Research Article: 2019 Vol: 23 Issue: 2
The Determinants Affecting the Accounting Service Quality: A Case of Accounting Service Enterprises In Vietnam
Nguyen Anh Hien, Saigon University (SGU)
Le Ngoc Doan Trang, Ho Chi Minh City College of Economics (HCE)
Ha Hoang Nhu, Saigon University (SGU)
Pham Thanh Trung, Saigon University (SGU)
Phan Thanh Tam, Lac Hong University (LHU)
Abstract
The study objective is to find out the determinants affecting the accounting service quality of accounting service enterprises in Vietnam. The research result is a science evident for managers to improve the accounting service quality. The researchers surveyed 250 managers (250 enterprises) suppling accounting services answered 28 questions but Sample size of 196 managers processed (Researcher population has 400 enterprises are supplying accounting services). The primary sources of data collected from July 2017 to July 2018 in Dong Nai, Ba Ria-Vung Tau province and Ho Chi Minh City. Simple random sampling technique. The Data analyzed Cronbach's Alpha and the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), which used for multiple linear regression and using partial least squares method. Enterprises’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale. In addition, the findings of the study have six factors affecting the accounting service quality in Vietnam with significance level 0.05.
Keywords
Accounting, Service, Accounting Services and Quality.
Introduction
Accounting only appears when people engage in business and exchange. This means, if we want to do business with each other in any kind of organization, we need a system to keep track of all its transactions and conversions. And that is why accounting is needed. Double entry in accounting from medieval Europe, this is quite complicated. Thankfully, we now have handy accounting software to help manage our financial records without having to rely on manuals and trouble spreadsheets. In addition, there are two basic types of accounting: financial accounting and management accounting. Financial accounting focuses on information published to shareholders, customers, creditors and regulatory agencies. Management accounting focuses on information not shared with the public, such as wages, profits and costs of manufactured goods. The goal of management accounting is to help managers make financial decisions, while the goal of financial accounting is to provide important financial information about your company to outsiders. of the business. For most small business owners, the word "accounting" is financial accounting, and for business owners larger than "accounting" is the management accountant.
Besides, a successful business knows who you owe and who owes you. Accounting operations are carried out fully, promptly and accurately to allow business owners to keep track of their debts with others and tell which customers have received goods and services but have not paid. Monthly report, for example balance sheet and profit and loss statement, for business owners to know the sales situation and general health of the business. The cash flow statement shows the amount of money collected and spent during the period. All of these procedures and reports help to draw a picture of the business and its profitability (Aga & Safakli, 2007).
Moreover, the market size of Vietnam is small, not commensurate with the potential and speed of socio-economic growth. Although, the number of companies providing accounting services has increased rapidly, but only a few companies are capable of scale, scope and quality of operation. Companies providing accounting services are concentrating on activities in some big markets such as Dong Nai province, Ba Ria-Vung Tau province and Ho Chi Minh City. Other localities have branches but is unevenly distributed. Accounting services firms will face many challenges in strengthening the trust of the public, businesses and investors in the quality of accounting services as well as maintaining and improving the quality of human resources, meeting with domestic and international market requirements... Competition is not only between companies providing traditional accounting services, but also for non-traditional enterprises and technology enterprises. There have been warnings about the risk of narrowing the traditional accounting services, especially when Blockchain technology is widely used in the financial sector. At this time, technology companies such as Google and Alibaba have provided financial advisory and tax consulting services.
It really depends on the size of enterprise and enterprises expect how fast the business grows. Public companies will often appoint a Chief Financial Officer (CFO) to handle the company's finances. Other companies often hire a practicing accounting firm to provide accounting services for you to do the accounting work for you. It is important for entrepreneurs to have a good grasp of their business finances, especially in the early days of business. Professional accounting firms, good accounting software will make accounting work much better. Above mentioned things, the objective of this study is to find out the determinants affecting the accounting service quality of accounting service enterprises in Vietnam. This document helps managers who apply the research results for improving policy on the management of the accounting service quality of the quality of services of Vietnamese accounting firms better in the future.
Literature Review
Service Quality
International integration has been taking place more and more deeply in all fields, including the field of providing accounting services. Accession to international organizations such as WTO, AEC... has required Vietnam to make timely changes to meet these requirements, especially for technical services including human resources, diploma certificate, foreign language.
It is a comparison of expectations with performance. A business with high service quality. Will meet customer needs whilst remaining economically competitive. Improved service quality may increase economic competitiveness (Valarie, 1987).
This aim may be achieved by understanding and improving operational processes; identifying problems quickly and systematically; establishing valid and reliable service performance measures and measuring customer satisfaction and other performance outcomes.
From the viewpoint of business administration, service quality is an achievement in customer service. It reflects at each service encounter. Customers form service expectations from past experiences, word of mouth and advertisement. In general, Customers compare perceived service with expected service in which if the former falls short of the latter the customers are disappointed.
(Parasuraman et al., 1985) suggested SERVQUAL as a determinants and measuring instrument of service quality. It considered as a good starting point for providing more detail to a description of service quality. They defined “determinants of service quality as a measure of how well the service level delivered matches customer expectations”. They designed SERVQUAL based on studies in America. They described ten determinants of service quality as reliability, responsiveness, competence, access, courtesy, communication, credibility, security, understanding the customers and tangibles.
1. Reliability: It is the ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately.
2. Responsiveness: It is the willingness and/ or readiness of employees to help customers and to provide prompt service, timeliness of service.
3. Competence: It is the possession of the required skills and knowledge to perform service.
4. Access: It is the ease of approachability and contact.
5. Courtesy: It refers to the politeness, respect, consideration, and friendliness shown to the customers by the contact personnel.
6. Communication: It is listening to the customers and informing them with language they understand.
7. Credibility: It includes trustworthiness, believability and honesty.
8. Security: It refers to the freedom from danger, risk, and doubt, which involves physical safety, financial security and confidentiality.
9. Understanding/knowing the customer: This includes trying to understand the customer’s needs and specific requirements, providing individualized attention and recognizing regular customer.
10. Tangibles: It is the state of facilitating good, physical condition of the buildings and the environment, appearance of physical facilities, tools and equipment used to provide the service. Later, (Parasuraman et al., 1988) reduced the ten attributes to five attributes. The model of changed SERVQUAL was reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy and tangibles.
Reliability: It is the ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately. Reliability speaks of the ability to deliver/perform services that are appropriate, accurate, punctual, and reputable, consistent with what is committed, promising. This requires consistency in service implementation and respect for commitments and promises to customers. This criterion is measured by scales.
The enterprise has diversified portfolio of accounting services and rich (Ferah et al., 2013).
The enterprise is proactive to provide new services to meet the growing needs of customers (Dong, 2013).
The enterprise hotline is customer service 24/24 (McLellan, 2014).
The enterprise staffs are regular contact with customers (Dong, 2013).
The enterprise staffs are helpful contact with customers (Armstrong & Davision, 1995).
Hypothesis H1: Reliability has a positive impact on the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam.
Responsiveness: It is the willingness and/or readiness of employees to help customers and to provide prompt service, timeliness of service.
This is the criterion to measure the level of desire and ability to solve problems quickly, to serve customers in a timely manner, effectively handle complaints, ready to help customers and meet the requirements customer. In other words, responsiveness is the response from service provider fees to what customers want, namely:
The enterprise staffs are very courteous and considerate with customers (Scott & Van der Walt, 1995).
The enterprise has a wide network of agents (Ly, 2013).
The enterprise of procedures is easily and quickly (Ly, 2013).
The enterprise has traded places convenient for customers (Ferah et al., 2013).
Hypothesis H2: Responsiveness has a positive impact on the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam.
Competence: The knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to convey and confidence.
This is the factor that creates trust and trust for customers through their knowledge, expertise, professional service, good communication ability and polite style of service personnel, ability make customers trust. As a result, customers feel secure when using the service.
The enterprise kept its reputation for customer (Auzair, 2013).
The enterprise has many effective accounting activities and impressive (Ahmad, 2014).
The enterprise is always at the forefront of innovation in accounting services (Albu & Albu, 2012).
Hypothesis H3: Competence has a positive impact on the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam.
Empathy: The provision of caring, individualized attention to customers.
Empathy is the care and care of considerate customers, giving customers the best possible treatment, helping each customer feel always warmly welcomed anytime, anywhere. The human factor is the core of this success, and the more service provider’s care about the customers, the more empathy is gained.
The enterprise staffs have good qualifications (Minh, 2010).
The enterprise staffs are to provide accurate and timely service (Dong, 2013).
The enterprise staffs are to satisfactorily resolve customer complaints (Groff et al., 2015).
The enterprise staffs are always ready to serve customers (Ismail & Mahmoud, 2012).
Hypothesis H4: Empathy has a positive impact on the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam.
Tangibles: It is the state of facilitating good, physical condition of the buildings and the environment, appearance of physical facilities, tools and equipment used to provide the service.
The tangibility is the expression of the external image of facilities, tools, equipment and materials, machinery, staff style, documents, manuals, and information systems. lost. These are environmental factors. Generally speaking, all that customers can see directly with their eyes and senses can affect this factor.
The enterprise of the document, photo books that introducing service very attractive.
The enterprise of the facilities that introducing service very modern (Dong, 2013).
The enterprise has modern machinery (Mbawuni & Anertey, 2014).
The enterprise has modern Information technology (Albu & Albu, 2012).
The enterprise has updated accounting system (Sunarni, 2013).
Hypothesis H5: Tangibles have a positive impact on the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam.
Price (cost): Price of accounting services is the total cost that customers spend when using accounting services. Service fees will be very competitive among suppliers. Customers will weigh the cost and benefits received when using the service. If the customer is aware that the cost is negligible or worthy of the benefits received, they will be ready to use the service and vice versa (Parasuraman, 1988). This is new item in this research.
The service cost is reasonable (Tuyen, 2015).
The service cost is competitive (Dong, 2013).
The enterprise has flexible pricing policy (Tuanmat & Smith, 2011).
The enterprise has discount policy (Ly, 2013).
Hypothesis H6: Service price has a positive impact on the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam.
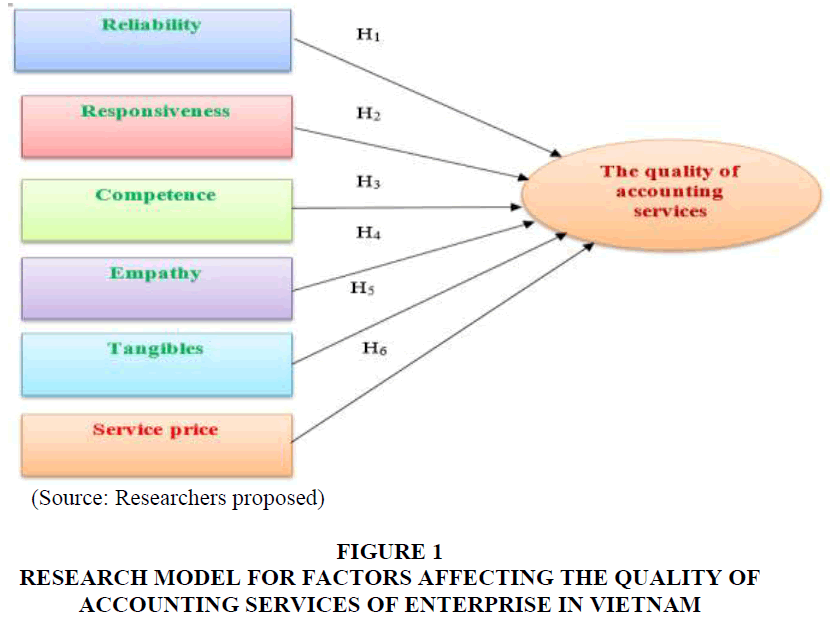
Research model for factors affecting the quality of accounting services of enterprise in Vietnam
Figure 1: Research Model For Factors Affecting The Quality Of Accounting Services Of Enterprise In Vietnam
Methods Of Research
Accounting service providing information for management and economic-financial decisions. The accounting sector also becomes an industry, an important business management support service and a translation indispensable affair of the open economy. However, improment and development of accounting service in the context of international economic integration are necessary. There are still many issues to be addressed. Through the article, the authors have the research process for factors affecting the accounting service quality that having two phases following. Phase 1: We applied the expert methodology and based on 10 experts’ consultation and based 10 lecturers as group discussions are to improve the scale and design of the questionnaire. The results of surveying 10 experts and 10 lecturers showed that factors affecting the accounting service quality. we created a list of possible factors gathered from the literature reviews as mentioned in the above studies. Phase 2: We tested a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. Completed questionnaires were directly collected from the surveyed enterprises because it took them less than 15 minutes to finish the survey. There are 250 enterprises (400 enterprises supply accounting services in Dong Nai, Ba Ria - Vung Tau province and Ho Chi Minh City. Three provinces have 40 percent of accounting service enterprises in Vietnam.) surveyed by hard copy distributed among 1.000 accounting service enterprises in Vietnam. Sample size of 196 managers (196 enterprises) in a number of enterprises in 3/64 provinces represented the quality of services of Vietnamese accounting firms. Because of the above mentioned provinces, population has 400 enterprises are supplying accounting services. All data collected from the questionnaire are coded, processed by SPSS 20.0. Any observational variables with a total correlation coefficient greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha coefficient greater than 0.7 would ensure reliability of the scale. This method is based on the Eigenvalue, the appropriate factorial analysis and the observed variables in the whole which are correlated when Average Variance Extracted is > 50%, the KMO coefficient is within 0.5 to 1, Sig coefficient ≤ 5%, the loading factors of all observed variables are > 0.5. In addition, the researchers testing scale reliability with Cronbach’s alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analyses (EFA) were performed. Finally, the least squares method and multiple linear regression used (Hair et al., 1998). The least squares method is a form of mathematical regression analysis that finds the line of best fit for a set of data, providing a visual demonstration of the relationship between the data points. Each point of data is representative of the relationship between a known independent variable and an unknown dependent variable (Hair & Anderson, 2010).
Research Results
Descriptive Statistics for the quality of accounting services
Table 1 showed that the mean of QAS1, QAS2 and QAS3 are 3.28; 3.25; 3.39 and Std. Deviation is 0.589; 0.754 and 0.682. Minimum is 2.0 and Maximum is 5.0.
| Table 1: Descriptive Statistics For The Quality Of Accounting Services | |||||
| Item | N | Mini | Max | Mean | Std. Deviation |
| The enterprise has satisfied with the quality of accounting service (QAS1) | 196 | 2 | 5 | 3.28 | 0.589 |
| The enterprise is to meet the needs of the customer (QAS2) | 196 | 2 | 5 | 3.25 | 0.754 |
| The enterprise continues to use accounting services (QAS3) | 196 | 2 | 5 | 3.39 | 0.682 |
Source: The researcher’s collecting data and SPSS 20.0.
The Scale Reliability Tests for Factors Affecting the Quality of Accounting Services
Table 2 showed that all of 28 variables surveyed Corrected Item-Total Correlation greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha if Item deleted greater than 0.7 (Cronbach's Alpha for the quality of accounting services: 0.673, can be acceptable, new item in Vietnamese firms, this is dependent variable) and Cronbach’s Alpha is very reliability. Such observations make it eligible for the survey variables after testing scale. This showed that data was suitable and reliability for researching.
| Table 2: The Scale Reliability Tests For Factors Affecting The Quality Of Accounting Services | ||||
| Items | Scale Mean if Item Deleted | Scale Variance if Item Deleted | Corrected Item-Total Correlation | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted |
| REL1 | 11.46 | 10.568 | 0.877 | 0.949 |
| REL2 | 11.38 | 10.802 | 0.886 | 0.947 |
| REL3 | 11.45 | 10.628 | 0.948 | 0.937 |
| REL4 | 11.43 | 10.882 | 0.843 | 0.954 |
| REL5 | 11.46 | 11.162 | 0.858 | 0.952 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Reliability (REL) | 0.958 | |||
| RES1 | 8.07 | 12.411 | 0.869 | 0.877 |
| RES2 | 7.88 | 13.718 | 0.781 | 0.907 |
| RES3 | 8.26 | 13.958 | 0.783 | 0.906 |
| RES4 | 8.11 | 13.614 | 0.831 | 0.891 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Responsiveness (RES) | 0.920 | |||
| COM1 | 6.64 | 4.231 | 0.822 | 0.750 |
| COM2 | 6.84 | 4.472 | 0.710 | 0.853 |
| COM3 | 6.83 | 4.510 | 0.722 | 0.842 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Competence (COM) | 0.870 | |||
| EMP1 | 8.44 | 12.945 | 0.711 | 0.889 |
| EMP2 | 8.44 | 12.812 | 0.754 | 0.874 |
| EMP3 | 8.31 | 11.772 | 0.860 | 0.834 |
| EMP4 | 8.35 | 12.433 | 0.764 | 0.870 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Empathy (EMP) | 0.897 | |||
| TAN1 | 12.79 | 12.918 | 0.778 | 0.910 |
| TAN2 | 12.71 | 12.544 | 0.786 | 0.909 |
| TAN3 | 12.62 | 12.790 | 0.824 | 0.901 |
| TAN4 | 12.81 | 13.049 | 0.832 | 0.900 |
| TAN5 | 12.70 | 13.102 | 0.783 | 0.909 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Tangibles (TAN) | 0.8923 | |||
| PRI1 | 10.65 | 11.265 | 0.870 | 0.893 |
| PRI2 | 11.31 | 10.726 | 0.769 | 0.914 |
| PRI3 | 10.97 | 9.307 | 0.845 | 0.890 |
| PRI4 | 11.24 | 9.119 | 0.842 | 0.892 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for Price (PRI) | 0.921 | |||
| QAS1 | 6.64 | 1.523 | 0.435 | 0.643 |
| QAS2 | 6.67 | 1.134 | 0.498 | 0.568 |
| QAS3 | 6.53 | 1.225 | 0.538 | 0.507 |
| Cronbach's Alpha for the quality of accounting services (QAS) | 0.673 | |||
Source: The researcher’s collecting data and SPSS 20.0.
Table 3 showed that column “Sig” < 0.05 with significance level 0.05 and column “Conclusion” H1: supported; H2: supported; H3: supported; H4: supported; H5: supported and H6: supported. This showed that six factors affecting the quality of accounting services with significance level 0.05.
| Table 3: Coefficients From The Multiple Linear Regression | ||||||||
| Relationships | Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | S.E | T | Sig | Conclusion | ||
| QAS | ß | REL | 0.116 | 0.116 | 0.049 | 2.376 | 0.019 | H1: Supported |
| QAS | ß | TAN | 0.340 | 0.340 | 0.052 | 6.490 | 0.000 | H5: Supported |
| QAS | ß | PRI | 0.369 | 0.369 | 0.049 | 7.518 | 0.000 | H6: Supported |
| QAS | ß | RES | 0.304 | 0.304 | 0.049 | 6.159 | 0.000 | H2: Supported |
| QAS | ß | EMP | 0.199 | 0.199 | 0.051 | 3.919 | 0.000 | H4: Supported |
| QAS | ß | COM | 0.220 | 0.220 | 0.052 | 4.188 | 0.000 | H3: Supported |
Note: Significant at 5% (All t-tests are one-tailed).
Source: The researcher’s collecting data and SPSS.
Conclusion & Managerial Implications
Conclusions
The contribution of this paper is to found that six factors affecting the quality of accounting services with significance level 0.05. Reliability (β = 0.116), Tangibles (β = 0.340), Price (β = 0.369), Responsiveness (β = 0.304), Empathy (β = 0.199) and Competence (β = 0.220).
This study is to find out the Price (β = 0.369) affected strongest in six factors with significance level 0.05. The researchers surveyed 250 enterprises (196 samples processed) and answered 28 items. Data collected from July 2017 to July 2018 in Vietnam. The Cronbach's Alpha had been analyzed, KMO test and the result of KMO analysis which used for multiple linear regression. enterprises’ responses measured through an adapted questionnaire on a 5-point Likert scale (Conventions: 1: Completely disagree, 2: Disagree, 3: Normal; 4: Agree; 5: completely agree). The researchers had managerial implications policymaker of Vietnam continued to improve the quality of accounting services.
Managerial implications
Price (β = 0.369) has the strongest impact on the quality of accounting services: The price (PRI) has a standardized regression coefficient of 0.369. Price factor is the most important factor affecting service quality: First, businesses need to develop diversified accounting services that bring benefits and more convenience to customers, helping customers have more options to suit their desires. Secondly, perfecting the existing accounting services, when there are changes, it is necessary to immediately notify customers to avoid errors that make customers unhappy. Thirdly, the fees need to be more reasonable and have preferential policies for customers to use the service. Finally, apply customer gratitude policies, give gifts to customers using many services to create a close feeling of closeness between businesses and customers.
Tangibles (β = 0.340) have the second impact on the quality of accounting services: Enterprises provide large-scale accounting services, ready to provide personnel suitable for all customer needs. To improve the quality of accounting services, businesses should pay attention to the issue of staff training and recruiting core personnel for businesses such as: (1) Number of employees with postgraduate qualifications, experts: this force is an indispensable force in improving the quality of accounting services. (2) There should be policies to encourage professional/professional research to improve service delivery. (3) Create favorable conditions for good and long-term employees to study overseas experience according to their capabilities. (4) Number of practicing accountants: practicing accountants are the core force of accounting service providers. However, the number of employees with this practice is quite modest in Vietnam, so businesses should: (1) Create more support conditions so that when qualified employees can actively participate in reviewing and taking the annual accounting practice certification exam of the Ministry of Finance. (2) Develop annual reward policies for employees who pass the exam to obtain a practicing accountant's certificate.
Responsiveness (β = 0.304) has the third impact on the quality of accounting services. Enterprise employees providing technical services with good professional knowledge and professional working skills: (1) Enterprises providing accounting services must develop a customer survey plan, explore diversified areas of customer operations before providing services. (2) Training fast, professional and effective for human resources. (3) Enterprises providing accounting services should have a professional recruitment process: recruiting employees with good qualifications, professional working skills and professional ethics; There is a training process to train new employees and organize knowledge updates for employees in the enterprise.
Enterprise employees providing accounting services provide accurate services: (1) Strengthen control of jobs after completing the process of providing services to customers to ensure that specific agreements, commitments or specific work contents are carried out by real employees show. (2) Develop a system and library for information and in-depth knowledge about the industry so that employees can consult and search for issues that require intensive research. (3) Continuously updating and implementing new regulations on accounting and legal documents relating to services provided. (4) Periodically every year, check the professional of the employees.
Competence (β = 0.220) has the fourth impact on the quality of accounting services.
Accounting service providers need to find solutions to further improve "Service Capacity" through the following solutions: (1) About knowledge and education: Strategic planning of budgets for funding in the training of employees at enterprises providing accounting services (such as tuition fees, scholarships with standard frameworks but business proposed). Complete the staff recruitment process to recruit employees with knowledge and education levels appropriate to the vacancy. (2) About experience, understanding: Experience is a cumulative process throughout the working life of each employee. However, an accounting service firm can still improve this issue of employees if it enhances the exchange of experiences among employees, organizes training sessions with specific circumstances to increase quality of the exchange, attracting the learning and participation of all employees in the enterprise providing accounting services.
In terms of ability, ability: It is difficult to increase this factor because of capacity and ability to favor each individual's qualities. Therefore, an accounting service provider should develop an annual employee assessment policy to eliminate too weak staff. At the same time, through that result, the enterprise will also recognize the employees who have real capacity in order to have a fostering policy to fully utilize the potential of these employees. number of exceptions, there should be a refresher policy for a period of time for employees to develop.
Soft skills: Soft skills are skills in communication, submission, communication, persuasion, listening, understanding, etc. Accounting service providers need to pay more attention to excavation. creating soft skills for employees in addition to training in professional knowledge, strengthening teaching courses from outside organizations, besides encouraging employees to cultivate these skills. Occasionally, a session should also be held for staff to discuss these soft skills.
Empathy (β = 0.199) has the fifth impact on the quality of accounting services: (1) Conduct annual customer surveys on the needs they want to receive from an accounting service provider. In this way, businesses will quickly understand the needs of customers to respond promptly. (3) Create conditions for the staff to participate in the class to communicate carefully, in which listening skills will help employees understand what customers want, because not all customers can express fluently, briefly what they really want. Enterprises providing accounting services always bring the highest benefits to customers.
The service sector is the field that places the highest interests and needs of customers, which are extremely diverse and rich because each customer has a different demand. Therefore, enterprises providing accounting services when contracting should pay attention to the interests of customers as well as placing enterprises in the position of customers to bring higher customer satisfaction in the future thereby improving the quality of your accounting services.
Reliability (β = 0.116) has the least impact on the quality of accounting services:
The enterprise fully fulfills its responsibilities with customers, the contract must clearly state the implementation contents of each type of service as well as the corresponding completion time. Specific regulations will contribute to improving the responsibility of enterprises providing accounting services and reducing risks during the implementation process related to accounting services. In today's high-tech technical conditions, the ability to steal customer information from the computer system is huge. Therefore, enterprises providing accounting services should also establish network information security system and specialized software of the industry in management and data encryption to prevent information theft risks; Regulations on confidentiality of customer information for employees, creating cultural features, self-confidence in information security throughout the enterprise. Despite the highlighted contributions of this research, some limitations have to be taken in this research results, thereby serving as proposals for future research. First of all, our model is tested on a sample of three provinces in Vietnam, so that the level of representativeness of the sample can be affected. Secondly, despite the high explanatory power of the model, it could be reinforced by adding control variables, such as the characteristics of enterprises, enterprise culture... Finally, the analysis of the longitudinal databases available to enterprises should allow them to make comparisons over time as a result of eventual changes in the variables.
References
- Aga, M., & Safakli, O.V. (2007). An empirical investigation of service and customer satisfaction in professional accounting firms: Evidence from North cyprus. Problem ang Perspectives in Management, 5(3), 84-98.
- Ahmad, K. (2014). The adoption of management accounting practices in Malaysian small and medium-sized enterprise. Asian Social Science, 10(2), 236-249.
- Albu, N., & Albu, C. (2012). Factors associated with the adoption and use of management accounting techniques in developing countries: The case of Romania. Journal of International Financial Management & Accounting, 23(3), 245-276.
- Armstrong, R.W., & Davision, A. (1995). An empirical investigation of the dimensions of service quality in australia accounting firms. Journal of Customer Service in Marketing & Management, 1(2), 105-122.
- Auzair. (2013). Management control in accounting outsourcing services. Business Strategy Series, 43-49.
- Dong, H.N. (2013). Solutions to improve the quality of audit services at DTL Auditing Co., Ltd. University of Economics Ho Chi Minh.
- Ferah, Y., Dinçel, G., & Yan?k, A. (2013). An assessment of account service quality from the customer perspective. European Journal of Scientific Research, 103(4), 598-609.
- Groff, M.Z., Slapni?ar, S., & Štumberger, N. (2015). The influence of professional qualification on customer perceptions of accounting services quality and retention decisions. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 16(4), 753-768.
- Hair, B.B., & Anderson, (2010). Multivariate data analysis, (7th edition). New York: US: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (1998). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Ismail, T.H., & Mahmoud, N. M. (2012). The influence of organizational and environmental factors on cost systems design in Egypt. British Journal of Economics, Finance and Management Science, 31-51.
- Ly, T.K. (2013). Factors affecting the decision to choose accounting services of small and medium enterprises in HCMC. University of Economics Ho Chi Minh.
- Mbawuni, J., & Anertey, A. (2014). Exploring management accounting practices in emerging telecommunication market in Ghana. Accounting and Finance Research, 71-85.
- McLellan, J.D. (2014). Management accounting theory and practice: Measuring the gap in United States Business. Journal of Accounting-Business & Management, 21(1), 53-68.
- Minh, M.T. (2010). Accounting and accounting services in the process of international economic integration. University of Economics. Ho Chi Minh.
- Parasuraman, A., Berry, L.L., & Zeithaml, V.A. (1988). The service-quality puzzle. Business Horizons, 35-43.
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V.A., & Berry, L. (1985). conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. The Journal of Marketing, 41-50.
- Scott, D.R., & Van der Walt, NT. (1995). Choice criteria in the selection of international accounting firms. European Journal of Marketing, 29(1), 27-29.
- Sunarni, C.W. (2013). Management accounting practices and the role of management accountant: Evidence from manufacturing companies throughout yogyakarta, Indonesia. Review Journal of Management, 233-248.
- Tuanmat, T.Z., & Smith, M. (2011). Changes in management accounting practices in Malaysia. Asian Review of Accounting, 221-242.
- Tuyen, H.T. (2015). Researching factors affecting the quality of accounting services in accounting service enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City. University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City.
- Valarie, Z.A. (1987). Defining and relating price, perceived quality, and perceived value. PercMarketing Science Institute, Cambridge, 87-101.