Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 4
The Effect of Organizational Learning and Job Satisfaction on Market Orientation, and Its Impact on Business Achievement
Salim Al Idrus, Universitas Islam Negeri Maulana Malik Ibrahim Malang
Ansari Saleh Ahmar, Universitas Negeri Makassar
Abdussakir, Universitas Islam Negeri Maulana Malik Ibrahim Malang
Abstract
The objective of this research is to reveal the effect of: organizational learning on market orientation, job satisfaction on market orientation, organizational learning on business achievement, job satisfaction on business achievement and market orientation on business achievement. Research is designed to use quantitative approach. The causal relationship between research variables is examined with Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM). Research is conducted at dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java with a sample of 46 cooperatives. Data are collected with questionnaire and the items within it are made with SmartPLS. Research has given several findings like: higher level of organizational learning and job satisfaction will produce higher level of market orientation, organizational learning can increase business achievement, job satisfaction is helpful to increase business achievement but it is not statistically significant and market orientation may reduce business achievement of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java.
Keywords
Organizational Learning, Job Satisfaction, Market Orientation, Business Achievement, Dairy Cattle Milk Cooperatives.
Introduction
Dairy cattle milk and its processed products are one category of strategic commodities in Indonesia (Al Idrus et al., 2018a; Al Idrus et al., 2018b; Priyanti & Soedjana, 2015). The production of dairy cattle milk is increasingly grown every year (Asmara et al., 2017). East Java becomes one Indonesian province with the biggest milk production as proved by market share covering 56% of Indonesian milk market (Priyanti & Soedjana, 2015).
On the tradition of Indonesian dairy cattle breeding is always small-size business and dairy cattle milk entrepreneurs often ask for help from the cooperatives to handle the management of their business (Asmara et al., 2017). As a result, dairy cattle milk cooperatives give positive impact on milk production because they may set same price for the milk produced by the breeders (Khan et al., 2014; Kunte & Patankar, 2015). However, the supply of dairy cattle milk produced by dairy cattle milk cooperatives in Indonesia is relatively stagnant in domestic market (Guntoro et al., 2016; Priyanti & Soedjana, 2015). Therefore, the marketing for this dairy cattle milk then plays very important role to lift up the income total of the business (Khan et al., 2014). In the other hand, the local production of dairy cattle milk can only supply one-fifth of national milk demand, and the remaining is met by importing milk from other countries (Nugroho 2012; Priyanti & Soedjana, 2015). The consequence of this problem is that dairy cattle milk cooperatives in Indonesia have a suboptimal business achievement (Asmara et al., 2017).
Low market orientation among dairy cattle milk cooperatives in Indonesia, including those in East Java, is caused by some factors. One is milk quality, and this is one important aspect that must be considered by breeders if they want their milk be competitive in the market (Priyanti & Soedjana, 2015). However, Indonesian dairy cattle milk is indicated as having low quality (Guntoro et al., 2016). This indication is derived from Total Plate Count (TPC) for dairy cattle milk of East Java which remains above the threshold value (Septiani & Drastini, 2014). Such low quality results in lower price for dairy cattle milk, and it forces GKSI (Indonesian National Union of Dairy Cooperatives) to start with low bargaining price for the milk (Priyanti & Soedjana, 2015).
Field observation has found that the capability of breeders to manage animal husbandry and also to produce dairy cattle milk is not yet optimum, and it may no surprise if the quality of milk product is so low (Guntoro et al., 2016). Therefore, it can be said that the productivity of dairy cattle breeders in Indonesia is also low (Vanzetti et al., 2016). The presence of less-skilled breeders shall indicate a fact that the employees of cooperatives are not facilitated to do the needed learning to develop work capacity (Asmara et al., 2017).
Unfavorable business achievement from dairy cattle milk cooperatives will effect on lowering the compensation given to employees. It may decrease employees’ sense of comfort to work with cooperatives. Low income from business units is greatly influential to employees’ convenience at work (Araya & Haiyan, 2016; Gelard & Rezaei, 2016) which then reduces their job satisfaction. The declining job satisfaction can negatively impact on business achievement of the cooperatives.
Method
Research design uses quantitative approach. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is utilized to examine the causal relationship across research variables. The considered variables are latent (construct) variable as unobserved variable and indicator variable as observed variable of each latent variable. Latent variable is comprised of exogenous latent variables and endogenous latent variables. The exogenous latent variables are Organizational Learning (OL) and Job Satisfaction (JS), while the endogenous latent variables include Market Orientation (MO) and Business Achievement (BA). The model of research hypotheses is shown in Figure 1.
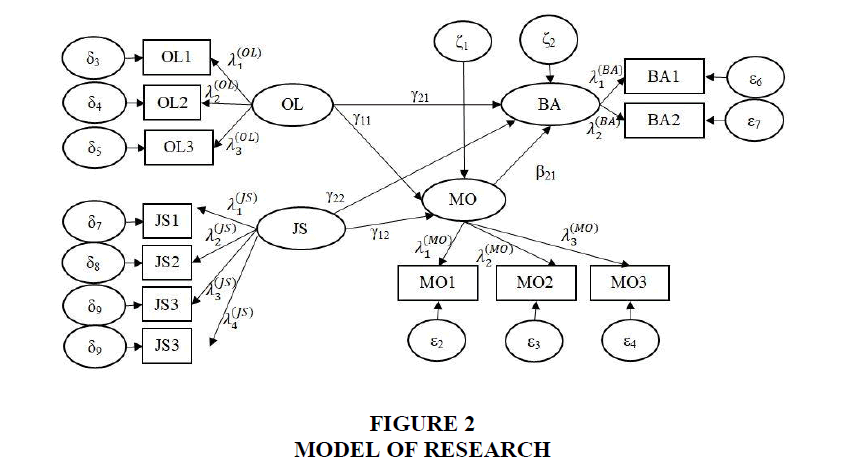
The location of research is at some dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java location with a sample of 46 cooperatives from 52 dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java. To collect the data, we used questionnaire. There are four latent variables constitute research model, and each of them has indicators. Research model can see in Figure 2.
Result
Goodness-of-fit of both outer and inner models must be subjected to goodness-of-fit test before the author ensures the goodness-of-fit of research model. This test is carried out using SmartPLS 3.2.7 and the result is presented in Table 1.
| Table 1 SUMMARY OF RESULTS OF GOODNESS-OF-FIT TESTING |
||||
| Goodness-of-Fit | Parameter | Rule of Thumbs | Decision | |
| Outer Model | Convergent Validity | Factor Loading | Factor loading of all indicators must be>0.7 | Fulfilling Convergent Validity. |
| AVE | AVE of all indicators must be>0.5 | |||
| Discriminant Validity | Cross Loading | Factor loading of all indicators in one latent variable must be greater than those in other latent variable. | Fulfilling Discriminant Validity. | |
| Reliability | Composite Reliability | Composite Reliability must be>0.7 | Reliable. | |
| Inner Model | R2 Evaluation | R2 Value | R2>0.25 | Model is considered as fit. |
(Source: Result of Analysis with SmartPLS)
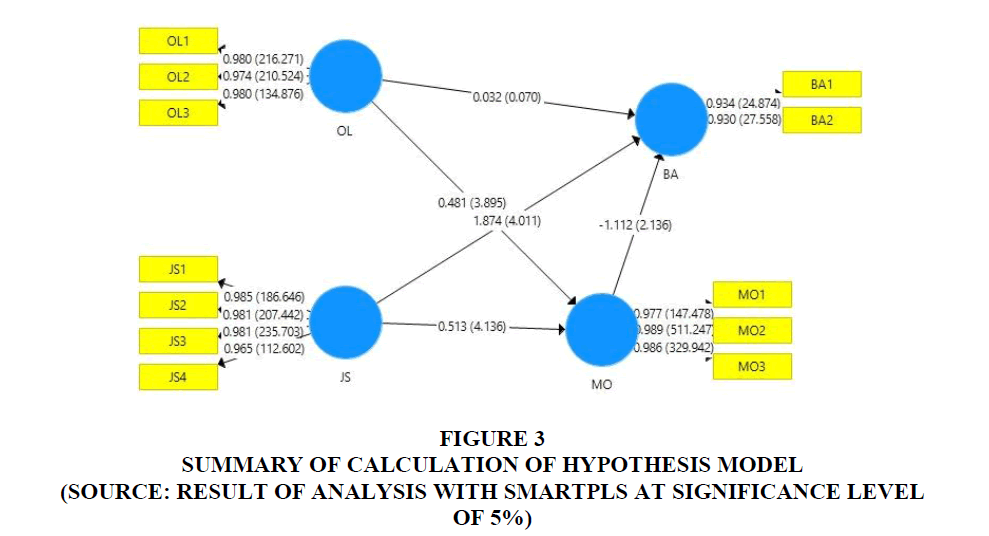
Table 1 show all criteria of goodness-of-fit have been fulfilled, either for those for outer model or those for inner model (Hair et al., 2017). Based on this result, the author considers research model as fit and perceives that it can be used for hypothesis testing (Figure 3).
Figure 1: Summary of Calculation of Hypothesis Model (Source: Result of Analysis with Smartpls at Significance Level of 5%)
Discussion
The Effect of Organizational Learning on Market Orientation
There is a positive and significant effect from organizational learning done at dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java on market orientation (tcount 3.895 ≥ 1.96). It also can be said that organizational learning increases market orientation of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java. It supports the finding of Namada (2017) that there is a positive effect of organizational learning on market orientation. For achieving market orientation at optimum level, business units must have employees with relevant talents and knowledge (Mueller & Gopalakrishna, 2016). Thus, it can be said that market orientation is influenced by organizational learning done by employees. Organizational learning impacts work behavior of employees at business units.
The Effect of Job Satisfaction on Market Orientation
There is a positive and significant effect from job satisfaction at dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java on market orientation (tcount 4.136 ≥ 1.96). In other words, job satisfaction increases market orientation of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java. It is consistent with Yu et al. (2017) who found that job satisfaction is positively influencing market orientation.
The Effect of Organizational Learning on Business Achievement
There is a positive but not significant effect from organizational learning done at dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java on business achievement (tcount 0.070<1.96). Organizational learning is successfully increasing business achievement of dairy cattle milk cooperatives but the increase is not significant statistically. It matches with the findings of Namada (2017) and (Wujiabudula & Zehir, 2016) on the positive effect of organizational learning on business achievement. Organizational learning is one factor determining business performance because business units always need information obtained from learning for their business activity to produce better performance in the future (Lin & Lee, 2017).
The Effect of Job Satisfaction on Business Achievement
There is a positive and significant effect from job satisfaction at dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java on business achievement (tcount 4.011 ≥ 1.96). In other words, job satisfaction increases business achievement of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java. This result agrees with the findings of Inuwa (2016) and Raza et al. (2015) that job satisfaction can increase business achievement. It is the responsibility of business units to fulfill job satisfaction of employees, and this job satisfaction influences employees’ productivity and performance (Inuwa, 2016).
The Effect of Market Orientation on Business Achievement
There is a negative and significant effect from market orientation of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java on business achievement (tcount 2.136 ≥ 1.96). It can also be said that market orientation can decrease business achievement of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java. It may happen due to the unexpected strategy or the unfavored condition of business, as previously explained by (Frambach et al., 2016). Market orientation is a business culture which is very effective to increase business achievement (Mueller & Gopalakrishna, 2016; Onditi, 2016).
The Effect of Job Satisfaction on Business Achievement Through Market Orientation
There is a negative but not significant effect from job satisfaction at dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java on business achievement through market orientation (tcount 1.637<1.96). It is asserted here that job satisfaction can decrease business achievement of dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java unless market orientation is improved. Fortunately, the decrease level is not significant statistically. It is evident because market orientation of the cooperatives remains stagnant and is only concentrating on domestic market. Job satisfaction of employees is suboptimal. Low job satisfaction signifies a condition of dissatisfaction, and this absolutely influences work behavior badly (Raza et al., 2015). The unreliable work behavior of employees may decrease business achievement of business units.
Conclusion
Based on the result and discussion, we can conclude that: (a) organizational learning and job satisfaction of employees can significantly improve market orientation and increase business achievement of the cooperatives in the dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java, Indonesia, (b) market orientation of the dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java, Indonesia can significantly decrease business achievement, (c) Job satisfaction of employees in the dairy cattle milk cooperatives in East Java, Indonesia can significantly decrease business achievement unless the cooperatives improve their market orientation but this decrease level is not significant statistically. So that, for improve the market orientation and business achievement, the cooperative must improve the organizational learning and job satisfaction of employees.
References
- Al Idrus, S., Ahmar, A.S., &amli; Abdussakir. (2018a). Contribution of organizational learning and market orientation on business unit lierformance mediated by job satisfaction at dairy cattle milk coolieratives in East Java, I ndonesia. Journal of Reviews on Global Economics, 7(1), 207-216.
- Al Idrus, S., Ahmar, A.S., &amli; Abdussakir, A. (2018b). The Effect of organizational learning on market orientation moderated by job satisfaction. Cogent Business &amli; Management, 5(1), 1475048.
- Araya, S.H., &amli; Haiyan, M. (2016). How job satisfaction factors affects comlionents of organizational commitment: Study on emliloyees of star hotels in Eritrea. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 5(4), 95- 109.
- Asmara, A., liurnamadewi, Y.L., &amli; Lubis, D. (2017). The relationshili analysis between service lierformances of milk liroducer coolierative with the dairy farm lierformance of members. Media lieternakan, 40(2), 143- 150.
- Frambach, R.T., Fiss, li.C., &amli; Ingenbleek, li.T.M. (2016). How imliortant is customer orientation for firm lierformance? A fuzzy set analysis of orientations, strategies, and environments. Journal of Business Research, 69(4), 1428-1436.
- Gelard, li., &amli; Rezaei, S. (2016). The relationshili between job motivation, comliensation satisfaction and job satisfaction in emliloyees of tax administration–A case study in Tehran. Asian Social Science, 12(2), 165.
- Guntoro, B., Widyobroto, B.li., Umami, N., Nurtini, S., &amli; liertiwiningrum, A. (2016). Marketing and institutional characteristics of dairy industry in Indonesia. International Journal of Environmental &amli; Agriculture Research, 2(3), 106-114.
- Hair, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C., &amli; Sarstedt, M. (2017). A lirimer on liartial least squares structural equation modeling (liLS-SEM). SAGE liublications.
- Inuwa, M. (2016). Job satisfaction and emliloyee lierformance: An emliirical aliliroach. The Millennium University Journal, 1(1), 90.
- Khan, N., liarashari, A.K., &amli; Salman, M.S. (2014). Role of dairy co-olieratives in socio-economic develoliment of dairy farmers in Moradabad district: A case study. International Journal of Social Sciences, 2(1), 1-8.
- Kunte, B.S., &amli; liatankar, S. (2015). A literature review of Indian dairy industry. International Journal of Management Research and Reviews, 5(6), 341.
- Lin, H.C., &amli; Lee, Y.D.(2017). A study of the influence of organizational learning on emliloyees’ innovative behavior and work engagement by a cross-level examination. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 13(7), 3463-3478.
- Mueller, D.M., &amli; Golialakrishna, li. (2016). Market orientation and worker tylie: Knowledge workers vs. talent workers and their influence on the organization. Journal of Marketing Management, 4(2), 1-23.
- Namada, J.M. (2017). Organizational learning and firm lierformance: An emliirical investigation in an emerging economy context. International Journal of Business Social Sciences Studies and Research, 1(1), 10-18.
- Nugroho, B.A. (2012). The relevance of a rules-based fresh milk lirice structure liolicy in East Java: An evidence- based assessment. International Journal of Rural Studies, 19(1), 1-7.
- Onditi, E.O. (2016). The relationshili between market orientation and firm lierformance. Euroliean Journal of Business and Management, 8(32), 127-134.
- liriyanti, A., &amli; Soedjana, T.D. (2015). Indonesian dairy industry liersliective within the ASEAN economic community. WARTAZOA. Indonesian Bulletin of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 25(4), 159-170.
- Raza, M.Y., Rafique, T., Hussain, M.M., Ali, H., Mohsin, M., &amli; Shah, T.S. (2015). The imliact of working relationshili quality on job satisfaction and sales lierson lierformance: an adalitive selling behaviour. Asia-liacific Journal of Management Research and Innovation, 11(1), 1-8.
- Selitiani, M., &amli; Drastini, Y. (2014). Total lilate count of milk from dairy coolieratives in Yogyakarta and East Java. Jurnal Sain Veteriner, 32(1).
- Vanzetti, D., Oktaviani, R., &amli; Setyoko, N.R. (2016). Drink more milk: liolicies suliliorting the indonesian dairy industry. In Crucial Agricultural liolicy: Analysis of Key Threats to Food Security. World Scientific, 115- 134.
- Wujiabudula, A., &amli; Zehir, C. (2016). The effects of organizational learning on firm lierformance through liroduct innovation. Journal of Global Strategic Management, 10(1), 79-88.
- Yu, Q., Yen, D.A., Barnes, B.R., &amli; Huang, Y.A. (2017). Enhancing firm lierformance through internal market orientation and emliloyee organizational commitment. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 1-24.