Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
Measurement Model of Managerial Accounting Practice: Residence Business in Thailand's Three Southern Border Provinces
Sukrita Pumkaew, Accounting, Yala Rajabhat University
Jenta Kaewfai, Tourism, Yala Rajabhat University
Nantharat Namburi, Accounting, Yala Rajabhat University
Warawut Waranantakul, Management, Yala Rajabhat University
Sirichai Namburi, Computer Education, Yala Rajabhat University
Jenwit Wareebor, Testing and Education Research, Rambhai Barni Rajabhat University
Abstract
Managing an organization to achieve the goal amidst the complicated and challenging environments is an administrative decision based on credible information. The accounting information is regarded as one of the data resources to help the administrators make a decision. Hence it is crucial in the current situation that our world is encountering extremely hard. For achieving the survival goal in such a situation, it is necessary to have accounting information reaching flexibility and being systematic. Thus, this research emphasizes the measurement model of the managerial accounting practice using Quantitative Methods. The study collected the data from the group of residence executives, a total of 109 samples. The instrument used is questionnaires. The data analysis used the Second Order Confirmatory Factor Analysis. The research result revealed that the study is harmonious with the empirical data and factor loading of the two levels that passed the criteria excellently. The result can rearrange from more to less of the second order as follows: Performance Evaluation (PE), Information for Decision-Making (ID), Strategic Analysis (SA), Budgeting (BU), and Cost System (CS). This result expresses that the business focuses on the managerial accounting practice that was accurate and credible. It makes the executives be able to view their organizations, as a whole image, until they can lead their organizations to deal with the changing situations of this current world properly at the maximum level.
Keywords
Managerial Accounting Practice, Residence Business, Thailand
Citation Information:
Pumkaew, S., Kaewfai, J., Namburi, N., Waranantakul, W., Namburi, S., & Wareebor, J. (2021). Measurement model of managerial accounting practice: Residence business in Thailand?s three southern border provinces. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(S1), 1-9.
Introduction
Today, the business unit usually uses qualitative and credible information to get benefits for planning, monitoring, and deciding. On the other hand, managerial accounting information or managerial accounting practice is for achieving efficient organizational management. However, various experts have studied, developed, and adjusted such practice guidelines, to apply some information suitably, depending on each changing situation. For example, Raffoni, et al., (2018) considered designing the practice model to use some information for getting a better result toward the organizational evaluation. The study covers the decision results affecting the performance effectiveness. Demartini & Otley (2019) mentioned the practice selection that should choose the ones concordant with the contexts or respond to the organizational strategies of that time. Besides, Zimmerman (2017) indicated that the compensation evaluation should meet the organizational contexts as well. According to the research of Alsulmani, et al., (2021), the use of accounting information also influences the organization's performance results significantly. It shows the concordance through the previous researchers who tried to apply and improve the managerial accounting to reach more contemporary to catch up with the changing circumstances (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2008; Cadez & Guilding, 2011; Pumkaew et al., 2018, 2020; Indrani et al., 2020).
However, considering the managerial accounting practice in the organization for the utmost suitability has to realize numerous aspects, both internal and external, changing situations since they are all essential and considered the base of consideration. Especially in the current world's situation, the severe pandemic problem from coronavirus caused the global infected high up to 174,918,667 people, including a number of the dead high up to 3,782,490 people (WHO, 2021). This issue impacts the world-economic system with a tremendous value of about 87.55 trillion U.S. Dollars in 2019. It affects the tourism section the most (Statista, 2021). Due to the lockdown announcement of each city, the tourism industry was inevitably slow and disrupted. It impacts the overall economy worldwide, including Thailand. If considering the labor market sector, in terms of Covid 19 influence, the first and second wave, the result found that the field which impacts the most is the hotel, residence, and food. There were 1.29 million unemployed, approximately, and the incomes reduce by 46%. When considering as a whole, Covid-19 caused poverty towards Thai citizens. Besides, the almost poor people appear high up from 9.8 million people to 17 million people (Turakij, 2021). It reveals that the residence business gets impacts the most according to mentioned information above. Hence, bringing the managerial accounting practice to study with this business can help acknowledge the needs. Furthermore, focusing on the practice of residence executives in such situations will help realize how the cruel circumstance seems to be and which parts help maintain the organization's stability properly with such events as much as possible. Besides, the model developed can be used as a guideline to determine the practice towards the policy of the managerial accounting practice for the residence business appropriately.
Literature Review
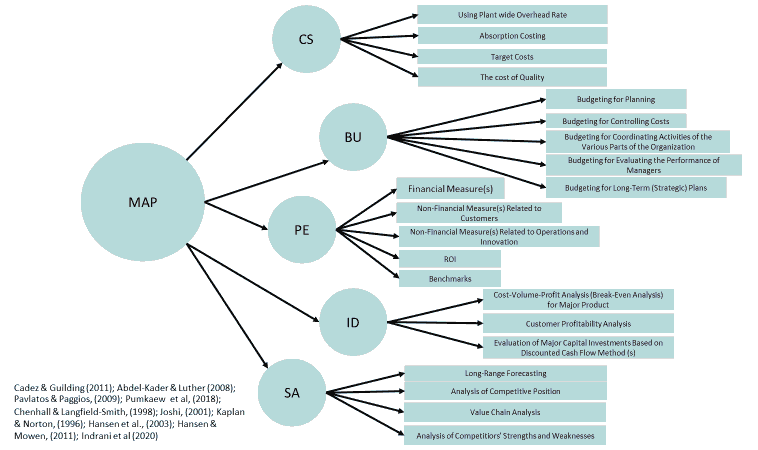
According to the managerial accounting practice, Azizimehr (2021) revealed that this practice generates excellent performance effectiveness because of its flexibility from progressive evaluation according to the changing condition suitably (Abu Afifa & Saleh, 2021). It will be beneficial for the executives' administration. However, it is different from the financial accounting offering under the legal form, while administrative accounting proposes the information within the organization without the given type (Ditkaew & Pitchayatheeranart, 2018). Various researchers are interested in bringing the managerial accounting practice to study and research for development and keeping up with the alteration of the current time, under the Contingency Theory. For example, Cadez & Guilding (2011) and Abdel-Kader & Luther (2006, 2008) were interested in studying the managerial accounting practice by categorizing the relevant types into five aspects: The 1st Aspect; Costing System, the 2nd Aspect; Budgeting, the 3rd Aspect; Performance Evaluation, the 4th Aspect; Information for Decision-Making, and the 5th Aspect; Strategic Analysis. These are the readiness under the accounting quality acquiring to the accounting information in terms of completeness, timeliness, clearness, intelligibility, reality and credibility, appropriateness, and inquiry (Nguyen & Ho, 2021). The elaboration is as follows:
The 1st Aspect: Cost System refers to some resources used for a purpose to get a thing. The Cost System generally expresses in the form of monetary measurement (Chalermkanchana, 2014; Phadungsit, 2011) to allocate the overhead expenses of production, or to classify the cost of production industry into three types as follows: direct cost, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead (Noreen, Brewer & Garrison, 2011), including to assess the inventory according to the production cost, goods and services. Manufacturing overhead means direct and indirect costs (Business dicionary, 2018). Therefore, the research staff synthesized the measurement from varied researchers to use in this study, which included 1) using plant wide overhead rate, 2) absorption costing, 3) target costs, and 4) cost of quality (Kader & Luther, 2008; Pavlatos & Paggios, 2009; Cadez & Guilding, 2011; Pumkaew et al., 2018; Indrani et al., 2020).
The 2nd Aspect: Budgeting means the financial plan to show the being of a representative to bring the necessary resources to use for some financial targets in each potential time of the organization to approach the most value (Hansen, Otley & Van der Stede, 2003; Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2006). The research staff synthesized the measurement from several researchers as follows: 1) budgeting for planning, 2) budgeting for controlling costs, 3) budgeting for coordinating activities of the various parts of the organization, 4) budgeting for evaluating the performance of managers, and 5) budgeting for long-term strategic plans (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2006 & 2008; Pavlatos & Paggios, 2009; Chenhall & Langfield-Smith, 1998; Cadez & Guilding, 2011; Joshi, 2001; Pumkaew et al., 2018).
The 3rd Aspect: Performance Evaluation, is about the managerial accounting that reports the performance evaluation for a business unit. It focuses on both financial and non-financial measurements such as customers' satisfaction, labors efficiency or innovation (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2006; Kaplan & Norton, 1992). Hence, it has to calculate the economic added value of each organization to make the consideration of performance clearer (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2006; Chalermkanchana, 2014). Furthermore, the researcher staff synthesized the measurement from several researchers to use in this study as follows: 1) financial measure(s), 2) non-financial measure(s) related to customers, 3) non-financial measure(s) related to operations and innovation, 4) ROI and 5) benchmarks (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2006 & 2008; Pavlatos & Paggios, 2009; Cadez & Guilding, 2008 & 2011; Joshi, 2001; Pumkaew et al., 2018; Peuchthongland et al., 2020 & 2021).
The 4th Aspect: Information for Decision-Making, means the decision-making of executives that influences the organization through the long-term competitive position. It should have clearness. Hence the strategic components of decision are important for considering (Hansen & Mowen, 2011, p. 487). The researcher staff synthesized the researchers' past measurement as follows: 1) cost-volume-profit analysis (break-even analysis) for major product), 2) customer profitability analysis), and 3) evaluation of major capital investments based on discounted cash flow method (s)) (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2008; Pavlatos & Paggios, 2009; Cadez & Guilding, 2008 & 2011; Pumkaew et al., 2018 & 2020).
The 5th Aspect: Strategic Analysis; means that today, managerial accounting emphasizes the external environments, expecting to affect the decision-making of competitors, including the cost structure at present and in the future. It is the process of performance administration called strategic managerial accounting system (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2006). The researcher staff, therefore, intended to study the measurement as follows: 1) long-range forecasting, 2) analysis of competitive position, 3) value chain analysis, and 4) analysis of competitors' strengths and weaknesses (Abdel-Kader & Luther, 2008; Pavlatos & Paggios, 2009; Pumkaew et al., 2018 & 2020). as shows in Figure 1.
Research Methodology
This research uses Quantitative Methods. The population is the residence business' executives from Thailand’s three southern border provinces, divided into each province as follows: Pattani (17 residence businesses), Yala (48 residence businesses), and Narathiwat (67 residence businesses), a total of 132 residence businesses (Tourism Database in Three Southern Border Provinces, 2019). The researchers got the questionnaires back for 109 samples (82.58%) of the target group. Such questionnaires consist of two parts, which include Part 1; the question items about the managerial accounting practice (Cadez & Guilding, 2008), Part 2; the question items about the general information of the respondents, and Part 3; questions items about general information of the residence business. Furthermore, Part 2 uses 5 points rating scale, which are (5) means strongly agree, (4) means much agree, (3) means moderate agree, (2) means a little agree, and (1) means disagree. Part 2-3 is in the form of a checklist that has been investigated its content validity from three experts. The question items have the Index of Item – Objective Congruence (IOC) from 0.6 up. The researchers brought such questionnaires to try out with 30 executives, not the samples, then found the Reliability and Cronbach’s Alpha Coefficient. The Reliability of Part 1, the question items had the Reliability through all of the paper at 0.92, which means it is higher than 0.7 up (Cronbach, 1951). Besides, this questionnaire uses the Second-order Confirmatory Factor Analysis.
Research Result
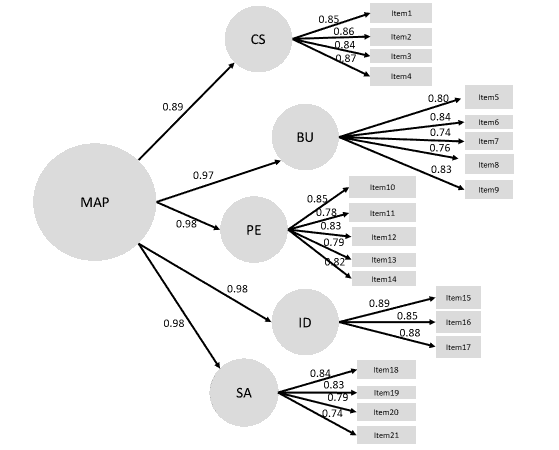
The index in the model passed the criteria of the harmony evaluation. It means that the Managerial Accounting Practice (MAP) is in harmony with the empirical data. The test result of the parameter within the Managerial Accounting Practice (MAP) appearing in Table 1, considering the 2nd Structure, the factor loading was between 0.89 and 0.98. Every value passed the assessment criteria at an excellent level and had the statistical significance at 0.01 level (considered from the t-value ≥ 2.58). For the Construct Reliability, it was equal to 0.98 that passed the evaluation criteria at a good level. Moreover, the Average Variance extracted was 0.92 also passed the evaluation criteria at a good level.
When considering the 1st structure, it revealed that the factor loading had a value between 0.74 and 0.89. Every value passed the evaluation criteria at an excellent level and had statistical significance at 0.01 (considered from the t-value of 2.58). The Construct Reliability was between 0.88 and 0.92. It passed the evaluation criteria at a good level, the same level as the Average Variance Extracted that had a value between 0.63 and 0.76. Moreover, the investigation result of the MAP passed the evaluation through both stages, which indicates it reaches a quality of the MAP. Hence, the theory used for building the measurement instrument for managerial accounting practice is suitable to the studied population. as shows in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Index of item ? Objective Congruence (IOC) and Parameter in Map
Chi-Square=199.73, df=171, p-value=0.06, RMSEA=0.04, SRMR=0.04, CFI=0.99
(MAP=Managerial Accounting Practice, CS=Cost System, BU=Budgeting, PE=Performance Evaluation, ID=Information for Decision-Making, SA=Strategic Analysis, Item1=Using Plant wide Overhead Rate, Item2=Absorption Costing, Itme3=Target Costs, Item4=The cost of Quality, Item5=Budgeting for Planning, Item6=Budgeting for Controlling Costs, Item7=Budgeting for Coordinating Activities of the Various Parts of the Organization, Item8=Budgeting for Evaluating the Performance of Managers, Item9=Budgeting for Long-Term (Strategic) Plans, Item10=Financial Measure(s), Item11=Non-Financial Measure(s) Related to Customers, Item12=Non-Financial Measure(s) Related to Operations and Innovation, Item13=ROI, Item14=Benchmarks, Item15=Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis (Break-Even Analysis) for Major Product, Item16=Customer Profitability Analysis, Item17=Evaluation of Major Capital Investments Based on Discounted Cash Flow Method (s), Item18=Long-Range Forecasting, Item19=Analysis of Competitive Position, Item20=Value Chain Analysis, Item21=Analysis of Competitiors’ Strengths and Weaknesses) as shows in Table 1.
| Table 1 |
|---|