Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 3S
The Effect of Liquidity, Solvability and Activity Ratios on Profit Growth (Study on Consumer Goods Industry that is Listed In Indonesia Stock Exchange on 2015-2019 Year of Period)
Hanan Haura Hazimah, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Suherman, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Umi Mardiyati, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Citation Information: Hazimah, H.H., Suherman, & Mardiyati, U. (2022). The effect of liquidity, solvability and activity ratios on profit growth (study on consumer goods industry that is listed in Indonesia stock exchange on 2015-2019 year of period). Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 26(S3), 1-07.
Abstract
Purpose: This research aims to determine the effect of liquidity, solvability and activity ratios on profit growth that is proxied by CR, QR, DAR, DER, ITO, TATO, on consumer goods industry that is listed on IDX for 2015-2019 year of period. Methodology: Samples used on this research were 34 companies that are chosen using purposive sampling technique. This research uses descriptive statistics, linear regression analysis and hypotheses test under Eviews9 as the software to cultivate the data. Findings: This research found that ITO and TATO have negative and significant effect on profit growth. On the other side, CR, QR, DAR and DER have no effect on profit growth.
Keywords
Liquidity, Solvability, Activity, Profit Growth.
Introduction
The determinants of profit growth have been discussed widely by researchers on economics. The fluctuation’s concerned by many, notably those that are inquisitive regarding the company’s potential. According to Indriyani, (2015), profit growth is the rise or reduction of profit within a company during certain period. There are many factors that bring out profit’s fluctuation and some of the research uses financial ratio analysis to examine their effect towards profit growth. As stated in (Gitman & Zutter, 2015), financial ratio is a method to measure and analyze financial performance of a company.
According to prior research by Silalahi current and quick ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Prakarsa (2019) stated that debt to equity ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Safitri, (2016) stated that debt to asset ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. According to Prakarsa (2019), inventory turnover has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Sulistyani et al. (2019) stated that total asset turnover has positive and significant effect on profit growth. It is noted that the higher the ratio, the higher the profit that company earns.
On the contrary, Safitri, (2020) stated that current ratio has no effect on profit growth and Purnama, (2019) stated that quick ratio has no effect on profit growth. According to Prakarsa (2019), debt to asset ratio and total asset turnover has no effect on profit growth. According to Zanora, (2013), inventory turnover has no effect on profit growth.
As one of the industry that is considered to have sustainability and indicates purchasing power of the country (Valintino & Sularto, 2013), consumer goods industry recently has been divided into several categories: cyclical and non-cyclical. However, to this extent, the research regarding the effect of financial ratios on profit growth within this industry after the separation has not been widely discussed(Indrasti, 2020).
Literature Review
According to prior research by Silalahi, current ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Consequently, the larger current ratio indicates adequate funds to pay off their current liabilities and step aside from the liquidity issue. Therefore, the company would obtain higher profits.
H1: Current ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth
According to prior research by Silalahi, quick ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. This ratio specifically put aside the inventory. Consequently, the larger quick ratio indicates adequate funds to pay off their current liabilities and step aside from the liquidity issue. Therefore, the company would obtain higher profits.
H2: Quick ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth
Safitri, (2016) stated that debt to asset ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Consequently, the larger quick ratio indicates adequate funds to pay off their current liabilities and step aside from the liquidity issue. Therefore, the company would obtain higher profits.
H3: Debt to asset ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth
(Prakarsa, 2019) stated that debt to equity ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Consequently, the larger ratio indicates the amount of debt to fund the asset and expand the company. Therefore, the company would obtain higher profits.
H4: Debt to equity ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth
According to Prakarsa, (2019), inventory turnover has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Consequently, the larger turnover indicates the outcome of sales to generate revenue. Therefore, the company would obtain higher profits.
H5: Inventory turnover ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth
Sulistyani et al. (2019) stated that total asset turnover has positive and significant effect on profit growth. Consequently, the larger turnover indicates the outcome of assets used to generate revenue. Therefore, the company would obtain higher profits.
H6: Total asset turnover ratio has positive and significant effect on profit growth.
Method
Data
Consumer non-cyclical companies applied to be the population. Samples used on this research were 34 companies that are chosen using purposive sampling technique. It requires company that publishes the financial or annual reports continuously and remains positive equity during the research period Table 1.
| Table 1 Variables |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Variable | Concept | Indicator |
| 1 | Profit Growth | Amount of profit in certain period of time | 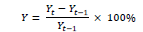 |
| 2 | Current Ratio | Ability to cover the current liabilities |  |
| 3 | Quick Ratio | Ability to cover the current liabilities by putting aside inventory | 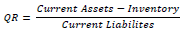 |
| 4 | Debt Ratio | Amount of debt compared to company’s assets | 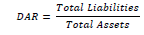 |
| 5 | Debt to Equity Ratio | Amount of debt compared to company’s equity | 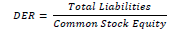 |
| 6 | Inventory Turnover | Amount of goods sold compared to those in the inventory | 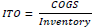 |
| 7 | Total Asset Turnover | Ability of total assets to maintain sales | 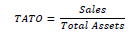 |
| 8 | Firm Age | Amount of time the firm established compared to research period | Firm Age = Log (Research Period – Firm’s Established Year) |
| 9 | Firm Size | Size measurement of the firm based on firm’s total asset | Firm Size = (Ln) Total Aset |
| 10 | Profitability | Ability to generate profit by comparing earnings after tax and total asset | ROA  |
Analysis Techniques
This research uses descriptive statistics, linear regression analysis and hypotheses test under Eviews9 as the software to cultivate the data. In order to conduct visible regression for variables that represent similar ratios, this research adopts different models:
Model 1:
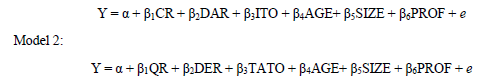
Profit growth has higher standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that profit growth is high in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Japfa Comfeed Indonesia Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Sekar Bumi Tbk Table 2.
| Table 2 Descriptive Statistics |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth | CR | QR | DAR | DER | ITO | TATO | |
| Mean | 0.1666 | 2.4064 | 1.5463 | 0.4594 | 1.1554 | 6.1258 | 1.3812 |
| Median | 0.0941 | 1.7272 | 1.0691 | 0.4815 | 0.9285 | 5.9051 | 1.1746 |
| Max | 3.1405 | 8.6378 | 7.3574 | 0.9445 | 4.2858 | 24.0573 | 4.4635 |
| Min | -0.9400 | 0.5813 | 0.2028 | 0.1406 | 0.1635 | 1.1108 | 0.2767 |
| Std. Dev | 0.6144 | 1.7470 | 1.3224 | 0.1974 | 0.9731 | 3.6966 | 0.8241 |
| Observations | 170 | 170 | 170 | 170 | 170 | 170 | 170 |
Source: Output Eviews9
Current ratio has lower standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that current ratio is low in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Delta Djakarta Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Sampoerna Agro Tbk.
Quick ratio has lower standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that quick ratio is low in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Delta Djakarta Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Gudang Garam Tbk.
Debt to asset ratio has lower standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that debt to asset ratio is low in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Perusahaan Perkebunan London Sumatra Indonesia Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Ultra Jaya Milk Industry & Trading Company Tbk.
Debt to equity ratio has lower standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that debt to equity ratio is low in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Midi Utama Indonesia Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Ultra Jaya Milk Industry & Trading Company Tbk.
Inventory turnover ratio has lower standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that inventory turnover ratio is low in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Nippon Indosari Corpindo Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Delta Djakarta Tbk.
Total asset turnover ratio has lower standard deviation compared to the average. The result indicates that total asset turnover ratio is low in variability and fluctuations. The maximum value obtained from PT Tigaraksa Satria Tbk. On the other side, the minimum value obtained from PT Sawit Sumbermas Sarana Tbk Table 3.
Within the significance level at 1%, 5%, 10% the empirical result shows that CR, QR, DAR and DER have no effect on profit growth, proven by the probability > 0.1. On the contrary, ITO has negative and significant effect on profit growth, proven by the negative coefficient at -0.073841 and probability 0.0517 < 0.1. TATO has negative and significant effect on profit growth, proven by the negative coefficient at -0.431562 and probability 0.0769 < 0.1.
As the control variables, firm age and firm size on both regression model has no effect on profit growth. On the contrary, ROA has positive and significant effect on profit growth, proven by the positive coefficient at 5.857895 and probability 0.0000 on the first regression model, also positive coefficient at 10.73959 and probability 0.0000 on the second regression model.
Discussion
Current ratio has negative coefficient at -0.048362 with 0.5367 probability test result. Quick ratio has positive coefficient at 0.022503 with 0.7821 probability test result. The evidence shows that both current and quick ratio has no effect on profit growth. This means whether the liquidity ratio increases or decreases, it has no effect on profit growth. The findings on current ratio aligned with prior research by (Puspasari et al., 2017; Susyana & Nugraha, 2021). Meanwhile, the findings on quick ratio aligned with prior research by (Purnama, 2019; Safitri, 2020).
Debt to asset ratio has negative coefficient at -0.650790 with 0.3251 probability test result. Debt to equity ratio has positive coefficient at 0.056726 with 0.7600 probability test result. The evidence shows that both debt to asset and debt to equity ratio have no effect on profit growth. This means whether the solvability ratio increases or decreases, it has no effect on profit growth. The findings on debt to asset ratio aligned with prior research by (Pamungkas et al., 2018; Pratiwi, 2018). Meanwhile, the findings on debt to equity ratio aligned with prior research by (Dianitha et al., 2020; Ayem et al., 2017).
Inventory turnover ratio has negative coefficient at -0.073841 with 0.0517 probability test result. Total asset turnover ratio has negative coefficient at -0.431562 with 0.0769 probability test result. The evidence shows that both inventory turnover and total asset turnover ratio have negative and significant effect on profit growth. This means, when the activity ratio increases, the profit growth decreases. The findings on inventory turnover ratio aligned with prior research by (Efendy, 2019). Meanwhile, the findings on total asset ratio aligned with prior research by (Puspasari et al., 2017).
Conclusion
This research focused on consumer non-cyclical firms to give empirical evidence that liquidity and solvability ratios have no effect on profit growth. Meanwhile, the activity ratio that is proxied by inventory turnover and total asset turnover has negative and significant effect on profit growth. It is noted that within this industry, the larger turnover regarding operational purpose, lowers the profit that companies earn. This finding provide additional frame of reference for further research, as the research on consumer goods industry becomes widely discussed.
Recommendations
For further research, additional variables should be included, as this research uses only financial ratios to examine the effect towards profit growth. We consider the analysis of consumer cyclical firm as additional material for educational purpose.
References
Ayem, S., Wahyuni, T., & Suyanto, S. (2017). Pengaruh Quick Ratio, Debt To Equity Ratio, Inventory Turnover Dan Net Profit Margin Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Pada Perusahaan Manufaktur Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia Tahun 2011-2015. Akuntansi Dewantara, 1(2), 117-126.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dianitha, K.A., Masitoh, E., & Siddi, P. (2020). Pengaruh Rasio Keuangan Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Pada Perusahaan Makanan dan Minuman di BEI. Berkala Akuntansi Dan Keuangan Indonesia, 5(1), 14-30.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Efendy, A. (2019). Pengaruh Kinerja Keuangan terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Perusahaan Otomotif dan Komponen yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia Tahun 2011-2017.
Gitman, L.J., & Zutter, C.J. (2015). Principles of Managerial Finance (14th ed.): Pearson.
Indriyani, I. (2015). Pengaruh rasio keuangan terhadap pertumbuhan laba pada perusahaan pertambangan yang terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia. Sriwijaya Journal of Management and Business, 13(3), 343-358.
Pamungkas, T.H., Nurlaela, S., & Titisari, K.H. (2018). Pengaruh Kinerja Keuangan Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Sektor Industri Dasar Kimia di BEI. In Prosiding Seminar Nasional: Manajemen, Accounting, and Banking, 1(1), 513-525.
Prakarsa, R.B. (2019). Effect of Financial Ratio Analysis on Profit Growth in the Future (in Mining Companies Registered on the Indonesia Stock Exchange for the 2013-2015 Period). Journal of Economic Appreciation, 7(1), 90-94.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Pratiwi, A.P. (2018). Analisis Pengaruh Rasio Keuangan Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba pada Perusahaan Food And Beverages yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode 2011-2015. Journal of Business Disruption, 1, 18.
Purnama, M. (2019). Pengaruh Qr, Der, Npm, Ito Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Pada Perusahaan Keramik, Porselen Dan Kaca Tahun 2008-2017. GOODWILL, 1(2), 119-129.
Puspasari, M.F., Suseno, Y.D., & Sriwidodo, U. (2017). Pengaruh Current Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Total Asset Turnover, Net Profit Margin dan Ukuran Perusahaan terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba. Journal of Human Resource Management, 11, 13.
Safitri, I.L.K. (2016). Pengaruh Rasio Keuangan Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Pada Perusahaan Manufaktur Sektor Industri Konsumsi Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia (Studi Kasus Pada Perusahaan Kalbe Farma Tbk Periode 2007-2014). Journal of Accounting and Business: Journal of Accounting Study Program, 2(2).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indrasti, A.W. (2020). Analisa Pengaruh Rasio Keuangan Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Pada Sektor Industri Barang Konsumsi Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia Tahun 2015-2018. Jurnal Ekonomika dan Manajemen, 9(1), 69-92.
Sulistyani, I., Wijaya, A.L., & Novitasari, M. (2019). Pengaruh Rasio Likuiditas, Solvabilitas, Dan Aktivitas Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba Dimoderasi Oleh Ukuran Perusahaan. In Simba: Seminar Inovasi Manajemen, Bisnis, dan Akuntansi (1).
Susyana, F.I., & Nugraha, N.M. (2021). Pengaruh Net Profit Margin, Return on Assets dan Current Ratio terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba. Journal of Banking Management Economics, 3, 14.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Valintino, R., & Sularto, L. (2013). Pengaruh Return On Asset (ROA), Current Ratio (CR), Return On Equity (ROE), Debt To Equity Ratio (DER), dan Earning Per Share (EPS) Terhadap Harga Saham Perusahaan Manufaktur Sektor Industri Barang Konsumsi di BEI. Prosiding PESAT, 5.
Zanora, V. (2013). Pengaruh Likuditas, Leverage Dan Aktivitas Terhadap Pertumbuhan Laba (Studi Empiris pada Perusahaan Manufaktur yang Terdaftar di BEI Periode 2009-2011). Accounting Journal, 1(3).
Received: 28-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. AAFSJ-21-10655; Editor assigned: 30-Dec-2021, PreQC No. AAFSJ-21-10655(PQ); Reviewed: 13-Jan-2022, QC No. AAFSJ-21-10655; Revised: 20-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. AAFSJ-21-10655(R); Published: 27-Jan-2022