Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 5
The Requirements of International Financial Reporting Standard (Ifrs) No. (9) And Its Expected Impact on Improving the Quality of Accounting Information that is Produced by Accounting Information Systems -A Study in Sample of Companies Operating in Iraq Stock Exchange
Emad Al-Harash, Madenat Alelem University College
AL- Rubaye Ahmed Hussein Radhi, University of Baghdad
Suhail Abdullah Al-Tamimi, University of Basrah College of Administration and Economics
Adriana Burlea-Schiopoiu, University of Craiova
Citation Information: Al-Harash, E., Radhi, A.R.A.H., Al-Tamimi, S.A., & Schiopoiu, A.B. (2022). The requirements of international financial reporting standard (ifrs) no. (9) and its expected impact on improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems -a study in sample of companies operating in iraq stock exchange. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 26(5), 1-13.
Abstract
The research aims to analyze and evaluate the expected impact of the requirements set forth in IFRS (9). New requirements for classification, measurement, depreciation and hedge accounting that came in this standard under the title of financial instruments (classification and measurement), in improving quality of the accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in Iraq Stock Exchange to contribute to simplifying the accounting procedures for financial instruments compared to international accounting standards that preceded it in improving the quality of this information. The experimental approach has been used to test the main hypothesis of research, and its sub-hypotheses on a sample of (138) distributed between a financial manager and an auditor in those companies and an analyzed it. Financial and academic, questionnaires were distributed to them, as its questionnaire was designed to collect data related to requirements stipulated in IFRS (9) entitled Financial Instruments (Classification and Measurement), which is the most important criterion in the financial instrument standards system. As the reactions of a sample of interested persons were measured and tested, distributed between a financial manager and an auditor in those companies and a financial and academic analyst who follows the market activity, the results of study showed a positive and significant impact on the adoption of the amendments made to the standards of financial instruments in improving the quality of the accounting information produced by Accounting Information Systems in the researched companies, with a positive and significant impact of adopting amendments to information users in the investment decision-making process.
Keywords
Requirements of IFRS (9), Quality of Accounting Information, Iraq Stock Exchange, Accounting Information Systems, Financial Instruments.
Introduction
Financial instruments are closely related to financial markets as a source for accounting measurement or as a receiver of financial information on measurement, presentation and disclosure results. This research examined the requirements that were mentioned in IFRS (9). New requirements for classification, measurement, depreciation and hedge accounting under the title of financial instruments (Classification and measurement) with the aim of simplifying the accounting ted in IFRS (9) entitled Financial Instruments (Classification and Measurement), which is the most important criterion in the financial instrument standards system ( Recognition and Measurement), which aims to define the principles of recognition, measurement and disclosure of information on financial instruments, while the main objective of the research is to identiprocedures for financial instruments in comparison with the international accounting standards that preceded it, that is, the accounting standards related to financial instruments, to understand their expected effects on improving the quality of the accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems, and then identifying its impact on the users of the information. In the process of making investment decisions by surveying the opinions of a group of interested and practitioners in the companies listed on the Iraq Stock Exchange in the banking sector and the financial investment companies sector, to solve the research problem that indicates that many users of accounting information in the process of making investment decisions have become aware that this information is any accounting information that is previously produced Accounting Information Systems in the researched companies may be based on concepts and principles that may be marred by many flaws that make them less representative. The experimental approach has been used to test the main hypothesis of the research, and its sub-hypotheses on a sample of (138) distributed between a financial manager and an auditor in those companies and an analyst. Financial and academic, questionnaires were distributed to them, as its questionnaire was designed to collect data related to the requirements stipulafy the impact of the accounting trend adopted by various professional organizations in applying accounting standards related to financial instruments as a new accounting trend, and the importance of this study is evident in as it deals with a very important issue in the life of companies due to the requirements of IFRS (9), and reflections that on the future of these companies, and the need to understand their expected effects on improving the quality of accounting information for accounting information systems that are produced by accounting information systems in companies listed on the Iraq Stock Exchange.
Requirements of International Financial Reporting Standard IFRS (9)
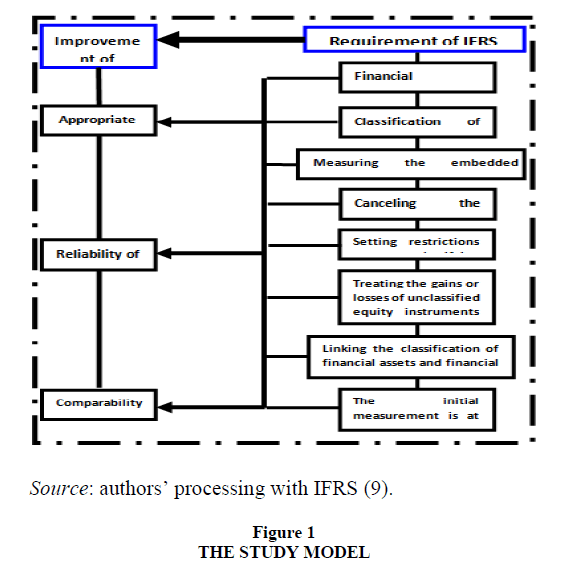
1. Classification of financial instruments into instruments measured at expired cost or fair value; 2. The possibility of classifying financial instruments to be measured at fair value; 3. Measuring the (implicit) derivative with a financial instrument, and measuring the financial instrument itself at fair value; 4. Canceling the classification of available for sale investments; 5. Setting restrictions on reclassifying assets and financial liabilities; 6. Treating gains or losses in equity instruments that are not classified for trading through comprehensive income and continuing to do so from year to year; 7. Linking the classification of assets and financial liabilities to the company's business model instead of the management decision; 8. Initial measurement at fair value even if the execution price is different from the fair value.
The financial instruments in this study were represented by the requirements stipulated in IFRS (9) new requirements for classification, measurement, depreciation and hedge accounting under the heading of financial instruments (classification and measurement). There is no doubt that the application of the requirements that this standard stated will effect on improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange, therefore it was necessary to highlight the effect of applying that model on indicators to improve the quality of accounting information. Rather, it became an independent variable to study in its model those requirements, which it was represented as follows (Hamid et al., 2020).
Because it is considered a contract according to the requirements of this standard and under the title of financial instruments (classification and measurement), a serious contribution to simplifying the accounting procedures for financial instruments compared to the International Accounting Standards IAS that preceded it. This contract creates a financial asset for a company, a financial commitment, or property rights. For another company, that is, the ownership rights of a company in another company, meaning a contractual right for the company to exchange financial instruments with another company Al-Hattami et al. (2021), and under conditions that are most likely in the interest of the company as shareholders, a main commodity for confrontation in the markets, because of its influence on the financial statements and their disclosure. On the one hand, it is widely owned and used in various parts of the world. On the other hand, financial instruments are considered as a financial obligation (as liabilities) that is a contractual obligation on the company for the purpose of delivering cash to another company (such as creditors' accounts), or to hand over a financial asset to a company a contractual obligation to exchange financial instruments with another company under conditions that are likely to be against the interest of this company as an issuer Equity rights. Under these requirements, the standard uses only two methods of accounting measurement, which are the fair value method and the depleted cost method. The requirements that this standard came up with were considered that the basic method for measuring liabilities is the depleted cost method, with the exception of derivatives, as they are measured at fair value through profits or financial losses and liabilities resulting from transfer of a financial asset that does not qualify for disposal, in addition to excluding financial guarantee contracts and commitments to provide a loan with interest lower than the market interest rate (Hamid et al., 2020; Al-Sa’ad et al., 2020; Malik et al., 2015).
Accounting Information
The accounting information in this study was represented by the characteristics identified by FASB with suitability, honest representation, and comparability as a dependent variable (dependent) in its model, because it is considered one of the most important information that allows predicting the project’s ability to achieve profits in the future and its ability to pay its obligations Hamid et al. (2020) and Adriana (2019), and contribute to rationalizing the decisions of the users of the financial statements. These statements, which are the final product of the accounting system and the main means that communicate information to them, provide them with necessary information appropriate for the purposes of the financial report, and help them to make and rationalize decisions on their various groups, that information is stored on the database for the accounting information system in companies, which was previously programmed in a way that this data is processed for use by its users, such as investors, creditors, and financial analysts, as well as financial managers and auditors in those companies, academics who follow market activity, and other stakeholders in decision-making, for their perception. The importance and impact of using that accounting information on their investment decisions in the stock market Finance (Hamid et al., 2020; Adriana, 2019). The accounting Institutions have contributed to framing the main characteristics and enhancing the quality of accounting information, with the aim of improving transparency to enhance disclosure and availability of more understandable financial data, and with the aim of increasing the level of awareness of financial statements users of that accounting information (Adriana et al., 2017). The quality of accounting information means the extent to which the accounting indicators or measures represent reliable measures of the company's performance (Harash, 2017; Mirza & Graham, 2011). Therefore, it can be defined by two inputs, the first of which is the information utility input for decision-making, the governance approach, to facilitate stakeholder monitoring of the company's performance. The usefulness of information for decision-makers depends on many factors related to the field of use, the nature and sources of the information they need, the amount and quality of the information available, the ability to analyze the information and level of understanding and perception available to the decision-maker (Gornjak, 2017).
The relationship between the requirements of (IFRS) and improving the quality of accounting information
Many studies have adopted the study of the relationship between standards of financial instruments and the improvement of the quality of accounting information, and came out with a number of recommendations among supporters of the existence of an impact on the application of these standards on improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems, and the weakness or lack of influence of the application of these standards. It showed the results to support the doubts of the implementers of the Financial Accounting Standard SFAS 115 through the decrease in the proportion of financial investment entitlements after the issuance of this standard and the decrease in the percentage of financial investments available for sale to avoid fluctuations in the value of property rights, after examining the study to the extent The effect of the trend towards fair value evaluation of financial investments on the management of the investment portfolio. The study concluded that there is a fundamental relationship between the difference between (fair value from the book value of securities and equity), meaning that the fair value of securities was fundamentally influential in explaining the difference between the market and book value of the share, as this study aimed to determine the role and impact of applying the American standard SFAS 107 by studying the relationship between the study of showed that the market value of commercial bank shares and the disclosure of the fair value included in this standard. The market value of some financial instruments with no disclosure of unrealized profits or losses, or how they are dealt with in commercial banks, by measuring this is the commitment of Jordanian commercial banks to the requirements of international accounting standards regarding fair value accounting and the disclosure that must be provided in the annual financial statements (Yaqoub et al., 2018).
The results of the study showed that there are gaps in the disclosure requirements, especially the financial liabilities that were measured at historical cost and not at fair value except for financial instruments held for trading or classified as derivative instruments. The direction of any small change in the fixed interest rate. The results of study indicate that there is a difference in the value of assets invested in public companies from their value invested in private companies, because public companies are protected, restructured and financed by the owner, and in which the state holds the majority rights. The study of found that the most important variables that have a direct impact on credit risk are management and investment of a portfolio of securitized assets, sources of financing, comprehensive fair value, hedge accounting in addition to cost and return. The results showed that. The more information that is collected to measure the value is expressed clearly, transparently and objectively, the more the value being measured will be closer to reality, and stressed the importance of not neglecting the prevailing interest rate in the market and the inflation rate when measuring the fair value because of its negative or positive effects on the fluctuation of the value. Dividends from securities held by companies to maturity have a direct impact on determining their value on a fair value basis as a FASB version of the standard 157. The results of study showed that the fair value is the most appropriate measure to determine the value of the new assets and the transferred financial assets, and the present value method of the expected cash flows generated from those transferred financial assets is the most appropriate way to estimate the value. The study itself stipulates that securitization operations must be disclosed in the body of the budget, with the necessity to disclose the accounting policies necessary to measure fair value, and it is preferable to treat securitization activity as a sale of assets than as borrowing against those assets, because of what it faces. The credit market is one of the problems as a result of the global financial crisis. The study believes that setting international standards on the basis of concepts is a very important step in the process of accounting harmonization despite the fact that relying on this basis is not possible through which accounting standards can be unified across different countries. And that the subject of controversy and discussion before and after the global financial crisis, regarding methods and procedures for measuring fair value, was clarified by the study and faltering companies and recognition of these losses, as well as the amendments made by the International Financial Reporting Standards Board to the International Accounting Standard Gornjak (2017) for recognition and measurement of financial instruments, which consisted in allowing banks and companies during a certain period to reclassify financial assets held for trading or prepared for sale. The findings indicate that the estimates of the financial instrument represented by the fair value were less biased, and more accurate than the use of historical cost figures. In addition, the fair value estimates made by an external person are more accurate and less biased than those estimated by an internal person. Contrary to historical cost information, that there is a correlation between stock prices and the fair value of financial investments on the one hand, a correlation between stock returns and fair value gains and losses, with the difference in the results of previous studies on the extent to which confidence in fair value information is achieved due to the lack of an integrated measure of fair value. Regarding the appropriateness and reliability of accounting information resulting from the application of international financial reporting standards, the study assumed that the accounting information resulting from the application of these standards is relevance and reliable, and the study concluded that the accounting information based on the application of international financial reporting standards is The results of the study concluded that the measurement tool used to evaluate the quality of financial reporting contributes to improving the quality of financial reporting information, and enhancing the characteristics emanating from each of the International Accounting Standards Board and the Accounting Standards Board. Financial: The results of the study concluded that the application of directed financial reporting standards towards fair value positively affects the qualitative characteristics of accounting information contained in the financial reports of investment companies listed on the Egyptian Stock Exchange. And that the application of international financial reporting standards reduces the scope of profit management, reached it by reducing information asymmetry and manipulating profits.
The results of the same study indicate that the application of international financial reporting standards contributes to reducing financial crises as a result of standardization. Accounting policies, and in increasing disclosure and transparency, as well as increasing the quality of accounting information. As for the effect of applying fair value on the qualitative characteristics of accounting information, the results stated that applying fair value accounting positively affects these characteristics (such as relevance, reliability and comparability).A study concluded that the transition to international financial reporting standards contributes to reducing management interference in accounting policies and profit management, and that there is a significant correlation between the quality of international financial reporting standards and the qualitative characteristics of accounting information. The results of the study showed that there is an impact of applying International Reporting Standard No.7 Financial Instruments (Disclosures) on the quality of accounting information, and on financial performance indicators such as return on shareholders, equity, earnings per share, the ratio of dividend distribution in the financial statements of commercial banks Jordanian.
In spite of the large number of studies related to standards of financial instruments, these studies did not address the amendments and requirements stipulated in IFRS, despite the importance of the information based on it in measurement and disclosure, and its impact on the qualitative characteristics that are required. Their availability in accounting information, in addition to that there is agreement between studies on the importance of financial instruments and their disclosure in financial reports. However, there is no agreement between those studies on the models used to measure the impact of these tools. The requirements stipulated in IFRS entitled Financial Instruments (Classification and Measurement), to contribute to simplifying accounting procedures for financial instruments compared to international accounting standards that preceded it in improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems. In companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange, so this was the study.
Study Model
After reviewing the previous studies, and identifying the most important variables that they dealt with, the study model was formulated in light of the study problem and its components, and in light of the relevant literature, and the model reflects the independent study variable represented by the requirements of IFRS (9) and the dependent variable (Approved) represented by improving the quality of accounting information, as well as the partial variables for each of them. As shown in Figure 1 below.
Analyzing and Interpreting Results
This section presents the analysis and interpretation of the findings of the study, related to the study sample responses on impact of independent variable, requirements of IFRS, which was measured based on (8) paragraphs.
We notice from Table 1, that this variable achieved an arithmetic mean (3.9311), a percentage (78%) of the total scale area of (5), and a standard deviation of (0.59855), which indicates that the level of application of IFRS in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange is high, from the viewpoint of the sample members. It also emerged from the results listed in Table 1, that the highest average arithmetic was for Paragraph No.5, which refers to “setting restrictions on reclassifying assets and financial liabilities,” as it reached (4.41) with a standard deviation of (0.721) With a high level of importance, while the lowest arithmetic average was for Paragraph No.3, which refers to “measuring the (implicit) derivative with a financial instrument, as well as the financial instrument itself at fair value,” as it reached (3.66) with a standard deviation of (0.993) and with a high level of Importance.
| Table 1 The Arithmetic Means And Standard Deviation Of 11the Response Of The Study Sample Individuals Following The Requirements Of (Ifrs). |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Se. | Description | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Priority level |
| 1 | 4 | Classification of financial instruments into instruments measured at amortized cost or fair value. | 4.01 | 0.904 | High |
| 2 | 5 | Ability to classify financial instruments measured at fair value. | 3.91 | 0.867 | High |
| 3 | 8 | Measuring the (implicit) derivative with a financial instrument, as well as the financial instrument itself at fair value. | 3.66 | 0.993 | High |
| 4 | 7 | De-classification of available-for-sale investments. | 3.7 | 0.956 | High |
| 5 | 1 | Setting restrictions on reclassifying assets and financial liabilities. | 4.41 | 0.721 | High |
| 6 | 3 | Treating gains or losses in equity instruments not classified for trading through comprehensive income and continuing to do so from year to year. | 4.07 | 0.832 | High |
| 7 | 6 | Linking the classification of assets and financial liabilities to the company's business model rather than the management decision. | 3.71 | 0.81 | High |
| 8 | 2 | Initial measurement at fair value even if the execution price is different from the fair value. | 4.3 | 0.812 | High |
| The overall Indicator | 3.9277 | 0.59857 | High | ||
As for the analysis and interpretation of the results of the study, related to the responses of the study sample on effect of dependent variable (adopted) improving quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in the companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange, which were determined by FASB as relevance and representative. reliable, comparability, as shown in Table 2, the arithmetic mean, standard deviation, and arrangement of the respondents' answers to the paragraphs related to improving the quality of accounting information, which are produced by the accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange, represented by suitability, and honest representation, and comparability, which was measured based on (9) items.
| Table 2 The Arithmetic Means And Standard Deviation Of The Response Of The Study Sample On The Impact Of Improving The Quality Of Accounting Information, Which Was Determined By The (Fasb) As Appropriate, Honest Representation, And Comparability |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Se. | Description | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Priority level |
| 1 | 5 | The relevancy of the accounting information that is produced by the accounting information systems in the companies to the investment decision-making process. | 4.11 | 0.611 | High |
| 2 | 7 | Relevancy of accounting information improves the concept of financial instruments and their importance in improving the future cash flows associated with them. | 3.95 | 0.729 | High |
| 3 | 8 | The relevancy of the accounting information enables the determination of whether the instrument should be classified and presented as liabilities or equity | 3.70 | 0.876 | High |
| 4 | 1 | The reliability of accounting information improves the concept of financial instruments and their importance in improving the future cash flows associated with them. | 4.30 | 0.731 | High |
| 5 | 2 | Reliability of accounting information that is produced by companies' accounting information systems for the investment decision-making process. | 4.18 | 0.774 | High |
| 6 | 4 | The reliability of the accounting information enables the determination of whether the instrument should be classified and presented as liabilities or equity | 4.11 | 0.703 | High |
| 7 | 9 | The applicability of the accounting information that is produced by the accounting information systems in the companies to the investment decision-making process for comparison. | 3.69 | 0.867 | High |
| 8 | 3 | Comparability of accounting information improves the concept of financial instruments and their importance in improving the future cash flows associated with them. | 4.11 | 0.768 | High |
| 9 | 6 | Comparability of accounting information enables the determination of whether an instrument should be classified and presented as liabilities or equity | 3.98 | 0.856 | High |
| The overall Indicator | 3.8983 | 0.54069 | High | ||
We notice that Table 2, indicates that this variable achieved an arithmetic mean (3.8983) with a percentage (78.9%) of the total scale area of 5, and a standard deviation of (0.54069), which indicates that the level of importance of the characteristics that you have. The accounting information that is produced by the accounting information systems in the companies operating in Iraq Stock Exchange, determined by FASB as appropriate, faithful representation, and comparability is high, from the viewpoint of the sample members.
It was found from the results in Table No.2, that the highest average arithmetic was for Paragraph No.4, which indicates that “the reliability of accounting information will improve the concept of financial instruments and their importance in improving the future cash flows associated with it”, as it reached (4.30).) With a standard deviation of (0.731), and with a high level of importance, while we find the lowest average arithmetic was paragraph No.7, which indicates that "the susceptibility of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies to the process of making investment decisions for comparison. As it reached (3.69), with a standard deviation of (0.867), with a high level of importance.
Main hypothesis and test the results
In order to clarify the behavior of the relationships between the study variables, by testing the hypothesis of the main study and the sub-hypotheses branching from it, the level of significance (0.05α≤) was adopted as a basis for rejecting or accepting the hypotheses, meaning if the value of (α) is equal to or less than (5%). ), We reject the null hypothesis (HO), if it is greater than (5%), then we accept the null hypothesis (HO), in addition to the fact that the computed value and the tabular value have also been relied upon. If the computed value is greater than the tabular value, we reject the null hypothesis (HO), and we accept the alternative hypothesis (Ha).
Ho1: There is no statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of International Financial Reporting Standard No.(9) for (IFRS) in improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraqi market Stock.
Ha1: The presence of a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS in improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in Iraq Stock Exchange Financial.
We note from the results shown in Table 3, for testing the main hypothesis by means of the One Sample T-Test that the significant Sig value is less than (0.05), which is (0.00), and the calculated (T) value of (23.064) is greater than its value. Tabular at the degree of freedom (N-1), which is 1.95, which means rejecting the null hypothesis (HO), and then accepting the alternative hypothesis (Ha), and this means that there is a statistically significant effect at a level of significance (0.05≥α) for the requirements of IFRS on improving the quality of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange.
| Table 3 Results Of The Main Hypothesis Test |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computed T value | Tabular T value | The degree of freedom DF | T Sig value | Simple Mean | Standard Deviation | Result of the null hypothesis HO |
| 23.064 | 1.95 | 175 | 0.00* | 3.8999 | 0.55012 | Refusal |
Significance at ≤ 0.05
The first sub hypothesis and its test results
HO.1.1: There is no statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the appropriateness of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange Financial.
Ha.1.1: The presence of a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the appropriateness of the accounting information that is produced by the accounting information systems in the companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange.
We also note that the results of Table 4, which relate to the first sub-hypothesis test, show that through the One Sample T-Test that the significant value of Sig is less than 0.05, which is 0.00 At the degree of freedom (N-1), which is 1.95, which requires the rejection of the null hypothesis (HO.1.1), and then that means acceptance of the alternative hypothesis (Ha.1.1), which indicates the existence of a statistically significant effect at a level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the appropriateness of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange.
| Table 4 Results Of The First Sub-Hypothesis Test |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computed T value | Tabular T value | The degree of freedom DF | T Sig value | Simple Mean | Standard deviation | Result of the null hypothesis HO |
| 24.001 | 1.95 | 175 | 0.00* | 3.9009 | 0.54066 | Refusal |
Significance at ≤ 0.05
The second sub-hypothesis and its test results
HO.1.2: There is no statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the reliability of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange Financial.
Ha.1.2: The presence of a statistically significant effect at the level of (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the reliability of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange.
We also note that the results of Table 5, related to the second sub-hypothesis test, are shown by the One Sample T-Test that the significant Sig value is less than (0.05), which is (0.00), and the calculated (T) value of (20.619) is greater than Its tabular value is at the degree of freedom (N-1) of (1.96), and this consequently leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis (HO.1.2), and then acceptance of the alternative hypothesis (Ha.1.2), which indicates the existence of a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) for the requirements of IFRS on the reliability of accounting information that is produced by accounting information systems in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange.
| Table 5 Results Of The First Sub-Hypothesis Test |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computed T value | Tabular T value | The degree of freedom DF | T Sig value | Simple Mean | Standard Deviation | Result of the null hypothesis HO |
| 21.009 | 1.95 | 175 | *0.00 | 3.9112 | 0.59000 | Refusal |
* Significance at ≤ 0.05
The second sub-hypothesis and its test results
HO.1.3: Not having a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the portability of accounting information produced by accounting information systems for comparison in companies operating in the Iraqi market Stock.
Ha.1.3: The presence of a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (0.05≥α) of the requirements of IFRS on the portability of accounting information produced by accounting information systems for comparison in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange Financial.
Finally, the results of Table 6, for testing the third sub-hypothesis through the One Sample T-Test show that the significant Sig value is less than (0.05), which is 0.00, while the calculated value of (T) is (20.619) It is greater than its tabular value at the degree of freedom (N-1), which is 1.96, and as a result, it is necessary to reject the null hypothesis (HO.1.3), and then accept the alternative hypothesis (Ha.1.3), which indicates the existence of a statistically significant effect At a level of significance (0.05≥α) for the requirements of IFRS on the portability of accounting information produced by accounting information systems for comparison in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange.
| Table 6 The Results Of The Third Sub-Hypothesis Test |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computed T value | Tabular T value | The degree of freedom DF | T Sig value | Simple Mean | Standard deviation | Result of the null hypothesis HO |
| 20.919 | 1.95 | 175 | *0.00 | 3.8999 | 0.59005 | Refusal |
* Significance at ≤ 0.05
Conclusion
Recommendations
By analyzing the data and relying on the results of testing the main hypothesis of the study and its three sub-hypotheses, these results showed that there is a relatively high level of desire of the study sample, which consisted of financial managers and auditors in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange, financial analysts, as well as academics who are actively observing and interested. These companies apply the requirements of IFRS because of their impact on improving the quality of the accounting information that is produced by the accounting information systems in the sample companies of the study, through its impact on the relevance, reliability and comparability of accounting information. The results of this study are consistent with the results of some previous studies that companies must provide high-quality information to their users in various investment decisions. In view of the results of the study, the recommendations of the companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange became binding on working to standardize the disclosure and presentation of the financial statements of these companies by seeking to implement the requirements of IFRS that is the subject of the study, because of its impact. The users of the accounting information that are produced by the accounting information systems in rationalizing their investment decisions on their various categories, in addition to providing training programs for the application of the requirements of IFRS because of their impact on improving the quality of accounting information Which is produced by the accounting information systems in it, the importance of adherence to it, and finally work to encourage researchers and those interested in conducting more research and studies related to the application of the requirements of IFRS in companies operating in the Iraq Stock Exchange, and other companies.
References
Adriana, B.S. (2019). The Impact of Triple Bottom Dispersal of Actions on Integrated Reporting: A Critical perspectives. In Integrated Reporting (pp. 141-152). Springer, Cham.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Adriana, B.S., Samuel, I., & Stephan, V. (2017). Corporate Social Responsibility in Times of Crisis: A Summary, Springer.
Al-Hattami, H.M., Hashed, A.A., Alnuzaili, K.M., Alsoufi, M.A., Al-Nakeeb, A.A., & Rageh, H. (2021). Effect of risk of using computerized AIS on external auditor's work quality in Yemen. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 8(1), 75-81.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Al-Sa’ad, Jasim, F., Harash, E., Al-Tamimi, & Abdullah, S. (2020). The Impact of the Accounting Information System on the Relationship between the Application of Fair Value Accounting and the Characteristics of Accounting Information. Journal of Science City University College, 12(1).
Gornjak, M. (2017). Comparison of IAS 39 and IFRS 9: The Analysisof Replacement. International Journal of Management Knowledge and Learning, 6(1).
Hamid, A., Shaheen, A., Omran, Muhammad, R., Al-Baghdadi, & Ahmed. (2020). Accounting Measurement of Credit Risk in Light of Banking Supervision Standards of Basel and the International Financial Reporting Standard IFRS (9), A Field study in Egyptian commercial banks, published research, Faculty of Commerce, Al-Sadaat University.
Harash, E. (2015). The Role of Environmental Uncertainty in the Link between Accounting Information System and Performance Small and Medium Enterprises in Iraq, Global Journal of Management and Business Research.
Harash, E. (2017). Accounting performance of SMEs and effect of accounting information system, a conceptual model, Global Journal of Management and Business Research.
Malik, B., Hassan, M., & Ghawali, M.B. (2015). The effect of accounting measurement based on fair value on the qualitative characteristics of accounting information for companies operating in the southeast. An applied study, the researcher Journal, 15(15), 171-178.
Mirza, A., & Graham, J.H. (2011). A guide and book for the practical implementation of IFRSs, 3rd Ed, Central Press, Amman, Jordan.
Yaqoub, I., Ismail, J., & Latif, A.R. (2018). Examining the impact of the transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) on the private banking sector in the Iraqi environment from a (qualitative and value) perspective. Administration and Economics Journal, 114.
Received: 17-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. AAFSJ-22-9815; Editor assigned: 20-Jun-2022, PreQC No. AAFSJ-22-9815(PQ); Reviewed: 04-Jul-2022, QC No. AAFSJ-22-9815; Revised: 26-Jul-2022, Manuscript No. AAFSJ-22-9815(R); Published: 02-Aug-2022