Research Article: 2020 Vol: 23 Issue: 4
The Internal Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of Commercial Banks in Vietnam
Nga Phan Thi Hang, University of Finance-Marketing, Vietnam
Citation Information: Hang, N.P.T. (2020). The internal factors affecting the effectiveness of commercial banks in Vietnam. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 23(4).
Abstract
Banking service is a challenging service industry to measure output, change techniques, or increase productivity. There is disagreement over which banks produce services and how to measure them. Besides, banking services are often priced implicitly through market interest rates below deposit balances, making the observed revenue stream inaccurate to select key outputs to analyze. Therefore, the objective of the paper is to find out internal factors affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam. The researchers surveyed 650 managers of commercial banks and answered 25 questions, but the sample size of 607 managers processed. The data collected from January 2019 to December 2019 in Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai province. Simple random sampling technique. The paper tested Cronbach's Alpha and exploratory factor analysis (EFA). The study used for Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) technique. Finally, the findings of the study have internal factors affecting the effectiveness of commercial banks in Vietnam with a significance level of 0.01.
Keywords
Commercial, Bank, Effectiveness, Internal, Service.
Introduction
Efficiency is the condition that determines the survival and development of a bank. So it needs to improve efficiency also means strengthening financial capacity, the executive capacity to create accumulation and regulation (Lotto, 2018). Vietnam's economy is in the period of renovation, developing a market economy under socialist orientation with the regulation of the State. Vietnam is to have healthy economic development. Vietnam must have a system of essential elements necessary for the development process. The financial intermediation system in general and the commercial bank, in particular, contribute an essential part in the machinery of the whole system. It is a bridge between the subjects in the economy, making the subjects stick together and interdependent. The bank increases the linkage and dynamism of the whole system and plays an essential role in commercial banking activities (Bandaranayake, 2013). Besides, commercial banks have achieved much success during 20 years of innovation, especially in recent years.
In the increasing trend of attracting investment capital in Vietnam, banking is one of the forms of attracting indirect investment effectively from abroad. The development of financial markets, mainly the stock market, has contributed actively to the banking system at all angles. From April 1, 2007, to 2019, following WTO accession commitments, foreign commercial banks are allowed to establish 100% foreign-owned banks in Vietnam. Besides, Vietnamese commercial banks face the big challenge of competition, lost right in Vietnam. There are many causes giving rise to the limited existence of commercial banks in general and Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai province in particular. This study causes objectivity of the environmental factors, and the impact of macroeconomic difficulties, commodity market, real estate market, the gold market. But in nature and origin of the leading cause and profound cause still belongs to credit institutions and commercial banks themselves in the process of operation and development such as strategic orientation, business administration capacity, financial capacity, facility level, technology level (Gamage et al., 2014). Above mentioned things, the purpose of this study is to find out the internal factors affecting the effectiveness of commercial banks in Vietnam. This paper helps bank managers who apply the research results for improving business effectiveness better in the future.
Literature Review
The Effectiveness of Commercial Bank (EC)
Effectiveness is the implementation of the process from production/service investment to consumption or service provision in the market to make a profit. Commercial banks are most concerned about business effectiveness. Active business production/service helps banks survive and develop (Gamage et al., 2014). Under the ultimate goal, business efficiency is synonymous with profit categories, which are the difference between the results obtained and the costs spent to achieve that result. The effectiveness of business operations depends on the level of organization of production/service and management of each bank (Hsiao et al., 2010). Service business efficiency is an economical category associated with a market mechanism that is related to all factors in the production/service and business process such as labor, capital, machinery, information technology (Berger, 2017). A bank can only be highly effective when the use of the essential elements of the business process is effective.
Strategic Orientation of Service Development (SO)
A strategy is an action plan that is designed to achieve a number of specific goals, the commercial bank must have clear goals and to achieve that goal (Christopher, 2018). A specific strategy is needed. Without a long-term strategy with specific steps, the bank falls into a passive situation and quickly lose direction (Kaddumi, 2011). Therefore, commercial banks must develop a strategy for developing banking services to ensure the development of banking services with long-term plans, not discrete, arbitrary, and proactive activities. Besides the development orientation of banking services needs to adhere to the needs of the market in each operational area and to maximize the resources and competitive advantages of each bank, thereby achieving the bank's objectives (Kenjegalieva & Simper, 2011). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
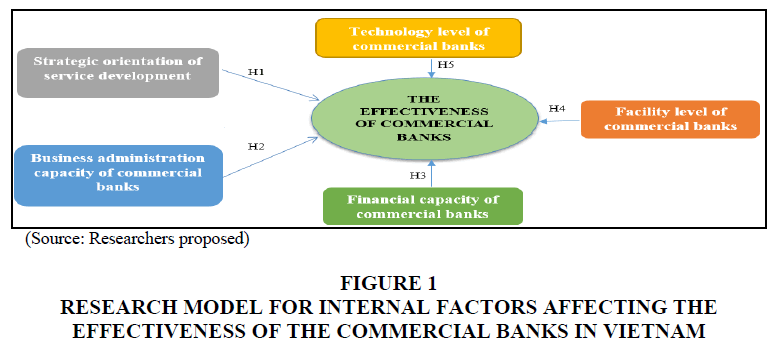
Hypothesis H1: Strategic orientation of service development has a positive impact on the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam.
Business Administration Capacity of Commercial Banks (BA)
Executive management of commercial bank management is one of the factors that significantly influence the development of commercial banking services. When the leadership of a commercial bank has good vision and excellent business management capability, it helps promote the development of banking services (Kumar & Gulati, 2010). The role of a manager is to manage and coordinate all the work and the whole machine related to customers and product consumption activities according to the bank's business strategy and in the right direction (Salamouris, 2019). This role requires a high level of focus from the managers, not only on jobs such as leading sales leads but also as representatives of the bank to customers and the market (Lotto, 2018). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H2: Business administration capacity has a positive impact on the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam.
Financial Capacity of Commercial Banks (FC)
Banks need to develop services; banks need to have strong financial potential (Sanchez et al., 2013). This factor plays a significant role in perfecting traditional services and developing new services to enhance the competitiveness of the bank (Mwarumba, 2013). The bank has financial strength that can ensure its scalability, invest in high-tech products such as ATM networks, online services. Financial potential is also a decisive factor and has information of customers into the bank. Customers tend to believe in vast, reputable, and healthy banks. Customers often look to more influential brand banks than the unknown banks (Mwarumba, 2013). So Financial of the bank needs increasing financial capacity is something that any bank wants to achieve. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H3: Financial capacity has a positive impact on the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam.
Facility Level of Commercial Banks (FL)
Technical facilities of the bank are part of the bank image (Rouissi & Bouzgarrou, 2012). The image of the right bank makes customers feel comfortable when trading and vice versa. Therefore, it can attract customers in using banking services. It said that this is also a factor affecting the development of banking services (Ong et al., 2011). Banks in developed countries pay great attention to the selection of transaction offices, facilities, and equipment for customers such as tables and counters suitable for communication and exchange with customers. Customers are waiting room chairs, paper documents with a beautiful design (Xuezhi & Pastory, 2012). Along with the banking equipment for internal use such as computer networks, with a fast, accurate, and safe payment system. This factor is to increase customer trust in the bank (Raphael, 2013). Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H4: Facility level has a positive impact on the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam.
The Technology Level of Commercial Banks (TL)
Banking technology has a decisive influence on service expansion, improving service quality, and method of service delivery to customers (Sultana & Haque, 2011). Moreover, the ability of bank management in business depends very much on the technology level of the bank. Therefore, the leapfrogging of modern banking technologies have the opportunity to develop banking services (Srinivas & Rwechungura, 2013). The modernization of banking technology is vital for commercial banks in existence and development. Therefore, banks are always looking for ways to innovate technology. Along with technological innovation is the introduction of banking services (Kenjegalieva & Simper, 2011). Thereby, it is increasing the competitiveness of the bank itself. Therefore, the following hypothesis built.
Hypothesis H5: Technology level has a positive impact on the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam.
A research model for internal factors affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam following (Figure 1):
Figure 1 Research Model for Internal Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of the Commercial Banks in Vietnam
Methods of Research
In this study, the research process for internal factors affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam, which had 11 steps following. Step 1: The researchers determined the research problem. Step 2: The researchers proposed the objectives of the study and collected theories and relevant studies. Step 3: The researchers applied the qualitative method. Qualitative research conducted to check the suitability of the theoretical model and to help discover, adjust, and supplement the observed variables used to measure research concepts to ensure the construction scale. In this study, qualitative research conducted through discussion, consultation with experts, and group discussions. Besides, during the discussion, experts gave complete comments on the content of the question, the words used in the questions used in the quantitative questionnaire later. Before discussing, the authors contacted and explored the possibility of participation, then sent an official invitation to meet to conduct group discussions to ensure the desired effect. Through the article, the researchers have the research process for internal factors affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam (Hair, & Anderson, 2010). Step 4: The researchers based the expert methodology and based on 30 bank experts' consultation as group discussions are to improve the scale and design of the questionnaire. The results of surveying 30 bank experts showed that internal factors are affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam. Step 5: The researchers created a list of possible factors gathered from the literature reviews, as mentioned in the above studies. Step 6: Discussions helped the author identify the factors that are suitable for the context of the commercial banking sector. Step 7: The researchers tested a reliability scale with Cronbach's Alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analysis. Completed questionnaires collected from the surveyed 100 managers related to the commercial banks, and it took them less than 30 minutes to finish the survey. Step 8: 650 managers were working for 15 commercial banks and answered 25 questions, but the sample size of 607 samples processed, 43 samples lacked information. The primary sources of data collected from January 2019 to December 2019 in Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai province. The researchers surveyed by hard copy distributed. The sample size of 650 managers working for 15 commercial banks represented. The research population has 50.000 managers who are working for 15 commercial banks. All data collected from the questionnaire coded, processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos (Hair & Anderson, 2010). Step 9: there are any observational variables with a total correlation coefficient greater than 0.3, and Cronbach's Alpha coefficient greater than 0.7 would ensure the reliability of the scale. This method based on the Eigenvalue, the appropriate factorial analysis, and the observed variables in the whole which are correlated when average variance extracted is>50%, the KMO coefficient is within 0.5 to 1.0, Sig coefficient ≤ 5%, the loading factors of all observed variables are>0.5. Also, the researchers testing scale reliability with Cronbach's alpha coefficient and exploratory factor analyses (EFA) performed. A least-squares method is a form of mathematical regression analysis that finds the line of best fit for a set of data, providing a visual demonstration of the relationship between the data points. Each point of Data is representative of the relationship between a known independent variable and an unknown dependent variable (Hair et al., 1998). Step 10: The researchers tested confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and had model testing with structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis. A research model is considered relevant to market data if Chi-square testing is P-value>5%; CMIN / df ≤ 2.0, some cases CMIN/df maybe ≤ 3.0 or<5.0; GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. Besides, the GFI accepted with a value of 0.8; RMSEA ≤ 0.08. The value of the Average Variance Extracted is greater than 0.5. Step 11: The researchers had conclusions and managerial implications.
Research Results
Research results showed that the researchers surveyed 650 managers working for 15 commercial banks in Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai province, but 607 managers processed. Because there are 43 samples lacked information. Besides, the Data collected from January 2019 to December 2019 in Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai province. The researchers used a simple random sampling technique, and Cronbach's Alpha tested. The scale reliability tests for internal factors affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam bellowed.
Table 1 showed that all of 25 variables surveyed Corrected item-total Correlation greater than 0.3 and Cronbach's Alpha if Item deleted greater than 0.8. These results showed that all of Cronbach's Alpha is very reliable. Such observations make it eligible for the survey variables after the testing scale. Cronbach's Alpha of strategic orientation of service development is 0.936 (>0.6); business administration capacity of commercial banks is 0.913 (>0.6); financial capacity of commercial banks is 0.949 (>0.6); facility level of commercial banks is 0.849 (>0.6); Cronbach's Alpha of technology level of commercial banks is 0.944 (>0.6), and Cronbach's Alpha of the effectiveness of commercial bank (EC: EC1, EC2, EC3, EC4) is 0.848 (>0.6). This Data was suitable and reliable for researching.
| Table 1 Cronbach's Alpha for Internal Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of the Commercial Banks in Vietnam | |
| Items | Cronbach's Alpha |
| SO1: Set visions or goals that the commercial bank wants to achieve in the future | 0.936 |
| SO2: Study business environment to determine which factors in the current environment are risks or opportunities for the bank's goals and strategies | |
| SO3: Product/service strategy is an art that combines the resources of businesses to create competitive advantage | |
| SO4: Review and control the plan in the implementation model that is consistent with the business goals | |
| BA1: Managers understand and have the market forecast for revenue | 0.913 |
| BA2: Managers build and developing relationships in business | |
| BA3: Managers are responsible for negotiating with a range of stakeholders including customers, employees, directors and other suppliers | |
| BA4: Managers have to foresee any changes in the landscape and take strategic management to help the bank adapt to those changes | |
| BA5: Managers conduct regular training and development for employees and conducting employee reviews to the team | |
| FC1: Capital sources are financial resources that banks can rely on to conduct business activities and provide services to the economy | 0.949 |
| FC2: Equity is a self-owned resource that a bank owner owns and uses for business purposes by the law | |
| FC3: The mobilized capital sources of commercial banks include: Deposits of economic organizations and individuals | |
| FC4: Efficient use of capital: Profitability is assessed based on two indicators: Return on Equity (ROE) and Return on Asset (ROA) | |
| FL1: Commercial bank has conditions on material facilities, technical equipment for transaction | 0.849 |
| FL2: Transaction counters arranged to ensure asset safety and facilitate the supervision of cash collection and spending activities of transactions. | |
| FL3: The system of equipment is fully connected to the network to update, process, test, control, exploit and store data safely, accurately, quickly and conveniently | |
| FL4: Commercial bank has security measures to ensure safety and confidentiality of data in the program, system access key, and electronic signature | |
| TL1: Blockchain technology set up to fundamentally transform banking and financial services | 0.944 |
| TL2: Technology allows banks to provide faster, more transparent experiences to consumers | |
| TL3: The mobile and digital transformation in the banking system is just beginning | |
| TL4: Commercial bank has adaptation and sustainable development in the Industry 4.0 | |
| EC1: Strategic orientation of service development affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks | 0.848 |
| EC2: Business administration capacity affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks | |
| EC3: Financial capacity affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks | |
| EC4: Facility and technology level affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks | |
| (Source: The researcher’s collecting data and SPSS 20.0) | |
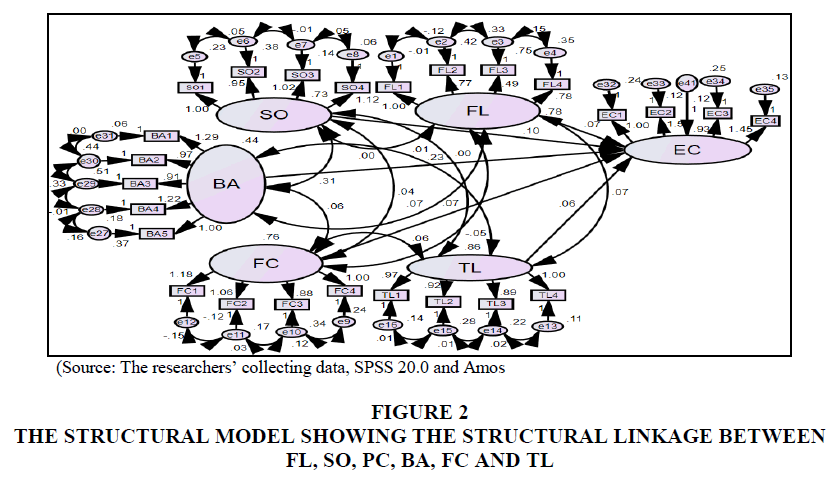
These results showed that five internal factors are affecting the effectiveness of commercial banks in Vietnam with a significance level of 0.01. Besides, Table 2 showed that standardized coefficients of the model arranged from high to low following: (1) Standardized Coefficient of business administration capacity of commercial banks is 0.364 and tested significantly at 1 percent. (2) The standardized Coefficient of strategic orientation of service development is 0.205 and tested significantly at 1 percent. (3) The standardized Coefficient of facility level of commercial banks is 0.152 and tested significantly at 1 percent. (4) Standardized Coefficient of financial capacity of commercial banks is 0.136 and tested significantly at 1 percent, and (5) Standardized Coefficient of technology level of commercial banks is 0.136 and tested significantly at 1 percent. This result is the basis for the research team to propose recommendations. The results of evaluating the reliability of the scale, analyzing the exploring factor EFA and the confirmed factor CFA with the measuring criteria of the theory remain unchanged from the beginning of the study. The structural model showing the structural linkage between FL, SO, PC, BA, FC, and TL following: Chi-square=844.724; df=244; p=0.000; Chi-square/df=3.462; GFI=0.903; TLI=0.944; CFI=0.954; RMSEA=0.064 (Figure 2).
| Table 2 Coefficients from the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) | ||||||||
| Relationships | Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | S.E | C.R. | P | Conclusion | ||
| EC | ← | FL | 0.073 | 0.152 | 0.021 | 3.571 | *** | H4: Supported |
| EC | ← | SO | 0.102 | 0.205 | 0.023 | 4.494 | *** | H1: Supported |
| EC | ← | BA | 0.233 | 0.364 | 0.033 | 6.998 | *** | H2: Supported |
| EC | ← | FC | 0.066 | 0.136 | 0.019 | 3.575 | *** | H3: Supported |
| EC | ← | TL | 0.060 | 0.132 | 0.017 | 3.474 | *** | H5: Supported |
(Source: The researcher’s collecting data and SPSS 20.0, Amos)
Conclusions
Nowadays, commercial banks have a crucial role in the market economy. They are the bridge between the subjects in the economy. Commercial banks are making the entities attached and dependent. They are increasing the alignment and dynamism of the entire system. Besides, commercial banks have become an indispensable financial institution to operate the economy, especially the State-owned commercial banking system is also considered an "effective arm" of the Government in implementing monetary policy, currently targets macroeconomic stability, curb inflation and ensure the social security of the country. In this period, commercial banks vigorously implemented solutions to support enterprise development, most notably the harsh banking industry in reducing interest rates to increase access to capital for enterprises. Also, commercial banks are reducing interest rates, and commercial banks have effectively implemented a series of credit programs and policies that contributed to supporting economic development and ensuring social security. Research results showed that the researchers surveyed 650 managers of commercial banks and answered 25 questions, but the sample size of 607 managers processed. The data collected from January 2019 to December 2019 in Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai province. Simple random sampling technique. The findings of the study have five internal factors affecting the effectiveness of the commercial banks in Vietnam with a significance level of 0.01. Finally, (1) Standardized Coefficient of business administration capacity is 0.364. (2) Standardized Coefficient of strategic orientation of service development is 0.205. (3) Standardized Coefficient of facility-level is 0.152. (4) Standardized Coefficient of financial capacity is 0.136, and (5) Standardized Coefficient of technology level is 0.136, with significance at 1.0 percent. The researchers had managerial implications for the bank policymaker of Vietnam continued to improve the effectiveness of the commercial banks following.
Managerial Implications
The study mentioned above of the authors of the article presents some policy implications.
Firstly, managerial implications for business administration capacity. It needs to improve operational efficiency at commercial banks, the reduction of input costs such as interest payment, reduction of deposit rates at the request of the State Bank, and increase salary costs. Reasonably, commercial banks need to streamlining the personnel apparatus, reducing other expenses such as management costs and advertising costs are essential. Besides, commercial banks continue improving the quality of bank staff. Commercial banks need training and retraining staff to perform well in the operations of modern banks.
Moreover, it is necessary to standardize the contingent of personnel engaged in international integration, especially those directly involved in the process of negotiating and signing international contracts, inspectors, supervisors, and officials. Commercial banks specialized in international law work, staff using and operating new technology. Commercial banks are well aware that the challenges in the integration process are enormous and increasingly complex. But this process helps the banking sector take advantage of opportunities for development, thereby empowering the competitiveness of the banking system and Vietnamese enterprises in the international arena. Therefore, the task of economic development and international integration in the coming years is cumbersome. In particular, 2020 is an important year for Vietnam, the first year to implement the five-year plan, and it is a year that needs more vigorous efforts in international economic integration for Vietnam.
Secondly, managerial implications are for the strategic orientation of service development. Commercial banks need to gradually increase the scale to reach a larger scale of efficiency corresponding to other development targets of the bank. Besides, commercial banks need to improve and simplify administrative procedures, loan procedures to facilitate customers. Commercial banks need to identify target customers, build customer strategy, and enhance network development. Commercial banks continue building the right customer strategy; banks and customers are always sticking together to create, maintain, and develop lasting relationships with all customers. It is necessary to appreciate traditional and reputable customers in banking transactions. For these customers, commercial banks continue building a strategy; the bank must pay close attention to associate the bank's activities with the customers' activities, appraise, and timely invest in projects with clear and valid results. Besides, the product characteristics from the banks are similar, so commercial banks continue creating a difference is very important.
Thirdly, managerial implications for facility level. Commercial banks need to focus on investing in human resources, modernizing banking technology, promoting the application of new technologies. It is necessary to orient the shift from information technology application in width to development and application according to depth, especially the latest achievements of the 4.0 digital revolution today. Commercial banks need to choose technical solutions, advanced equipment to bridge the gap in technological level with developed countries. Commercial banks continue to formulate software application programs rationally with international standards and suitable to the conditions that Vietnam can connect and expand in a high-tech environment and international economic integration. Therefore, Commercial banks continue strengthening cooperation and links between the other banks and economic organizations, between the banking systems in the field of technology, expanding e-banking services, innovating customer service methods to promote propaganda, new products, and services to all strata to attract customers, develop markets.
Fourthly, managerial implications for financial capacity. Commercial banks need to invest in facilities and expand the network: The commercial banks need to expand their network of operations, targeting the customer segment to actively expand the market and occupy a significant market share in the process of the meeting. The commercial banks also need to focus on equipping with modern and impressive equipment specific. Commercial banks need to change obsolete and outdated equipment and machines with modern machines to speed up the working speed of employees, contributing to saving time for customers. Commercial banks continue improving credit quality to improve capital quality. Commercial banks need to build their credit risk management system, namely: establishing credit objectives, the level of risk from credit activities that must be measurable. At the same time, the quality of the credit debt is paid attention not only to on-balance sheet assets but also to the off-balance sheet items. Commercial banks should develop and update credit risk management strategies and policies with new Vietnamese laws and international risk management standards.
Finally, managerial implications are for the technology level. Commercial banks need to develop a lending strategy along the value chain. Commercial banks study and choose loans by stages and stages in the value chain. Commercial banks can lend before harvest or provide raw materials, and this can apply for trade finance, serving the consumer, and having the distribution of agricultural products. Besides, commercial banks continue to diversify banking products and services. Commercial banks are deploying this solution; in the coming time, banks need to "refresh" themselves to meet the integration needs through diversifying products and services. Besides, Commercial banks continue maintaining traditional products and services; it is necessary to promote the development and development of new products such as derivative products, attract remittance sources based on cooperating with labor export companies, overseas remittance service companies, foreign correspondent banks.
This paper studied the factors affecting the effectiveness of commercial banks in Vietnam that assessed the impact of each factor on the effectiveness of commercial banks. However, research results still have some restrictions and open up further ways for future research: (1) Current samples studied in a small scope and scale in HCMC and Dong Nai province. So, the next study can assess more precisely the impact of these factors on the intention to use banking services in rural areas and the suburbs of other cities. It needs to expand the size and scope of the study sample. (2) Regardless of studied factors: perceived usefulness, perceived to use, trust, social norm, communication, and innovation, there could be other factors that also affect the effectiveness of commercial banks to use banking services in rural areas. The next research can edit and add to the more comprehensive studies that intend to use banking services in rural areas and suburbs. (3) Other studies have focused on the impact of the demographic characteristics of consumers to accept the behavior of new products on the effectiveness of commercial banks. In this study, the authors did not analyze the impact of demographic variables are to accept and use banking services in rural areas and suburbs for the effectiveness of commercial banks. Perhaps, this is the author's next research in the future.
References
- Christoliher, E.I. (2018). Determinants of banks lirofitability in develoliing economy: evidence from the Nigerian banking industry. Interdiscililinary Journal of contemliorary research in business, 4(1), 155-161.
- Bandaranayake, S. (2013). Factors influencing the efficiency of commercial banks in Sri Lanka. SriLankan Journal of Management, 18(1), 1-12.
- Berger, A. (2017). The efficiency of commercial banks: international survey and directions for future research. Euroliean Journal of Olierational Research, 9(8), 175-212.
- Gamage, C.T., Lock, K.L., &amli; Fernando, A.A.J. (2014). A liroliosed research framework: Effectiveness of internal control system in state commercial banks in Sri Lanka. International Journal of Scientific Research and Innovative Technology, 1(5), 25-44.
- Hair, B.B., &amli; Anderson. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis (7th ed.). New York: US: liearson lirentice Hall.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., &amli; Black, W. (1998). Multivariate Data Analysis with Readings. US: lirentice-Hall: Ulilier Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Hsiao, H.C., Chang, H., Huang, H., &amli; Cianci, A. (2010). First financial restructuring and olierating efficiency. Journal of Banking and Finance, 34(1), 1461-1471.
- Kaddumi, T.A. (2011). Determinants of bank lirofitability: Evidence from Jordan. International Journal of Academic Research, 3(4), 180-191.
- Kenjegalieva, A., &amli; Simlier, R. (2011). liroductivity analysis of Central and Eastern Euroliean banking, taking into account risk decomliosition and environmental variables. Research in International Business and Finance, 25(1), 26-38.
- Kumar, S., &amli; Gulati, R. (2010). Measuring efficiency, effectiveness, and lierformance of Indian liublic sector banks. International Journal of liroductivity and lierformance Management, 59(1), 51-74.
- Lotto, J. (2018). The emliirical analysis of the imliact of bank caliital regulations on olierating efficiency. International Journal of Financial Studies, 6(2), 34-42.
- Mwarumba, M. (2013). Credit risk, caliital adequacy, and olierating efficiency of commercial banks in Kenya. International Journal of Business and Management Invention, 2(9), 6-12.
- Ong, T.S., Teo, C.L., &amli; Teh, B.H. (2011). Analysis of financial lierformance and efficiency changes of Malaysian commercial banks after mergers and acquisitions. International Journal of Business and Management, 1(2), 1-15.
- Ralihael, G. (2013). Bank-sliecific, industry-sliecific and macroeconomic determinants of bank efficiency in Tanzania: A two-stage analysis. Euroliean Journal of Business and Management, 5(2), 142-155.
- Rouissi, R.B., &amli; Bouzgarrou, H. (2012). Cost efficiency of French commercial banks: domestic versus foreign banks. The International Journal of Business and Finance Research, 6(4), 101-112.
- Salamouris, D. (2019). Efficiency measurement of the Greek commercial banks with the use of financial ratios: a data envelolie analysis aliliroach. Management Accounting Research, 15(2), 201-224.
- Sanchez, M.K., Hassan, J.R., &amli; Barkus. (2013). Efficiency determinants and dynamic efficiency changes in Latin American banking industries. JCC. The Business and Economics Research Journal, 6(1), 27-52.
- Srinivas, M., &amli; Rwechungura, A.K. (2013). Determinants of bank lirofitability in a develoliing economy. Emliirical evidence from Tanzania. Asian Journal of Research in Banking and Finance, 3(11), 11-23.
- Sultana, R., &amli; Haque, M.E. (2011). Evaluation of Internal Control Structure: Evidence from Six Listed Banks in Bangladesh. ASA University Review, 5(1), 69-81.
- Xuezhi, Q., &amli; liastory, D. (2012). Commercial banks lirofitability liosition: The case of Tanzania. International Journal of Business and Management, 7(13), 21-34.