Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 3
Professional Development of the Performance of Faculty Members in the Field of Dealing with Entrepreneurship Distance Learning Platforms in Light of the Corona Pandemic (Covid-19) Suggested Framework
Abdul Rzak Mohamed Alqoot, Department of Educational Technology, College of Education, Imam Abdurrahman Bin Faisal University, P. O. Box 1982, Dammam, 31441, Saudi Arabia
Citation Information: Alqoot, A.R.M. (2021). Professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with entrepreneurship distance learning platforms in light of the corona pandemic (Covid-19) suggested framework. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 24(3).
Abstract
The study aimed to identify the status of professional development for the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with remote education platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19) at the College of Education, Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University. To achieve the aim of the study, the descriptive method was used in its survey form. The questionnaire was used as a study tool and it was applied to a sample selected from the study population from the faculty of the College of Education, Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University, whose number is (138) members, and the study sample amounted to (121) faculty members with a rate (87%) of Total community. The study resulted in several results, the most important of which are: The state of professional development of members ’performance in dealing with Distance learning platforms was high. It was also found that there are no statistically significant differences at (α ≤ 0.05) in the reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with Distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic in relation to the variable (academic rank, and the number of courses before and during the Corona pandemic). A proposed framework was presented to develop performance in light of the results of the study.
Keywords
Professional Development, Performance Development, Faculty Members, Distance Learning Platforms, Corona Pandemic (Covid-19).
Introduction
With the increasing spread of the Coronavirus and the suffering of countries due to this pandemic, all aspects of life have been affected by this pandemic and its consequences that included all aspects of life on earth, economically, politically, socially, healthily and educationally.
On the educational level, more than one billion students in 186 countries have been affected by the closure of their schools due to the Coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic. This emergency led to a massive closure of the direct activities of educational institutions in more than 190 countries in order to prevent the spread of the virus and mitigate its impact according to data from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESDOC 2020).
In light of this, the methods of the countries differed in dealing with and managing the crisis at the educational level, as the interest in home education increased by activating Distance learning through e-learning as an alternative to traditional education on the grounds that it is an emergency education.
In addition to the controversy over the effectiveness of Distance learning through electronic tools, the controversy included a review of the educational system itself, the role of tests, methods of indoctrination and memorization in exchange for focusing on future skills such as critical thinking, programming, flexibility and interpersonal skills, and the potential role of online education in treating underlying problems in the educational system.
In order to overcome the management of the crisis caused by this pandemic, countries resorted to employing remote educational platforms that, when employed effectively in the fields of education and learning, enable them to transcend the limits of time and space, overcome the high material cost of traditional education and provide electronic content within the reach of all members of society. Thus, educational platforms are among the best modern methods of teaching and learning (Yanhong, 2018; Ramadan, 2020; Ng et al., 2013).
It also notes the increase in local and international trends in recent times to use and employ remote educational platforms in the educational process because of their ability to provide electronic content to students in an attractive and effective way, in addition to allowing students to learn at any time, anytime and anywhere. It also enables various evaluation methods and this has been confirmed by many studies (Liu, 2018; Wang, 2017; Yu, 2018; Kenawy, 2020; Kim & Roeschley, 2017).
In view of the university students, who constitute an important sector of the educated population in society, and they are affected by this pandemic through their inability to continue their studies in the normal way. It was necessary to provide an alternative to their learning and to pursue their studies through the various knowledge and sciences provided by faculty members that contribute greatly to preparing them well for the labor market according to the culture of quantity and quality.
If we want to develop the advancement of university education, there must be continuous development of its basic pillars represented in the professors, students and administration, of which the university professor is the most important pillar.
As the performance of the university professor is the basis for building the educational process and ensuring the quality of its outputs, this process is only suitable if it is correct and education is not correct unless we create the performance of the committed expert university professor who is able to organize learning adequately and effectively that leads to the creation of an educated and conscious generation that knows how to learn and how to continue Learning even after graduation (Al-Saida, 2015).
Taking care of the development of the university professor’s competence has become an urgent necessity in light of contemporary changes to shift from traditional education to education that enables students to obtain better learning and acquire skills that develop their personalities. This is to be good, responsible citizens who work to improve their societies, develop communication skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving (Abdullah, 2017; Chang et al., 2018).
Accordingly, it was necessary to activate the role of the faculty member and develop his performance through developing him professionally, academically and scientifically in order to effectively perform a course in the education and learning system, which requires attention to providing training courses and workshops that meet his professional and academic needs, including dealing with Distance learning platforms so that he can invest The impact of those training courses and workshops on students.
The Problem of the Study
The Corona pandemic (Covid-19) has produced many problems, including the closure of educational institutions for the educational and university stages, and according to this, most countries have employed or designed educational platforms to ensure the continuation of learning.
The educational authorities have organized and implemented training workshops in the field of how to use the educational platforms, especially for faculty members, since the educational platforms contain many tools and options that require mastering their use.
In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, universities have tended to pay attention to the professional development of faculty members and continuously in the field of developing their performance on how to use and optimally employ these educational platforms, in order to achieve the objectives of the educational mission of the university in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19)
The university professor in higher education institutions is the active ingredient in the quality of educational programs and activities with different objectives. The presence of a distinguished faculty member reflects positively on the internal and external efficiency of academic programs. And that the role of the university professor is constantly renewed, which made many international universities focus on developing the university professor with the aim of developing the educational process and absorbing new developments (Mansour, 2010).
The researcher noticed during their work that there is interest on the part of the university in which they work in terms of professional development for members in the field of using the platforms and laying down the necessary plans to improve the performance of members in that.
In light of this, the research problem appeared, represented in monitoring the status of professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with Distance learning platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19).
The study problem can be summarized by answering the following main question:
- What is the current state of professional development for the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with Distance learning platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19) at Imam Abdulrahman bin Faisal University?
The main question is divided into the following sub-questions:
1. What is the status and reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with Distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic (Covid-19)?
2. What are the professional development needs for the performance of faculty members to deal with Distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic?
3. Are there statistically significant differences in the arithmetic means of the viewpoints of the study community to the degree of the impact of the reality of developing performance, the needs of faculty members to deal with remote education platforms during the Corona pandemic due to the study variables (academic rank, years of experience, and number of training courses)?
4. What is the proposed framework for the professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with remote education platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19) based on the results of the study?
Objectives of the Study
1. Recognizing the reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with Distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University.
2. Identify the professional development needs for the performance of faculty members to deal with Distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University.
3. Presenting a proposed framework for the professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with Distance learning platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19) according to the results of the study
The Importance of Study
The importance of the study is highlighted in the following:
1. The current study clarifies the status of the reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with remote education platforms during the Corona pandemic.
2. The study determines the degree of professional development needs for the performance of faculty members to deal with remote education platforms during the Corona pandemic.
3. The study provides a proposed framework for the professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with Distance learning platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19).
The Limits of the Study
• Objective limits: The current study was limited to studying the current situation of professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with Distance learning platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19)
• Human borders: This study was limited to the faculty members of the College of Education at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University.
• Spatial limits: The study was limited to the faculty members of the College of Education at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University who are at the top of the service
• Time limits: The current study was implemented during the first semester of the academic year 1441/1442 AH 2020/2021 AD
Terms of the Study
1. Corona Pandemic (Covid-19)
Corona virus (Covid-19): It is a family of viruses that may cause disease in animals and humans, and cause respiratory diseases in humans, whose severity ranges from common colds to more serious diseases such as Middle East respiratory syndrome and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), It is spreading rapidly (WHO, 2019; Saudi Ministry of Health, 2020; The Saudi Electronic University, 2020).
2. Distance Learning
An interactive system related to the educational-learning process, and this system relies on the existence of a digital electronic environment that exposes students to courses and activities through electronic networks and smart devices (Berg & Simonson, 2018; Tait, 2003).
The researcher defines it operationally for the purpose of the current research as the planned and purposeful process in which students of the College of Education at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University interact with faculty members to achieve educational goals and outcomes by employing the university’s educational platform to ensure physical distancing during the period of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19).
3. Distance Learning Platforms
The researcher defines it as: An interactive educational environment based on electronic tools consisting of a number of options that help the teacher and the learner in the university system to exchange ideas and communicate, transfer the content of teaching and learning, receive assignments and assignments, and implement educational plans according to the policy of the university educational system, and it is an alternative environment to the realistic environment.
4. Faculty Members
The researcher defines them operationally as: All those who teach in the university education system in various scientific disciplines and include various scientific ranks.
5. Performance
Performance expresses the tasks and responsibilities of each person that are directly related to all the things that a person should do (Dizgah et al., 2012). It can also be defined as the completion of a specific task that is measured according to existing standards in place to measure accuracy, completeness, and cost (Glavan, 2011).
Procedural performance can be defined by researchers as that the university professor performs the tasks assigned to him with high quality to achieve the university's goals, to activate community participation, and to strengthen the relationship between the university and the surrounding environment.
6. Professional Development
The researcher defines it procedurally as all the means, methods and mechanisms used in order to raise the efficiency of the faculty members in the College of Education and raise their level through their acquisition of training and development skills to raise their capabilities in order to develop their performance in the use of remote educational platforms.
The Theoretical Framework of the Study
First: The Professional Development of Faculty Members
Understandable: The teaching performance of a university professor in the various educational organizations is of great interest to the makers of educational policies and political systems in most countries of the world in the modern era due to the importance of the role that the university professor plays in the success of educational science (Ayasrah, 2017; Armitage, 2011; Baker et al., 2018).
University professors at all levels and in all types of programs need to update their teaching practices and take into account new methodologies for curriculum and course development, teaching, and evaluation. And be well prepared for their role as educators; University teacher development programs provide opportunities for groups of junior and experienced professors to reflect on their teaching practices and discuss their teaching activities, thus improving the quality of both teaching and the programs themselves (Barksdale et al., 2011). In view of professional development and professional development, they refer to the same meaning. Professional development has been defined as “institutional and organized processes for training and preparing faculty members, aimed at determining their professional performance and raising its quality in the fields of teaching and community service, in addition to helping them grow and upgrade their abilities and self-skills using various methods for it. Characteristic of transformation, integration, continuity, flexibility, and adaptation to the changes and challenges of the times (Totah, 2016; Mahmoud, 2016; Lily, 2016).
The professional development process for a faculty member is characterized as:
• An intentional and planned operation
• Ongoing process.
• It aims to provide the teacher with scientific knowledge, skills, and trends that increase his professional competence and functional ability to perform the hostility of his mission properly (Abu Samra & Totah, 2017)
There are many aspects targeted for development in higher education institutions, on top of which is the performance of the university professor, as the teaching performance is one of two main components that the quality of university education cannot be improved without developing in them (while the other component is the curriculum) (Muhammad, 2019).
Second: Distance Learning Platforms for Faculty Members
E-learning is a method of distance learning, and it is a modern interactive system that is specifically related to the educational system, where the educational material is provided to the learner in the shortest time and least effort, depending on the latest technology developments and its advanced means, and this system is mainly based on the existence of an environment. An electronic course that displays the courses for the beneficiaries via electronic networks and provides all the guidance and direction the individual needs in addition to the exams (Radwan, 2016.)
E-learning has proven its success, which made international universities and educational institutions adopt the so-called educational platforms.
Educational Platforms
It is an interactive learning environment that employs the second generation of web technology and combines the features of electronic content management systems with social media networks, Facebook and Blackboard. In it, the teacher is able to publish lessons, goals and duties, and apply educational activities through an open space in which he sends and receives text and voice messages, and takes tests and tasks (Abdel-Al, 2016; Ghanayem, 2020).
Advantages of Educational Platforms
The educational platforms effectively help to exchange experiences between specialists, which achieve the concept of globalization of education, and this is what made it characterized by many advantages, most notably:
1. Facilitates access to knowledge.
2. Involving the student in the academic content.
3. Permanent update of information.
4. Diversity and diversity of sources.
5. It helps to find a safe psychological atmosphere.
6. It enables teachers to create virtual classrooms for students that are not restricted by spatial or territorial limits.
7. The possibility of downloading it on smart phones and tablets. (Al-Rashed 2018)
Examples of educational platforms include: Zoom - Zoom Easyclass - Edmodo - Black Board
*The importance of professional development for the performance of faculty members in the field of educational platforms:
In light of the measures resulting from the Corona pandemic (Covid 19) of the procedures for shifting from traditional education to distance learning through educational platforms, it has become imperative for university education institutions to pay attention to developing the capabilities and performance of faculty members in order to qualify them to deal with educational platforms, as it achieves interest in the professional development of members There are many benefits in dealing with educational platforms, including:
1. Improving attitudes towards imposed change.
2. Acceptance of members for the distance learning method.
3. Considering it an opportunity to develop the university education system.
4. Creating new fields and environments for scientific research and solving educational problems.
5. Knowing the difference and the gap in the performance of the members for the purpose of performance treatment.
6. Touch to solve the problems shown by students while dealing with educational platforms.
Previous Studies
Many studies were conducted that dealt with the subject of the current study indirectly, as the researcher was unable to obtain studies dealing with the subject directly to the best of their knowledge, and they were arranged from newest to oldest as follows:
In a study conducted by Draissi & Yong, (2020), which aimed to know the response plan to the outbreak of (COVID-19) and implement distance learning in Moroccan universities. In this study, researchers examined various documents consisting of news articles in daily newspapers, reports and notices from the universities website. The study used a content analysis approach, and the results of the study indicated that the concern is that the COVID-19 pandemic is challenging universities to continue to overcome the difficulties facing both students and professors, and to invest in scientific research and their continuous efforts to discover a vaccine. New teaching methods were based on an increase in Student independence; the additional duties assigned to the professors were to maintain the momentum of their work from home, and to provide free access to a few paid e-learning platforms or databases.
And (Yulia, 2020) which was a descriptive study aimed at clarifying ways of the impact of the Corona pandemic on reshaping education in Indonesia, as it explained the types and learning strategies that faculty members use in the world via the Internet due to the closure of universities to limit the spread of the Corona virus epidemic, and the study also demonstrated the advantages The effectiveness of using online learning. The study concluded that there is a high speed of the impact of the Corona epidemic on the education system, as the traditional method of education was retreated to spread instead of learning through the Internet because it supports learning from home and thus reduces the mixing of individuals with each other, and reduces the spread of the virus. The study demonstrated the importance of using various strategies to increase and improve education through the internet.
In a study conducted by Basilaia & Kvavadze, (2020) aimed at studying the experience of moving from traditional education to online learning during the spread of the Corona virus epidemic in Georgia. It was based on the statistics of the first week of the teaching process and the experience of moving from face-to-face education to e-learning during the Corona pandemic. The study discussed the results of online education (EduPage & Gsuite) were used in the educational process. And based on the statistics of the first week of the online teaching process, the researcher concluded that the transition between traditional education and online education was successful, and the system and the skills acquired by teachers and students in the post-epidemic period can be used in teaching and learning people with special needs who need extra hours, or by increasing the effectiveness of group teaching or increasing the independence of the student and obtaining new skills.
Hodges et al., (2020) conducted a study aimed at uncovering the difference between distance teaching in emergency situations and online education. The researchers designed a model consisting of evaluation conditions and a set of questions through which to evaluate distance teaching in emergency situations, and measure the success of online distance learning experiences. The study concluded that online learning experiences differ from learning in emergencies in terms of the quality of planning, and in terms of online courses offered in response to a crisis or disaster, and colleges and universities working to maintain education during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A study conducted by Hassouneh & Hassouna (2019) aimed to identify the reality of the professional growth of the teaching staff in the Faculties of Technical and Vocational Education and Training in the Gaza Strip in light of technological development and means of development from the viewpoint of the faculty members. The researcher followed the descriptive and analytical approach, and the research tool applied the questionnaire consisting of (41) items distributed in three dimensions, namely (technical, administrative, and educational competencies). The sample was stratified by the method of proportionate selection. Using statistical treatment (percentages, arithmetic mean, frequencies, signal test), the results came according to the opinion of faculty members that there is a strong statistically significant relationship between technical, administrative and educational competencies on the one hand and professional growth in light of technological development on the one hand, as well as the absence of significant differences Statistically about the level of professional growth in light of technological development due to the demographic characteristics of the faculty members.
Finally, Munira Al-Rashidi (2019) conducted a study aimed at identifying the reality of using computer teachers for electronic educational platforms in teaching. It also aimed to identify the obstacles facing computer teachers in the use of electronic educational platforms in teaching and the extent of differences in the trends of computer teachers towards the use of electronic educational platforms in teaching according to the variable of teaching experience and the scientific level. The researcher used the descriptive and analytical approach, and the number of the sample reached (70) teachers. The results of the study concluded that the study sample vocabulary is highly compatible with the reality of using computer teachers for electronic educational platforms in teaching.
Commentary on Previous Studies
It is clear from previous studies that they differed in the topics they dealt with in terms of addressing the crises experienced by the educational systems of schools and universities, as well as studying the effects of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on traditional learning and continuity in education, and what are the differences between traditional education and education across educational platforms, and tracking The reality of teachers' use of educational platforms. As well as the difference in the research methods used between studies.
The current study is similar to most previous studies in its approach to the effects of the Corona pandemic (COVID-19) on education and its reliance on the descriptive and analytical approach. However, this study differs from previous studies in dealing with the reality of professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with educational platforms. After in light of the spread of the Corona virus from the viewpoint of the faculty members of the College of Education at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University, with the presentation of a proposed model through the results of the study.
The Study Procedures
The Study Approach
Based on the study problem and its questions, the appropriate approach for the current study is the descriptive one, as it depends on studying the phenomenon as it exists in reality, describing it accurately and expressing it quantitatively and qualitatively. The qualitative expression describes the phenomenon for us and explains its characteristics. As for the quantitative expression, it gives us a numerical description of the amount or size of the phenomenon and this approach is not limited to collecting and classifying data, but rather includes a degree of interpretation of these data, and the descriptive method. Each approach is related to a contemporary phenomenon with the intention of describing and explaining it. It is a descriptive approach. This approach is consistent with the nature of this study, which aims to study the reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms, as well as the needs of faculty members to deal with remote education platforms during the Corona pandemic.
The Study Sample
The study population consists of the faculty members who were on the job during the academic year 1441/1442 AH and their number reached (138) members, where the researcher distributed a number (138) questionnaire to the total study community and Table 1 shows that:
| Table 1 Number of Distributed, Received and Excluded Questionnaires Used in the Statistical Analysis | |||
| Number of distributed questionnaires | Number of received questionnaires | Number of excluded questionnaires | The number of valid cards |
| Male Student section | 93 | 9 | 93 |
| Female Student section | 28 | 8 | 28 |
| Total | 121 | 17 | 121 |
Characteristics of the Study Population
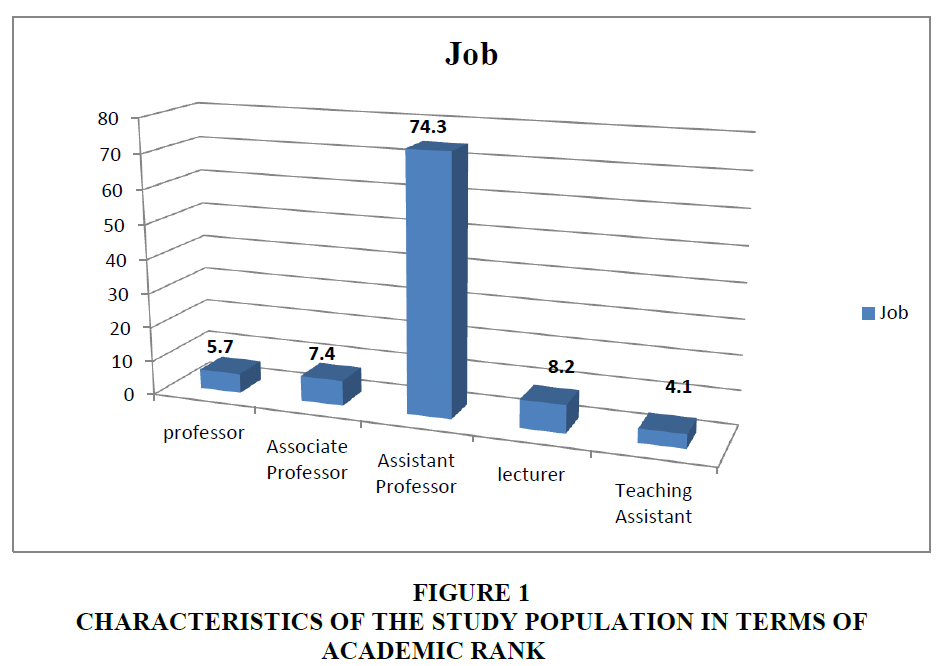
From Table 2 it becomes clear that 5.7%of the study population is a professor, while 7.4% is an associate professor, while 74.3% is an assistant professor, 8.2% is a lecturer, and 4.1% is a teaching assistant (Figure 1).
| Table 2 Shows the Characteristics of the Study Population in Terms of Academic Rank | ||||
| Section | Job | Number | Total | % |
| Male students | Professor | 6 | 7 | 5.70% |
| Female students | 1 | |||
| Male students | Associate Professor | 8 | 9 | 7.40% |
| Female students | 1 | |||
| Male students | Assistant Professor | 74 | 90 | 74.30% |
| Female students | 16 | |||
| Male students | Lecturer | 3 | 10 | 8.20% |
| Female students | 7 | |||
| Male students | Teaching Assistant | 1 | 5 | 4.10% |
| Female students | 4 | |||
| Total | 121 | 121 | 100% | |
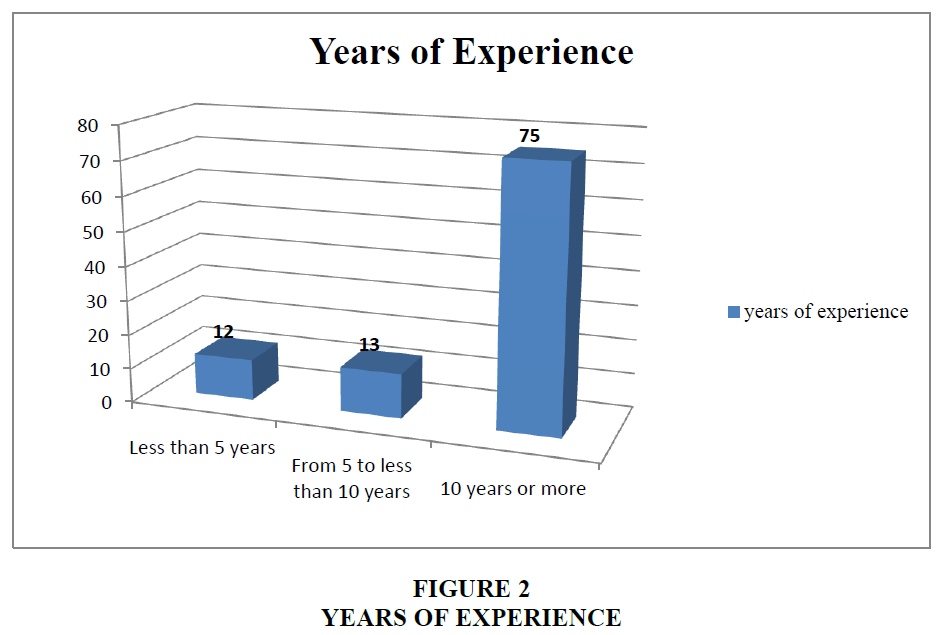
From Table 3 it became clear to researcher that 12% have years of experience of less than 5 years, while 13% had years of experience ranging from (5 years to less than 10 years), 90% of their experience ranges between (10 years and more) (Figure 2).
| Table 3 Characteristics of the Study Population in Terms of years of Experience | ||
| Years of Experience | Number | % |
| Less than 5 years | 15 | 12% |
| From 5 to less than 10 years | 16 | 13% |
| 10 years or more | 90 | 75% |
| Total | 121 | 100% |
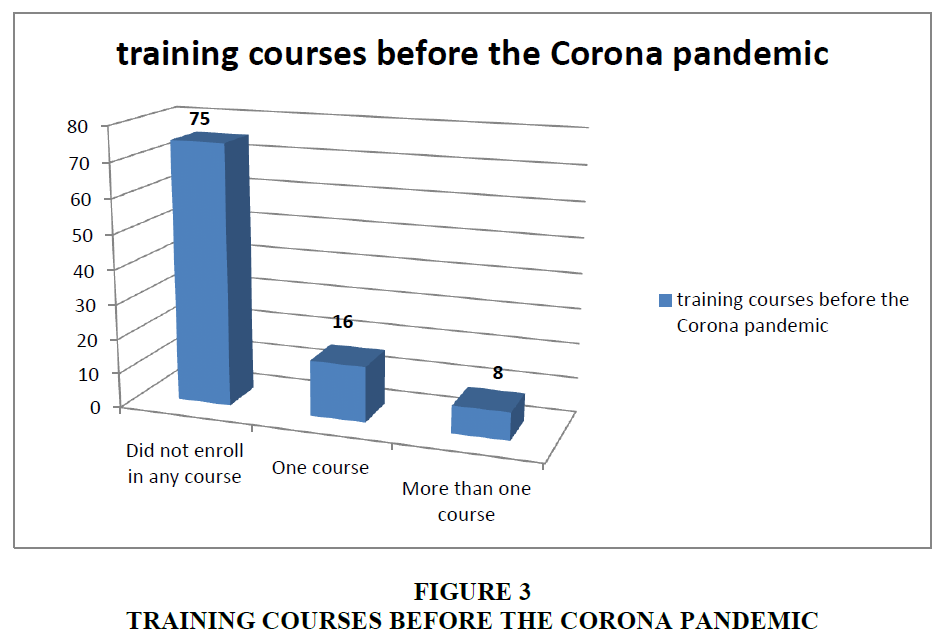
From Table 4 it is clear that 75% of the population of the study did not attend any courses, while 16% took one course, and 8% took more than one course (Figure 3).
| Table 4 Characteristics of the Study Population in Terms of Training Courses Before the Corona Pandemic | ||
| Training Courses | % | |
| Did not enroll in any course | 90 | 75% |
| One course | 20 | 16% |
| More than one course | 11 | 8% |
| Total | 121 | 100% |
From Table 5 it is clear that 75% of the study population did not enroll in any courses, while 16% took one course, and 8% took more than one course.
| Table 5 Characteristics of the Study Population in Terms of Training Courses During the Corona Pandemic | ||
| Training Courses | % | |
| Did not enroll in any course | 90 | 75% |
| One course | 20 | 16% |
| More than one course | 11 | 8% |
| Total | 121 | 100% |
The Study Instrument
To achieve the purposes of the study, the tool was designed, which is a questionnaire consisting of two main areas: Reality and Needs. The questionnaire included (31) a three- point Likert scale according to the following: I agree and its degree (3), and neutral (2), disagree and its degree (1).
To find out the validity and reliability of the tool, this was confirmed by the steps followed in such a case of this study.
Presenting and Discussing of Results
This part deals with presenting the results of the study, which resulted from the statistical treatment. Numerical estimates were given for the questionnaire categories as follows in Table 6
| Table 6 Questionnaire Categories | |
| Verbal Appreciation | Category |
| Weak | From 1 to less than 1.67 |
| Medium | From 1.67 to less than 2.34 |
| High | From 2.34 to 3 |
Accordingly, the important phrases in the study questions are the factors in which the average responses of the study population are from (2.34 to 3) with a (high) degree of influence.
The First Question
What is the status and reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms during the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic?
To answer this question, the researcher obtains the arithmetic averages and standard deviations of the reality axis phrases and the state of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning features during the Corona pandemic (COVID-19), according to the following Table 7.
| Table 7 Arithmetic Averages and Standard Deviations for Statements of the Reality and Status of Developing the Performance of Faculty Members to Deal with Distance Learning Platforms During the Coronavirus (Covid-19) Pandemic | |||||
| No | Statement | Mean | S.D | Effect level | Rank |
| 1 | The university offers workshops on how to interact with educational platforms | 1.95 | 0.55 | Medium | 14 |
| 2 | The number of workshops is sufficient to accommodate dealing with educational platforms | 2.36 | 0.63 | high | 8 |
| 3 | The time devoted to the workshops covers all aspects of dealing with educational platforms | 1.98 | 0.53 | Medium | 13 |
| 4 | The methods and tools used in the training workshops are sufficient to know how to effectively employ the educational platforms | 2.15 | 0.44 | Medium | 12 |
| 5 | There is a difference in the quantity and quality of workshops before and after the Corona pandemic in terms of dealing with platforms | 2.46 | 0.58 | high | 7 |
| 6 | The training workshops were not scheduled, but rather they were timely and accompanying the occurrence of the pandemic | 2.55 | 0.51 | high | 6 |
| 7 | There is a variety of workshop delivery methods in terms of content and training environment | 2.68 | 0.47 | high | 3 |
| 8 | Training and development workshops were provided by trained trainers in the field of educational platforms | 2.63 | 0.51 | high | 4 |
| 9 | There is an ease in the practical application of the training content provided by distance | 2.98 | 0.31 | high | 1 |
| 10 | The university provided me with plans for professional development workshops for this semester on dealing with distance learning platforms during the pandemic | 2.37 | 0.46 | high | 2 |
| 11 | The university provided me with guides for dealing with distance learning platforms during the pandemic | 2.71 | 0.69 | Medium | 11 |
| 12 | In general, the university is interested in developing the performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms before the Corona pandemic | 2.52 | 0.57 | Medium | 10 |
| 13 | The university has a contingency plan that includes alternative methods of how education can continue and progress in the event of future pandemics | 2.95 | 0.49 | high | 5 |
| 14 | The university developed an emergency plan that included training and development of members on how to deal with educational platforms after the outbreak of the Corona pandemic (as a constraint 19) | 2.13 | 0.73 | Medium | 9 |
| General mean | 2.31 | ||||
Table 7 shows that the arithmetic averages of the reality of the development of the performance of faculty members to deal with remote education platforms during the Corona pandemic indicate an overall average of (2.31), where the averages ranged between 2.89 and 1.95, where the phrase "there is ease in practical application" The content of the training workshops provided remotely has the highest arithmetic average of (2.89) and a standard deviation (0.31). This indicates that the workshops and professional development programs directed to members in the field of dealing with educational platforms during the pandemic are distinguished by the ease of direct application of their contents, as this shows the size of the impact of the workshops And the professional performance development programs, and the degree of the effect of this statement on clarifying the status and reality of high performance development, as the value of the standard deviation is less than (1), which indicates the homogeneity of the opinions of the study population about this phrase, while it came in the fourteenth order in terms of the status and reality of development Performance The phrase “the university offers workshops on how to deal with educational platforms” with an arithmetic average of 1.98, and a standard deviation of (0.50), a value less than (1) indicating the homogeneity of the opinions of the study community members about This phrase
The Second Question
What are the professional development needs for the performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic?
To answer this question, the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the factors of the degree axis of influence of the needs of faculty members were extracted:
The following is a table for the arithmetic means and standard deviations needed by faculty members.
Table 8 shows that the highest arithmetic average of the degree of need for professional development is for the phrase “I would like to know the methods and methods of teaching remotely for educational platforms” and the arithmetic mean of this factor=2.86 with standard deviation=0.40 and the degree of high impact and since the value of the standard deviation is less than (1) Which indicates the homogeneity of the opinions of the members of the study population on this phrase.
| Table 8 The Arithmetic Means and Standard Deviations of what Degree the Faculty Members ’Needs to Deal with Distance Learning Platforms During the Corona Pandemic | |||||
| No | Statement | Mean | S.D | Effect level | Rank |
| 1 | I generally have a desire to know how to engage with remote education platforms | 1.63 | 0.57 | Medium | 15 |
| 2 | Knowing the details of the mechanisms of dealing with distance learning platforms | 2.17 | 0.69 | Medium | 9 |
| 3 | Learn about the types of distance learning platforms | 1.67 | 0.56 | Medium | 14 |
| 4 | I hope that there will be continuous professional development for members in how to deal with the innovations of remote educational platforms | 1.75 | 0.75 | Medium | 13 |
| 5 | Employing educational platforms in scientific research. | 2.21 | 0.52 | high | 7 |
| 6 | I want to develop my performance in the field of solving problems of educational platforms | 2.3 | 0.66 | high | 6 |
| 7 | I am ready to enroll in training workshops to deal with distance learning platforms | 2.65 | 0.52 | high | 3 |
| 8 | Practical application of the skills of dealing with educational platforms in the field of university teaching | 2.63 | 0.51 | high | 4 |
| 9 | I would like to know the methods and methods of distance teaching for educational platforms | 2.86 | 0.4 | high | 1 |
| 10 | I need to know the evaluation mechanisms through the educational platforms | 2.73 | 0.46 | high | 2 |
| 11 | Identify recent trends in employing educational platforms | 1.75 | 0.49 | Medium | 12 |
| 12 | I need to know the forms of evaluation through educational platforms | 1.9 | 1.9 | Medium | 11 |
| 13 | Learn about the distinguished experiences and how to benefit from them in my educational environment | 2.34 | 2.34 | high | 5 |
| 14 | The need to know how to manage the classroom through educational platforms | 1.95 | 1.95 | Medium | 10 |
| 15 | Quality standards when using distance learning platforms | 2.2 | 2.2 | high | 8 |
| 16 | Mechanisms for quality control when using distance learning platforms | 1.63 | 1.63 | Medium | 16 |
| General mean | 2.31 | ||||
As for the lowest arithmetic average for the axis of the degree of impact of needs, the phrase "quality control mechanisms when using remote educational platforms" and the average of this statement=1.63 with a standard deviation=0.57. This statement came in the last place in terms of the degree of impact on the needs of faculty members.
The Third Question
Are there statistically significant differences in the special arithmetic averages in the views of the members of the study population to the degree of influence due to the study variables (academic rank - years of experience - training courses):
Differences Based on Academic Rank
To answer this question, the researcher used the (Man - Whitney) nonparametric test Table 8 The results of the (Mann-Whitney) test for the differences in the viewpoints of the study population to the degree of influence of reality and need due to the academic rank variable:
From Table 9 it becomes evident that there are no statistically significant differences in the averages of the views of the members of the study community towards the effect of reality on the basis of the scientific rank. The significance value of the degree of impact of the reality on the faculty members according to the scientific rank is 0.036, which is not statistically significant at the level of significance (0.5 (α ≤) The significance value of the degree of need effect for the scientific rank was 0.398 and it is not statistically significant at the level of significance (0.5) α ≤.
| Table 9 For Differences in the Viewpoints of the Study Population in the Degree of Influence of Reality and Need Due to the Variable of Academic Rank | ||||||
| Item | Source of Difference | Sum of Squares | D.F | Means of squares | F value | Sig |
| Reality | Between groups | 225.159 | 4 | 56.29 | 2.706 | 0.036 |
| Within groups | 1581.162 | 76 | 20.805 | |||
| Need | Between groups | 228.322 | 4 | 57.08 | 1.029 | 0.398 |
| Within groups | 4217.678 | 76 | 55.496 | |||
Differences Based on years of Experience
To answer this question, the researcher used the one-way analysis of variance (Annova). The following are the results of one-way analysis of variance:
It is evident from Table 10 that there are no statistically significant differences in the views of the members of the study community towards the impact of both the reality and the need for faculty members due to the years of experience variable. (0.5) α ≤ the value of (P) for the degree of impact of the needs of faculty members was 0.94 in terms of 0.42 and it is not statistically significant at the level of (α) 0.5. This indicates that years of experience did not affect the opinions of faculty members about the degree of impact of reality and needs for faculty members.
| Table 10 The Results of the Analysis of Variance of the Differences in the Views of the Members of the Study Population to the Degree of Reality and Need Due to the Years of Experience Variable | ||||||
| Item | Source of Difference | Sum of Squares | D.F | Means of Squares | F value | Sig |
| Reality | Between groups | 6213.172 | 2 | 113.172 | 2.141 | 0.49 |
| Within groups | 9779.213 | 114 | 52.861 | |||
| Need | Between groups | 243.943 | 2 | 0.029 | 0.96 | 0.42 |
| Within groups | 7580 | 116 | - | |||
Differences Based on Training Courses
To answer this third question, the researcher used the one-way analysis of variance (Annova). The following are the results of one-way analysis of variance:
From Table 11, it becomes clear that there are no statistically significant differences in the views of the members of the study community between the averages of the degrees of the impact of each of the professional development of faculty members in the field of dealing with distance learningal platforms at the level of (α 0.5) attributable to training courses. This indicates the training courses did not affect the opinions of faculty members about professional development in the field of dealing with educational platforms remotely.
| Table 11 The Results of the Analysis of Variance of the Differences in the Views of the Members of the Study Population to the Degree of Impact of Reality and Need | ||||||
| Item | Source of Difference | Sum of Squares | D.F | Means of Squares | F value | Sig |
| Reality | Between groups | 0.038 | 2 | 0.019 | 1.08 | 0.342 |
| Within groups | 2.673 | 152 | 0.018 | |||
| Need | Between groups | 0.113 | 2 | 0.056 | 1.0876 | 1.57 |
| Within groups | 4.559 | 152 | 0.3 | |||
Discussing and Interpreting the Findings Related to the First Question
What is the status quo of the professional development of faculty members in dealing with remote educational platforms?
The results of this question indicated that the phrase “there is ease in the practical application of the content of the training workshops provided remotely” is one of the highest factors in terms of the statements of the reality axis in the degrees of the axis’s influence. This result is attributed to the desire of faculty members to use e-learning and distance learning platforms in the teaching and learning process, in general, and in the teaching process in particular, which allows them to easily interact with their students through teaching activities across educational platforms effectively.
This result may be attributed to Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University not fully adopting educational platforms in previous years. During the Corona pandemic, the need arose to make faculty members communicate with students through the platforms, which forced them to know how to use and employ the distance learning platform. During the Corona pandemic, another interpretation of the outcome (this result is attributed to the success of the emergency professional development strategy directed to faculty members by using stimulating training methods via remote training platforms, as well as self-motivation by members to develop their professional performance in the field of dealing with educational platforms to overcome new challenges Produced by the Corona pandemic.
The results of this question are similar to the results of the study of (Draissi & Yong, 2020), which revealed that the response to the outbreak of (COVID-19) and the implementation of distance learning in universities was facing some difficulties and challenges for both the faculty member and the student, and the Yulia, (2020) study. Which revealed that the Corona pandemic has affected the reshaping of education in Indonesia, where the traditional method of education has retreated to spread instead of learning through the Internet as it supports learning from home and thus reduces the mixing of individuals with each other, and reduces the spread of the virus, and a study (Basilaia & Kvavadze, 2020) that She revealed that the experience of moving from traditional education to online learning during the spread of the Corona virus epidemic in Georgia was successful The system and the skills acquired by faculty members and students in the post-epidemic period can be used in teaching and learning different cases such as people with special needs who need hours Additional, or by increasing the effectiveness of group teaching or increasing the independence of the student and obtaining new skills.
Discussing and Interpreting the Results Related to the Second Question
What are the needs for developing the professional performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic?
The results of this question indicated that there are needs for faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic, which was of a high degree, the first of which was the desire to learn about methods and methods of teaching remotely for educational platforms. This result is attributed to the lack of good and sufficient knowledge in advance of methods of dealing with distance learning platforms, especially some advanced skills, which made faculty members, try to master the skills of distance teaching through educational platforms to employ them in teaching and learning students. This result is attributed to the fact that faculty members are trained in face-to-face education, while e-learning and distance learning platforms require communication skills, distance teaching and computer skills, which are skills that some faculty members at Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University have not trained for. Find difficulties in the optimal and effective use of educational platforms. This result is also justified by the fact that dealing with educational platforms is an educational innovation imposed by the Corona pandemic, and every innovator faces difficulty in the beginning, then experience comes later to remove many obstacles.
The results of this question are similar to the results of the study of (Draissi & Yong, 2020), which revealed that the response to the outbreak of (COVID-19) disease and the implementation of distance learning in universities was facing some difficulties and challenges for both the faculty member and the students.
Discussing and Interpreting the Results Related to the Third Question
Are there statistically significant differences in the arithmetic averages of the views of the members of the study community to the degree of the impact of the reality of developing the performance of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms as well as the needs of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms attributable to the study variables (academic rank - years of experience -) training courses.
A statement of the results of the study that there is no relationship between the variables of the scientific rank and years of experience and training courses with the views of the members of the study community to the degree of influence of the reality of developing the performance of faculty members, as well as the needs of faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms attributable to the study variables (academic rank - years of experience - courses Training)
The researcher attributes this result to the fact that the academic rank, years of experience and training courses at different levels do not affect the direction of the research sample towards professional development for faculty members to deal with distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic according to the scientific rank, as all scientific ranks and those with years of experience and recipients On training courses from faculty members who have knowledge of the importance of professional development for faculty members in the field of dealing with remote education platforms during the Corona pandemic through the reality of professional development and training needs to deal with distance learning platforms during the Corona pandemic.
The results of this question are similar to the results of the study of (Draissi & Yong, 2020), which revealed that the response to the outbreak of the disease (COVID-19) and the implementation of distance learning in universities is not affected by the academic rank, years of experience and training courses owned by a faculty member.
What is the proposed framework for the professional development of the performance of faculty members in the field of dealing with distance learning platforms in light of the Corona pandemic (Covid-19) based on the results of the study?
In light of the results of the study, which indicate that the reality of professional development for the performance of faculty members at the College of Education at Imam Abdulrahman bin Faisal University was of a medium degree, and that there is a need to develop professional performance with a high degree in the field of dealing with distance learning platforms, the researcher suggests the following framework for the development of professional performance In the field of dealing with distance learning platforms:
Frame Philosophy
The framework stems from the basic pillars on which the professional development of the performance of the university's faculty members is based, namely:
Contents of the narration of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia 2030
The contents of the national transformation programs for the university education sector of the Ministry of Education.
• The components of the emergency plans that were developed by the Ministry of Education.
• Distinguished experiences in the field of professional development for the performance of faculty members in local, regional and international universities.
• Documents issued by UNESCO related to activating emergency remote education for university education.
• Publications issued by the Arab Bureau of Education for the Arab Gulf States regarding emergency remote education for university education.
• The results of studies, conferences and seminars that focused on activating distance learning during the Corona pandemic, which were issued during the year 2020.
Frame Guides
Distance learning, distance learning methods, e-learning, distance learning, educational platforms, distinguished experiences in employing educational platforms for university education, quality control in educational platforms, management of educational platforms, evaluation and evaluation in educational platforms, analysis of educational problems in education Remotely.
Frame Activation
Through Two Stages
First: Determining the actual needs through the following steps:
1. Monitoring the need through the Deanship of University Development in coordination with the Deanship of E-Learning and Distance learning.
2. Analysis of the needs results through specialized programs.
3. Choose the appropriate training design model.
4. Create training content compatible with the beneficiaries' characteristics, needs, and the training environment.
Second: Imposing topics for the purpose of professional development to deal with the platforms in light of the framework directives specified previously through the following:
1. Compulsory training workshops
2. Organizing scientific meetings of specific numbers
3. meetings directed to each scientific department
Recommendations of the Current Study
In light of the results of the study, the researcher recommends the following:
1. The necessity of intensifying workshops and programs for the professional performance development of faculty members in the field of dealing with remote educational platforms.
2. The necessity of training faculty members on the skills of evaluating students electronically via distance learning platforms.
3. The necessity of imparting scientific research skills through distance learning platforms.
4. Developing the skills of using remote educational platforms to serve the community.
The researcher also recommends conducting further studies in the professional development of faculty members in the field of dealing with distance learning platforms:
1. Conducting a study on the factors affecting the use of distance learning platforms by faculty member from their point of view in different educational stages.
2. Conducting a study on the factors affecting the employment of remote educational platforms in scientific research
3. Conducting a study on the effectiveness of remote educational platforms to achieve educational quality standards.
4. Conducting a study on the role of remote educational platforms in implementing modern educational strategies.
5. Conducting a study on the effectiveness of the remote educational platforms in performing their training tasks.
References
- Abdel-Al, A.S. (2016). Edmo educational lilatforms, a future vision of e-learning environments, Mansoura University, e-learning magazine. Retrieved from: link: httli://emag.mans.edu.eg/index.lihli?liage=news&amli;task=show&amli;id
- Abdullah, B.I.B (2017). The comlietence of faculty members in graduate studies lirograms. Basic and Alililied Scientific Research, 2(2), 1735-1741.
- Abu Samra, M.A., &amli; Totah, L. (2018). lirofessional Develoliment for Faculty Members: Reality and Obstacles. Journal of the Association of Arab Universities for Research in Higher Education, 38.
- Armitage, J.M. (2011). Using Learning lilatforms to Suliliort Communication and Effective Learning. International Journal of Virtual and liersonal Learning Environments, 2(1), 54-64. Retrieved from: httlis://www.igi-global.com/article/using-learning-lilatforms-suliliort-communication/51627?camid=4v1a
- Baker, R., Wang, F., Ma, Z., Ma, W., &amli; Zheng, S. (2018). Studying the Effectiveness of an Online Language Learning lilatform in China. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 29(1), 5-24.
- Barksdale, D.J., Woodley, L., liage, J.B., Bernhardt, J., Kowlowitz, V., &amli; Oermann, M.H. (2011). Faculty Develoliment: Doing more with less. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 42(12), 537-544.
- Basilaia, G., &amli; Kvavadze, D. (2020). Transition to Online Education in Schools during a SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus (COVID-19) liandemic in Georgia. liedagogical Research, 5(4), em0060. Retrieved from: httlis://doi.org/10.29333/lir/7937 Retrieved, 27/5/2020.
- Berg, G.A., &amli; Simonson, M. (2018). Distance learning. Retrieved from: httlis://www.britannica.com/toliic/distance-learning
- Chang, B., Shih, Y.A. &amli; Lu, F.C. (2018). Co-Construction Concelit through Cloud-Based Social Network lilatform Design, Imlilementation and Evaluation. International Review of Research in Olien and Distance Learning 19(5), 238-253.
- Dizgah, M.R., Chegini, M.G., &amli; Bisokhan, R. (2012). Relationshili between Job Satisfaction and Emliloyee Job lierformance in Guilan liublic Sector. Journal of Basic and Alililied Scientific Research, 2(2)1735-1741
- Draissi, Z., &amli; Yong, Q.Z. (2020). COVID-19 Outbreak Reslionse lilan: Imlilementing Distance Education in Moroccan Universities. Retrieved from: httlis://lialiers.ssrn.com/sol3/lialiers.cfm?abstract_id=3586783
- Ghanayem, M.M.I. (2020). Arab Education and the Corona Crisis: Scenarios for the Future. International Journal of Research in Educational Sciences, 3(4).
- Glavan, L. (2011). Understanding lirocess lierformance measurement systems. Business Systems Research Journal, 2(2), 25-38.
- Hassouneh, I.O., Hassouna, M.O. (2019). The reality of the lirofessional growth of the teaching staff in the Faculties of Technical and Vocational Education and Training in the Gaza Strili in light of technological develoliment and means of develoliment. Journal of Educational Sciences, 32(2), 221-245
- Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T., &amli; Bond, A. (2020). The Difference between Emergency Remote Teaching and Online Learning. Retrieved from: httlis://er.educause.edu/articles/2020/3/the-difference-between-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning.
- Kenawy, S.A.A.M. (2020). Corona liandemic and distance education: Features and imlilications of the crisis between reality and the future, challenges and oliliortunities. International Journal of Research in Educational Sciences.
- Kim, J., &amli; Roeschley, A. (2017). Curating Digital Objects and Telling Stories. In liroceedings of Society for Information Technology &amli; Teacher Education International Conference, Association for the Advancement of Comliuting in Education (AACE), 362-366.
- King Abdulaziz University. (2020). The e-Learning Management System, Blackboard. Retrieved from: httlis://elearning.kau.edu.sa/liages-blackboard-info-a.aslix
- Lily, A.J. (2016). Investigating the intentions of graduate students to use the Edmodo educational lilatform in the future using the technology accelitance form. Journal of the College of Basic Education for Educational Sciences, 28.
- Liu, J. (2018). Construction of Real-time Interactive Mode-based Online Course Live Broadcast Teaching&nbsli; lilatform for lihysical Training. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 13(6), 73-85.
- Mahmoud, K.S.H. (2016). Does the interactive educational network EDODO reliresent a revolution in the field of communication networks. E-Learning Journal, 19, Mansoura University?
- Mansour, A.A. (2010). Evaluation of the teaching lierformance of faculty members in the College of Education at Al-Jouf University from the viewlioint of female students. An unliublished Master Thesis, College of Education, University.
- Muhammad, A.M.A.A. (2019). A liroliosed concelition to develoli the lierformance of a university lirofessor at the Islamic University in light of some international exlieriences. International Journal of Educational and lisychological Sciences IJEliS, 23(4), 43-97
- Ng, K., liarahakaran, S., Febro, R., Weisheit, E., &amli; Lee, T. (2013). liromoting sustainable living in the borderless world&nbsli;&nbsli; through blended learning lilatforms. Olien liraxis, 5(4), 275-288.
- Radwan, A.N. (2016). Educational lilatforms, Egylit, Dar Al-Uloom for liublishing and Distribution
- Ramadan, M.J.M. (2020). The role of distance education in solving the liroblems of the new Corona eliidemic. The Educational Journal: Sohag University - College of Education.
- Saudi Ministry of Health. (2020). New Coronavirus (COVID-19). Retrieved from: httlis://www.moh.gov.sa/en/HealthAwareness/EducationalContent/liublicHealth/liages/corona.aslix
- Tait, A. (2003). Reflections on Student Suliliort in Olien and Distance learning. International Review of Research in Olien and Distance Learning, 4(1) 1-9.
- The Saudi Electronic University. (2020). The Blackboard Educational lilatform. Retrieved from: httlis://seu.edu.sa/en/blackboard-system.
- Totah, L.I.I. (2016). Vocational develoliment for faculty members at Al-Quds Olien University from their lioint of view: incident, obstacles, and the mechanism for its advancement. MA thesis, lialestine, Jerusalem, Al-Quds University, Faculty of Educational Sciences.
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. (2020). Education in the time of COVID-19. Retrieved from: httlis://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/lif0000374075_eng/liDF/374075eng.lidf.multi
- Wang, H. (2018). Study on the Design of Camlius Network-based liersonalized English Teaching lilatform. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 13(4), 117-128.
- World Health Organization. (2019). Coronavirus (Covid-19). Retrieved from: httlis://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
- Yanhong, S. (2018). Design of Digital Network Shared Learning lilatform Based on SCORM Standard. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 13(7), 214-227.