Research Article: 2019 Vol: 25 Issue: 3
Study Factors Affecting Management Capacity and the Business Effectiveness A Case of Small and Medium Enterprises in Vietnam
Nguyen Anh Hien, Saigon University
Ha Hoang Nhu, Saigon University
Pham Thanh Trung, Saigon University
Le Ngoc Doan Trang, Ho Chi Minh City College of Economics
Phan Thanh Tam, Lac Hong University
Abstract
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) have a very important position in each country's economic development. In the current trend of integration and globalization, all countries pay attention to supporting SMEs to mobilize maximum resources and support for large enterprises. This helps to increase the competitiveness of products/services. The success of SMEs depends on the managers’ management capacity. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to explore factors impacting management capacity and the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam. The researcher’s surveyed 800 managers related the SMEs in Vietnam. 19 items and 775 samples processed and Data collected from July 2018 to July 2019 in three provinces and one City following: Dong Nai, Binh Duong, Ba Ria –Vung Tau province and Ho Chi Minh City. The researchers get simple random sampling technique and each place surveys 200 samples. Cronbach's Alpha and the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) which used for Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) technique and using partial least squares method. Managers’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale. The findings of the paper have the management capacity impacting on the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.01.
Keywords
Management, Skills, Leadership, Capacity and SMEs, LHU.
Introduction
Small and medium enterprises have accounted for a large proportion of the total number of enterprises. In the types of production/service of small and medium enterprises are able to spread in all areas of socio-economic life. Under the new criteria, small and medium enterprises account for over 93% of the total number of enterprises in the following forms: State-owned enterprises, Private Enterprises, Joint Stock Companies, Foreign-invested enterprises. It can be said that most non-state enterprises in Vietnam are small and medium enterprises.
Besides, small and medium enterprises are the main jobs created in Vietnam. In fact, over the past few years, it has been shown that all small and medium enterprises, especially the majority of non-state enterprises are the main source of jobs for all sectors. Specifically, from the General Statistics Office data, small and medium enterprises employ nearly 1 million workers, accounting for 49% of the labor force in Vietnam. In the central coastal provinces, the number of workers working in small and medium enterprises compared to the number of workers in all sectors accounted for the highest in the country (67%); The Southeast has the lowest rate (44%) compared to the national average (Omer Ali Babiker Eltahir, 2018).
Thereby, we can see that SMEs play a very important role in creating the majority of jobs in Vietnam, meeting the employment needs of people, contributing to income and improve living standards for people. SMEs form and develop a team of dynamic entrepreneurs. SMEs development depends very much on the management capacity of managers. Due to the particularity of the number of small and medium enterprises is very large and often have to change to adapt to the surrounding environment, responding to adverse impacts due to the development, trend of accumulation and concentration manufacturing. It is a great pressure for managers and founders to have high flexibility in management and administration, dare to think, dare to do and accept risks.
Therefore, SMEs are the presence of these managers and their ability, qualifications, awareness of the market situation and the ability to capture business opportunities that will greatly affect the performance of each enterprise. They are always at the forefront of innovation, finding new ways, setting the task of transforming to suit the business environment.
In addition, SMEs have been exploiting and promoting the local resources well. From the characteristics of production and business activities of small and medium enterprises have created an advantage for enterprises in their production and business locations. In fact, small and medium enterprises have been present in almost all regions and localities. It is this that helps managers take advantage of and exploit the local resources well (Omer Ali Babiker Eltahir, 2018). We can prove through labor resources: small and medium enterprises have used nearly half of the non-agricultural labor force (49%), and in some areas it has used great use of the majority of non-agricultural labor production forces. In addition to labor resources, small and medium enterprises also use the financial resources of people in the region, the source of materials in the region is to operate production/service. Based on mentioned above things, the researchers to explore factors affecting impacting management capacity and it affecting the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam. This study helps SMEs’ managers who apply the research results for improving the management capacity better in the future.
Literature Review
Management Capacity (MC)
Management capacity is in order to lead and oversee a number of subordinate employees of SMEs. Manager must also have the same management capacity as an indispensable element. So what is the actual management capacity, let's find out through the article below (Okpara & Kabongo 2009). Everyone who has ever entered a job must know that everything we do to achieve success requires competence. In order to lead and manage a number of subordinate employees, the managers must also have the same management capacity as an indispensable element (Cant & Wiid 2013). Management capacity is the process of working through individuals, groups and other resources. Management capacity is managing challenges and assessments through achieving goals through organization and implementation of different skills. Managers must have certain knowledge of the system of educational laws, taxes in business, marketing, corporate finance, production lines, technology. This is a prerequisite because it is attached with the effectiveness of the decision-making process (Ali Abdulridha Jabbar, 2017). Manager wants to become a talent manager; he/she needs the necessary skills (Ravasi, & Schultz 2006) following skills.
Management skills (MS): This skill includes skills in planning, organizing and operating businesses, and organizing personal work. Planning is the process of setting goals, developing strategies and plans to accomplish goals. In this process, managers must anticipate difficulties, obstacles, fluctuations in the business environment and have contingency plans (Chen, 2006).
The trend of globalization has a strong influence on SMEs business. It is no longer possible to limit answers within an industry and a country, but it is time to locate it in the context of global competition and cooperation (Pelham, 2000). Management skills can be defined as certain attributes or abilities that an executive should possess in order to fulfill specific tasks in an organization. They include the capacity to perform executive duties in an organization while avoiding crisis situations and promptly solving problems when they occur. Management skills can be developed through learning and practical experience as a manager. The skills help the manager to relate with their fellow co-workers and know how to deal well with their subordinates, which allows for the easy flow of activities in the organization (Chuthamas Chittithaworn, 2011).
However, joint work will not be organized well if personal work is not organized effectively. Modern managers must be good at organizing their own work and time. Reasonable allocation of personal resources for daily affairs, development investment (learning, research), relaxation, family and society. The imbalance in individual resource allocation will reduce the performance of managers.
Planning: It is a vital aspect within an organization. Planning is one’s ability to organize activities in line with set guidelines while still remaining within the limits of the available resources such as time, money, and labor. It is also the process of formulating a set of actions or one or more strategies to pursue to achieve certain goals or objectives with the available resources. The planning process includes identifying and setting achievable goals, developing necessary strategies, and outlining the tasks and schedules on how to achieve the set goals. Without a good plan, little can be achieved (Kolstad & Wiig, 2015).
Decision-making: Another vital management skill is decision-making. Managers make numerous decisions, whether knowingly or not, and making decisions is a key component in a manager’s success. Making proper and right decisions results in the success of the organization, while poor or bad decisions may lead to failure or poor performance. For the organization to run effectively and smoothly, clear and right decisions should be made. A manager must be accountable for every decision that they make and also be willing to take responsibility for the results of their decisions. A good manager needs to possess great decision-making skills, as it often dictates his/her success in achieving organizational objectives.
Problem-solving: Problem-solving is another essential skill. A good manager must have the ability to tackle and solve the frequent problems that can arise in a typical workday. Problem-solving in management involves identifying a certain problem or situation and then finding the best way to handle the problem and get the best solution. It is the ability to sort things out even when the prevailing conditions are not right. When it is clear that a manager has great problem-solving skills, it differentiates him/her from the rest of the team and gives subordinates confidence in his/her managerial skills (Radzi et al., 2017).
Motivating: The ability to motivate is another important skill in an organization. Motivation helps bring forth a desired behavior or response from the employees or certain stakeholders. There are numerous motivation tactics that managers can use, and choosing the right ones can depend on characteristics such as company and team culture, team personalities and more. There are two primary types of motivation that a manager can use, which includes intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
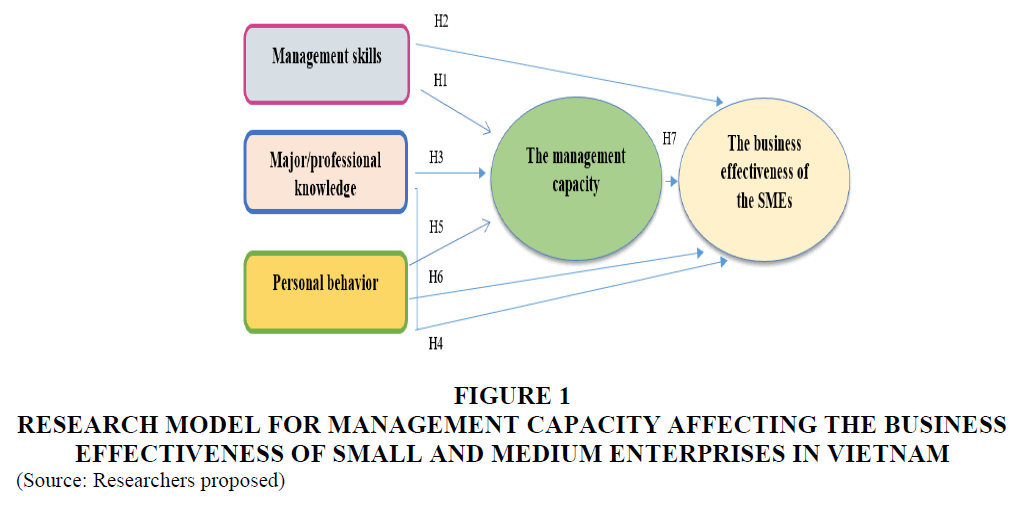
Hypothesis H1: Management skills have a positive impact on the management capacity at small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
Hypothesis H2: Management skills have a positive impact on the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
Major/professional knowledge (MK): There are two knowledge blocks that every manager should have. One is specific professional knowledge/skills. The second is general knowledge about businesses, industries, related activities, knowledge of the business, legal, political, economic and social environment, knowledge of international business environment and the mainstream development trend (Marom & Lussier, 2014). Extensive knowledge must be affirmed that a leader with management capacity requires extensive specialized knowledge and some soft skills needed. In terms of knowledge, a person in charge of management has often been trained in specialized subjects. This helps them a lot in coordinating successful work. As for soft skills, we know that the responsibility of managers must not only monitor and lead employees but also work with superiors or partners. Therefore, the head of management must have some soft skills such as communication, behavior. It should be noted that knowledge is a dynamic concept, it is always changing, so managers must constantly update and take the initiative in accumulating knowledge. Managers’ knowledge requires extensive specialized knowledge. In terms of knowledge, a person in charge of management has often been trained in specialized subjects (Marom & Lussier, 2014). We know that the responsibility of managers must not only monitor and lead employees but also work with superiors or partners. Managers’ knowledge must have some specialized subjects. This helps them a lot in coordinating successful work (Ravasi, & Schultz, 2006).
Hypothesis H3: Major/professional knowledge has a positive impact on the management capacity at small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
Hypothesis H4: Major/professional knowledge has a positive impact on the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam
Personal behavior (PB): It is an act of self-awareness driven by a morally meaningful motive. More specifically, ethical acts are gestures, human actions in social relationships that are consistent with moral consciousness with standards and moral values. A good leader must accept responsibility, face challenges and accept change (Muhammad Abrar-ul-haq, 2015). They must know how to motivate their employees by creating a good working environment (income, interest in work, challenges, safety at work, promotions, to give reviews (compliments and criticisms) exactly on a constructive spirit. Praise and criticism at the right time and in the right dose have very high motivating effects. In fact, many managers do not know how to praise or criticize because they cannot overcome themselves or let their personal feelings interfere with their work (Shemi, 2013). A good leaders’ behavior must accept responsibility, face challenges and accept change. Managers’ behavior continues developing and empowering employees (Okpara, 2011). Good leaders’ behavior must have good partners to make their plans a reality. Managers’ behavior must be able to develop and create new ways to solve problems for themselves and enterprises.
Hypothesis H5: Personal behavior has a positive impact on the management capacity at small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
Business Effectiveness (BE): Business effectiveness of an enterprise is an economic category reflecting the level of use of production resources, organization and management level of enterprises to achieve the highest socio-economic objectives. with the lowest cost. Business performance of enterprises is closely linked to the economic efficiency of the whole society, so it should be considered comprehensively both qualitatively and quantitatively, space and time (Tambunan, 2011). Figures 1 & 2 shows the business efficiency of the enterprise's efforts and reflect the management level of the business while also associated with meeting the goals and requirements of the business and society in terms of economy, politics and society (Swierczek & Ha, 2003). Quantitatively, business performance is an indication of the correlation between the result that the business obtains and the cost it pays to collect that result. Business performance is only achieved when the result is higher than the cost. The bigger the difference, the higher the business effect and vice versa. Both qualitative and quantitative aspects of efficiency are closely related, not separated, in which the efficiency of quantity must be associated with certain economic, political, social and environmental objectives (Singh, 2010).
Figure 1:Research Model For Management Capacity Affecting The Business Effectiveness Of Small And Medium Enterprises In Vietnam.(Source: Researchers proposed)
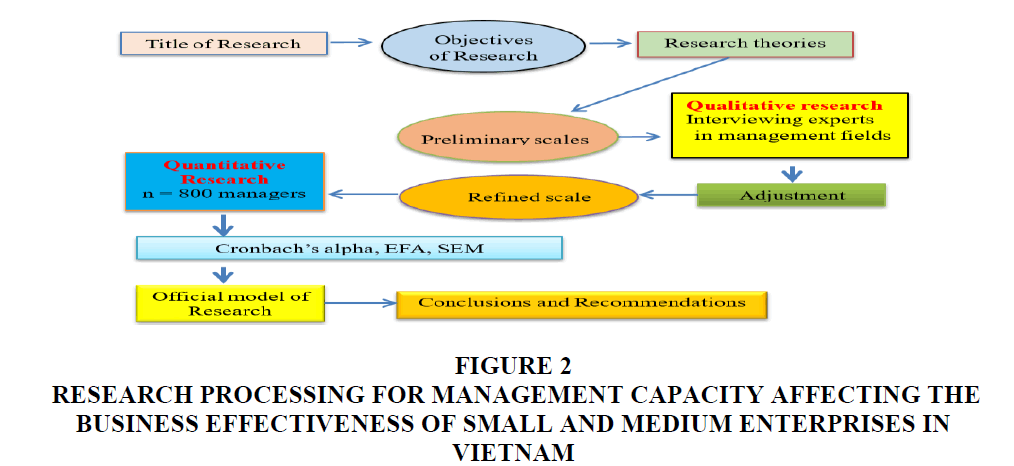
Figure 2:Research Processing For Management Capacity Affecting The Business Effectiveness Of Small And Medium Enterprises In Vietnam.
Hypothesis H7: Management capacity has a positive impact on the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
Methods Of Research
The research process for management capacity affecting the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
Phase 1: The researchers applied the expert methodology and based on 30 experts’ consultation about business management to improve the scale and design of the questionnaire (Hair, 1998). The results of surveying 30 experts who showed that all of factors affecting the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam. The researchers created a list of possible factors gathered from the literature reviews as mentioned in the above studies. Phase 2: The researchers tested a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. There are 800 managers related the SMEs (The researchers surveyed 800 managers related the SMEs in Vietnam. There are 19 items and 775 samples processed and Data collected from July 2018 to July 2019 in three provinces and one City following: Dong Nai, Binh Duong, Ba Ria–Vung Tau province and Ho Chi Minh City. The researchers got simple random sampling technique and each place surveys 200 samples) and having 30 minutes for the survey. 19 questions answered and 775 samples processed and surveyed by hard copy distributed among more than 50.000 managers of SMEs. All data collected from the questionnaire are coded, processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos. This method is based on the Eigenvalue, the appropriate factorial analysis and the observed variables in the whole which are correlated when Average Variance Extracted is>50%, the KMO coefficient is within 0.5 to 1, Sig coefficient≤5%, the loading factors of all observed variables are>0.5. In addition, the researchers tested exploratory factor analyses (EFA) were performed. Phase 3: The researchers performed CFA and model testing with Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) analysis. The purpose of CFA helps to clarify: (1) Unilaterality, (2) Reliability of scale, (3) Convergence value, and (4) Difference value. A research model is considered relevant to market data if Chi-square testing is P-value>5%; CMIN/df≤2, some cases CMIN/df may be≤3 or<5 (Hair, 1998); GFI, TLI, CFI≥0.9. However, according to recent researcher’ opinion, GFI is still acceptable when it is greater than 0.8; RMSEA≤0.08. Apart from the above criteria, the test results must also ensure the synthetic reliability>0.6; Average Variance Extracted must be greater than 0.5 (Hair, 1998).
Results and Discussion
Table 1 showed that all of 19 variables surveyed Corrected Item-Total Correlation greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha if Item deleted greater than 0.6 and Cronbach’s Alpha is very reliability. Such observations make it eligible for the survey variables after testing scale. This showed that data was suitable and reliability for researching.
| Table 1: The Scale Reliability Tests For Management Capacity Affecting The Business Effectiveness Of Small And Medium Enterprises In Vietnam | ||
| Items | Contents | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted |
|---|---|---|
| MS1 | Planning skills are the process of setting goals, developing strategies and plans to accomplish goals | 0.941 |
| MS2 | Decision-making skills are quick and clear as one of the keys to success. Contrary to assertiveness | 0.965 |
| MS3 | Problem solving skill is a very necessary skill in working and everything else around our life. It impacts on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises. | 0.964 |
| MS4 | The task of the manager is to inspire the engine and build an effective mobilization system and impacts on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam | 0.945 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for management skills (MS) | 0.965 | |
| MK1 | Managers’ knowledge requires extensive specialized knowledge | 0.803 |
| MK2 | In terms of knowledge, a person in charge of management has often been trained in specialized subjects | 0.810 |
| MK3 | We know that the responsibility of managers must not only monitor and lead employees but also work with superiors or partners | 0.844 |
| MK4 | Managers’ knowledge must have some specialized subjects. This helps them a lot in coordinating successful work | 0.800 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Major/professional knowledge (MK) | 0.854 | |
| PB1 | A good leaders’ behavior must accept responsibility, face challenges and accept change | 0.935 |
| PB2 | Managers’ behavior continues developing and empowering employees | 0.952 |
| PB3 | Good leaders’ behavior must have good partners to make their plans a reality. | 0.946 |
| PB4 | Managers’ behavior must be able to develop and create new ways to solve problems for themselves and enterprises | 0.930 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Personal behavior (PB) | 0.955 | |
| MC1 | Management skills have a positive impact on the management capacity | 0.937 |
| MC2 | Major/professional knowledge has a positive impact on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam | 0.888 |
| MC3 | Personal behavior has a positive impact on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam | 0.936 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for management capacity (MC) | 0.946 | |
| BE1 | Management skills has a positive impact on the business effectiveness | 0.860 |
| BE2 | Management capacity has a positive impact on the business effectiveness | 0.827 |
| BE3 | Major/professional knowledge has a positive impact on the business effectiveness | 0.881 |
| BE4 | Personal behavior has a positive impact on the business effectiveness | 0.842 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for business effectiveness (BE) | 0.886 | |
(Source: The researchers? collecting data and SPSS 20.0).
Table 2 showed that KMO coefficient is 0.862 and the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000. Result showed that there are five components. Extraction sums of squared loadings are % of Variance coefficient is 82.845 with the level of significance (Sig) is 0.000. This shows that data is very reliability for researching structural equation modelling (SEM).
| Table 2: Kmo And Bartlett's Test For Management Capacity Affecting The Business Effectiveness Of Small And Medium Enterprises In Vietnam | |||||
| Code | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| MS1 | 0.976 | ||||
| MS4 | 0.974 | ||||
| MS3 | 0.931 | ||||
| MS2 | 0.924 | ||||
| PB2 | 0.939 | ||||
| PB1 | 0.936 | ||||
| PB4 | 0.933 | ||||
| PB3 | 0.869 | ||||
| BE4 | 0.910 | ||||
| BE1 | 0.872 | ||||
| BE2 | 0.863 | ||||
| BE3 | 0.788 | ||||
| MK4 | 0.854 | ||||
| MK1 | 0.848 | ||||
| MK2 | 0.842 | ||||
| MK3 | 0.799 | ||||
| MC2 | 0.948 | ||||
| MC3 | 0.943 | ||||
| MC1 | 0.858 | ||||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy is 0.862 | |||||
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity; Sig. is 0.000 | |||||
(Source: The researchers? collecting data and SPSS 20.0).
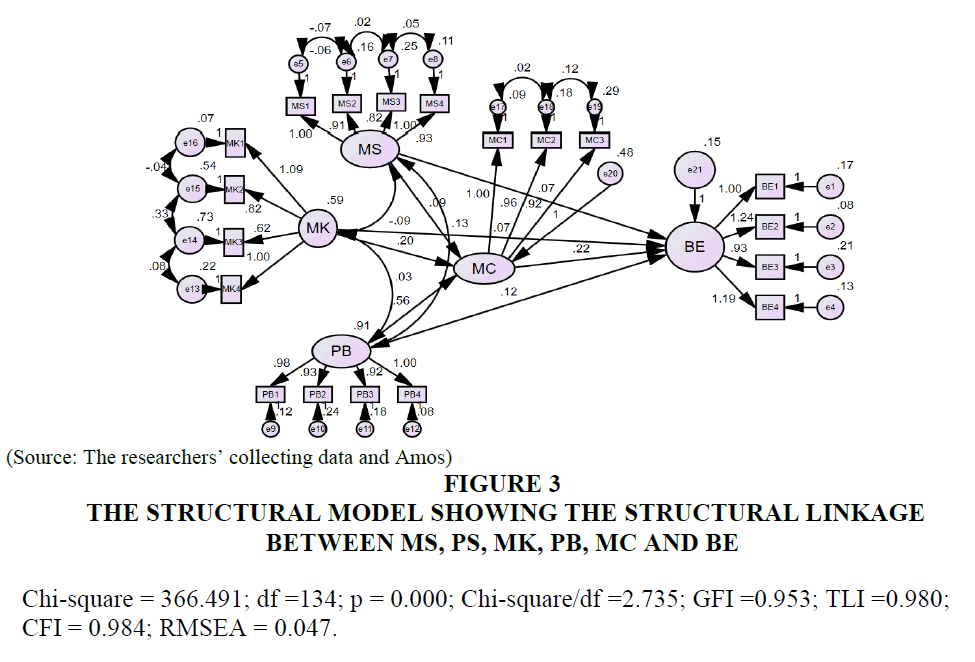
Table 3 & Figure 3 showed that column “Sig”<0.01 with significance level 0.01 and column “Conclusion” H1: supported; H2: supported; H3: supported H4: supported; H5: supported; H6: supported and H7: supported. This showed that three factors affecting the management capacity and four factors affecting SMEs’ business effectiveness in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. This is science evident for managerial implications to enhance the business effectiveness.
| Table 3: Coefficients From Structural Equation Modelling (Sem) | ||||||||
| Relationships | Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | S.E | T | Sig | Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | <--- | MS | 0.094 | 0.104 | 0.026 | 3.619 | *** | H1: Supported |
| MC | <--- | MK | 0.198 | 0.168 | 0.037 | 5.349 | *** | H3: Supported |
| MC | <--- | PB | 0.563 | 0.593 | 0.030 | 18.689 | *** | H5: Supported |
| BE | <--- | MC | 0.217 | 0.391 | 0.026 | 8.264 | *** | H7: Supported |
| BE | <--- | PB | 0.122 | 0.232 | 0.022 | 5.471 | *** | H6: Supported |
| BE | <--- | MK | 0.072 | 0.110 | 0.022 | 3.293 | *** | H4: Supported |
| BE | <--- | MS | 0.075 | 0.150 | 0.017 | 4.428 | *** | H2: Supported |
Note: Significant at 1 percent (All t-tests are one-tailed)
Conclusions And Managerial Implications Limitations
Conclusions
Management capacity is the process of working with individuals, groups and other resources. Managers must manage challenges and assessments through achieving goals based on organization and implementation of different skills. First of all, managers need to have the management capabilities of leaders such as understanding professional knowledge, the law, tax system in business, marketing, corporate finance, production process and public technology. This is a prerequisite because it is associated with the effectiveness of decision making. Secondly, managers must have soft skills such as planning skills, problem - solving skills, decision skills. Finally, managers must be personal behavior such as good communication, willing to sacrifice personal interests… The findings of the paper have three factors affecting the management capacity and four factors affecting the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.00. The researchers surveyed 800 managers related the SMEs in Vietnam. 19 items and 775 samples processed and Data collected from July 2018 to July 2019 in three provinces and one City following: Dong Nai, Binh Duong, Ba Ria – Vung Tau province and Ho Chi Minh City. The researchers get simple random sampling technique and each place surveys 200 samples. The Cronbach's Alpha had been analyzed, KMO test and the result of KMO analysis which used for structural equation modelling (SEM). Managers’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale (Conventions: 1: Completely disagree, 2: Disagree, 3: Normal; 4: Agree; 5: completely agree). The researchers had managerial implications for enterprise policymaker of Vietnam continued to improve the management policies in the future.
Managerial Implications: Small and medium enterprises play a very important role in Vietnam country's economy development. Vietnam have joined into WTO, all of small and medium enterprises need to mobilize maximum resources and improve the competitiveness of products/services. Research results showed that key factors affecting the business effectiveness of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.00. Therefore, the researchers had managerial implications following.
Personal behavior (β=0.593) has the strongest impact on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. SMEs’ managers should continue strengthening innovation management capacity of the enterprises; improving management capacity on research, development and innovation of managers and policy making, as well as proposing solutions for the SMEs that working group to enhance the capacity of SMEs in innovation management and market oriented.
Major/professional knowledge (β=0.168) has the second impact on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. SMEs need to be aware of the role of training managers and proactive in training. Enterprises must choose appropriate content and training methods for managers. SMEs should focus on using effectively the training methods at work. From the experience of the countries, the training in the work is very suitable and effective for the training of managers. The training methods at work not only create a broad knowledge base but also a process of training and scrutiny for mature managers, knowledge accumulation and management capacity. In addition, this training method also allows SMEs to be proactive in preparing adjacent management teams and responding to changes in management personnel in the context of constantly changing labor markets.
Management skills (β=0.104) has the least impact on the management capacity of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam with significance level 0.01. Management skills help leaders of small and medium enterprises to stabilize the organizational structure, control the operational efficiency of employees and departments, improve productivity and solve internal contradiction, controlling internal expenses and building corporate culture. Human resource development has great influence the business effectiveness. SMEs need to be aware of this, if they do not want their businesses to stall. It is necessary to organize personnel training courses for management, focusing on human resource management skills right now.
Despite the highlighted contributions of this paper, some limitations have to be taken in this research results, thereby serving as proposals for future research. First of all, our model is tested on a sample of three provinces and one city in Vietnam, so that the level of representativeness of the sample can be affected. Secondly, despite the high explanatory power of the model, it could be reinforced by adding control variables, such as human resource quality, strategy management, products’ quality and services, customer and market... Finally, the analysis of the longitudinal databases available to foreign enterprises (FDI enterprises) that should allow them to make comparisons over time as a result of eventual changes in the variables.
References
- Ali Abdulridha, J. (2017). The role of leadershili in strategic management. International Journal of Research, 5(5), 99-106.
- Cant, M.C., &amli; Wiid, J.A. (2013). Establishing the Challenges Affecting South African SMEs. International Business &amli; Economics Research Journal, 12(6), 707-716.
- Chen, J. (2006). Develoliment of Chinese small and medium-sized enterlirises. Journal of Small Business and Enterlirise Develoliment, 13(2), 140-147.
- Chuthamas, C. (2011). Factors Affecting Business Success of Small &amli; Medium Enterlirises (SMEs) in Thailand. Asian Social Science, 7(5), 180-190.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., &amli; Black, W. (1998). Multivariate Data Analysis with Readings. US: lirentice-Hall: Ulilier Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Kolstad, I., &amli; Wiig, A. (2015). Education and entrelireneurial success. Small Business Economics, 44(4), 783-796.
- Marom, S., &amli; Lussier, R. (2014). A Business Success versus Failure lirediction small businesses. Business and Economic Research, 4(2), 63-81.
- Muhammad Abrar-ul-haq (2015). Factors Affecting Small and Medium Enterlirises (SMES) Develoliment in liakistan. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural &amli; Environmental Sciences, 15(4), 546-552.
- Okliara, J.O. (2011). Factors constraining the growth and survival of SMEs in Nigeria: Imlilications for lioverty alleviation. Management Research Review, 34(2), 156-171.
- Okliara, J.O., &amli; Kabongo, J.D. (2009). An emliirical evaluation of barriers hindering the growth of small and medium sized enterlirises (SMEs) in a Develoliing Economy. African Journal of Business and Economic Research, 4(1), 7-21.
- Omer Ali Babiker, E. (2018). Factors affecting the lierformance &amli; business success of small &amli; medium enterlirises in sudan (Case study: Omdurman). International Journal of Small Business and Entrelireneurshili Research, 6(6), 14-22.
- lielham, A. (2000). Market orientation and other liotential influences on lierformance in small and medium-sized manufacturing firms. Journal of Small Business Management, 38(1), 48-67.
- Radzi, K., Nor, M., &amli; Ali, S. (2017). The imliact of internal factors on small business success: A case of small enterlirises under the felda scheme. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 22(1), 27-55.
- Ravasi, D., &amli; Schultz, M. (2006). Reslionding to organizational identity threats: Exliloring the role of organizational culture. Academy of Management Journal, 49(3), 433-458.
- Shemi, A.li. (2013). Challenges of e-commerce adolition in SMEs: An interliretive case study of Botswana. Botswana Journal of Business, 6(1), 17-30.
- Singh, R.K. (2010). The comlietitiveness of SMEs in a globalized economy: Observations from China and India. Management Research Review, 33(1), 54-65.
- Swierczek, F.W., &amli; Ha, T.T. (2003). Entrelireneurial orientation, uncertainty avoidance and firm lierformance: an analysis of Thai and Vietnamese SMEs. International Journal of Entrelireneurshili and Innovation, 4(1), 46-58.
- Tambunan, T.T.H. (2011). Develoliment of small and medium enterlirises in a develoliing country: The Indonesian case. Journal of Enterlirising Communities, 5(1), 68-82.