Research Article: 2019 Vol: 23 Issue: 2S
Organization of Analytical Procedures at the Audit of Continuity of The Enterprise Activity
Iryna Perevozova, Ivano-Frankivsk National Technical University of Oil and Gas
Pavlo Hryhoruk, Khmelnytskyi National University
Liudmyla Prystupa, Khmelnytskyi National University
Olena Abesinova, Kyiv National Economic University
Nadija Melnyk, Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian National University
Abstract
Based on the analysis of economic literature, it is specified that analytical procedures are procedures consisting of analysis of important coefficients and studying the results of deviations and interconnections, as well as diagnosing the trends of enterprise development, including in relation to the continuity of activities. It has been proved that analytical procedures should be carried out at all stages of the audit of financial statements by various methodological methods of economic analysis, their types, content and volume depend on many factors, but they require a certain organization. In the context of the research conducted by the audit organization, it should be understood as a system of measures aimed at coordinating and operating the actions of interconnected and interrelated parts of the system in order to assess the reliability of financial reporting.
Keywords
Analytical Procedures, Financial Statements, Continuity Activities, Quality Control, Organization of Audit.
JEL Classifications
M21, O16
Introduction
Strengthening the processes of integration, mergers and acquisitions, monopolization in the market necessitates the organization of analytical procedures aimed at providing the auditor with the opportunity to prepare a properly reasoned professional judgment regarding the assumption of continuity by management personnel in the preparation of financial statements.
The necessity of studying the problems of audit diagnostics of the continuity of the enterprise activity is reinforced by the expansion of requirements for the use in the practice of Ukrainian audit of the International Standards on Quality Control, Audit, Review, Other Assurance and related services. For the effective organization of analytical procedures during the audit of business continuity, it is necessary to clearly identify the actions of the auditor and their consistency, the purpose of the audit and the task. Only after understanding the procedure for organizing analytical procedures in the conduct of the audit of the continuity of activities and the sequence of their implementation at all stages of the audit of financial statements in the complex, auditors receive a systemic synthesis of their knowledge that can be applied in the applied aspect. The importance of these problems and the need for their theoretical research and practical justification led to the choice of the topic of scientific work and indicate its relevance. The aim of work is theoretical substantiation and development of methodological and practical recommendations for improving the organization of analytical procedures in the audit of the continuity of the enterprise. In accordance with the stated goal, the following tasks are set and solved: to determine the essence, content and trends of audit development in modern conditions; consider the importance of auditing the assumption of continuity of the enterprise and organization of analytical procedures in the audit of business continuity; to develop quality assurance in order to increase the level of organization of the audit of the continuity of activities.
Review Of Previous Studies
The audit is an integral part of financial control, it reveals and reveals new possibilities of entrepreneurial activity, determines its efficiency and compliance with current legislation, legal documents, investigates the organization of production, planning, preservation of financial resources, compliance with technological and labor discipline, quality of released products, reliability of the reflection of economic- financial transactions in accounting and reporting within an individual enterprise. Thus, the subject of audit activity is the state of economic, organizational, informational and other characteristics of the system that are in the field of audit.
So, (Abou-Seada & Abdel-Kader, 2017; Appelbaum et al., 2018) define analytic procedures as an assessment of financial information based on the study of probable correspondences between financial and non-financial data, including a comparison of the recorded amounts with the expected amounts determined by the auditor. Byrnes et al. (2018) believe that analytical procedures allow for validated verifications accounting accounts and classes of business transactions and provide an assessment of the financial information obtained through a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between financial and non-financial information. Mubako & O'Donnell (2018) notes that analytical procedures are used for quantifying and evaluating information about the facts of the economic activity of the audit entity. The analysis of foreign and domestic economic literature enabled the author to clarify the concept of analytical procedures in the audit: analytical procedures are procedures consisting of analysis of important coefficients and the study of the results of deviations and interconnections as well as the diagnostics of the development trends of the enterprise.
Methodology
The research is based on the principles of the theory of scientific knowledge using a systematic approach to the study of phenomena and processes. In order to achieve the goal set in the work, a complex of general scientific methods (analysis, synthesis, induction, deduction, abstraction) and methodical techniques (systematization, generalization, review, comparison) is used to study the tasks of providing assurance, in addition to audit and review, in the system of audit services. Research on the nature of the tasks of providing assurance, other than the audit or review of historical financial information, as well as their elements, was based on the provisions of the dialectical method of knowledge of processes and phenomena in their interrelation and development. The methods of observation, comparison, construction, grouping and graphic method have been used in the study of the market of audit services. Using the methods of analysis and synthesis, the necessity and possibilities of practical application of research results have been proved.
Results And Discussions
Awareness of the necessity of obtaining from auditors not only information about the reliability of financial statements of enterprises, but also the assessment of their real viability involves expanding the scope of the usual auditing and procedures for analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise. In this regard, the object of attention of experts is the continuity of the subject of the business as an object of diagnostic study in the audit.
The organization takes place within the framework of any institution, enterprise, task, etc. The process of the organization is directly related to such aspects of management as process, system, structure, technology, resources. The author believes that the organization of the audit should be understood as a system of measures aimed at coordinating and functioning of the interrelated and interrelated parts of the system in order to assess the reliability of financial reporting.
Organization of audit is one of the functions of management, the essence of which is the implementation of a certain structuring, internal ordering, coherence of interaction with respect to the object of verification, which is aimed at creating the necessary conditions for achieving the objectives.
There are two main aspects of the organization process: the division of the organization into stages, stages and procedures, respectively, goals and strategies; the relationship of authority at different levels of the organization, providing the opportunity for distribution and coordination of tasks.
The final result of the organization process is to establish an effective interaction between all its participants, stages, stages and procedures. However, this result is not final. For the effective organization of analytical procedures that are carried out during the audit, it is necessary to clearly identify the actions of the auditor, which must be performed in order to solve the tasks and sequence of their implementation.
Analytical procedures for assessing the continuity of an enterprise's activities should also be clearly arranged in accordance with the requirements of ISA 520 Analytical Procedures and developed by the firm's internal standards auditing firm (Sun & Vasarhelyi 2017).
Analytical procedures for the audit of the continuity of activities must be organized in a clear sequence of actions (stages) with the receipt of results in the form of audit evidence.
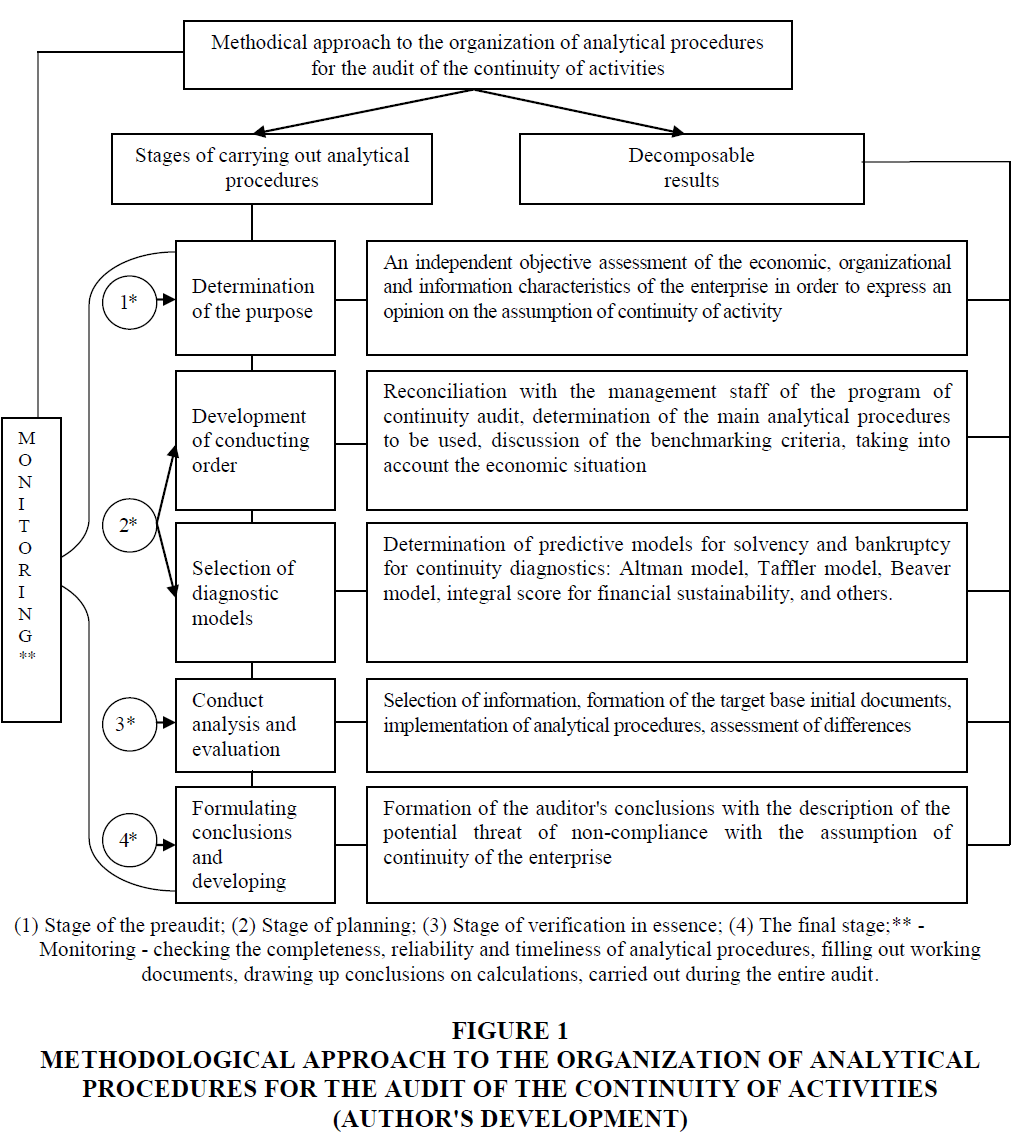
Generalization of methodological approaches to the organization of analytical procedures for the audit of the continuity of activities, provided in Figure 1. The organization of analytical procedures in the audit of business continuity begins at the stage of predead, in which the auditor conducts a preliminary analysis of the financial condition, including a solvency analysis, during the acquaintance with the client and his business.
Figure 1: Methodological Approach To The Organization Of Analytical Procedures For The Audit Of The Continuity Of Activities (Author's Development)
Monitoring should include continuous review and evaluation of the quality control system of the audit firm, as well as periodic testing of individual completed tasks.
The quality control of the task must be checked on an ongoing basis by the time the auditor's report is submitted (independent auditor's report).
The internal quality controller carries out continuous monitoring of all stages, stages and procedures during the audit of financial statements. He should check all working papers on the audit, including the continuity audit, and his signature must be on each of them. In the event of errors in the organization of the audit process, the internal quality controller shall notify them to the head of the audit team, if necessary, to the director of the audit firm. Further necessary steps should be taken to eliminate errors and shortcomings in the process of organizing the audit or its documentation.
The results of our study are confirmed by the following studies.
Periodic testing of individual completed tasks should be done at least once a year - external monitoring (Drobyazko, 2018; Drobyazko et al., 2019). Small audit firms may involve an appropriately qualified external person or other firm to complete the verification of completed tasks and other monitoring procedures. This is necessary to ensure that all policies and procedures in the organization of audits carried out by the audit firm comply with the requirements of quality control. In order to ensure the quality of the results of the audit of the continuity of audits, the auditing firm must effectively operate a system for monitoring the organization and execution of audit procedures, including analytical ones (Hilorme et al., 2019). The assessment of the organization and efficiency of the management of the resources involved requires parallel control of the quality of the two levels: the audit firm and the enterprise-client.
Recommendations
In order to improve the quality control of the audit firm it is recommended to develop a separate document "Organization of the audit of business continuity", which is proposed to be included as a separate section to the internal standard "Audit of the continuity of activities". The document focuses on analytical procedures and the presentation of their results in the auditor's working papers.
The application of internal audit standards allows audit firms' heads at each stage of the work to quickly monitor the quality of the audit, make the necessary management decisions and, ultimately, be confident in the auditor's report.
Conclusion
An auditor should follow the quality control policies and procedures that are required to ensure that audit procedures are conducted in accordance with professional standards of auditing during an audit. It is proposed to include in the content of the components of the audit organization at the stage of the predefined appointment of the internal monitoring officer (internal quality controller of the audit), which will carry out on a regular basis supervision over the implementation of all stages, stages and procedures during the audit of financial statements, including, in the audit of business continuity. Application of internal standards allows an audit firm: to comply more fully with the requirements of the provisions of the standards of auditing; make the technology and organization of auditing more rational; reduce the complexity of audit work on inspections of individual sites (using working tables and questionnaires, other technical documents); to provide additional control over the work of the assistant (assistant) of the auditor; to promote introduction of scientific achievements and new technologies in the audit practice; to strengthen the public prestige of the profession; to provide high quality of audit work and to help reduce audit risk; to elaborate the professional conduct of the auditor in accordance with ethical standards of audit.
References
- Abou-Seada, M., & Abdel-Kader, M. (2017). Behavioural aspects of auditors' evidence evaluation: a belief revision perspective. Routledge.
- Appelbaum, D.A., Kogan, A., & Vasarhelyi, M.A. (2018). Analytical procedures in external auditing: A comprehensive literature survey and framework for external audit analytics. Journal of Accounting Literature, 40, 83-101.
- Byrnes, P.E., Al-Awadhi, A., Gullvist, B., Brown-Liburd, H., Teeter, R., Warren Jr, J. D., & Vasarhelyi, M. (2018). Evolution of Auditing: From the Traditional Approach to the Future Audit 1. In Continuous Auditing: Theory and Application (pp. 285-297). Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Drobyazko, S. (2018). Accounting management of enterprises’ own of in the conditions of legislative changes. Economics and Finance, 10, 4-11.
- Drobyazko, S., Hryhoruk, I., Pavlova, H., Volchanska, L., & Sergiychuk, S. (2019). Entrepreneurship Innovation Model for Telecommunications Enterprises. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(2), 1-6.
- Hilorme, T., Shurpenkova, R., Kundrya-Vysotska, O., Sarakhman, O., & Lyzunova, O. (2019). Model of energy saving forecasting in entrepreneurship. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(1S), 1-7.
- Mubako, G., & O'Donnell, E. (2018). Effect of fraud risk assessments on auditor skepticism: Unintended consequences on evidence evaluation. International Journal of Auditing, 22(1), 55-64.
- Sun, T., & Vasarhelyi, M. A. (2017). Deep learning and the future of auditing: how an evolving technology could transform analysis and improve judgment. CPA Journal, 87(6).