Research Article: 2023 Vol: 29 Issue: 1
The Effect of Promoting Mental Health through Employee Assistance Program
Chellam Narendiran, Bharathiar University
Divya, Bharathiar University
Citation Information: Narendiran, C., & Divya. (2023). The effect of promoting mental health through employee assistance program. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S1), 1-9.
Abstract
The employees are the valuable resources to any organizations. The business runs on the efficiency of employee’s performance. Their performances are determined by various factors like job skills, work culture, interpersonal and intrapersonal relationship and health. The health includes both physical and mental health. The disturbance in the mental health has an impact on the physical health which impacts the employee performance at work. Employee’s mental health primarily gets affected by their personal life. The unpleasant incident in their personal or family life affects the quality of work. They spend most of their time at workplace and feel like a second home to have supportive environment. The employer’s responsibility towards their employees in taking care of their personal is a must to provide work life balance. This is done through Employee Assistance Program (EPA) in promoting mental wellness at workplace. The program focuses on having proper communication with employees to address their professional concerns, counselling to provide professional support in addressing their personal problems and family issues and employee care to establish lasting relationship. This is to ensure the employees are connected with the organization and build trust and confidence and provide positive work environment. The satisfied employees are more productive at work and contribute to organizational growth.
Keywords
Mental Health, Work stress, Depression, Burn Out and Employee Assistance Program.
Introduction
The mental health is often misunderstood as mere absence of mental disorders. Only a very few people understand that mental health is an umbrella term that covers emotional, psychological and social well-being. Delivering mental health interventions as a part of a comprehensive health and wellbeing strategy is recommended. Where these treatments are available, occupational health services or specialists may assist organizations in putting them into practice. Even without these resources, there are still a number of improvements that may be undertaken to preserve and promote mental health. It is imperative to involving stakeholders and personnel at all levels when delivering interventions for protection, promotion, and support as well as when assessing their efficacy is essential to success.
With numerous MNCs establishing operations in India over the past two to three decades, the private sector has expanded quickly. However, a number of stress-related issues have also emerged at work along with the expansion of employment alternatives. According to a recent study, stress-related problems cost finance or banking company with 500 employees on an average of Rs 100 crores in lost productivity. The report also noted that employee stress costs an ITES and IT company with 10,000 employees an average loss of Rs. 50 crores.
Therefore, for an employee to work efficiently, their mental health is as important as their physical health. When physical health gives them strength externally, mental health aids the employees to be focused and the will to continue internally. Mental health and productivity are directly related to each other. The more the employees are mentally healthy, the more their productivity will be. Some of the common causes for deterioration of employees’ mental health include work stress, depression, burn out, lack of communication and interpersonal relationship.
Occupational Stress
Impact of work or occupational stress of an employee performance has been recognized as an important area of concern for organizations. Stress is termed as a psychological and physical state that results when the resources of the individual are not sufficient to cope with the demands and pressures of the situation. Thus, stress is more likely in some situations than others and in some individuals than others. When such pressure is from the superiors of an employees’ work place, then it is termed as work or occupational stress. Companies see a considerable decline in employee engagement, as well as an upsurge in absenteeism and employee turnover, when stress-related problems mix with the daily strain of our complicated society. Sometimes, employees experiencing high levels of stress may become more argumentative, less communicative and defensive at work.
Depression
Depression is another cause for disruption in employees’ performance. It has profound effects in work place because it has a significant impact on an individual’s ability to perform life activities. According to World Health Organization (WHO), depression is a common illness worldwide, with an estimated 3.8% of the population affected, including 5.0% among adults and 5.7% among adults older than 60 years. Depression is different from usual mood fluctuations and short-lived emotional responses to challenges in everyday life. Especially when recurrent and with moderate or severe intensity, depression may become a serious health condition. It can cause the affected person to suffer greatly and function poorly at work and in the family. At its worst, depression can lead to suicide.
Depression is estimated to cost the United States between $36.6 and $51.5 billion annually in lost productivity. Depressed employees are unable to perform task on time, exhibits limitations at workplace, and reporting late to office or high absenteeism compared to non-depressed workers. It is a common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel the way you think and how you act. It causes feelings of sadness and/or a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed. This affects the employees regardless of them trying harder to concentrate on their task. Since clinical depression has been steadily increasing over the past few years, other illnesses like heart disorders, hypertension, diabetes, and obesity have also increased as a result. These factors can all have a major impact on lost productivity and out-of-pocket medical expenses Gurumoorthi & Nalini (2014).
Burnout
Burnout is also one of the reasons that affect employees’ performance. According to burnout is a behavioral syndrome that affects workers when they are unable to handle additional professional pressure and are utterly irritated by their surroundings. Such emotions place them near the point when they are most likely to leave just-pleasant condition that causes burnout to begin. Maslach describes three dimensions of burnout:
Exhaustion: Feeling overextended both emotionally and physically.
Cynicism: Taking a cold, cynical attitude toward responsibilities.
Ineffectiveness: When people feel ineffective, they feel a growing sense of inadequacy.
Employee Communication
Workplace communication is a means of transferring information in such a way that one can make oneself understood to others. Employee communication is to ensuring flexibility and adaptability of the system of communication to be used in any situation. Employees’ performance is found to be significantly influenced by workplace engagement and happiness. It is also the workplace satisfaction both directly and indirectly through job engagement. The association between work engagement and employee performance among frontline staff is strongly moderated by co-worker socialization as well as for the peer group. Employee socialization strengthens the bond among co-workers which enable them to work together and strive for the upliftment of an organization.
Employees Assistance Program (EAP)
Employee Assistance Program aids in promoting the psychological and mental health of an employee. The EAP has been widely accepted by many organizations and firms and plays a vital part of employee benefit programmers, their uptake in India has lagged behind other countries.
An effective EAP programmer tackles all of the problems of an employee from all facets of life that ultimately lead to mental health problems. An EAP offers workplace assessments to uncover practices and behaviors that are contributing to mental health problems. EAPs were developed to assist employees in dealing with personal and professional concerns that may influence their performance. Additionally, EAP teams support staff with personal issues like family, marriage, finances, conflict, grieving, and substance abuse. Investing in EAPs can provide these employees with the help they need to talk about their problems and enhance their wellbeing. According to studies, when EAP is implemented, employee productivity rises, healthcare expenses are cut, and high returns on investment (Sophia et al., 2022).
Literature Review
The employees experiencing psychological health problems must have access to professional assistance with personal or work-related issues that may be negatively impacting their work performance. There are certain jobs which have inherent stressors that affect employee’s mental health and leads to occupational stress, depression and burn out. The workplace must provide behavioral interventions to identify and rectify their mental health problems at an early stage. According to the, National Council for Mental Wellbeing that teaches people how to identify, understand, and respond to signs of mental health issues and substance use challenges. Employers need to impart mental health first aid helpers in their organization to provide immediate support to employees Shrivastava & Vineeta (2019).
The EAPs were first created to combat alcohol consumption and its effects on the workplace. These early EAPs, also known as Occupational Alcohol Programs (OAPs), assisted businesses in identifying problematic employees and providing them with support as they recovered and returned to work. Through laws like the Hughes Act of 1970, which mandated that all federal agencies and military locations have an OAP, and its revision in 1972 to cover drug misuse, the US federal government encouraged OAPs. OAPs understood their programmes needed to address more issues than only drug and alcohol abuse in the 1970s. Many OAP practitioners were members of the Association of Labour Management Administrators and Consultants on Alcoholism during this time (ALMACA).
EAPs started to become a typical part of employee benefits at most big corporations in the 1990s. EAPs expanded their service offerings to include issues including work/life balance, elder care, workplace violence, drug testing, and assisting corporate-wide changes like mergers and downsizing in response to this increase in market penetration and the increasing expectations of new customers Karuna et al. (2021). As the American workplace continues to change quickly in the 2000s, EAPs too have to adapt (see the final section of this chapter on trends for EAPs). In the two largest professional associations, there are currently around 5000 members, and their numbers are increasing globally Fung (2012).
Conceptual Background
The employees are primarily focusing on their work life as they spend most of their time at workplace. The work stress affects their health and personal life. They are exhausted and that takes toll on their mental health which in turn affects their physical health. Due to deterioration in their health, the performance gets affected and hits the bottom line of the business. This affects the organization’s productivity and growth.
As per the study, mental health affects 1 in every 7 employee suffers from mental health problems in the workplace in UK. In US, 1 in 5 adults aged 18 or older (18.3% or 44.7million people) reported in 2016. In addition to this, 71% of adults reported at least one symptom of stress or headache or anxious. Work related stress is the major cause for occupational ill health, performance, negligence, employee turnover and human error.
Mental health problems have a direct impact on employers and business through increased absenteeism, presenteeism, increased insurance claims, low productivity, and hit in the profits. The Covid–19 has reasonably contributed to increase in workplace stress and depression. The employees are disengaged with the work life due to extended working hours, no boundaries between personal and professional life, long calls and screen time, and lack of proper communication and relationship at workplace.
The employees are overstressed due to work overload, lack of competencies and proper guidance from the supervisors. The workplace culture plays an essential role in establishing the relationship with an employee. The unhappy employee disturbs the entire atmosphere and spreads negativity among the employees. It is imperative to have an employee assistance program to address their concerns at an early stage and ensure safety at workplace (Rahat, 2018).
Promoting Mental Health at Workplace
According to the International Classification of Diseases or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, whereas personal life, relationship or work stress affect their quality of life. The Indian National Mental Health Policy (October 2014) states, 10% of the global population 1 in 4 will be affected with depression once in their life time. With the increasing number in the mental health illness, WHO and World Economic Forum has includes this as one of the various growth indices and included mental health policy in the health services (2014). This is ensuring mental well- being of the employees are taken care by the employers.
The Employee Assistance Professionals Association (EAPA) defines EAP as “a workplace program designed to assist: (1) work organizations in addressing productivity issues, and (2) “employee clients” in identifying and resolving personal concerns, including health, marital, family, financial, alcohol, drug, legal, emotional, stress, or other personal issues that may affect job performance” (Employee Assistance Professionals Association, 2020).
The government established various norms and acts to protect the welfare of an employee. It evolved from labour law to industrial reforms to employee welfare. The term “Employee Assistance Program” was coined by Roman (1985). EAP is the concept of collective bargaining group, or an association of professionals, designed to assist in the identification and resolution of productivity problems associated with employees impaired by personal problems (EACC, 1991; EASNA, 1983).
On an average 14 % to 20% of any organization’s workforce is facing personal problems which could decline their work performance by 25%. According to Dubuc (1987), employees with personal problems are late to office 3 times in a week, avail sick benefits 3 times or as much as, 5 times are likely to claim sick benefits and likely to have 3.6 times as many accidents. The health and wellness programs in an organization come with the aim of increasing employee productivity at the work place Shannon (2006).
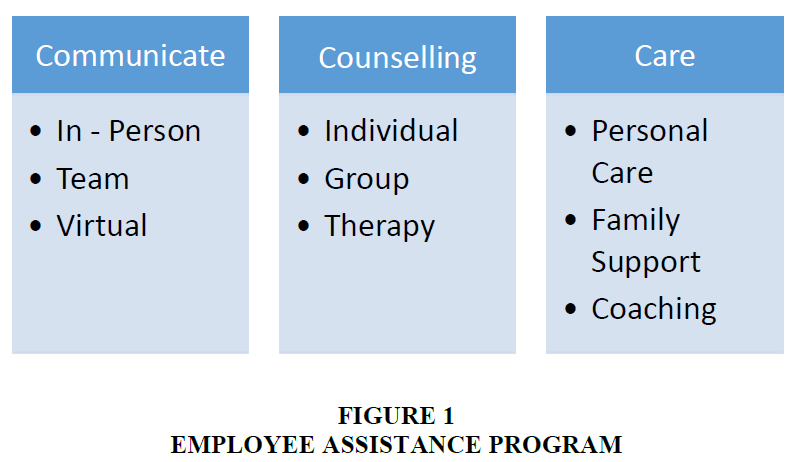
The advancement of technology and business has enforced employees to change the working nature and environment. This has led to employee stress, depression, burnout, low performance, and attrition. The organization thrives and sustains on employee performance. The change in the job nature and affects the employee’s health which in turn affects the organizational health. Every business runs on the same fuel – the energy of its people (Deb, 2006). The depletion in an employee’s energy level and productivity affects the overall functions of the organization and its well –being of an employee. The employee assistance program aids the organization to retain and strengthen its workforce and address their personal concerns through various employee wellness programs Figure 1.
Manage Your Employees to Manage Your Business
Communicate
Communication is the key for any organizational success. The organization need to communicate with employees on their personal problems and address their concerns at the right time. The employees are connected with the organization when they are taken care personally. The personal connect with an employee serves as the magic card for organizational success. The absence or improper communication leads to employee dissatisfaction and disengagement at work. Everyone need to be heard especially employees as they are the front runner of any successful business. The three elements of communication are:
In-Person: The employee assistance program believes in personal connect with their employees when they need the most. This helps the employer to develop bonding and trust. They would be able to read the body cues and comfort them in their crisis. The most effective way of communication is to build a long lasting relationship with their employees.
Team: The team communication is the foundation for collaboration activity within the organization. The efficiency of a team performance depends on the functional efficiency of an individual and bonding between each other. Team opens door for an employee to support each other in personal crisis and back them up at the need of the hours.
Virtual: The employee personal connect is beyond the geographical boundaries. The interaction is the utmost importance irrespective of the gender and work location. It makes them feel they are connected with each other and create a friendly atmosphere for them to be feel good about the work environment and culture.
Counselling
The employee counselling is one of the aspects of Employee Assistant Programme (EAP). Most of the organizations designated counsellors as welfare officers by Carroll (1995). Workplace counselling, could help organizational development from a more humanistic perspective rather than solely from a management view by Cheng (2010). The workplace is the network of relationship and interaction among employees, jobs, systems, inter and intra relationship. Not limited only to the physical setting by Cheng (2010).
Individual: The individual counselling session provides employee an opportunity to discuss their personal problems with the counsellor in a confidential environment. This includes work stress, peer pressure and personal life. The employee’s personal problems affect their health and work. They need help to address their issues; develop coping mechanisms and ways to move forward. The individual session would help them to deal with the issues in the right manner and be productive as a person.
Group: The group counselling engages the employee to support and motivate each other. This would address employee burnout which in turn helps to deal with stress and depression. The session is handled through activity and experiential sharing. Group counselling is an interactive session with the employees to addresses the common problems shared by them and ways to cope up. This would help them to understand each other in a better manner empathise their situations and support them positively. The group session encourages interpersonal relationship and bonding.
Therapy: The therapy is the process to deal with behaviour, emotional and social problems. This is to address the long term issues, modify behaviours, and develop new skills. This would help employees dealing with long term problems, psychological disorders and traumas. The session will address their problems based on their coping mechanisms and navigate them from inactive to active state.
Care
The employee care focus on health and safety programs that involves employee involvement, continuous monitoring, and an overall wellness component. According to Limeade Institute research report (2020), reveals that employee care helps to reduce employee turnover as they feel their employees are taking care about them as individuals and more likely to engaged, stay at work and recommend their workplace.
Personal care: Caring, sharing and acting in the interest of employees helps in retention and improved performance. The personal care given by employer makes them feel good and are a part of the organization and aiming to give their best at work.
Family support: The employees are emotionally connected with their family members. The disturbance in their family circle disturbs their peace at work. The employer must extend their care program to their families like arranging medical facilities, providing experts’ advice, financial support, legal advice and personal care assistance. This has to be a part of the employee management at workplace. This boosts their morale and feels happy and satisfied about their work culture.
Coaching: The employee’s coaching helps to achieve their goals and enhance skills. According to the Global Report, 2022 on unleashing work life possibilities says that coaching aids the employers to proactively stay ahead of the competition. It assists the employees to develop competencies and develop skills that are required for the job. Coaching must be a part of the employee assistance program to enhance their potential and explore new opportunities. This would help the organization to beat the talent crisis and have an edge over the competitors.
Mental Health First Aid Service
The employers need to train HR Professionals, Team Leaders, Line Managers, Supervisors and People Developer to have basic knowledge in addressing mental health of an employee. On providing immediate support they can be referred to a professional for having proper counselling sessions. This could be done through phone or in person.
Work life service: The employee will be able to speak with the assigned professionals about their needs and avail services to address workplace problems like financial stress, work stress, family issues, medical support, references, interpersonal relational issues, and skill development.
Professional assistance: The Managers are trained in addressing employee’s professional concerns like time management, communication, employee conflict resolution, and giving constructive criticism. They can reach out to them and can get associate with them as coachee or mentee.
Critical support care
The employee can reach out to the assigned mental health first aid helper for anxiety, panic attack, emotional turmoil, mood swings, personal crisis and special care. They make you feel settled with your emotions and provide assistance to professional help.
Suggesstions
The organizations are the gateways to promote mental health at workplace. It’s a comprehensive and integrated approach for the well-being of an employee. This has to be an established system within the organization for the employees to reach out for professional help as and when they needed. The employee’s mental health needed to be the primary focus for the organization’s growth and development. The organization should implement the employee assistance program across all levels to ensuring care and support to their employees. The employee counselling needs to be planned at regular intervals to ensuring availability of the mental health first aid helper during working and non - working hours. The employee’s personal problems need to be taken care on priority basis and the organization must be volunteered to give their primary support and care for the employees. The team must be trained to empathize and act on their personal need to make them feel safe and secure within the organization. The employee assistance program renders positive mental health support services to address their personal problems and connect positively with the organization.
Conclusion
The mental health of an employee is the need of the hour. Employers need to promote mental health continuously to make them aware of the programs that are run by the organization for their benefits. The change in the professional and personal life affects their mental health which in turn affects the organization productivity. The employee assistance program needs to be established with proper guidelines and ensuring the confidence of the employees. The organization should communicate with the employees frequently to understand their personal problems and address them with the expert solutions. The employer’s personally taken care employees are the greatest resource and assets to the organization.
References
Debra L., M.S, PhD, David A., Adler, M.D, William, H., & Rogers, F. (2010). Work performance of employees with depression: The impact of work stressors. American Journal of Health Promotion, 24(3), 205-213.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Fung, K.C. (2012). Workplace counseling in Hong Kong: A pilot study. Journal of International Social Issues, 2012.
Gurumoorthi, V., & Nalini, R. (2014). Employee assistance programmes a stress reliever in the workplace. International Research Journal of Business and Management.
Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx). http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool?params=gbd-api-2019-permalinkd780dffbe 8a381b25e1416884959e88b (Accessed 1 May 2021).
Jill Joyce. (2013). Facing the challenge of mental ill health in the workplace, 2013, ISSN: 1746-5729.
Karuna, B., Ellen, M.B., & Shinde, A. (2021). Promoting mental well-being through employee assistance programmes, NHRD Network Journal.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rahat, A.C. (2018). Burnout and its organizational effects: A study on literature review. Journal of Business & Financial Affairs, 7(4).
Richard, W., Donal, M., Isabelle, J., & Merike, S. (2013). Mental health promotion. The workplace mental health promotion handbook, published by the MHP Hands Consortium, ISBN 978-0-9575815-0-0.
Shrivastava, S., & Vineeta, P. (2019). Importance of effective communication strategies to improve workplace communication. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineerin, 8(3S3).
Sophia, B., Ali, A., Maureen, D., & Oliver, B. (2022). Contextualising the effectiveness of an employee assistance program intervention on psychological health: The role of corporate climate, 19, 5067.
Susmita, H., Akash, M. Mental Health at Work Place. The International Journal of Occupational Health & Safety, 2(1).
Received: 04-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-12657; Editor assigned: 07-Nov-2022, PreQC No. AEJ-22-12657(PQ); Reviewed: 18-Nov-2022, QC No. AEJ-22-12657; Revised: 22-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-12657(R); Published: 25-Nov-2022