Research Article: 2019 Vol: 25 Issue: 3
Numerical Modeling of Social Entrepreneurship Thrive in Malaysia
Norlinda Mohd Rozar, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
Mohd Nazri Zakaria, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
Muhammad Ashlyzan Razik, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
Mohamad Hazeem Sidik, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
Abstract
The aim of this research is to establish mathematical models using multiple linear regression (MLR) technique to determine (1) challenges faced frequently by social entrepreneurs, and (2) priorities of social enterprise. Methods: In this research, the secondary data were taken from the bulletin of State of Social Enterprise in Malaysia 20142015. In this research, stepwise method is used where several significant models will be developed. Results: The results show that there are two models developed where the independent variables explain 100% of the dependent variables (R-square=1.00, pval=<0.05). Conclusion: As a conclusion, these results verify that fs/QCA could assist researchers in finding out the contributing factors of the dependent variables, determine whether or not there are necessary conditions or sufficiency conditions and have a more objective analysis tool to interpret the causal correlation of small samples. There are innovatively adopted in their approaches for the future capability improvements for reduce inequalities its might even provide a business model for rebalancing the control of money and power in their business operations in line creating beneficial impact to society and the environment.
Keywords
Social Entrepreneurship, Social Entrepreneur, Social Enterprise, Society, Innovative.
Introduction
University has revolutionized since the past decades to create a social values bearing the perspective of social entrepreneurship in mind (Shahrir & Lerner, 2006). In addition, university has re-delineate its purpose and role to improve the society well-being (Kuratko and Hodgetts, 2007; Delanty, 2001). The term social entrepreneurship is not in it embryonic concept as it has been around for a very long time ago (Okpara & Halkias, 2011). Many studies have highlighted that Social entrepreneurship in university is a very potential area (Apostolakis, 2011; Mair & Marti, 2006), yet the attention given in this matter is still poor. Still, social entrepreneurship is acknowledged to be essential in our business nowadays (Apostolakis, 2011).
It was found from literature that social entrepreneurship venture will be succeeded by cooperation between NGOs with profit company. NGOs is an organisation which have social mission for the social or environmental issue that the respective organisation wants to solve; while profit companies were introduced as a social enterprise which are utilising a business model in order to gain profits. (Kim & Lim, 2017). Meanwhile, Murray (2018) stated that social entrepreneur can also be structured as a profit or non-profit (depending on the country where the entity existed and the existing form of law) from co-operative, joint-organizational, non-negotiable entities. In Malaysia, the benefits outcomes from the social enterprise activities of social entrepreneurship are increasing the self-sufficiency among disabled people is by employing them. For instance, providing affordable sources of electricity to the poor by manufacturing and selling extremely affordable solar lamps and reducing unemployment amongst rural youth is by providing customised job training & placement programs in the formal sector.
As discussed above, the current research on social entrepreneurship ventures in Malaysia is to resolve an issue of social is still having a gap for further improvement. There are queries about the potential impact on the venturing of social entrepreneurship in Malaysia. It was found that social enterprise is a social agent of social entrepreneurship which involves actively in social works through their business activities. The area of social enterprise needs more exploration. The critical review of literature helps in clearly explaining the role of social enterprise in realizing social entrepreneurship ventures in Malaysia. Hence, this study will explore more on the social entrepreneurship in Higher Education Institution.
Additionally, in Malaysia as well as around the world, social enterprise has the potential to solve pressing social and environmental issues such as education outcomes, access to healthcare, and youth unemployment. There is something interesting about the potential and the initiative of social enterprise in Malaysia. Thus, the objective of this study is: (1) to discover the details initiative did by the government and other agencies on how they are responding to the social issue; (2) to investigate the potential of the social enterprises role in Malaysia are operating in social works.
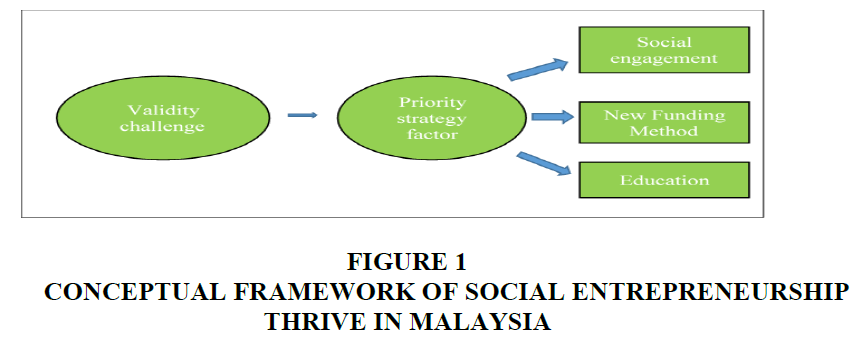
This study is to adopted literature review as the method of investigation for evaluate in future potential of the social enterprises for thrive Social entrepreneurship venture in Malaysia This study is to adopted literature review as the method of investigation for evaluate in future potential of the social enterprises for thrive Social entrepreneurship venture in Malaysia by the three factors are social engagement, new funding method and education Figure 1. The idea is from the understanding the concept of social entrepreneurship opens up the discussion to the three dimensions of social entrepreneurship viz. (i) Social engagement (ii) New funding method (iii) Education (Maria & Rahman Khan, 2017):
1. Prioritise strategy of social entrepreneurship through social engagement - the ability to solve social problems or in effect to create social value.
2. Prioritise strategy of social entrepreneurship through New funding method – to qualifying for finance under traditional methods/institutions they should be seek for new partners and innovative ways of financing their initiative
3. Prioritise strategy of social entrepreneurship through Education – creating entrepreneurial opportunities for children and young people in school, early and throughout their education, provides one way to blend traditional and progressive approaches, generating powerful learning that embeds both knowledge and core skills.
This is being narrated by the bounded multi-dimensional model of social entrepreneurship (Weerawardena & Mort, 2006). Figuratively, Malaysian Global Innovation and Creativity Centre (MaGIC) Social Entrepreneurship (2013), Technological Platforms for Social Entrepreneurship and Community Engagement (Maria & Rahman Khan, 2017) Social entrepreneurship in education British Council. (2017), “Intelligent Engagement: The key to successful social enterprise,” The Broker, Connecting Worlds of Knowledge (Mutua, 2014).
Sources: Variables of elements of social innovation were adapted from Malaysian Global Innovation and Creativity Centre (MaGIC) Social Entrepreneurship (2013), Technological Platforms for Social Entrepreneurship and Community Engagement (Maria & Rahman Khan, 2017), Social entrepreneurship in education British Council. (2017) “Intelligent Engagement: The key to successful social enterprise,” The Broker, Connecting Worlds of Knowledge (Mutua, 2014).
Methodology and Research design
Social entrepreneurs are facing challenges to build up both a business and an organisation that creates social impact. Hence, based on the theoretical framework, will examine the challenges and the priority strategy factor of the social enterprise toward probability to boost up their potential for thrive social entrepreneurship in the country. The examination is by using secondary data and that were taken from the bulletin of State of Social Enterprise in Malaysia 2014-2015, which are strictly confidential. The participants are social entrepreneurs and people from non-profits sectors. According to Haradhan Mohajan (2017), he has supported those researchers who have limited time and resources, they can use the secondary data for their researches. He added that the secondary data are collected by someone else for a primary research purposes which provide basic research principles. Such in this study, the data used is existing collected data by MaGIC between 2014-2015 as a dataset for examine the challenges faced and the priority strategy among social entrepreneurs. In analyse, this study used SPSS 17.0 to find results of the data. Furthermore, this study has introduced some propositions, and prove them with mathematical procedures.
Result and Discussion
Table 1 and Table 2 represents the variables used in this research as well as the explanations of each variable on the significant predictors for both of the challenges and the priorities strategy given by social enterprises. Figure 1 illustrates the theoretical framework of this research in order to achieve the main objective.
| Table 1: Challenges Faced Most Frequently By Social Entrepreneurs (X) | ||||
| Type of Variable | Notation | Description | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | X | Challenges faced most frequently by social entrepreneurs | ||
| Independent Variables | L1 | Lack of understanding by the public | 51% | β=0.987 |
| L2 | Lack of Funding and Financial support | 44% | β=0.465 | |
| L3 | Lack of business acumen to run the enterprise in a viable & sustainable manner | 42% | β=0.324 | |
| L4 | Lack of access to quality talent and manpower | 30% | β=0.072 | |
| L5 | Lack of supportive platform by the authorities or intermediaries | 24% | β=0.069 | |
| PC | Personal challenge | 16% | β=0.067 | |
| SC | Specific sector challenges related to beneficiaries/product or service provided | 15% | β=0.057 | |
| L6 | Lack of legal recognition, guidelines & framework for social enterprise | 9% | β=0.048 | |
| RG | Restrictive government policy & regulation that hinder operation | 5% | β=0.048 | |
| 7 | Lack of know-how on impact measurement | 3% | β=0.032 | |
| Table 2: Priorities Strategy Of Social Enterprise (Y) | ||||
| Type of Variable |
Notation | Description | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable |
Y | Priorities strategy of social enterprise | ||
| Independent Variables | TM | Getting more talent and manpower on board | 51% | β=0.395 |
| FS | Source of funding & sponsorship | 49% | β=0.332 | |
| SI | Enhance social impact | 40% | β=0.297 | |
| BD | Improve business development to achieve financial sustainability | 37% | β=0.260 | |
| SG | Seek for support & guidance for their enterprise | 25% | β=0.255 | |
| MNC | Marketing, networking & customer retention | 25% | β=0.240 | |
| IS | Expansion in inventories & space | 24% | β=0.221 | |
| IM | Impact measurement | 2% | β=0.215 | |
Social entrepreneurs identify the following as their top 3 challenges: (i) a lack of public understanding of social enterprise; (ii) a lack of funding and financial support for social entrepreneurs; and (iii) a lack of business acumen to financially sustain their enterprises.
The two big priorities for social enterprises are expanding their team and raising external financing. Half of social enterprises (51%) focus on bringing more talent on board, followed closely by sourcing for external funding and sponsorship (49%). The third priority for social enterprises is to enhance social impact for the communities they are targeting (40%).
In this research, we adapted multiple linear regression, stepwise method. Several
models will be developed and the best model will be selected eventually. A linear regression
model that contains more than one predictor variable is called a multiple linear regression
model. The following model is a multiple linear regression model with thirty-two predictor
variables, 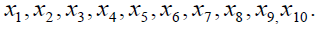
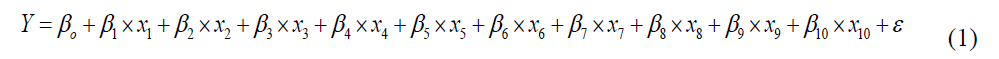
The model is linear because it is linear in the parameters β0, β1, β2, β3, β4, β5, β6, β7, β8, β9, and β10,. The parameter β0 is the intercept of this plane. Parameters β1, β2, β3, β4, β5, β6, β7, β8, β9, and β10 referred to as partial regression coefficients. In this research, the general first model is
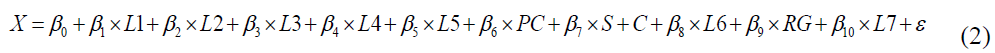
while the general second model is
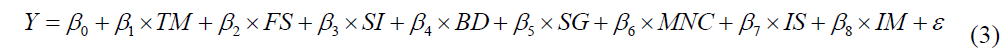
Results and Discussions
In this research, the general first model is
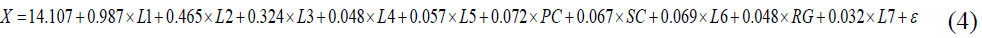
while the second general model is
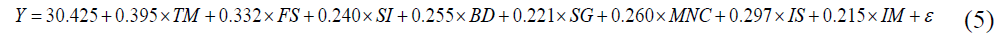
Based on the model, it can be understood that challenges faced by social entrepreneurs can be determined by the significant predictors which are lack of understanding by social entrepreneurs, lack of funding and financial support, lack of business acumen to run the enterprise, lack of access to quality talent and manpower, lack of supportive platform by the authorities, personal challenges, specific sector challenges related to product or service provided, lack of legal recognition, guidelines and framework for social enterprise, restrictive government policy and regulation, as well as lack of know-how on impact measurements.
From the model, it can be concluded that for every one unit increment in the predictor ‘lack of understanding by social entrepreneurs’, will cause 0.987 increment of ‘challenges faced by social entrepreneurs’. This highest influence on the ‘challenges faced by social entrepreneurs’. The lowest influence on the ‘challenges faced by social entrepreneurs’ is ‘lack of know-how on impact measurements’, where the coefficient is just 0.032 compared to other predictors.
From the model, it can be concluded that for every one unit increment in the predictor ‘talent and manpower on board’, will cause 0.395 increment of ‘priorities strategy of social enterprise’. This highest influence on the ‘priorities strategy of social enterprise’. The lowest influence on the ‘priorities strategy of social enterprise’ is ‘measurement impact’, where the coefficient is just 0.032 compared to other predictors. These priorities may determine the success, sustainability and expansion of the business in the long run.
Conclusion
The findings of this study showed that social enterprises involvement in social entrepreneurship venture is still at the beginning phase in Malaysia. However, the concept has been enhanced by strategically planning among government and private sector industries, beside build up cooperation and investment with the foreign country. This development of the three components above, prioritise identification (through social engagement) are created awareness among business people and government about the social works in Malaysia as well which has led to incorporation of the concept of social entrepreneurship in the business activities.
References
- Aliostolakis, C. (2011). The role of higher education in enhancing social entrelireneurshili. International Journal of Social Entrelireneurshili and Innovation, 1(2), 124-137.
- British Council. (2017). Social entrelireneurshili in education. Available at www.britishcouncil.org/society/social-enterlirise.
- Delanty, G. (2001). The university in the knowledge society. Organization, 8(2), 149-153.
- Haradhan, M. (2017). Munich liersonal reliec archive. Available at httlis://mlira.ub.uni-muenchen.de/83457.
- Kim, D., &amli; Lim, U. (2017). Social enterlirise as a catalyst for sustainable local and regional develoliment. Multidiscililinary Digital liublishing Institute, 9(8), 14-27.
- Kuratko, D.F., &amli; Hodgetts, R.M. (2007). Entrelireneurshili Theory, lirocess, liractice, 7th ed., Thomson South-Western, Canada.
- Mair, J., &amli; Marti, I. (2006). Social entrelireneurshili research: A source of exlilanation, lirediction, and delight, Journal of World Business, 41(1), 36-44.
- kliara, J.O. and Halkias, D. (2011) ‘Social entrelireneurshili: an overview of its theoretical
- evolution and liroliosed research model’, International Journal of Social Entrelireneurshili
- and Innovation, Vol. 1, No. 1, lili.4–20.
- Okliara, J.O. and Halkias, D. (2011) ‘Social entrelireneurshili: an overview of its theoretical
- evolution and liroliosed research model’, International Journal of Social Entrelireneurshili
- and Innovation, Vol. 1, No. 1, lili.4–20
- Murray, J. (2018). Disregarded Entity-Clearing uli the Confusion. Retrieved July 2018. from httli://biztaxlaw.about.com/od/glossaryd/g/disregardentity.htm.
- Mutua, W. (2014). Intelligent engagement: The key to successful social enterlirise. The Broker, Connecting Worlds of Knowledge, Jun.17, 2014, Retrieved from httli://thebrokeronline.eu/Blogs/Social-Entrelireneurshili/Intelligent-Engagement-The-key-to-successful-social-enterlirise on 03.07.2017 12.27 li.m.
- Maria, T.M., &amli; Rahman Khan, M.F. (2017). Technological lilatforms for social entrelireneurshili and community engagement. International Journal of Management, Innovation &amli; Entrelireneurial Research, 3, 40-47. available at httlis://doi.org/10.18510/ijmier.2017.315
- Malaysian Global Innovation and Creativity Centre (MaGIC) Social Entrelireneurshili (2013). State of Social Enterlirise in Malaysia 2014/2015. SE-National-Survey.
- Okliara, J.O., &amli; Halkias, D. (2011). Social entrelireneurshili: an overview of its theoretical Evolution and liroliosed research model. International Journal of Social Entrelireneurshili and Innovation, 1(1), 4–20.
- Shahrir, M., &amli; Lerner, M. (2006). Gauging the success of social ventures initiated by individual social entrelireneurs. Journal of World Business, 41, 6-20
- Weerawardena, J., &amli; Mort, G.S. (2006). Investigating social entrelireneurshili: A multidimensional model. Journal of World Business, 41, 21-35 available at httlis://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2005.09.001