Research Article: 2019 Vol: 22 Issue: 1
Market Orientation and Distinctive Competence Toward Service Mix on Study Programs of Higher Education in Maluku, Indonesia
Dian Utami Sutiksno, Politeknik Negeri Ambon, Indonesia
Ansari Saleh Ahmar, Universitas Negeri Makasar, Indonesia
Irma Setyawati, University of Bhayangkara Jakarta Raya, Indonesia
Muh. Yamin Noch, Universitas Yapis Papua, Indonesia
Victor Pattiasina, Universitas Yapis Papua, Indonesia
Abstract
This study aims to find out the market orientation and the distinctive competence toward the service mix in study programs of higher education in Maluku Province, Indonesia. The research method used is descriptive method and explanatory method. The technique analysis used is Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). The total population of 242 departments/study programs, but respondents analyzed only consists of 221 of study programs. The result of this study is the relationship of market orientation with distinctive competence is included in the strong sufficient category. Partially and simultaneously, market orientation and distinctive competence have a positive influence toward service mix.
Keywords
Service Mix, Distinctive Competence, Market Orientation, Higher Education.
Introduction
Globally, there has been development of agreement from several international forums. Like AFTA, C-AFTA, AEC and WTO in the next year of 2020. The reason that also underlies the higher education to implement the marketing concept, namely the change of government policies that occur in various countries, include in Indonesia. The policy is like reducing government subsidies to higher educations (particularly State Higher Education or PTN), for example; in Indonesia today, to obtain the grant funds toward higher education (both State Higher Educations and Private Higher Educations or PTS) must compete to get the funds. The reduction of government subsidies, of course, leads to more creative institutions and seeks to seek sources of non-government funding. Caruana et al. (1998) found that market oriented colleges were relatively easy to obtain non-government funding. These findings can serve as the basis for Indonesian higher educations to implement the marketing concept (Soegoto, 2010).
The number of private higher education and state higher education in Maluku province until now: 6 State Higher Educations (1 University, 3 Polytechnics, 1 College and 1 Institute), and 36 Private Higher Educations consisting of 3 Universities, 1 Institute, 29 Colleges, and 3 Academies. From the 242 study programs, more bachelor programs (S1) offered by higher educations are 173 study programs (72%), followed by three-year diploma programs (D3) as much as 29 study programs (12%). The total of 161 study programs are located in Ambon City, the rest are spread in cities and districts in Maluku province, Indonesia.
The transformation of the paradigm from higher education in Indonesia is also provides an opportunity for the implementation of market orientation. This is in line with the Renstra of Higher Education Directorate of Institutional and Cooperation Directorate General of Higher Education, Ministry of Education and Cultural (Kemdikbud) Year 2014 which is formulated according to the global trend of higher education namely massification, globalization, and technology influence. The market orientation is a business culture that generates exceptional performance through a commitment in order to create superior value for customers. The implicit values and beliefs in encouraging this culture are:
1. To continuous cross-functional learning about customers 'ability to express customers and latent needs and about competitors' capabilities and strategic matters.
2. Cross-functional coordination with actions to create exploited learning (Slater and Narver, 2000).
Capability or competence is a set of skill and knowledge accumulation, which is done through an organizational process, allowing the company to coordinate activities and to make the use of company assets. The main components of distinctive capabilities or competencies are: organizational processes, skills and knowledge accumulation, coordination of activities and assets (Cravens & Piercy, 2013). The university marketing strategies in relation with the institutional higher education strategies such as directing efforts and resources to achieve mission and strategic objectives, facilitating decision making on the marketing mix component (Diaconu & Pandelica, 2011).
This paper wants to know how the influence of market orientation and distinctive competence toward service mix on partial and simultaneous with combining some new dimensions and indicators in one variable that rare to be use.
Literature Review
Market Orientation
Market orientation is a business perspective that combining customer focus or customer orientation, competitor orientation and inter-functional coordination or cross-function that is committed for creating superior customer value on an ongoing basis that will ultimately create a superior performance (Narver & Slater, 1990; Cravens & Piercy, 2013; Best, 2009; Casidy, 2014; Algarni & Talib, 2014).
Distinctive Competence
The unique capabilities of an organization or company, which are offering superior services, superior images, knowledge of customers, competitors, and planning and allocating skills, which are difficult to replicate by competitors that will affect the competitive advantage of the organization or company (Conant et al., 1990; Woodside et al., 1999).
Service Mix
A set of tools or key elements of marketing that can be controlled by a company or an organization to achieve marketing objectives, through 4P from the company side (process, people, physical evidence and productivity & quality) and 4C from the consumer's perceived side (capabilities, caliber/champion, charisma/collateral and customer experience) (Booms & Bitner, 1981; Lovelock & Wirtz, 2011; Newman & Jahdi, 2009).
Methods
The research method used is descriptive method and explanatory method. Descriptive is a research method that aims to obtain a description of the research object and explanatory is a research method that aims to determine the characteristics, and to explain the relationship between variables studied (Cooper & Schindler, 2008). The previous research paradigm showed that there was 3 (three) construct variables in the research model include: Market Orientation (MO); and Disctintive Competence (DC), which are a group of exogenous variables, as well as the Service Mix (SM) as the endogenous variables of the study.
The sampling technique used is census that the entire population is given a questionnaire. In addition, to obtain accurate information about the variables studied, the interviews conducted with Kopertis Region XII primarily about the data and the situation of private higher education (PTS) in Maluku Province.
From total population of 242 study programs after the questionnaires were distributed and interviews and field visits were conducted, only 221 questionnaires were returned for analysis, with reasons that some of them were inaccessible, some were registered in College Database (PDDIKTI) but not in the field and also the difficulty to meet the leader of its study program. Thus from 242 study programs in Maluku Province there were only 221 study programs have been analyzed (108 study programs of private higher education and 113 study programs of state higher education) or 91.3% from the total studying population of Higher Education in Maluku Province.
In this research, the analysis technique used is Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). SEM is a procedure for estimating and testing a series of relationships that depend on a set of concepts or measurable variables and incorporated into several integrated models. This study using two types of analysis, including:
1. The descriptive analysis especially for qualitative variables.
2. The quantitative analysis in the form of hypothesis testing by using statistical test.
Descriptive analysis is used to see the causal factors while the quantitative analysis emphasizes in the disclosure behavior of research variables, using SEM-LISREL. Through the use of analytical methods combination can be obtained a comprehensible generalization. Testing of research model to measure identified factors was done with Confirmatory Factor Analysis Approach. Questionnaire tool with 3 variables: market orientation (dimensions: customer orientation, competitor orientation, and cross-function, with a total of 29 indicators); distinctive competence (dimensions; superiority, knowledge of customers & competitors, and planning & allocating skills, with a total of 22 indicators); and service mix (dimensions: process, people, physical evidence, and productivity & quality, with a total of 24 indicators); totaling there are 3 variables, 11 dimensions, and 75 indicators.
Result
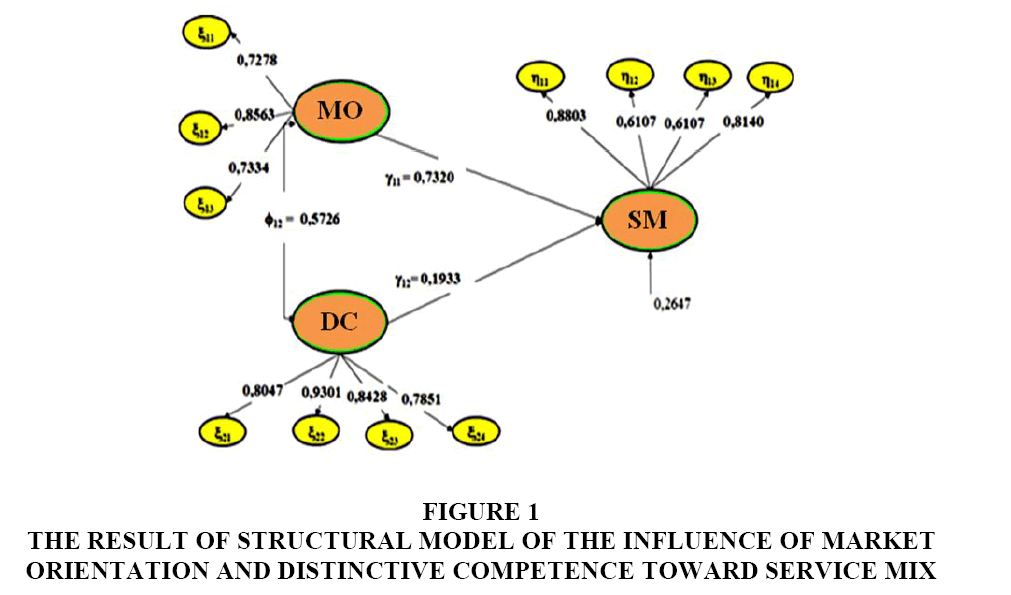
From the results of calculations for the hypothesis that the influence of market orientation and distinctive competence on service mix can be obtained structural equations that are hypothesized as follows: SM=0.7320 MO+0.1933 DC+0.2647.
Based on the calculation results obtained can be seen the coefficient of the influence of Market Orientation (MO) on the Service Mix (SM) of 0.7320 with the tcount value for the statistical test of 6.2403 and the coefficient of influence of Disctintive Competence (DC) on the Service Mix (SM) of 0.1933 with the tcount value for the statistical test of 2.8295 (Table 1).
| Table 1 The Result of Structural Model Computation from the Influence of Market Orientation and Distinctive Competence Toward Service Mix |
|||||
| Latent Endogen Variable | Latent Exogenous Variable | Coefficient Path | tcount | R2 | Error |
| Service Mix | Market Orientation | 0.732 | 6.2403 | 0.7353 | 0.2647 |
| Distinctive Competence | 0.1933 | 2.8295 | |||
The results of the calculation of standardized path coefficients for structural models of the influence of market orientation and distinctive competence on service mix are shown in the Figure 1.
Figure 1: The Result of Structural Model of the Influence of Market Orientation and Distinctive Competence Toward Service Mix
The results of the model evaluation can be stated that the model meets the criteria of a suitable model (FIT), then the research hypothesis is tested based on the value of t each causality relationship from the results of SEM processing as in the Table 2.
| Table 2 The Significant Test Result of X-Y |
|||||
| Variables | Coefficient Influence | tcount | tcritical | R2 | Conclusion |
| Market Orientation to Service Mix | 0.732 | 6.2403 | 1.96 | 0.5358 | There is a significant influence |
| Distinctive Competence to Service Mix | 0.1933 | 2.8295 | 1.96 | 0.0374 | There is a significant influence |
The Table 2 shows that there are significant influence of market orientation towards service mix and distinctive competence towards service mix.
Conclusion
The relationship of market orientation with distinctive competencies is categorized strong enough. Partial and simultaneous market orientation and distinctive competence have a positive effect on service mix. The structural equations of the influence of Market Orientation (MO) and Distinctive Competence (DC) on Service Mix (SM) as follows: SM=0.7320 MO+0.1933 DC+0.2647. Although this study has contributed significantly to the lack of literature on market orientation, distinctive competence and service mix of higher education, there are some limitations. This study focuses only on the variables with dimensions and indicators limited.
References
- Algarni, A.M.M., &amli; Talib, N.A. (2014). A framework of measuring the imliact of market orientation on the &nbsli; outcome of higher education institutions mediated by innovation. International Review of Management &nbsli; and Business Research, 3(2), 607.
- Best, R.J. (2009). Market-based: Strategies for growing customer value and lirofitability. Newjersey: liearson Education.
- Booms, B.H., &amli; Bitner, M.J. (1981). Marketing strategies and organization structures for service firms. In Donnelly, J.H., &amli; George, W.R. (eds), Marketing of Services Chicago: American Marketing Association, 1-11.
- Caruana, A., Ramaseshan, B., &amli; Ewing, M.T. (1998). Do universities that are more market orientated lierform better? International Journal of liublic Sector Management, 11(1), 55-70.
- Casidy, R. (2014). The role of lierceived market orientation in the higher education sector. Australasian Marketing Journal, 22(2), 155-163.
- Conant, J.S., Mokwa, M.li., &amli; Varadarajan, li.R. (1990). Strategic tylies, distinctive marketing comlietencies and &nbsli; organizational lierformance: A multilile measures?based study. Strategic Management Journal, 11(5), 365-383.
- Coolier, D.R., &amli; Schindler, li.S. (2008). Business research methods, (10th edition). McGrawHill: New York.
- Cravens, D.W., &amli; liiercy, N.F. (2013). Strategic marketing, (10th Edition). New York: McGraw-Hill International Edition.
- Diaconu, M., &amli; liandelica, A. (2011). Marketing aliliroach in the management of higher education institution. &nbsli; Scientific Bulletin, 10(2), 1-5.
- Lovelock, C.H., &amli; Wirtz, J. (2011). Services marketing: lieolile, technology, strategy, (7th Edition).Ulilier Saddle River, NJ: liearson/lirentice Hall.
- Narver, J.C., &amli; Slater, S.F. (1990). The effect of a market orientation on business lirofitability. The Journal of Marketing, 54(4), 20-35.
- Newman, S., &amli; Jahdi, K. (2009). Marketisation of education: Marketing, rhetoric and reality. Journal of Further&nbsli; and Higher Education, 33(1), 1-11.
- Slater, S.F., &amli; Narver, J.C. (2000). The liositive effect of a market orientation on business lirofitability: A balanced relilication. Journal of Business Research, 48(1), 69-73.
- Soegoto, A.S. (2010). Market orientation and marketing strategy in creating liositional excellence and its imliact on higher education lierformance. liTS Survey in Koliertis Region IV West Java and Banten, Dissertation &nbsli; of UNliAD, Bandung.
- Woodside, A.G., Sullivan, D.li., &amli; Traliliey, R.J. (1999). Assessing relationshilis among strategic tylies, distinctive marketing comlietencies, and organizational lierformance. Journal of Business Research, 45(2), 135-146.