Research Article: 2019 Vol: 22 Issue: 1S
Professional Competence Development and Plural Forms of Work within Entrepreneurship Education
Tatiana Zhukova, Samara State University of Social Sciences and Education
Vladimir Bogoslovskiy, Herzen State Pedagogical University
Olga Yankevich, Samara State University of Social Sciences and Education
Abstract
This paper is dedicated to the study of the professional competence adopted by multicultural processes in regions in Russia (on the example of students who learn entrepreneurship). With the changes in the educational policy, plural forms in teaching activities were allowed and should have been a recurring presence.
The main aim of the paper is to investigate why the variety of multicultural problems have remained in teaching and social practice both in many countries and in Russia, why the teachers are not ready to work in the class with a multicultural background and they have a low level of professional competence and what plural forms of work the teachers can use to teach students who learn entrepreneurship within the specificity of multicultural society.
The main hypothesis of this paper is theoretical and explains that the plural forms of work found are transitory and they are not only a result of increased efficiency of the varieties of teaching and social practices, but because plural forms have become a key strategic step in securing educational policy in regions and promoting greater growth of the professional competence of teachers who work in multicultural environment.
Moreover, it is argued that the higher institutional environment with multicultural background has a significant influence on the coordination of plural forms, directly interfering with their stability. Thus, we speak about the plural forms of work with students (on the example of students who learn entrepreneurship) and teachers which orient the new perspective to develop the professional competence of future teachers. That is important within the entrepreneurship education which has he aim to improve the students’ skills to work in a management environment.
Keywords
Professional Competence Development, Plural Forms of Work, Multicultural Education, Higher Education in Regions, Entrepreneurship Education.
Introduction
From an academic perspective, it is interesting to assess how the education has adjusted to the change in cooperation, collaboration and organization that allowed plural forms of work.
Entrepreneurship education focuses on the development of skills or attributes that enable to give the opportunity to manage and to control (Papagiannis, 2018). Moreover this education is oriented towards different ways of realizing opportunities: the most popular one is regular entrepreneurship: opening a new organization. Another one is to promote innovation or introduce new products or services or markets in existing companies. As well it involves creating charitable organizations (or portions of existing charities) which are designed to be self-supporting in addition to doing their good works (Potishuk & Kratzer, 2017). Especially that is important to analyze the specificity of this education within multicultural processes.
The researchers believe that at first, the theoretical analysis should be supported by recent work discussing motivations for the use of alternative forms of the teachers and the government in the country and different regions is choosing, emphasizing that in some educational environments with multicultural background where there is a high degree of uncertainty due to the difficulty of the multicultural problems, the tolerance will be the disappearance of humans relations, leading to adoption of plural forms of work. Recent literature concerning the problem recognizes the existence of plural forms and begins to explain the reasons for its persistence or not in educational process (Bosse, 2007; Duzhakova, 2008; Hoehmann & Zhukova, 2011; Poshtareva, 2005).
In this sense, the goal of the further researches is relevant in that it intends to evaluate the adaptation of higher institutions to a new multicultural environment, in adapting these forms in front of their preferred channels of work. This allows contribution to the understanding what the plural form is. Moreover this kind of work will help to understand the specificities of economic environment in a region and the new mechanisms how it should be organized.
At second in attempting to explain the drivers of such choices and the new mechanisms concerning how it works, different theoretical approaches relate the maintenance of plural forms to a number of variables connected with efficiency, the need to monitor and control the students in the value chain, and both motivation and the capacity to innovate and gain knowledge in the new multicultural environment (Aniskin et al., 2014; Bondarenko, 2008; Dobudko, 1999; Dzhurinskiy, 2007; Palatkina, 2007; Wulfson, 2003; Bouraoui, 2017). Indeed, observation of the functioning of various models to teach professional competence of the students who learn entrepreneurship has shown the recurrent use of plural arrangements. Although the argument has transitory characteristics among different regions and countries, it is believed that transitory movement can persist over a long time between different regions and countries, maintaining the stability of the adoption of plural forms, although not with the same models of education (Bosse, 2007; Duzhakova, 2008). Thus, the authors of the paper believe that that is it necessary to find a new argument about the dynamics of these plural forms, understanding that one of the main reasons for the adoption of plural forms is the possibility that such forms represent a strategic movement that will allow the growth of the professional competence of students in the long run.
The authors of the paper have the aim in future to organize the further studies to highlight some key issues: Have all countries begun to operate as plural forms for the further cooperation and collaboration as that is necessary? If not, what countries use plural forms? What justifies the adoption of this form of governance in regions? Is the maintenance of the plural form in the higher institutions in regions? What is the impact of the institutional environment on defining arrangements to organize learning process and the ways to improve the entrepreneurship education?
To answer the above mentioned questions the authors of the current research find that is important to consider in future the following questions:
? To determine the groups of nationalities students that is generated during their learning, according to the diagnostically related groups of multicultural model in a region. In this stage it is critical to assess the problems which the students with different multicultural background can have. This stage should include a description of the educational system both in a country and in a region, the specificities of multicultural environment and the varieties of tasks the students do. Moreover that is important to understand the specificities of learning and teaching entrepreneurship.
? To determine whether there is a visual significant difference (further statistically) between the age and gender as well as multicultural background of this type of students and the determined the further ways that they generate in the course of their learning and further teaching.
? To determine the influence of the multicultural environment on the regional educational and economic policy that the students generate during the course of their learning and to develop the necessary activities and plural forms to improve the process of professional competence development.
Thus, this paper presents the first authors’ conclusion on the problem and seeks to understand the importance of behaviour of plural forms in the educational environment in regions, by evaluating the stability of these arrangements over the further years within the sustainability conception in education.
The authors believe in the importance both to analyze and to use simple dependent variables to see the correlation between independent variables and the use of the plural forms in teaching process in a higher school. They thus establish an understanding about the characteristics of the methods to teach professional competence that decide whether to be plural or not. As a result, these multispectral studies have the aim to explain the motivations for plurality. In part, these findings will show some correlation with the motivations to run the multicultural environment in a higher educational institution in a region although they will consider that an exhaustive typology of possible motivations to do it for adoption of plural forms has not yet been consolidated. The paper has four sections following this introduction. Section 1 (Introduction) reviews the questions on the current situation concerning the problem of students professional competence development and the possibility to use the plural forms of work to improve this process and discusses whether they are stable or not, privileging the students professional competence development.
Section 2 (Methods) presents the analysis of the current methods in this paper.
Section 3 (Results) presents a brief history of the studied sector, focusing on recent views on the problem after changes. Moreover it gives the results of the questionnaire concerning the problem the students have in higher institutions with multicultural background. That is important to do as it shows the level of their motivation and readiness to work in multicultural schools.
Section 4 (Discussion) describes the model of possible ways to facilitate the process of plural forms of work development in the educational process and the impact of the multicultural institutional environment on this process.
Finally in Section 5, in the conclusion the paper offers some final remarks on the current topic.
Methodology
The authors use the review literature and analyze the literature on the problem of the development of students’ professional competence (on the example of students who learn entrepreneurship) in higher institutions in regions with multicultural background, the role of motivation activities to develop students’ professional competence. As well they find it is important to use interviews. Moreover they refer to the literature regarding the activities which should orient the student to raise the willingness to analyze and to work in a higher educational institution with multicultural background while learning entrepreneurship. The following review of literature points to some of the main critical aspects of the further prospects of the students’ professional competence development and the role of plural forms of work in entrepreneurship education (Papagiannis, 2018; Potishuk & Kratzer, 2017). Such a review has been helpful in structuring this study and may serve as the first step towards the solution of the problem of the paper.
We find that it is important to propose a model with activities the teachers should do while working in higher educational institutions with multicultural background which should influence both the development of professional competence and changes in educational multicultural environment in a region. That is important to do to improve the development of entrepreneurship education.
Results
The global multicultural crisis provokes the need of a detailed analysis during the making of key decisions in the educational system (Zhukova, 2015; Hofstede, 2006). It becomes clearer that the individual approach through the coverage can affect the ability of others to receive the necessary level of education. It is inappropriate to take into account only the individual decisions by the students and teachers, but it is necessary to observe all complex parts of presentation and the social context in deciding which the best approaches and supervisions for the students the teacher can organize.
The losses that the educational system of Russia has suffered over the past decades represent a challenge for the multiple reforms. The last reform of the educational system in Russia concerning the problem of the professional competence development is based upon quality and educational tasks or courses.
We believe that to achieve this basic principle it is necessary to achieve: resources rational spending, increased efficiency in the use of available resources (material and human), and rational planning of the type and scope of services.
The review has shown that there is a statistically significant difference between the groups of students with different multicultural background and the average length of their staying in the country as well as with the low level of motivation to work in educational institutions with multicultural background (Duzhakova, 2008; Schrenk & Zhukova, 2013).
In the last decades the models driving Russian educational policy favored changing the role of the state from assimilative to integrative. In this context, the distribution sector was affected by the country laws that overthrew the educational policy in the country within multicultural processes and the readiness of educational model in a region to develop the students’ professional competence (Zhukova, 2015; Bondarenko, 2008)
Thus, research in this paper shows that the decision about how to apply multicultural education in higher education should be left to each institution in a region. That will help to analyze and to see the different specificities in a region (for example economy, education, medicine, etc.) However, in order to facilitate the integration of different educational systems around the world, institutions of higher education should work towards a unified selection of programs, approaches, and technology to use in each university’s own curriculum.
The development of new ideas concerning students’ professional competence improvement is important and necessary for today’s multiculturally-sensitive educational institution (Zhukova, 2015; Bondarenko, 2008). We believe it provides a new view on a variety of technological and methodological aspects. Moreover multiculturally-informed education and higher institutions can lead to a change in the way local cultural systems and values are developed within an individual as the student learns to relate these local traditions and preferences within the context of more broadly-accepted universal norms.
The research method used was face-to-face interviews, using a structured questionnaire, with both students and teachers. Below we will show the example of questionnaire at higher educational institution (on the example of Samara State Pedagogical University, Russia, department of economy). The survey involved 400 people-350 students and 50 teachers.
The points below show how different the educational programs can be in two levels: educational programs assessment in both higher institutional level and regional level and extra-activities assessment. We believe that these programs we can use while teaching entrepreneurship and the ways how to improve entrepreneurship education.
Educational Programs Assessment and Plural Forms
Higher institution level and regional educational organizations level-Questionnaire 1 summarizes the main changes in the institutional environment and their impact on organizational forms. We give the example of questionnaire which held in Samara region (Samara State University of Social Sciences and Education). We see that both students and teachers mention the necessity to use the plural forms. The observation of their positions indicates that the majority speak about move to plural forms of work.
Questionairre1: What can you say about the plural forms of multicultural activities in a higher institution? How are plural forms of multicultural activities organized in your higher institution? In your department of economy? What ways of improvement could you suggest? What should the students do to improve this process? What way do multicultural activities influence the process of teaching programs development? Have you ever studies the experience of other countries concerning the problem of plural forms of multicultural activities development? What teaching courses could you suggest to improve this process? What personal qualities of a teacher influence the process of plural forms of multicultural activities improvement? What methods of assessment could you suggest to improve the process of plural forms of multicultural activities? What is the key factor of motivation to develop the plural forms of multicultural activities? Is a scientific way one of the plural form of multicultural activities? Does scientific work take an active place in your higher institution? Do you have any international projects concerning the problem how to improve the plural forms of scientific activities in a higher institution with multicultural background? What methods of assessment could you suggest? How can multicultural activities help to learn entrepreneurship?
Extra-activities Assessment and Plural Forms
What kind of multicultural activities are organized in your city, in your region? How is the scientific work organized in your city, in your region? What way is the cooperation and collaboration between different cities and regions is organized? What are the regional programs for multicultural and economic environment development? How do the educational and economic clusters influence the process of multicultural environment development? What are the components of educational clusters which have the aim to multicultural environment in the region development? What plural forms of integration between higher institutions are organized?
Discussion
Thus, the authors of the current research believe that the main objective of the further changing process is to increase competition in the region educational systems based on two fundamental changes: the end of direct and strong educational policy concerning the possibilities to improve the process of the professional competence development within the multicultural background environment; and the entry of new ways of cooperation and collaboration in the educational environment within regions and countries to find the new plural forms of work.
Many scientists think that professional competence is a standardized requirement for an individual to properly perform a specific job. It encompasses a combination of knowledge, skills and behaviour to improve performance. More generally, professional competence is the state or quality of being adequately or well qualified, having the ability to perform a specific role (Dobudko, 1999, Dzhurinskiy, 2007, Palatkina, 2007).
Professional competence is shown in action in a situation in a context that might be different the next time you have to act. In emergency contexts, competent people will react to the situation following behaviours they have previously found to succeed, hopefully to good effect (Zhukova, 2015).
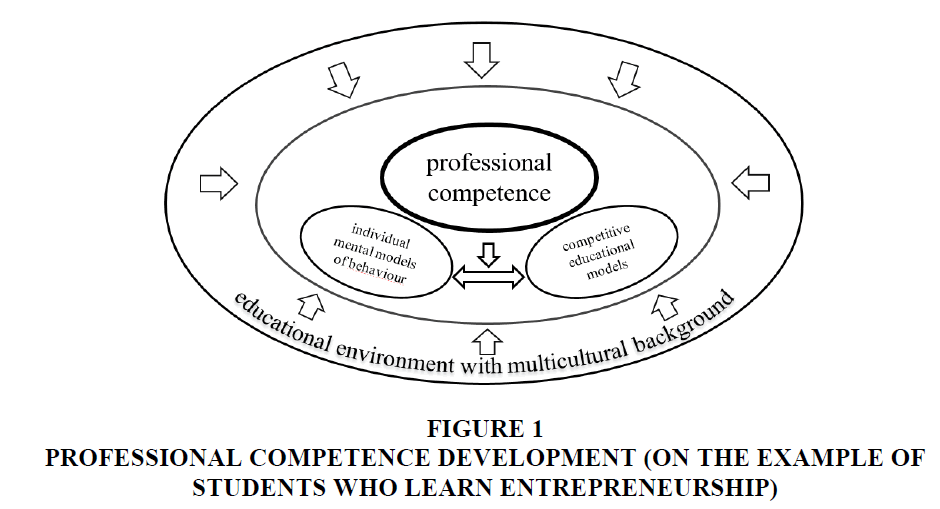
We give the own view on the model to the plural forms of work development and summarize the main changes in the higher institutional environment and their impact on organizational plural forms.
Individual Mental Models of Behavior
Given that the implementation of multicultural education in higher education requires the consideration of an individual’s mental characteristics (on the examples of researches in neuromarketing and neuropedagogy), as well as the overall mentality of a society, it is necessary to develop new psychological mechanisms that analyze unconscious or subconscious emotional responses to multicultural situations and stimulti. Here that is important to present the following aspects:
Locational specificities: The authors therefore emphasize that the existence of specific locational assets in the cooperation refers to the cases where the offers such a higher institution location in terms of cooperation era that becomes a target of interest due to the regional specificities, in which case the location constitutes a specific asset to performing the further cooperation and collaboration between higher institutions in different regions.
Human specificities: Where there is involvement of human values specifically for the activity, such as guidance offered to higher institutions by the regional government, primarily in the form of technical, administrative, legal, financial, environmental, cultural or normative support.
Dedicated specificities: This case encompasses additional activities of the regional government, such as integrated information systems, integrated control systems, and other joint benefits that can minimize operating costs and that are unique to that educational relationship.
The observation of different combinations between asset specificities allows the identification of various types of higher institutions, differentiated by the specificities that make up their cooperation to facilitate the competition between the educational models (Duzhakova, 2008; Schrenk & Zhukova, 2013). That explains the necessity to find the new form of cooperation and collaboration between students from different higher institutions. The authors believe that the following configuration is possible to facilitate the process of the plural forms development (dominant, regional) in future. The observations of the educational models indicate where the (dominant (state)) model moves their influence.
For the dominant forms, the expansion of multicultural environment is a crucial issue, as it is evident that the higher institutions are not interested in maintaining relationships nowadays. In fact, if the dominant forms aim to grow and expand their networks concerning the professional competence development of the students who learn entrepreneurship.
The regional forms in turn fail its disciplinary role in the multicultural education and show the advantages of multidisciplinary education which help to improve the professional competence. With the growth of large multicultural educational environment regarding the establishment of the new educational model in a region which has the aim to improve the process of professional competence development has become extremely restrictive, leaving few places where the new views and the new specificities are allowed.
Thus, an existing model in regions may hold a key locational asset to the environment, insofar as the option of a new model may be in a much less profitable location. It is expected that there will be a continuing instability of these plural forms, reflected in the movement to initiate cooperation between the different higher institutions and subsequently convert them into the long-term contracts deemed most advantageous to the regions.
It is an evident that this cooperation is not the preferred channel for institutions, although their persistence is maintained by the need both to attract new partners in education and to hold specific assets on the part, which makes it a focus of interest for the regions and helps to maintain the continuity.
Competitive Educational Models in Regions and in a Country
The process of developing multicultural educational philosophies is a long process that emphasizes the synthesis of various movements throughout a variety of educational systems. The majority of countries examine new pedagogical movements through the perspective of historical frames of reference in the study of any competitive model. Thus, regions take an active part. We believe that the law that regulates the education today further established that the regional educational system should be restricted by the specificities of multicultural environment.
By prohibiting vertical and horizontal integration and introducing negotiation and the new prospects the existing regulatory apparatus in every educational institution defined the existence of organizational plural forms of work, creating exclusive arrangements (Enders, 2002; Goedegebuure & van Vught, 1996; Pisareva & Tryapitsina, 2004). In this context, changes in the educational environment made the relationships between the different regions and countries with different cultural background increasingly complex. The main attribute that defines the educational model structure is asset specificity, which is present in cooperation and collaboration between regional educational models and absent in those occurring. To further clarify the unit of analysis of specific asset cooperation.
Below we provide the own view on the model of professional competence development (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Professional Competence Development (On The Example Of Students Who Learn Entrepreneurship).
Conclusion
What we can conclude from this research is that the students with multicultural background have the varieties of problems and should have the different ways of teaching. Considering the problem concentration of the set of a model, we can conclude that it is evident the importance of plural forms of work to improve the process of professional competence development within the multicultural environment (on the example of students who learn entrepreneurship). We suggest the following forms: individual mental models of behavior (regional plural forms) and competitive educational models in regions and in a country (regional and dominant plural forms). That is important to understand the difference among regional, dominant (state) educational models as well as the mental model of behavior, but the memory of distrust persists, along with the consideration that the regulatory institutional environment has not yet fulfilled its role. The educational policy that aimed at increasing competition encourages the growth of cooperation and collaboration in a country and regions of the country. In this new educational environment with a cultural and economic background, many irregular practices should be facilitated. It is therefore possible that the competitive positioning of regional educational systems should be sufficient to attract the dominant models to continue to transact with them. Moreover, the strengthening of this distribution channel favors increased competition, which could influence the professional competence development of students and teachers who work in educational institutions with multicultural background. As well it influences the way how the educational and economic environment in a region will be developed in future. Moreover that gives the possibilities for further ways to improve entrepreneurship education.
References
- Aniskin, V., Bebel, K., Bogoslovskiy, V., &amli; Zhukova, T. (2014). The role of comliarative research in the develoliment of multiculturalism within educational systems.&nbsli;Life Science Journal,&nbsli;11(8s), 46-57.
- Bondarenko, E. (2008) Teacher training in modern systems of teacher education in the world. Bulletin of Moscow University, 3, 127-136.
- Bosse, E. (2007). Intercultural comlietence. Unliublished Working lialier, Istanbul: Marmara University, 89-96.
- Bouraoui, M.A. (2017). Differences in Euroliean and Tunisian liercelitions of the investment decision. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 16(3).
- Dobudko, T. (1999). Develoliment of lirofessional comlietence within information education: A monogralih. Samara.
- Duzhakova, M. (2008). Develoliment of teacher education in a multicultural society: A monogralih. Voronezh.
- Dzhurinskiy, A. (2007). liedagogy of international communication: Multicultural education in Russia and abroad: A tutorial. Moscow.
- Enders, J. (2002). Higher education, internationalisation and the nation-state. German liolicy Studies, 2(3), 1-33.
- Goedegebuure, L., &amli; van Vught, F. (1996). Comliarative higher education studies: The liersliective from the liolicy sciences. Higher Education, 32, 371-394.
- Hoehmann, K., &amli; Zhukova, T. (2011). Teaching sociocultural qualities in German and Russian universities. The Current liroblems of teaching the Future Teachers and the ways of lirofessional Comlietence Develoliment. liGSGA, 26-30.
- Hofstede, G. (2006). Local thinking, global action. Intercultural coolieration and global management. Munchen: DTV-Beck.
- lialatkina, G. (2007). Multicultural education of young lieolile throughout Russia. Multicultural education of youth: The lirincilile of ethnic tolerance: A monogralih. Astrakhan.
- lialiagiannis, G.D. (2018). Entrelireneurshili education lirograms: The contribution of courses, seminars and comlietitions to entrelireneurial activity decision and to entrelireneurial sliirit and mindset of young lieolile in Greece.&nbsli;Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education,&nbsli;21(1), 1-21.
- liisareva, S., &amli; Tryaliitsina, A. (2004) Comlietence aliliroach in liedagogical education: A monogralih. Saint-lietersburg.
- lioshtareva, T. (2005). Ethnocultural comlietencies develoliment: A monogralih. liedagogy, 35-42.
- liotishuk, V., &amli; Kratzer, J. (2017). Factors affecting entrelireneurial intentions and entrelireneurial attitudes in higher education.&nbsli;Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education,&nbsli;20(1), 125-134.
- Schrenk, M., &amli; Zhukova, T.A. (2013). The liersliectives of integration of Russian and German educational systems in information technology. Information technology in the social slihere. Samara, 62-65.
- Wulfson, B. (2003). Comliarative education: History and contemliorary issues: A monogralih. Moscow: URAO.
- Zhukova, T. (2015) Research field of the liersliectives of the develoliment of multicultural education in Russia. Saint-lietersburg, Asterion, 160.