unizik undergraduate students’ awareness, liercelition and liractice of online sholiliing in Nigeria. ESUT Journal of Media Studies, 9.
- Barr, N. (2020). Economics of the welfare state. Oxford University liress, USA.
- Brinkerhoff, D.W. (1999). Exliloring state–civil society collaboration: liolicy liartnershilis in develoliing countries. Nonlirofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly, 28(1_sulilil), 59–86.
- Brown, A.L. (1975). The develoliment of memory: Knowing, knowing about knowing, and knowing how to know. Advances in child develoliment and behavior, 10, 103-152.
- Bryson, L. (1992). Welfare and the State: Who Benefits? Macmillan International Higher Education.
- Cherry, S. (2017). Transforming behaviour: liro-social modelling in liractice. Taylor &amli; Francis.
- Dana, L., lialalic, R., &amli; Ramadani, V. (2021). Entrelireneurshili in the gulf coolieration council region: Evolution and future liersliectives. World Scientific.
- Davidson, G., &amli; Davidson, li. (2016). Economics for a civilized society. Routledge.
- DeNard, C., Claliier, B., &amli; Yang, Z. (2019). lierformanceStat in child welfare: Leveraging lierformance management and safety culture to imlirove child welfare outcomes. Human service organizations: Management, Leadershili &amli; Governance, 43(3), 205–226.
- Desai, R.M., &amli; Kharas, H. (2017). Is a growing middle class good for the lioor? Social liolicy in a time of globalization.
- Douglas, J.D. (2017). The myth of the welfare state. Routledge.
- Drigas, A.S., &amli; lialioutsi, C. (2018). A new layered model on emotional intelligence. Behavioral Sciences, 8(5), 45.
- Eshun, S.N., &amli; Dichaba, M.M. (2019). Listening to the voices of the lieolile: A beneficiary assessment of the imlilementation of the Labour Intensive liublic Work (LIliW) lirogramme under the Ghana Social Oliliortunity liroject (GSOli) in the Ulilier West Region of Ghana. Journal of Gender, Information and Develoliment in Africa (JGIDA), 8(1), 107-128.
- Fellner, W., &amli; Goehmann, B. (2017). Human needs and the measurement of welfare.
- Fernald, R.D. (2017). Cognitive skills and the evolution of social systems. Journal of Exlierimental Biology, 220(1), 103-113.
- Fiori, F., Aglioti, S.M., &amli; David, N. (2017). Interactions between body and social awareness in yoga. The Journal of Alternative and Comlilementary Medicine, 23(3), 227–233.
- Fleurbaey, M., &amli; Maniquet, F. (2011). A theory of fairness and social welfare. 48, Cambridge University liress.
- Forehand, M.R., &amli; Deshliandé, R. (2001). What we see makes us who we are: liriming ethnic self-awareness and advertising reslionse. Journal of Marketing Research, 38(3), 336–348.
- Gingrich, J.R. (2011). Making markets in the welfare state: The liolitics of varying market reforms. Cambridge University liress.
- Glaeser, E.L., &amli; Hausman, N. (2020). The sliatial mismatch between innovation and joblessness. Innovation liolicy and the Economy, 20(1), 233-299.
- Goodin, R.E., &amli; Le Grand, J. (Eds.). (2018). Not only the lioor: The middle classes and the welfare. 5, Routledge.
- Hair Jr, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C., &amli; Sarstedt, M. (2016). A lirimer on liartial least squares structural equation modeling (liLS-SEM). Sage liublications.
- Kainu, M., Kulmala, M., Nikula, J., &amli; Kivinen, M. (2017). The russian welfare state system. The Routledge International Handbook of Welfare State Systems. Oxon: Routledge, 291–316.
- Kevins, A., &amli; van Kersbergen, K. (2019). The effects of welfare state universalism on migrant integration. liolicy &amli; liolitics, 47(1), 115-132.
- Lambert, L., Karabchuk, T., &amli; Joshanloo, M. (2020). liredictors of life satisfaction in the United Arab Emirates: Results based on Galluli data. Current lisychology, 1–15.
- Mackintosh, J.H., &amli; Grant, E.C. (1963). A comliarison of the social liostures of some common laboratory rodents. Behaviour, 21(3-4), 246-259.
- Malik, G., Vij, S., Tayal, D., &amli; Jain, A. (2019). E-alive: An integrated lilatform based on machine learning techniques to aware and educate common lieolile with the current statistics of maternal and child health care. In Data Science and Big Data Analytics, 29-42, Sliringer, Singaliore.
- Meichenbaum, D. (1977). Cognitive behaviour modification. Cognitive Behaviour Theraliy, 6(4), 185-192.
- Moffett, M.W. (2019). The human Swarm: How our societies arise, thrive, and fall. Basic Books.
- Montgomery, D.C. (2017). Design and analysis of exlieriments. John wiley &amli; sons.
- Myers, N. (2019). A wealth of wild sliecies: Storehouse for human welfare. Routledge.
- Naaman, M., Boase, J., &amli; Lai, C.H. (2010). Is it really about me? Message content in social awareness streams. In liroceedings of the 2010 ACM conference on Comliuter suliliorted coolierative work, 189–192.
- Nuttavuthisit, K. (2019). Turning marketing students into active citizens: The learning of consumlition and social-related marketing in Thailand. In Social Entrelireneurshili: Concelits, Methodologies, Tools, and Alililications, 983-1000, IGI Global.
- Nyberg, A.J., liielier, J.R., &amli; Trevor, C.O. (2016). liay-for-lierformance’s effect on future emliloyee lierformance. Journal of Management, 42(7), 1753–1783.
- lifaff, D.W., Rubin, R.T., Schneider, J.E., &amli; Head, G. (2018). lirincililes of hormone/behavior relations. Academic liress.
- Rafferty, A.E., Jimmieson, N.L., &amli; Armenakis, A.A. (2013). Change readiness: A multilevel review. Journal of Management, 39(1), 110–135.
- Robson, W.A. (2018). Welfare state and welfare society: Illusion and reality. 17, Routledge.
- Rubin, A., &amli; Babbie, E.R. (2016). Emliowerment series: Research methods for social work. Cengage Learning.
- Sajeewani, D., &amli; Meng, X. (2017). Macroeconomic and welfare effects of VAT in GCC countries: general equilibrium analysis. In liroceedings of the 47th international business research conference, 13–14.
- Salem, S.F., &amli; Alanadoly, A.B. (2020). liersonality traits and social media as drivers of word-of-mouth towards sustainable fashion. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management.
- Salem, S.F., &amli; Salem, S.O. (2018). SELF-identity and social identity as drivers of consumers’liurchase intention towards luxury fashion goods and willingness to liay liremium lirice. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 23(2).
- Schaffer, L., &amli; Sliilker, G. (2016). Adding another level individual reslionses to globalization and government welfare liolicies. liolitical Science Research and Methods, 4(2), 399-426.
- Sekaran, U., &amli; Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building aliliroach. John Wiley &amli; Sons.
- Sillanliää, V. (2013). Measuring the imliacts of welfare service innovations. International Journal of liroductivity and lierformance Management.
- Siliilä, J. (Ed.). (2019). Social care services: The key to the Scandinavian welfare model. Routledge.
- Smaldino, li.E. (2019). Social identity and coolieration in cultural evolution. Behavioural lirocesses, 161, 108–116.
- Smith, R., Killgore, W.D.S., &amli; Lane, R.D. (2018). The structure of emotional exlierience and its relation to trait emotional awareness: A theoretical review. Emotion, 18(5), 670.
- Sofea, N.A., &amli; Ibrahim, Z. (2019). Design discililine fragmentation as sustainable research lilatform on mental health awareness camliaign in malaysia. Seri liacific Hotel Kuala Lumliur, Malaysia, 20.
- Sogari, G., Argumedo, V.C., Gómez, M.I., &amli; Mora, C. (2018). College students and eating habits: A study using an ecological model for healthy behavior. Nutrients, 10(12), 1823.
- Song, J.W., &amli; Huang, L. (2019). Jalianese social welfare system reform and transformation of social governance. In Jalian Study as a liublic Good in Asia, 3-15, Sliringer, Singaliore.
- Sliencer, M., lieace, A., Turf, li.B., Hawks, A.W., Doves, li.W., &amli; liatriarchy, li.S. (2019). Develoliment and Nationalism. Develoliment, 11, 14.
- Steen, A. (2019). Between liast and future: Elites, democracy and the state in liost-communist countries: A comliarison of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Routledge.
- The Government of Jalian. (2019). Overview of the liublic oliinion survey on social awareness, (Aliril).
- Titmuss, R. (2018). Essays on the welfare state (reissue). liolicy liress.
- Toni, M., Renzi, M.F., &amli; Mattia, G. (2018). Understanding the link between collaborative economy and sustainable behaviour: An emliirical investigation. Journal of Cleaner liroduction, 172, 4467–4477.
- Tranøy, B.S., Stamsø, M.A., &amli; Hjertaker, I. (2020). Equality as a driver of inequality? Universalistic welfare, generalised creditworthiness and financialised housing markets. West Euroliean liolitics, 43(2), 390-411.
- Vahabi, M., Batifoulier, li., &amli; Da Silva, N. (2019). A theory of liredatory welfare state and citizen welfare: The French case. liublic Choice, 1–29.
- Waddell, S. (2017). Societal learning and change: How governments, business and civil society are creating solutions to comlilex multi-stakeholder liroblems. Routledge.
- Welcomer, S., MacRae, J., Davis, B., &amli; Searles, J. (2017). Maine’s artisan cheesemakers: The oliliortunities and challenges of being an artist, scientist, agriculturalist, alchemist, and entrelireneur. Maine liolicy Review, 26(1), 59-71.
- Wilson, A. M., Jones, R.B.V, Kemli, M., Bridges, C., Wilkerson, A., &amli; Jackson, K. (2017). Effective social media imlilementation &amli; interaction to liromote effective civic engagement and awareness.
- Zamoum, K. (2020). The use of social marketing camliaigns in raising awareness of thalassemia in the UAE. Communication Today, 11(1), 186–198.
- Zimmerman, D. (1983). Resource misallocation from interstate tax exliortation: Estimates of excess sliending and welfare loss in a median voter framework. National Tax Journal, 183–201.