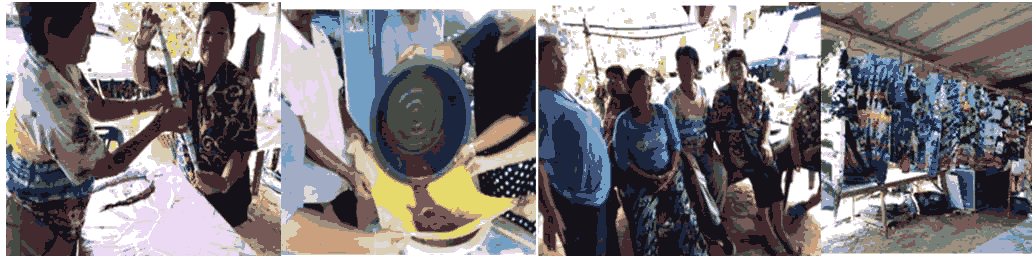Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 2S
The Model of Product Development for the Elderly, Thasap Subdistrict, Mueang District, Yala Province, Thailand
Sasadee Kamphaengdee, Yala Rajabhat University
Piyada Maneenin, Yala Rajabhat University
Chompunuch Sriphong, Yala Rajabhat University
Citation Information: Kamphaengdee, S., Maneenin, P., & Sriphong, C. (2022). The model of product development for the elderly, Thasap Subdistrict, Mueang district, Yala province, Thailand. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S2), 1-8.
Keywords
Model, Elderly, Product Development
Abstract
The increasing number of the elderly is one of the social struggles that urgently need to be solved by enhancing the potential for their self-reliance. Therefore, this research aims to synthesize factors related to the development of the elderly creating model and the development of elderly products. The research was conducted qualitatively by analyzing the data from the concepts and related theories. This was done by creating model form factors used in the development of elderly products in-depth interviews and group discussions with 10 elderly who received job skills training. The results of the study found that there are 6 components. 1) The personal factors of the elderly including personal attitudes and personal skills and abilities. 2) Job skills training consists of job skills training methods and content in job skills training of the elderly. 3) Environment aspect which consists of group gathering, training tools, and budget support. 4) Decision-making consists of understanding problems and discrimination. 5) Motivation consists of building relationships, careers opportunity, and incomes. 6) Product skills development consists of job skills training satisfaction, applying knowledge to create products which led to the creation of a career development model for the elderly. These help the elderly to develop products, build a career, and earn money. All mentioned factors can be taken into consideration when applied with the elderly in other communities and also be a policy guideline in career management which to increase the potential of the elderly in a sustainable way.
Introduction
The Situation of the Elderly
The situation of the number of the elderly nowadays is rapidly increasing. This may vary in different environments such as the advancement in medical, contraception, and the daily competition which is affecting the decline of fertility. In the near future, many countries are gradually emerging into an aging society. In Thailand, the old-age rations have steadily increased since 2010 (Office of the National Economics and Social Development Council, 2021). (Table 1)
| Table 1 The Number and Estimated Elderly Population |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total population | Population of age over 60 | Proportion of population age over 60 |
| 2010 | 67,313,000 | 8,011,000 | 11.9 |
| 2020 | 70,100,000 | 12,272,000 | 17.5 |
By the year 2021, Thailand is considered as an Aged society, there is an estimation of the proportion of elderly over 60 as 20 % of the total population. Entering into the Aging Society affects a country long term country’s development and the economic growth rate in terms of economic growth, budget, economy, and overall welfare (Department of Older Persons, 2019). Almost older persons have mainly had health problems and chronic diseases, which cause high expenses of self-care. However, the fact that almost all people still understand of coping with the situation is only dealing with the elderly’s health. Therefore, the solution is limited to the certain group such as the elderly subsistence allowance payment, management of various welfares. The situation of an aging society in the country is highly focused which affecting the overall national economy. The learning environment and sharp decline of participation in social activities (Maurer, 2001) can cause unemployed and lack of income that relatively low in economic potential. However, a new generation of elderly who is educated can remain powerful and potential in society if they have been supported in career, earning money, this can be created more opportunity of self-development of elderly. Some business sectors provide an opportunity for long-term experience and skill elderly workers to operate in business. As a result, the numbers of hiring elderly workers are increasing and relate with local elderly workers enter into the labor market. However, this is not enough of decreasing society's burden. Many areas have realized the problem; therefore, they encourage elderly people and manage local natural resources to become products or services. This is a way for self-reliance and support among elderly people (Community Development Department Ministry of Interior, 2021). The government probably supports and facilitates in various fields to encourage the elderly to use their full potential. From mentioned reason, there is an interesting of researching in elderly to perceive factors and important components of promoting and improving the life quality of elderly in sustainable from many parties and able to generate their income to be self-reliant.
Objective
To determine the factors associated with the occupation development for the elderly and create a model of product development for the elderly to apply the model as a guideline for product development for the elderly, Thasap Subdistrict, Mueang District, Yala Province, Thailand.
Literature Review
The product development for the elderly, Thasap Subdistrict, Mueang District, Yala Province, Thailand, has theories and related research with this research as follows;
Social Theory Relevant With Aging Society Concept
Social theory is a theory that discusses the tendency of roles, relationship and social adaption in elderly. This theory tries to analyze the reason of changing social status and help the elderly have a happy life in society. Robert (1960) described that the elderly social status emphasizes on the positive relationship while doing activities and the elderly’s life satisfaction. This means that when people are getting older, their status and social role will be declined. However, the elderly’s social needs remain the same as when they are in the middle age with the belief that elderly wants to participate in activities for their happiness and quality life as if they were adult. In addition, they expected to participate in the activity that they are interested in. This includes the activity that they do it to themselves and the activity that they do it for others for example, friends and social or community. The activity can make the elderly feel valuable and useful for the community. The satisfaction of elderly derives from being able to continuously do the activities that they have been doing from the past until present. The mentioned activities can be divided into 3 categories which are, first, an informal activity, the activity related to other person both in a family and in a society with no time boundary or any particular roles. The activities can be cooperated by elderly and family or close ones. Moreover, craft is one of activity that can support financial of the family, this none-format activity benefits to both elderly and family. Second, a formal activity refers to the activity in which the elderly participates in the organization such as community, club or group activity. Finally, solitary is the activity that can be done independently, or the elderly can do it alone such as hobbies, sleep, relaxing activities, etc. The elderly will get the benefit and obtain satisfaction as well as being relaxed and having pleasure (Palo, Limone, Monacis, Ceglie & Sinatra, 2018). The activities were adjusted to be appropriated to facilitate learning and support elderly to participate various activities.
Learning Theory of Elderly
The elderly learning is important and beneficial for living. Strauch & Alomar (2014) stated that learning is a complex process which able to convert information and experience into knowledge, skill, behaviors, and attitudes. Dollard& Miller (1950) suggested that the learning theory consists of four processes: 1) Drive is motivation force in person and can be learned by person’s entire brain, sensory system and muscles. Drive also defined as stimulus which impels action and readiness to be learned. 2) Stimulus is environment of a situation that person notices at the time and affect to behavior and response. In learning environment, stimulus is teacher, learning activities and learning tools. 3) Responses are aspects of person’s behavior after they are stimulated that can be noticeable and unnoticeable such as movement, thinking, perception, interesting and feeling. 4) Reinforcement is to reward something to person which enhancing the power of connection between stimulus and responses. Reinforcement has both negative and positive aspect which is huge effects to learning process in person. This complies with Bryan & Duay (2008) and Knowles & Malcom (1970) that learning needs to be supported by different elements such as environment, experience, interesting topics and curriculum organized according to the learners’ interest with the consideration on the elderly basic needs in order to create training atmosphere that can stimulate their interests.
Discussion Concept
The decision making is one of the most important factors because it depends on the person who makes the decision. Therefore, the decision maker needs to have accurate information and rationale to achieve their goal (Walters, 1978). Making decision is about selecting the options from various options. Decision-making is the process of resolving what we have known as problem, by searching options and select the best choice in order to achieve objectives or goal of the organization’s regulation otherwise it is the decision process to select which service and what objectives of this selection. The guideline of making decision is came from marketing strategy ( Assael, 1998) therefore, making decision means action of decision with no time for searching the fact and to adjusted according to what is need. The decision-making process consist of 1) Problem recognition 2) Analyzing and identify cause of the problem 3) Searching options 4) Evaluate options 5) Select the best options and 6) Apply chosen option into practice.
Motivation
Motivation is behavior’s controller of human which caused by demand, pressure, and desire to achieve objectives Noe (1986) stated that develop skills in a career can be predicted significantly of motivation of development skill in career. Therefore, the motivation in develop skill in career will happen when elderly are confident with their ability to enhance their skill and knowledge in a career with the result. Personal motivation is about a good relationship, self-valuable, and the opportunity of earning money from development skills (Baldwin & Ford, 1988) which consists of the pleasure of training in a career and satisfaction of using skill and knowledge in their career. Satisfaction in job skills training affects learning behaviors, interests, and learning motivation, satisfaction with occupational skills and knowledge refers to the likelihood that the elderly develop occupational skills and apply the knowledge, skills, and attitudes gained from development in the practice of providing resources and functions that can be applied to what is gained from the development program.
Training
Training is the process of learning for participants to gain new knowledge to enhance or develop competence in various fields as well as improved behavior which is value expression that complies with the objectives (Baldwin & Ford, 1988). This is the training plan which consists of the ways of training and contents. The job skills is aimed for many purposes whether the learning content, which can use the knowledge for their career, teachers who is the one to encourage the elder have thinking process and participate in the skill development like (Rogers, 1969) has said that the role of the instructor should be making it convenient for learning. The important qualification consists of 1) the trust and respect in students, being honest with students, understanding, and empathy including paying attention what the learners said; 2) the content is consistent with learners ‘requirement, it refer to the elderly have right to participate of select content of training to meet their interest and can be used contents for their career 3) the environment in job skills training including with technology support, which Noe (1986) added grouping opportunity, funding to support the promotion, facilitate for elderly who are trained to exercise their knowledge, skills, and attitudes in their career. Moreover, technology support is also used to enhance the ability to apply knowledge, skills, and attitudes from training into their career. By providing important and necessary information for the elderly who entering development training to be an additional resource and transfer their knowledge from training.
Occupational Development in Elderly Concept
Group activity is an important key for changing in the elderly because the development in elderly will lead to behavior change that will lead to quality in work and effective in any activities. This is because the elderly have functional thinking, long experience, knowledge, and leadership. The elderly have clear communication and ability to experience to the young generation. Dewalertsakul, Siriworasakul & Rodyim (2016) said that development is driven people to create good performance according to their responsibilities, especially if they are fully supported (Tungsakul, 2010), with factors of knowledge, skills, confidence, leadership, goals, or achievements. These factors can create a career, earn money to be self-reliant and be able to manage a group with efficiency and sustainability by using business. Gillian & Boulton, 2010 proposed a model to increase opportunities for the elderly, this is based on participation and stability to enhance the quality of life for their age.
Research Methodology
This research is qualitative research that consists of documentary analysis, in-depth interviews, and focus group discussions with elderly who enrolled in job skills training and analysis of key points from the interview (major theme). The main themes are then divided into sub-themes and the research results are presented using a descriptive research method. The researcher studied the data of 10 elderly people in Tha Sap Sub-district, Muang District, Yala Province, aged 60 years and over, using homogeneous sampling with backgrounds or experiences similar to those with research’s objectives (Suthiwasinnon & Phasunon, 2016) and participation continuously in elderly activities not less than 1 year. This research is participatory, the variables consisted of; personal data, training, knowledge, decision-making, motivation, and occupational development in the elderly. This research was conducted by an in-depth interview with individuals to let the sample group feel free to express their opinions for various information and also recorded group conversation and validated information by using the data triangulation method, examining different data sources which can help to validate data before analysis.
Results
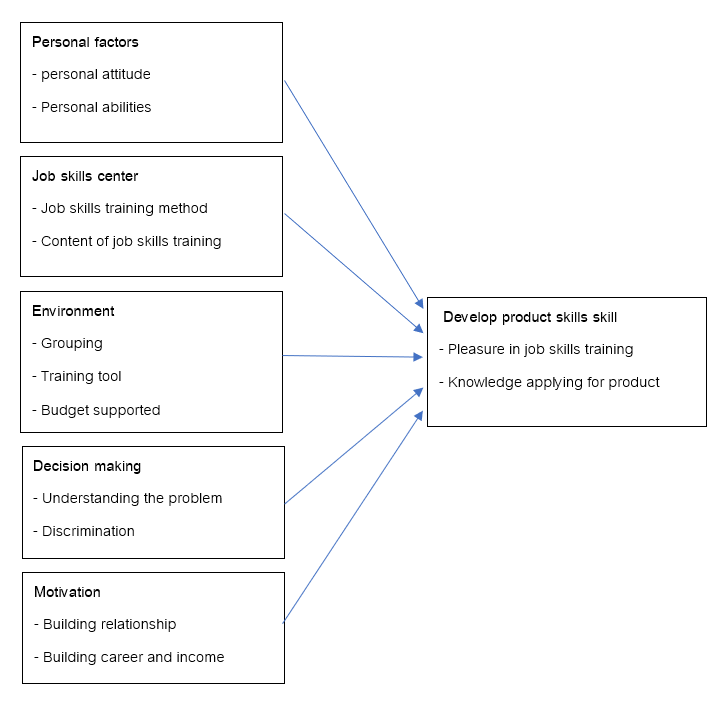
This research collected data from 10 elderly people who were female with marital status and age in a range between 61-65 years old. The highest education is a primary school, and occupation almost agriculture. They have an average income of 3,000 baht. The proportion of business experience is 80% and regularly participates in activities of government for elderly with their convenience. From the review of concepts, theories, and related research, it was found that the factors of the skills development of the elderly consisted of personal factors, training, environment, decision-making, motivation, and product skill development. It can be modeled as follows. (Figure 1)
Figure 1: Model of Product development of Elderly
Resource: Product development model of elderly developed from concept, theory and research study
Factor Analysis Related To the Development of Elderly
According to the individual interviews and group discussions, the results show 6 important factors; this can be described as 13 sub-points as follows.
1. Personal factors of the elderly can be classified into 2 components: 1) personal attitude, the elderly didn’t recognize how much knowledge that they have, participate in the group is aimed to enhancing their job skills. Almost the elder have business knowledge but joining a group is for pleasure. 2) Personal abilities, the elder have different knowledge and skill, but are still useful and can be applied in their career in the future. Their knowledge is reinforcement for self-improvement and uses their free time productively, not to be a burden.
2. Job skills training can be classified into 2 components which are 1) Job skills training methodology, the elder have been inquired for what they interest in content and train method. They are grouping and training in each section, this is prevented of stress and well focus on content including time allocation for elderly to join and exercise to understand the process and can bring knowledge to develop a new product for commercial 2) content of job skills training has to comply with their interest, not too complicated, easy and quick understanding. When it in practice, the elderly feels relieved and not much stress until give up and can do it by themselves and also be a tool for earning money, reduce family burden by creating a model to be a guideline for the elderly to follow and the product can be sold and meet customers ‘requirement.
3. Environment can be classified into 3 components 1) Grouping is to gather elderly who want to develop their self into creating an opportunity to use their knowledge, exchange knowledge and support each other in work because each elderly has different skill so that their knowledge can be transfer to other people. The place of group gathering must be able to travel easily, safe and close to their residence because the elderly cannot travel long distances and the group activities must be continuous. Groups gathering must be at least 2 days a week, including important calendar days. 2) Training tools, there should have enough tools for elderly to facilitate in training, such as production equipment, computers, and the internet which suitable and easy understand for elderly to research more information and media 3) Budget support, the budget should be provided by local government agencies, this is to provide long term support for training, including the budget for after the training to elderly to have funds for their careers, and also register community products or community enterprises to create awareness and expand the market to increase selling product as well.
4. Decision making can be classified into 2 components: 1) Understanding the problem, the elderly need to understand the lack of job skills knowledge, skills, and work processes, therefore they are willing to participate in job skills training to solve problems in operation. This is also to make the elderly have good mental health because they can meet, talk, exchange knowledge with people of the same age and adapt to society well, making them appreciate the value of life and use their free time productively; 2) discrimination, the elderly understanding of job skills training, able to apply knowledge for their preferences. This can brings happiness, self-esteem and can generate income for self-reliance in the future.
5. In terms of motivation, it can be classified into 2 components: 1) building relationships in participating in job skills training activities, this lead to elderly meet, discuss, and exchange their feelings about life. Therefore, they can understand each other and be able to help each other when it's a time of trouble and also train their life to live in society as well; and 2) for career and income, entering in job skills training that meets their requirements can create opportunities for career building. They can produce the products for sale and can earn money, therefore to bring that income for daily life or help the family.
6. Product skill development can be classified into 2 components: 1) satisfaction with job skills training, the elderly can apply knowledge from the job skills training in the long term of their career and also able to create new products earn more money. Supported by the government which provided market and products are accepted by customers. That will bring the elderly satisfied with the job skills training and wanted to have more training continuously. 2) Using knowledge to create products, the elderly design products that meet their requirement and expand their knowledge. Knowledge gained from job skills training is shared with the elderly within the group and outsiders. There is a plan to develop it as a learning center in the community as well.
The Development of Product Produced from Job Skills Training
According to the creating of elderly product development model, all elements can be included into the process of product development. This can be done by brainstorming knowledge from job skills training and gather individual ability. This is in order to to select and create products that the elderly is interested in including finding methods that can be performed easily and quickly. There is a procurement plan for production which is suitable for the budget and work together to achieve the goal, grouping of elders can developed a tie-dye product , they worked together to design patterns that were used in various productions, bright colors, using readily available and local materials until the product came out in the form of new tie-dye pattern, tie-dye fabric and tie-dye fabric bag as an alternative to customers until able to generate income and create a career to support themselves. Therefore, the elder have a goal to bring products into applying for community product standards and registering community enterprises in the future, this to enhance product quality and adding more value.
Discussion and Conclusion
From the study of the product development for elderly by synthesizing the concept theory and research with the relevant factors which related to product development for elderly which consists of 6 factors, including personal factors, job skills training, environment, decision-making, motivation, and product skill development and then synthesize each component to obtain a model that meets elderly’s requirement. Then apply the model to the elderly group. This creates a process of job skills learning and enhancing the elderly’s potential from the experience, applying knowledge from job skills training to create an opportunity of earning money. This is consistent with the concepts of (Bryan & Duay, 2008; Knowles & Malcolm, 1970) that identified factors to support job skills learning such as the environment, experiences, and interest topic. Provide courses according to the needs of the learners focus on basic needs of the elderly to create an atmosphere suitable for training to motivate them more interested, which is consistent with (Palo, Limone, Monacis, Ceglie & Sinatra, 2018) that adjusted learning to be appropriate and facilitate the learning process and encourage the elderly to participate in learning activities, the course should have content that is easy to understand, not complicated, and has activities to exchange of knowledge, therefore the elderly can do activities together. The factors should also be considered, such as the elderly's specific goals, abilities, and level of experience, this consists of (Gillian & Boulton, 2010) that has proposed a model to increase opportunities for the elderly based on participation and stability to enhance the life quality for their age which will focus on learning and participation from the activities, the results of the research can apply all 6 factors to apply to the elderly in other communities and also to be used for developing a variety of products. This enables the elderly to be self-reliant and also leads to creating a guideline of policies for the development of the elderly.
References
Assael, H. (1998). Consumer behavior and marketing action. Ohio: South Western.
Baldwin, T.T. & Ford, J.K. (1988). Transfer of training. Personal Psychology, 41(65).
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Bryan, V.C., & Duay, D.L. (2008). Learning in later life: What seniors want in a learning experience. Educational Gerontology Journal, 34(12), 1070-1086.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Community Development Department Ministry of Interior. OTOP concepts and principles.
Dewalertsakul, N., Siriworasakul, W., & Rodyim, C. (2016). The development of the elderly as a burden to power: Case study of Rangsit city municipality. Veridian E-Journal, Silpakorn University, 9(1), 529-545.
Dollard, J., & Miller, N.E. (1950). Personality and psychotherapy and analysis in terms of learning and thinking and culture. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
George, J., & Jones, G. (1996). Understanding and managing organizational behavior. New York: Addison-Wesley.
Gillian, M., & Boulton-Lewis (2010). Education and learning for the elderly: Why, how, what. Educational Gerontology Journal, 36(3), 213-228.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Knowles, M.S. (1970). The modern practice of adult education. New York: Association Press.
Maurer, T.C. (2001). Career-relevant learning and development, worker age, and beliefs about self-efficacy for development. Journal of Management, 27, 123-140.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Noe, R.A. (1986). Trainee attributes and attitudes: Neglected influences on training effectiveness. Academy of Management Review, 7, 433-441.
Office of the National Economics and Social Development Council. Population statistics.
Palo, V.D., Limone, P., Monacis, L., Ceglie, F., & Sinatra, M. (2018). Enhancing e-learning in old age. Australian Journal of Adult Learning, 58(1), 88-109.
Peck, R.F., & Havighurst, R.J. (1960). The psychology of character development. New York: Wiley.
Roger, C.R. (1969). Freedom to Learn. Columbus. Ohio: Charles E. Merril.
Schiffman, L.G., & Kanuk, L.L. (1994). Consumer behavior (5th Edition). Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall.
Strauch, C.C., & Alomar, M.J. (2014). Critical analysis of learning theories and ideologies and their impact on learning: “Review article ". Journal of Counseling and Education, 3(2), 62-77.
Sutheewasinnon, P., & Pasunon, P. (2016). Sampling strategies for qualitative research. Parichart Journal Thaksin University, 29(2), 31-48.
Tangsakul, P. (2010). Guidelines for the development of operational potential of personnel of Pha Kru Subdistrict administrative Organization Mueang Buriram District Buriram Province: Independent study degree in Public Administration Master of Local Administration. Khon Kaen: Khon Kaen University.
Walters, C.J. (1986). Adaptive management of renewable resources. New York: Mc Graw - Hill.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Received: 01-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. AEJ-21-9231; Editor assigned: 03-Dec-2021, PreQC No AEJ-21-9231 (PQ); Reviewed: 13-Dec-2021, QC No. AEJ-21-9231; Revised: 21-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. AEJ-21-9231 (R); Published: 04-Jan-2022.