Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 1S
The Role of Decision-Making Quality and Innovation Culture On Company Performance and Business Sustainability
Liestya Padmawidjaja, Ciputra University Surabaya
Timotius F.C.W Sutrisno, Ciputra University Surabaya
Elia Ardyan, Ciputra University Surabaya
Istiatin Istiatin, Ciputra University Surabaya
Devi R Wijayadne, Ciputra University Surabaya
Citation Information: Padmawidjaja, L., Sutrisno, T.F.C.W., Ardyan, E., Istiatin, I., & Wijayadne, D.R. (2022). The role of decisionmaking quality and innovation culture on company performance and business sustainability. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S1), 1-11.
Abstract
Business performance and business sustainability are the main things for companies to survive amid the implementation of global economic openness, to investigate this, the purpose of this paper is to examine the relationship between decision making quality and innovation culture to business sustainability through firm performance in the context of a family business. Using a sample of 160 family business owners who already have a business license in Indonesia and content analysis based on their performance reports, evidence was gathered to test the hypothesis through structural equation modeling–partial least square (SEM-PLS) The results reveal that decision-making quality and innovation culture improve company performance, which in turn results in business sustainability. Decision-making quality and innovation culture positively affect firm performance, and firm performance mediates the creation of business sustainability. This study provides insight into how firm performance mediates decision making quality and innovation culture in business sustainability in the context of family businesses in Indonesia.
Keywords
Family Business, Decision-making Quality, Innovation Culture, Firm Performance, Business Sustainability.
Introduction
Making decisions is a great responsibility of a leader not only to the Company but also to their employees, family members in the family business circle. A successful Family Business makes the right decisions. The quality of decision-making affects all the major issues faced by family businesses: succession planning, business process planning, family strategy planning, and even future business sustainability strategies.
In the decision-making model, there has been a lot of literature written to explore the practice of thinking frameworks in making strategic decisions in companies (Negulescu & Doval, 2014), some of them use quantitative and qualitative approaches that can help decision-makers to determine and clarify different criteria (Azemi et al., 2018). The quality of decision-making emphasizes that time and information is the main things that influence the outcome of decisions, especially in the context of a family business where the core stakeholders of the Company are the core family. They almost have the same opportunity in making decisions so that wrong information will result in decision consequences in Firm performance in family businesses.
The quality and speed of decision-making are the main determinants of the success or failure of a family business (Thomas, 2006). Identifying goals, providing alternative problem solving, and balancing values in a family business is very important in the quality of decision making. Indonesia as one of the countries that have a much larger percentage of family businesses than joint corporations proves that the sustainability of family businesses is the backbone of a strong economy for developing countries. Especially considering the current developments, not many businesses can survive the disruption of the COVID-19 pandemic that has hit almost every part of the world. This pandemic not only has an impact on public health but more than that as if the wheels of the economy have stopped for a moment to spin (Vijayakumar, 2020 ). It takes more than just good quality decision-making in a family business to be able to perform to survive in the future, but additional strategies are needed such as an innovation culture that allows family companies to have product or service advantages to be able to compete with similar competitors and even survive the COVID-19 pandemic (Lin, 2007).
An important challenge in effective decision making is to evaluate the extent to which the Company's leadership utilizes quantitative and qualitative criteria in decision making. However, to do this, the family business leader needs to have three skills, dare to be rational, think creatively, and balance the results of the assessment. Thus, family business leaders must have effective decisions to cope with unexpected changes in the business environment to achieve business success. The current business environment is more dynamic and complex than the last decade and the strategic decision-making process must consider things that are uncertain, unclear, and sometimes contradictory from previous conditions, this is a challenge for business sustainability (Yu et al., 2019). This study intends to examine the impact of Quality Decision Making (DMQ) and innovation culture (IC) on firm performance (FP) achievement and then on firm sustainability (FS) in the context of Family Business in Indonesia. The findings will not only help to enrich the literature on management knowledge and strategic decision making, but also provide valuable insights for family business managers to improve the quality of their decision-making in dynamic innovation culture to improve company performance and maintain business sustainability in the future.
In addition, the economic condition that is currently being disrupted by the Covid-19 Pandemic has prompted the importance of exploring the quality of decision-making and an innovation culture that has an impact on business performance and business sustainability during this crisis period in the context of a family business. However, there is paucity in the current literature on the impact of quality decision-making practices and innovation culture in the family business context and a lack of impact on business performance and business sustainability. This study will explore the relationship between the quality of decision-making and the innovation culture in the context of a family business in Indonesia, which is one of the most populous countries in Southeast Asia (Teofilus et al., 2020). In the context of its development, many family companies in Indonesia have tried to develop an innovation culture to respond to global challenges (Ongkowijoyo et al., 2020), this is evidenced by the increasing number of family companies that have recognized quality and standardized quality in their operations (Sutrisno, 2019b).
Literature Review
The arrival of the Covid-19 pandemic presents a major challenge for entrepreneurs as decision-makers and the innovation culture has become an important resource for creating and maintaining a company's competitive advantage (Johannessen & Johannessen, 2018). Decision-making is the Company's response to the problems encountered to solve the problem. This is reinforced by the existence of innovation culture as a strategy to strengthen more efficient processes to achieve business performance (Lin, 2007) and business sustainability in uncertain times.
A. The Influence of Decision-Making Quality on Company Performance and Business Sustainability
Quality decision-making is a source of competitive advantage for companies in uncertain conditions, and it helps companies to make improvements in the future. Several empirical studies (Lumpkin et al., 2000; Ongkowijoyo et al., 2020; Pimentel et al., 2018) have suggested that a family business owner's failure to make prompt and quality strategic decisions is a major factor hindering firm performance.
Most of the firm performance failures are caused by low-quality decision-making, this is often caused by the uncertainty of information received the pressure of time or money, the emotion of decision-makers, and social pressure (Wieder & Ossimitz, 2015). Wrong strategic decisions as a result of misunderstanding receiving information and market conditions can have an impact on the achievement of company performance. High-quality decisions on family business trips in this study have several indicators developed previously (Sanz de Acedo Lizarraga et al., 2009) including Uncertainty (1), Pressure (1), Information (1), Motivation (1), Self-regulation (1).
High-quality decisions, on the other hand, can help companies adopt strategic decisions by seizing market opportunities to achieve sustainable growth, especially in complex environments. Therefore, the quality of decision-making will directly affect the performance of the company or the Company and have an impact on the sustainability of the company in the future. The firm performance in this study has several indicators that were previously developed (Ongkowijoyo et al., 2020), including financial performance (2) and non-financial performance (2). And Business Sustainability has several indicators that were previously developed, including Customer Satisfaction (1), Environmental Performance (1), Social Performance (2) Thus, the hypotheses in this study are:
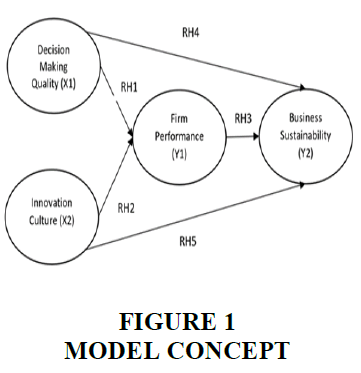
RH1: The decision-making quality has a positive impact on Firm performance
RH4: The decision-making quality has a positive impact on business sustainability
B. The Influence of Innovation Culture on Company Performance and Business Sustainability
The importance of innovation for business success is well understood and several empirical studies have shown that there is a positive relationship between innovation and business performance (Tang et al., 2020; Uzkurt et al., 2013). Innovation in an organization will not be created without the encouragement of the innovation culture that was created previously. Innovation culture reflects shared values, team beliefs, and behaviours that influence the creation of innovation (Hilmarsson et al., 2013).
The relationship between innovation culture and business performance has previously been well described (Damanpour & Evan, 1984). He argues that the innovation culture created within the organization is the only contributor to increasing company revenue. The increase in corporate income is one of the company's financial performances which is expected to grow over time to achieve business sustainability. The importance of responding to market needs quickly has increased in the era of information disclosure, this is due to increased competition, and information transparency increased consumer power due to social and internet access. The impact of an innovation culture on business performance is not only related to innovation in products and services, but it is an important part of the value chain to support the sustainability of a family business amid uncertainty.
Family businesses that are closely related to the peculiarities of business management (Lumpkin et al., 2000), need to consider an innovation culture to achieve business performance in an era of uncertainty. The behavioural aspect of innovation culture is more market-driven than market-driven in a family business (Ongkowijoyo et al., 2020), this shows that companies utilize internal-based competencies in their innovation processes which have an impact on the creation of new ideas through communication with customers so that it has an impact on family business performance. The innovation culture in the family business creates an entrepreneurial spirit and unites members of the organization who are mostly nuclear families as decision-makers towards innovative behaviour, resulting in increased business dynamics and flexibility which are expected to have an impact on the sustainability of the family business. The innovation culture therefore not only encourages gradual improvement and makes the company more responsive to the needs of the existing market, but also supports the company in achieving a competitive advantage in the future. Thus, the hypothesis in this study is:
RH2: Innovation culture has a positive impact on Firm performance
RH5: Innovation culture has a positive impact on business sustainability
C. The Influence of Innovation Culture on Company Performance and Business Sustainability
Looking at current developments, the company not only aims to increase flexibility in terms of delivery, quality, and cost, but also must have a competitive advantage. If not, the company will not be able to survive amid free-market competition even though it is a family company whose overall decisions are taken by family members who take on the role. business sustainability means creating long-term value that includes opportunities and risks arising from social, environmental, and economic factors (Aggarwal, 2013).
Performance in a family business is the main goal for strategic decision-makers to achieve business sustainability in the future. Business sustainability in a family business is one of the main goals of business achievement to extend the business trip managed by family members. There are three aspects used to measure the sustainability of a family business, including customer satisfaction, environmental and social performance. These three aspects are considered to represent a picture of the sustainability of the family business (Maria, 2016). Family businesses are the backbone of the economic strength of developing countries such as Indonesia, so achieving business performance is a strategic effort that must be achieved. The achievement of business performance is expected to have an impact on business sustainability so that it has an impact on improving the company's position in the social environment (Figure 1). Thus, the hypothesis in this study is:
RH3: Firm performance has a positive impact on business sustainability
Methodology
The method used in this study is quantitative. This study uses quantitative methods to test the hypotheses that have been made, namely to analyze the influence of Decision Making Quality and Innovation Culture on the Firm performance and business sustainability. The population and sample in this study are family business owners who are domiciled in the provinces of East Java and Central Java, which are the two provinces with the largest number of citizenships in Indonesia. The sample used in this study is a non-probability sampling technique using the purposive sampling method.
This study takes data sources, namely primary data. Primary data was obtained directly through the distribution of online questionnaires using an online questionnaire platform containing statements regarding the variables of Decision Making Quality, innovation culture, Firm Performance, and Business sustainability in the context of a family business. This study uses a primary data measurement scale using an interval scale. There are seven interval scale indicators in answering, namely: Strongly disagree (1) to Strongly agree (7).
Results
Researchers distributed 300 questionnaires, which were divided into 8 cities in two provinces of East Java and Central Java. These two provinces were chosen because they have the largest population and family business community in Indonesia. A total of 167 questionnaires were returned and only 160 questionnaires could be processed, the rest could not be processed due to incomplete filling, so the response rate in this study was 53.3 percent, of which all respondents consisted of members of the family business community that had been established for more than five years. in the production of household processed fabrics, light construction, food and beverages, agribusiness, final processing products, and handicrafts. Respondents have more than 20-40 employees and are located in eight cities in 2 provinces of East Java (89 respondents) and Central Java (71 Respondents) in the Territory of the Republic of Indonesia.
Confirmatory Factor Analysis
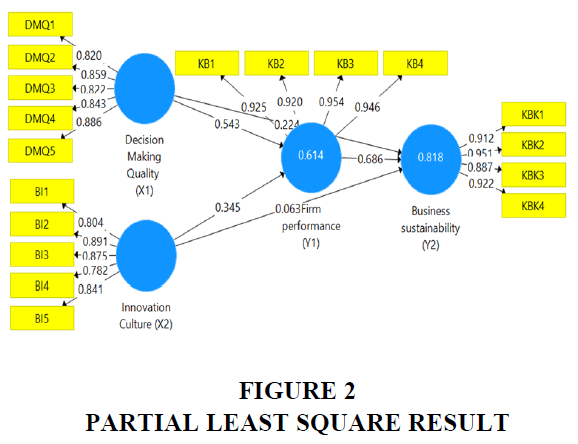
The measured (observed) values for the questions, obtained from the respondents, are the measured variables of the model, which are used as indicators of each latent construct (Factor). Table 1 describes the results of the criteria using Partial Least Square involving Composite variables on indicators, Validity and Reliability Tests using Product moment and Cronbach alpha. Meanwhile, the latent variables were tested for validity and reliability through CFA for each latent variable. Based on Table 1. All indicators on the variable have a value greater than 0.5, which means that the indicator is valid in measuring the latent variable.
| Table 1 Confirmatory Factor Analysis | ||
| Laten Construct | Observed Variable | Factor Loading |
| Decision Making Quality-DMQ (X1) | Uncertainty | 0.803 |
| Time/Money Pressure | 0.891 | |
| Information & Purpose | 0.872 | |
| Consequences Of Decision | 0.784 | |
| Self-Regulation | 0.840 | |
| Innovation Culture-IC (X2) | Product Innovation | 0.821 |
| Service Innovation | 0.860 | |
| Innovation Process | 0.823 | |
| Innovation Flexibility | 0.841 | |
| Innovation Mindset | 0.884 | |
| Firm performance-FP (Y1) | Financial Performance-1 | 0.925 |
| Financial Performance-2 | 0.919 | |
| Non-Financial Performance-1 | 0.953 | |
| Non-Financial Performance-2 | 0.946 | |
| Customer Satisfaction | 0.913 | |
| Environmental Performance | 0.951 | |
| Social Performance | 0.886 | |
| Company Image | ||
The reliability of the above latent constructs was checked according to Hair et al. (2005), by calculating Cronbach's alpha coefficient which is higher than 0.7 (Table 1). Confirmatory factor analysis by evaluating convergent validity (factor loading > 0.5, Extracted mean-variance >0.5, Combined reliability>0.7). The results of model testing get an R-square value that describes the goodness-of-fit of a model. The expected value of r-squared is greater than zero. Table 2 shows that the R-Square Firm Performance (Y1) value is 0.818, and Business sustainability (Y2) is 0.614. It means that this study model is eligible. The goodness of measurement of the inner model with Q Square calculation results from Table 2 is obtained using the following formulation:
| Table 2 Model Reliability and Validity | ||||
| Laten Construct | Cronbach’s Alpha | Average Variance Extracted | Composite Reliability | R Square |
| X1 | 0.938 | 0.843 | 0.956 | |
| X2 | 0.901 | 0.716 | 0.927 | |
| Y1 | 0.953 | 0.877 | 0.966 | 0.818 |
| Y2 | 0.896 | 0.705 | 0.923 | 0.614 |
Q2= 1-(1-0.818) x (1-0.614) = 0.929
The results of the above calculations can be interpreted that the model can explain business sustainability (Y2) by 92.9% and 7.1% explained by other variables.
Hypothesis Test
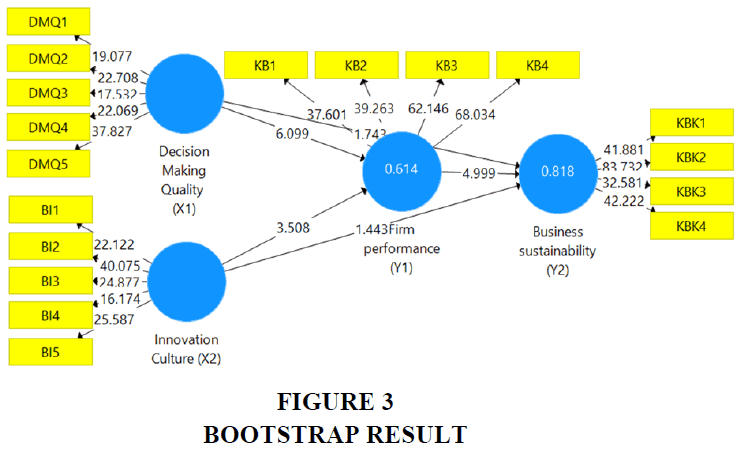
The results of the inner path coefficients, together with the full significance value are shown in Table 3. Based on Table 3, the interpretation of each coefficient with a sample of 160 respondents (t table: 1,974) path then: RH1- Decision-making quality has a positive impact on Firm performance, accepted which is seen from the path coefficient value of 0.542, the T-Statistic value of 6.099 and the P-Value value of 0.000. RH2- Innovation culture has a positive impact on Firm performance, which is accepted which is seen from the path coefficient value of 0.347, the T-Statistic value of 3.508, and the P-Value value of 0.000. RH3- Firm performance has a positive impact on business sustainability, which is accepted which is seen from the path coefficient value of 0.889, the T-Statistic value of 4.999, and the P-Value value of 0.000. RH4- The quality of decision-making has a positive impact on business sustainability, which is accepted which is seen from the path coefficient value of 0.482, the T-Statistic value of 7.475, and the P-Value value of 0.000. RH5- Innovation culture has a positive impact on business sustainability, which is accepted which is seen from the path coefficient value of 0.308, the T-Statistic value of 4.634, and the P-Value value of 0.000..” shows in Figure 2 &3.
| Table 3 Hypothesis Testing | |||||
| Research Hypothesis | Description | Path Coefficient | T-Statistics | P-Value | Result |
| RH | Decision Making Quality -> Firm Performance | 0.542 | 6.099 | 0.000 | Supported |
| RH | Innovation Culture -> Firm Performance | 0.347 | 3.508 | 0.001 | Supported |
| RH | Firm Performance -> Business Sustainability | 0.889 | 4.999 | 0.000 | Supported |
| RH (indirect) |
Decision Making Quality -> Business Sustainability | 0.482 | 7.475 | 0.000 | Supported |
| RH (indirect) |
Innovation Culture -> Business Sustainability | 0.308 | 4.634 | 0.000 | Supported |
Discussion and Conclusion
This study focuses on examining the relationship between decision-making quality and innovation culture to business sustainability through firm performance in the context of a family business. This study conducted a survey of family business actors in the provinces of East Java and West Java, which are part of the Indonesian state, where these two provinces rank among the most densely populated. The results show that decision-making quality and innovation culture on business sustainability through firm performance all have a significant positive impact. These findings are in agreement with previous studies and our study provides a new and more nuanced explanation of the mechanisms that affect corporate performance and business sustainability.
This study explores mechanisms through the decision-making quality and an innovation culture to business sustainability through firm performance in the context of a family business. The findings of this study have several theoretical implications and can make important contributions to studies on decision-making quality and innovation culture. First, this study complements the existing literature on decision-making quality and innovation culture on firm performance and business sustainability. While previous studies have found a positive relationship between firm performance and business sustainability (Chen, 2015; Maria, 2016), some of them consider company performance an important component to achieve business sustainability in the future in this context of a family business. In addition, this study raises two assertions that are thought to have an impact on firm performance, namely decision-making quality and innovation culture. While previous studies have supported a positive relationship between the two on firm performance (Damanpour & Evan, 1984; Hilmarsson et al., 2013; Wieder & Ossimitz, 2015), some consider decision making quality and innovation culture to be factors that need to be considered in achieving company performance. In this case study, we systematically analyse and develop hypotheses about the impact of decision-making quality and innovation culture on firm performance and business sustainability and the results support our hypothesis. The results of this study can help to better understand decision-making quality and innovation culture on firm performance and business sustainability in a more nuanced way, which will have important practical implications for family business managers.
Finally, we test this model in the context of family businesses in the two largest provinces in Indonesia, which are culturally diverse. The results show that the values of decision-making quality such as Uncertainty, Time/Money Pressure, Information & Purpose, Consequences of Decision, and Self-regulation and values on innovation culture such as Product Innovation, Service Innovation, Innovation Process, Innovation Flexibility, and Innovation Mindset influence firm performance generated in the family business. We see the quality of decision-making as an important step to achieve future goals when companies are required to be more efficient and effective in producing products, this is part of the implementation of total quality management (Sutrisno, 2019a). The achievement of the company's performance will not last long in the current era of competitive openness. It takes an innovation culture as one of the strategies to achieve continuous company performance and provides opportunities to achieve business sustainability in the future. When the company can achieve consistent company performance, business sustainability will likely be achieved in the future so that the company has resilience from the risks that may occur. This study advances the study of decision-making quality and innovation culture to business sustainability through firm performance in the context of a family business.
Limitation and Future Research
This study tries to explore decision-making quality and innovation culture for business sustainability through firm performance from a family business perspective, but caution must be exercised in applying the findings of this study. First, this study only examines one mediator- firm performance and two independent variables of decision-making quality and innovation culture. This study does not consider the possibility of other mediating or moderating factors that support the achievement of firm performance and business sustainability. Future research should explore more factors to investigate the causes and impacts on the relationship between firm performance and business sustainability.
Second, our research is based on organizational level data to explore the impact of decision-making quality and innovation culture on business sustainability through firm performance from a family business perspective. However, it is known that many companies have experienced disruptions in maintaining business sustainability, especially during the disruption of the global COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, future research should explore how global disruption affects firm performance and business sustainability. Finally, this study was a cross-sectional design, and conclusions about causality in our model cannot be easily drawn. Future research should derive data from experimental and longitudinal designs and from various sectors within to better identify the underlying causal directions.
Acknowledgement
We wish to express our gratitude to The Directorate General of Higher Education, The Ministry of Education, Culture, Research and Technology, Republic of Indonesia. The authors also would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their constructive comments and suggestions.
This study was fully supported via a Research Grant Program namely “The Penelitian Dasar Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi” (The PDUPT) which financed by The Directorate General of Higher Education, The Ministry of Education, Culture, Research and Technology, Republic of Indonesia.
References
Chen, L. (2015). Sustainability and company performance: Evidence from the manufacturing industry (Vol. 1698). Linköping University Electronic Press.
Damanpour, F., & Evan, W.M. (1984). Organizational and Performance. Administrative Science Quarterly, 29(3), 392-409.
Johannessen, J.A., & Johannessen, J.A. (2018). Knowledge Management and Organizational Learning. Knowledge Management as a Strategic Asset, 95–111.
Lin, H.F. (2007). Knowledge sharing and firm innovation capability: an empirical study. International Journal of Manpower.
Lumpkin, G.T.L.S., & Wright, M. (2000). Family Business and Non-Family Business in the. Management, 78(3), 34.
Negulescu, O., & Doval, E. (2014). The quality of decision making process related to organizations’ effectiveness. Procedia Economics and Finance, 15, 858-863.
Ongkowijoyo, G., Christian, T.F., & Teofilus, T. (2020). Performance achievements of family business through successor readiness and the relationship between family and business members.
Sy, M.V. (2016). Impact of sustainability practices on the firms’ performance. Asia Pacific Business & Economics Perspectives, 4, 4-21.
Teofilus, T., Sutrisno, T.F., Hongdiyanto, C., & Wananda, V. (2020). A Study of Indonesian online marketplace: Information processing theory paradigm. The Journal of Distribution Science, 18(8), 75-87.
Thomas, J. (2006). Family presence: Implications for decision-making in family business.
Uzkurt, C., Kumar, R., Kimzan, H.S., & Eminoğlu, G. (2013). Role of innovation in the relationship between organizational culture and firm performance: A study of the banking sector in Turkey. European Journal of Innovation Management.
Vijayakumar, V. (2020). A meta-analysis on effect on the economy due to labour loss during epidemic Outbreaks. May.
Yu, H., Shang, Y., Wang, N., & Ma,Z. (2019). The mediating effect of decision quality on knowledge management and firm performance for Chinese entrepreneurs: An empirical study. Sustainability, 11(13), 3660.