Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 2
Relationship Banking - Prospects for Indian Banking System
Mulabagula Geeta, KLH University
C. Naga Sivanand, Management Consultant, Hyderabad
Citation Information: Geeta, M., & Sivanand, C.N. (2022). Relationship banking – prospects for indian banking system. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 26(2), 1-10.
Abstract
The banking system in India is moving towards lot of amalgamations and absorptions. The banks which are profitable are absorbing the banks which are not profitable and possess lot of Nonperforming assets. The banks which followed relationship banking strategies by offering a variety of different products, and strived to maintain a loyal customer base, made profits, and banks which followed less relationship banking strategies proved to be with fewer profits, with huge Nonperforming assets. In the light of mergers that took place in Indian banking system, a study has become necessary to know the reasons of banks failure in the Indian context. Relationship banking model is not a recent concept and many allege that it is the cause for Asian crisis 1997 which demonstrated the potential traps of relationship banking. Despite this crisis, there are many advantages too with the relationship banking. Relationship banking is a strategy followed by banks to strengthen the customer base and loyalty and provide a single point of contact to provide a range of different products and services. The main function of banks is credit creation. The banks lend from the deposits of customers. According to modern banking theory the two pillars of the bank are deposits and loans. In both the cases banks have to have a loyal customer base. Hence it is important for the banks to follow relationship banking strategies. Relationship banking involves both assurance and uncertainty. A customer has to be careful that he should not be caught in a net and proven to be more expensive rather than maximizing profits. This paper is based on review of theoretical and empirical literature to study whether the objectives of relationship banking are achieved or not by the Indian banks. The present study is made on one private bank and one public sector bank named HDFC and SBI. The data is obtained from the secondary sources like bank reports, international blogs and journals. Even though study is based on secondary data a thorough literature review has been done and many authors like M. Murugan and Senthil Kumar (2011) have empirically studied that the modern banking is wholly customer driven and proved that “better service better business”. Analysis is done through inferential statistical method, T test and descriptive statistical methods namely coefficient of correlation and arithmetic mean are used to find whether the relationship banking plays a crucial role in making banks profitable or not. It is found that gross nonperforming assets has positive relationship with net profits in HDFC bank and where as for State Bank of India there is a negative relationship between the gross nonperforming assets and gross profits. The Arithmetic Mean for gross nonperforming assets of HDFC is low when analyzed with SBI. Based on (Chril Nicholas 2018)” relationship banking value add pyramid” a new model is developed and suggested for implementing better relationship banking strategies by the bank.
Keywords
Relationship Banking, Gross Nonperforming Assets, Profitability.
Introduction
Relationship banking may be defined as the provision of financial services by a financial intermediary on the basis of long-term investment in obtaining firm-specific information through multiple interactions with diverse financial services (Boot, 2000). Relationship banking is a strategy of banks to offer a range of different financial instruments to strengthen the base and loyalty of the customer, for generating additional income. Relationship banking often approaches the customers for selling insurances, investments and also to lend personal loans. Whether the customers are individuals or a small enterprise, the relationship bankers will attempt to engage in making their banks the 'one-stop shop' for their customer's “A-to-Z needs”. “Examples of products offered in the banking world include certificates of deposit, safe deposit boxes, insurance plans, investments, credit cards, all types of loans, and business services” (Will Kenton, 2020). Relationship bankers also indulge in selling some specialized financial products based on demographics involves, students, senior citizens, and high income individuals.
While understanding the relationship banking the banks has to take a consultative approach to know the need and preference of the customers derived from their financial and economic situation. At times the client may resist the universal banking model, because they may think it as selling tactic rather than personalized approach.
The relationship banking may be advantageous that banks may not search for new customer. But at times it is a costly affair for the banks when customer starts bargaining the credit rates because of the long lasting relationship.
A liaison banker is also known as personal banker who works for the organization and acts as a financial advisor to bank customers. He is considered as a financial Professional expert in investment management, who helps the customer in decision making of their bank accounts and informs the investment avenues that are promoted by the bank.
Justification of Study on Significance of Relationship Banking Strategies in Banking Sector in India
As “Drucker” pointed out that a satisfied customer paves the way to earn profits meant to be the objective of business. The corporate banking which act as the financial intermediaries play a vital role in a financial system to mobilize savings and reduce the transaction costs and acts as middlemen between banks and funds.
According to traditional banking theory the pillars of banking are deposits and loans. The loans are lent from the deposits collected.
Perry Mehrling(2016) from Boston University has discussed three banking theories “credit creation theory, fractional reserve theory and debt intermediation theory”.
According to credit creation theory the banks will collect the deposits and has to create new money by lending to customers. The banks do not solely depend on the deposits for money creation.
Dewatripont et al. (2010), has discussed about the financial intermediation theory which emphasizes on bank deposits with short maturities and lending with long maturity periods.
The fraction reserve theory states that bank will keep some amount as reserve for day to day operations and the rest they will lend as loans.
The fractional reserve theory and financial intermediation theory has been rejected by Werner (2016) with evidence.
Based on the above theories mentioned by various researchers lending money and selling diversified products are considered as the major money creation strategies for the banks. Many public sector banks in India has observed and lent loans to the customers. The result is “ballooning nonperforming assets” and many economists call it as a legacy of bad debts, which followed by the assets market value decreased than liabilities of banks. Consequently a study is to probe the reason of nonperforming assets in these banks and whether the banks has followed “Know your customer” a relationship banking strategy by the most of public sector banks in India.
Nonperforming Assets
Any kind of default in loan repayment is considered as nonperforming asset. A non-performing asset is a loan that is in default or close to being in default. Many loans become non-performing assets after being in default for 90 days, but this can depend on the contract terms. There could be various other types of NPAs, including residential mortgage, home equity loans, credit card loans, and non-credit card out standings, direct and indirect consumer loans. The nonperforming asset ratio is a measure of your nonperforming assets relative to the total value of the loans that you have made is indicated as your loan book. To evaluate this ratio, simply divide your nonperforming assets by your total loans. The result of the ratio will be in decimal. The banking sector is facing severe Nonperforming assets problems in public Sector units than private sector banks. The reasons are external like, ineffective tribunal, willful defaults, industrial sickness etc. Also there are some internal reasons like defective lending processes, Managerial deficiency and significant reason is relationship banking strategy which is not followed by government operated banks.
Literature Review
The Indian Financial system is dominated by banking system. Where in banks has to meet the clients demands and expectations (Kuldeep, 2019). Maximum number of banks in India and around the world follows transactional banking, which includes payments, handling documentation, transacting in foreign currencies (Digital finance group, 2017) which led to more administration expenses and the association is not personalized with the client. (Nicholas, 2017). More over information about the banking customer’s preferences are ignored. (Digital Finance group, 2017). Searching a new customer has become expensive, this has given a scope to develop a new concept relationship banking to create customer data base and also to improve the banks performance (Arnoud, 2000). Relationship bank has emerged and created a value for the customer and borrowing firm with more chances of loan availability, lower interest rates and less collateral requirements (Hamid Ullah & Shah, 2011). The relationship attributes are connected with the consumer credit markets by and large deal with the borrowing rates and profits to the organization and customers related with micro and macro businesses. As the relationship matures the loan premiums will decrease (Peltoniemi, 2007). Apart from the loan premiums, the customers default rate also will reduce tremendously. Dynamic changes in the customer’s account can provide the information of credit risk (Sumit Agarwal et al., 2018). Though there are numerous studies conducted in both market-based and bank-based economies, the specific factors which determine the value of relationship lending are ambiguous (Peltoniemi, 2004).
To exploit advantages of association banking first of all we should understand the elements of relationship banking and the relation between banker and customers. Kuldip Singh (2019) going deep into relationship banking model, “it is explained as more service, more data and more expense. In building a relationship banking program, the senior bank management authorities should have intent and how they want to provide service, engaging the customer and delivery of services” (Chris, 2018). Whether for an individual or small business, relationship bankers will engage in high-touch service to try to make their banks the 'one-stop shop' for their customer's A-to-Z needs. Examples of products offered in the banking world include certificates of deposit, safe deposit boxes, insurance plans, investments, credit cards, all types of loans, and business services (e.g., credit card or payroll processing). Relationship bankers may also include specialized financial products designed for specific demographics, such as students, seniors, and high net worth individuals (Will Kenton, 2020).
“If banks want to compete more effectively, they have to focus on customer’s preferences’ and satisfaction more effectively” (Deboshree Chattargee & AVS Kamesh, 2019) In this context, “Customer relationship management strategy is needed and also measurement of customer relationship is required for retaining the existing customers to maximize the efficiencies and reduce the cost of acquisition” (Nagar & Rajan, 2005).
It was found that relation with the customer was considered as a valuable asset. Customer information can be acquired from various touch points. Later the relationship banking strategies should be developed to market the products of the organization (Guo, 2018). To implement relationship banking marketing strategies the banks has to maintain a loyal customer base. These strategies benefit the bank employers and customers in reducing the operating costs and attracting the new customers (Madan et al., 2015). “The main purpose of utilization of relationship banking as a marketing strategy to improve customer retention rate, create customer loyalty and ultimately Increase long-term profits started from the 1980s and gradually increased during 1990s” (Ravesteyn, Louis Johannes van 2005). The impact of relationship marketing strategy is more on the customer loyalty, customer retention, consumer satisfaction, better commitment in providing the service (Husnain & Akhtar, 2015). The consumer has become choosy in selecting the bank financial products. The bank has to fulfill the requirement and supply of products to the banking customers in order to compete with the other banks (Liao & Cheung, 2002).
Consumer preferences and habits are changing rapidly in the wake of technology adoption. More specifically, there has been a declining reliance on branches as both consumers and transactions are shifted to a greater share of their service and banking transactions toward self-service banking channels such as online, mobile and the call center (FIS Enterprise strategy, 2011) In view of this building the trust is important in non face to face transactions and interactions. A model of trust in online relationship banking approach has to be developed for retaining the existing customers (Avinandan & Prithwiraj, 2003). Simultaneously, banks should not avoid latest developments like Artificial Intelligence, and FinTech. Banks might be attracted to the transaction banking because of technological developments and cost effective processes. This is to be found that long term orientation of relationship banking benefits both bank and the customer( Marco Jaksic & Matej Marinc, 2019) A competent theme for profitable relationship banking driven model was developed to have a positive customer experience in completing a transaction with financial information and technology (FIS Enterprise Strategy, 2011).
In conclusion the relationship banking strategies has positive effect nevertheless of economic crisis (Giovanni et al., 2013).
Objectives
1. To assess the success of relationship banking strategies in Indian Banking sector through analyzing Nonperforming assets ratio.
2. To study how the relationship strategies and techniques assisted to improve customer value and profitability of banks.
Research Methodology
To achieve the objectives, the research has been done on relationship banking management by retails banks in India. Even though the relationship management has been considered as a crucial strategy since its initiation, it is not considered as a major relative component to earn more profits and reduce the gross Nonperforming assets of the banks. The study includes appraising of effectiveness of relationship banking approach through analyzing Nonperforming assets percentage of the banks with its net profits. And also to study how customer value is related with profitability of the banks. The present study is empirical and descriptive study by analyzing the secondary data, from international journals, blogs, websites and reports generated by banks. The Analysis is quantitative analysis with descriptive statistical analyses to interpret how the relationship banking approach reduces the percentage of Nonperforming assets and improve profitability.
The data is secondary data from one private bank HDFC and one Public bank SBI. The data is acquired for accounting years 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 19 and collected from annual reports of the banks.
Data Analysis
Objective 1: To appraise the effectiveness of relationship banking strategies in Indian Banking sector through analyzing Nonperforming assets ratio.
The below analysis is a trial to relate the relationship banking strategies of banks with Nonperforming assets ratio of banks namely HDFC and SBI in Tables 1 to 3.
| Table 1 Calculation of Gnpas to Gadv Ratios. (In Crores.) HDFC | |||
| Year | Gross NPAs | Gross Advances | Gross NPAs/Gross Advances X 100 |
| 2015 | 3,438.38 | 365495.03 | 0.941 |
| 2016 | 4392.83 | 464,593.06 | 0.946 |
| 2017 | 5885.66 | 554,568.20 | 1.061 |
| 2018 | 8,606.97 | 658,333.09 | 1.307 |
| 2019 | 11,224.16 | 819,401.22 | 1.37 |
| Table 2 Calculation of Gnpas to Gadv Ratios. (In Crores.) SBI | |||
| Year | Gross NPAs | Gross Advances | Gross NPAs/Gross Advances X 100 |
| 2015 | 56725.34 | 1329161.15 | 4.27 |
| 2016 | 98172.80 | 1604108.82 | 6.12 |
| 2017 | 112342.99 | 1725086.11 | 6.51 |
| 2018 | 223427.46 | 2161874.39 | 10.33 |
| 2019 | 172,750.36 | 2452204.62 | 7.05 |
| Table 3 Comparison and Analysis of Gnpas to Gadv Ratios. | ||
| Year | HDFC | SBI |
| 2015 | 0.941 | 4.27 |
| 2016 | 0.946 | 6.12 |
| 2017 | 1.061 | 6.51 |
| 2018 | 1.307 | 10.33 |
| 2019 | 1.37 | 7.05 |
Interpretation
From the above calculations the Gross NPA ratios to Gross Advances of HDFC Bank are for the years 2015, 16,17,18,19 are 0.941, 0.946, 1.061, 1.307, and 1.37.
The result from the above analysis, the Gross NPA ratios to Gross Advances for SBI bank for the years 2015, 16, 17, 18, 19, is 4.27, 6.12, 6.51, 10.33, and 7.05.
The GNPAs ratios of HDFC when compared with GNPAs ratios of SBI are considered better.
The HDFC bank is following all the ways of relationship banking approach to reach and transmit the necessary credit and other products. Whereas SBI’s approach is also same but it seems to be, not that effective when compared with HDFC in Table 4.
| Table 4 Correlation Coefficient for HDFC. | ||
| Year | Gross NPAs | Net Profit |
| 2015 | 3,438.38 | 10,215.92 |
| 2016 | 4392.83 | 12,296.23 |
| 2017 | 5885.66 | 14,549.66 |
| 2018 | 8,606.97 | 17,486.75 |
| 2019 | 11,224.16 | 21,078.14 |
0.995405 is the correlation of coefficient for HDFC bank when gross nonperforming assets and net profits are taken as variables in Table 5.
| Table 5 Orrelation of Coefficient for State Bank of India. | ||
| Year | Gross NPAs | Net Profit. |
| 2015 | 56725.34 | 13,101.57 |
| 2016 | 98172.80 | 9,950.65 |
| 2017 | 112342.99 | 10,484.10 |
| 2018 | 223427.46 | -6,547.45 |
| 2019 | 172,750.36 | 862.23 |
-0.979025 is the coefficient of correlation when gross nonperforming assets and net profits are taken as variables.
Interpretation
The correlation coefficient of Gross Nonperforming assets and Net profits for HDFC is positively related and for State bank of India it is negatively correlated. In HDFC bank growth in GNPAs will increase net Profits. This communicates that the HDFC is having a very effective tribunal to collect the loans. Whereas In SBI growth GNPAs will decrease net profits. Form this we can analyze that the SBI’s tribunal for collecting the loans may not be that effective as HDFC. Moreover the market share of SBI is 70% and HDFC is somewhere around 15%. From the above analysis it is stated that more relationship banking strategies are required for SBI to recover the NPAs and also to provide better customer service Tables 6 to 7.
| Table 6 Group Statistics | |||||
| Bank | NPA(variable) | N | MEAN | Std deviation |
Std error Mean. |
| SBI | NPA | 5 | 132663.7820 | 65586.16063 | 29331.02271 |
| HDFC | NPA | 5 | 6709.6000 | 3190.94208 | 1427.03268 |
| Table 7 Independent Samples Test | |||||||||
| Levin’s test for Equality of variances | T-test for Equality of Means. |
||||||||
| F | Sig. | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | Mean Difference | Std. Error Difference | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference Lower upper |
||
| NPA Equal variances assumed |
13.985 | .006 | 4.289 | 8 | 0.003 | 125954.18200 | 29365.71667 | 58236.71793 | 193671.64607 |
| Equal variances not assumed |
4.289 | 4.019 | 0.013 | 125954.18200 | 29365.71667 | 44573.16608 | 207335.19792 | ||
Interpretation
From the above table it is noted that the level of significance for GNPAs is .003. From the analysis it is stated that the gross Nonperforming assets of HDFC and SBI has a significant difference.
Discussion
The preceding analyzes is to appraise the Relationship banking strategies, which is intuitive in nature, through Gross Non Performing assets ratio to Gross advances of the banks. Despite the SBIs market share is increasing day by day and considered as white elephant in banking industry in India, the Gross Nonperforming assets are exceeding the HDFC bank which is having a less market share. From the analysis it is clearly identified that the relationship banking strategies of HDFC are more effective than SBI relationship banking strategies.
Objective 2: To study how the relationship strategies and techniques assisted to improve customer value and profitability of banks
Before going in to deep analysis subjectively about how the relationship banking strategies are connected with profitability; we should know what it means to be a relationship bank. Is it guiding about the operations, human resource, or common aspects about the banks products?
There are some core assumptions that the bank has to follow, if it considers itself as relationship bank. (Nicholas 17)
1. The relationship management is seen as trusted advisor.
2. Offering products according to customer preferences.
3. Offers ideas which improve the financial performance of customers.
4. Customer engagement.To fulfill these assumptions the banks has to build customer relationships and personalized approach for customers leads to an increase in customer value.
Failures in Indian Banking Sector
The recent failures in Indian banking system caused by bad loans and poor management of debt recovery system.
The public sector bank mergers in India in 2020.
1. Andhra bank and corporation bank has merged with Union bank.
2. Oriental Bank of Commerce and United Bank were merged with Punjab National Bank.
3. Syndicate Bank has been merged with Canara Bank.
4. Allahabad Bank with Indian Bank.
The main reason behind these mergers is lack of customer relationships and ignoring the value of customer where as the private sector banks like HDFC and ICICI are avoiding losses and concentrating more on customer retention. In light of this, a study has been done and found out ways to build customer relationship.
Ways to build customer relationships and increase customer value (will kenton 20) communication:
A significant role in maintaining and building the customer relationship is being more transparent while communicating about the Banks products.
Better Services than Expected: The customers of the bank expect to have a quality service from the bank. The bank has to exceed their expectations by serving them in time, with empathy and personalized approach.
Feed Back: The observation and reaction is important for the bank to maintain and build relationships. The banker has to find out whether their services are up to the mark or if there are any flaws, then immediately they have to rectify it immediately without any delay.
Constant Relationship: The bank has to maintain constant and continuous relationship with them and inform them about profits they earned from the investments if not advise them to diversify their portfolios. This enhances a trustworthy relationship between banker and customer.
The banker has to appreciate the customer at times for managing their investments. This motivates the customer to increase his investments.
To follow the ways mentioned above to build customer relationships the bank has to hire and train the relationship banker to achieve the target.
Hiring and Training a Relationship Banker
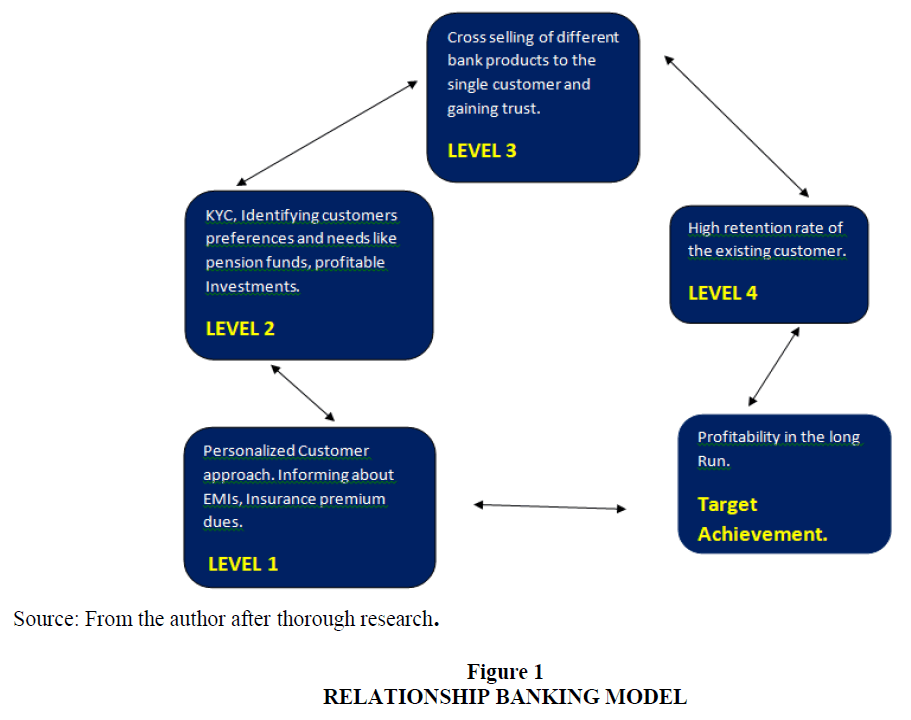
Apart from building customer relationship the banks has to develop their own relationship banking model which helps them to mitigate risk. Nevertheless, a costly affair to maintain a relationship banker for the banks, it is relevant and requisite. Based on Chris (2018) relationship banking value add pyramid the banks should follow a relationship banking approach to take a position of financial planner approach with the customers. They also should guide the clients in agreement with their income and risk levels for the investments. In relationship banking model, risk exposure is avoided or mitigated or hedged based on the risk taking ability of the customer.
The main success factor in relationship banking is the insight and the advice provided by the banker to the customer. For this the bank has to hire a person who has banking expertise. It comes from experience and curiosity to learn new things. Not only hiring training is also important factor. There are different levels of training for a relationship banker.
LEVEL 1: The banker has to understand the basic and general product knowledge of the bank. And at times he also has to understand special products which are offered by the bank.
LEVEL 2: Once he acquires the knowledge of bank products then he has to develop his community networks through cold calling, tele calling and Social Media promotion.
LEVEL 3: This level requires specialty business expertise. The banker has to understand several of ways of capital raising, Marketing and operating procedures.
LEVEL 4: This level requires industry experience and finance expertise in Banking, Risk management and Investment management etc.
Relationship Banking Model
The banks have to develop their own relationship banking model in order to make them more competitive. For money creation, by attracting more deposits and also to sell various diversified products to the customer. The author has tried a model which is based on the “Chris Nicholas 2018 pyramid model”.
Below model may be used by the banks in India to increase their profitability and customer retention Figure 1.
Findings
1. The relationship banking strategies are fundamental to reduce the ratio of Nonperforming assets ratio for the banks.
2. The correlation of coefficient of HDFC is highly positively related and for SBI is negatively related with the net profits.
3. The HDFCs Nonperforming loans are meager when related to SBIs Nonperforming assets. But at the same time we also have to keep in view that SBI s market share is more than HDFC.
4. Being a market leader the SBIs profitability is not increasing in increasing manner. In 2018 they incurred loss of 6,547.54.
5. Though the SBI has started relationship bank approach way back in 2000, there seems to be a deficiency in implementing KYC model.
6. The relationship banker should be properly trained and has to acquire industry expertise, so that he can achieve his targets in cross selling.
7. The relationship bank approach work only with the right talent, education and motivation to achieve the targets.Conclusion
Nonetheless, considered as an old concept, in India, It has not developed synonymously as in western world. According to the three banking theories which mentioned by the earlier in the study, lending loans are the major money creation for banks. The resultant phenomenon is increase in Nonperforming assets which has become main reason for the failure of the Indian banks. The bad loans and mismanagement of risk has led banks to merge with other banks. The KYC model a relationship strategy followed by many banks has some inadequacies and not implemented properly. For better implementation the bank has to train relationship bankers at all levels which have been mentioned by the author through research process. Not only that according to Chris (2018) concentric relationship building which is very simple, learning from one account and usage of knowledge in next account. It depends on the Banks expertise and trust it has developed in customers mind. The two banks, HDFC and SBI may follow the ways and paths to build the customer value and profitability which mentioned in the discussion for objective II. Even concentric relationship building requires training and learning about several products, finance aspects and industry experience. If the public sector banks in India, improve their relationship banking strategies then the prospects of earning profits in banking industry will definitely increase.
References
Boot, A.W. (2000). lRelationship Banking: What Do We Know? Journal of Financial Intermediation.
Chris, N. (2018). Here Is A Major Part of Our Relationship Banking Model. Centre stage correspondent division.
Dewatripont, M., Rochet, J.C., & Tirole, J. (2010). Balancing the banks. Princeton University Press.