Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
The Role of Technological Management, Idea Implementation, Sustainable Process Innovation and Logistic Competency
Komson Sommanawat, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University
Chattrarat Hotrawaisaya, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University
Phutthiwat Waiyawuththanapoom, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University
Supamit Srisawat, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University
Wissawa Aunyawong, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University
Kittisak Jermsittiparsert, Dhurakij Pundit University, Universitas
Muhammadiyah Makassar, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sinjai
Abstract
This study is an attempt to highlight the role of technological management and idea implementation in logistic firm competency. The role of process innovation is used as mediating variables, consequently, this study examined the relationship between technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency. As this study considered the logistic companies of Indonesia, therefore, data were collected from the Indonesian logistic companies and employees of logistic companies were selected to get the response with the help of questionnaire. Therefore, a survey with the help of questionnaire was carried to collect data from the employees of logistic firms in Indonesia. Results of the study shows that technological management has positive effect on logistic firm competency. Moreover, the positive effect of idea implementation was found on logistic firm competency. Additionally, process innovation is one of the factors which has positive role to promote logistic firm competency
Keywords
Technological Management, Idea Implementation, Sustainable Process Innovation, Logistic Firm Competency, Logistic Industry
Introduction
Competency is one of the vital elements of individuals as well as organizations (Jermsittiparsert & Wajeetongratana, 2019). In case of individual people, it has vital influence on the performance. Among the organizations, competency in employees of the organization is most important. It is a major part of organizations. Competency has the ability to influence positively on the operations of the company. Operations involve all the processes from the start to the end. Each area of the organization require competency to perform better. Finally, the competency is one of the most important elements among the firms (Chada, Leethongdee, Pengpid & Chualinfa, 2020). All the organizations always try to increase the competency to increase the overall firm performance which has major role in firm success.
Competency among the logistic firms is also important along with the other organizations. Organizational competency is consisting of various elements. First of all, the competency belongs to the employees of the logistic firms. Better competency of the employees leads to the organizational competency. Secondly, the logistic firm competency is based on the operations of the firm. If the operations have better competency level, it effects positively on the firm operations. Increase in operations competency increases the logistic firm competency. Furthermore, thirdly, competency is also belonging to the process. Most of the companies always want to enhance the process with the help of technology. Better process though new technology is called competent process. It is the competency of overall logistic firm which shows positive effect. Therefore, competency is required in operations, employees and process to achieve the competency in logistic companies. As given in the previous studies that competency is belong to the employees, operations and process (Butschan, Heidenreich, Weber & Kraemer, 2019; Moh’d Abu Bakir, 2019) which finally shows positive role in logistic firm competency.
Indonesian logistic companies have significant importance as this industry has key participation among all other industries. This industry providing significant support to the other companies by facilitating supply chain process. Both the supply chain and logistic has relationship with each other’s and providing important platform for the companies to grow. There are many companies are working in Indonesia related to the logistic services. These companies have vital contribution to the economic development of Indonesia as well as key contribution for the other companies in Indonesia (Erna, Surachman, Sunaryo, & Djajuli, 2019; Kusdarjito, 2019). Figure 1 shows various important logistic companies working in Indonesia.
However, these companies are facing several issues related to the logistic firm competency. The most important issues which has effect on the performance of these companies is firm competency. Firm competency has major role in firm performance. However, the issues related to the logistic companies has negative role in performance. Therefore, it is really important to have better firm competency to increase the overall performance. The low competency may be due to the inappropriate operations or low competency among the operations. Moreover, it is also based on the employee competency. Employee competency is the major in firm competency (Sabuhari, Sudiro, Irawanto, & Rahayu, 2020; van Esch, Wei & Chiang, 2018). The companies should investigate the factor which has role to increase the firm competency to enhance logistic firm competency in Indonesia.
However, the problems in the logistic companies can be resolved with the help of various factors to enhance the logistic firm competency. First of all, the introduction of technological management can increase the logistic firm competency. Management of operations with the help of technology has positive role in logistic firm competency. Secondly, idea implementation should be encouraged among the logistic companies to enhance the performance of firm competency. Both elements; technological management and idea implementations has major contribution in logistic firm competency. Furthermore, innovation also has vital role in all companies. Better innovation has the ability to promote firm performance as described in various studies (De Guimarães, Severo Dorion, Coallier & Olea, 2016; Hameed, Basheer, Iqbal, Anwar & Ahmad, 2018).
Therefore, this study is an attempt to highlight the role of technological management and idea implementation in logistic firm competency. The role of process innovation is used as mediating variables in the current study. Therefore, this study examined the relationship between technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency. Various previous studies also highlighted the logistic companies in Indonesia (Erna et al., 2019; Sriyakul, Umam & Jermsittiparsert, 2019; Sumantri & Lau, 2011), however, these studies have not consider the role of logistic firm competency. More importantly, the effect of technological management and idea implementations is not examined along with the mediating role of process innovation to facilitate logistic firm competency.
Literature Review
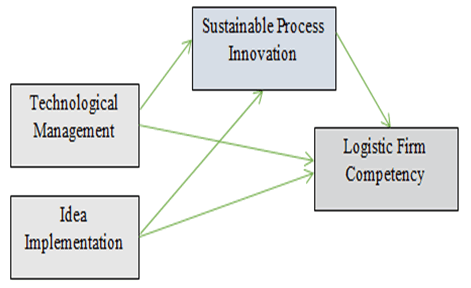
Competency is one of the major strengthen of the any company. Especially, competency by the logistic firm has major role in supply chain. Competent firms lead to the higher performance in the market along with the higher achievement which lead to the success. Generally, the success rate remains high for the companies having high competency. Competency among the companies comes from different resources. Most of the times it comes from the employees as competent employees is the major sources of firm competency. Therefore, the organizational competency is based on the individual competency. Furthermore, technology is also one of the sources of competency among the logistic companies. Better implementations of technology are the major sources of competency among the companies. Furthermore, idea generation capability by the employee in the companies is also another major sources of firm competency. The current study also examined the role of technology and idea generation among the logistic firm which causes to increase the competency. Hence, the relationship between technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency is highlighted in Figure 2. This relationship is also showing the mediating role of sustainable process innovation. As innovation is vital part of competency which is also clear from the previous studies (Michaelis & Markham, 2017).
Figure 2: Theoritical Framework of the Study Showing The Relationship Between Technological Management, Idea Implementation, Sustainble Process Innovation and Logistic Firm Competency
Technological Innovation and Logistic Firm Competency
Innovation is the process of new ideas generation in the process, services or new product development. Innovation can be described as the new idea generation for any process, operation or any other segment of the organization for the welfare of the company as well as for the benefit of the consumer. Innovation has several features as innovation is based on the reduction in cost or increase in the quality or decrease in production time. It has several benefits to the companies as well as for the customers. It has important relationship with the logistic firm competency. Increase in the innovation also increases the competency. The current study is dealing with the technological innovation in the logistic. Introduction of new technology to the existing system is important for the firm competency. This study introduced technological innovation because it is always important for the performance of the company. It increases the performance because technological innovation has vital role in the satisfaction of customers which ultimately increases the logistic firm competency. As revealed in the previous studies that technological innovation has positive role with firm performance (Abdul Basit, Kuhn & Ahmed, 2018; Latan, Jabbour, de Sousa Jabbour, de Camargo Fiorini & Foropon, 2020).
H1-Technological innovation has positive effect on logistic firm competency.
Technological Innovation and Sustainable Process Innovation
Along with the technological innovation effect on logistic firm competency, it also has positive role in sustainable process innovation. Among all innovations, process innovation is also most important among the companies to achieve the competency. Process is the duration of services development and steps in service development. As the current study is dealing with the service sector, therefore, it is dealing with process innovation in the service sector. Service has major role in the logistic performance after increasing the satisfaction among the customers. Therefore, the process of service development is also dependent on the technological innovation. Process innovation is heavily based on the technological innovation. Innovation in the technology increases the innovation in the process which further enhances the performance. However, low level technological innovation has adverse effect on the innovation in process. Therefore, technological innovation has positive role in logistic firm competency. Previous studies also show the most important role of process innovation in companies (Najafi-Tavani, Najafi-Tavani, Naudé, Oghazi & Zeynaloo, 2018; Sjödin, Parida, Leksell & Petrovic, 2018). Therefore, in the logistic firm competency improvement, technological innovation is most important which facilitate sustainable process innovation.
H2- Technological innovation has positive effect on sustainable process innovation.
Idea Implementation and Logistic Firm Competency
Idea is one of the new thoughts which may be valuable for the people as well as companies. In case of employees in the organization, employee provide various ideas related to the increase in the performance of any operation or process. However, the implementation of the idea is very low among the companies. Because, top management do not give the importance to low level employees and do not implement their ideas. Even the employee in the organization have not proper opportunities to share the idea. Therefore, idea sharing among the companies is at very initial level. Ideas cannot reach to the top management from the lower level employees. If the ideas reach to the top management, most of the time top management do not give the importance to these ideas. In this case the idea implementation is very low at the organizational level. It causes to the wastage of valuable ideas. If the idea implemented properly; it shows positive role in logistic firm competency. Better implementation of ideas increases the firm competency and increase in the competency increases the performance of the companies. Therefore, it is really important to implement the different ideas come from the lower level as well as top level employees of the logistic firms. Previous studies show the most valuable role of idea implementation among the organization (Brykman & Raver, 2018; He et al., 2019). Hence, this discussion lead to the following hypothesis.
H3- Idea implementation has positive effect on logistic firm competency.
Idea Implementation and Sustainable Process Innovation
Innovation in its up-to-date meaning is "a new idea, imaginative thoughts, new dreams in form of device as well as method". Innovation is frequently also observed as the application of better solutions that encounter new necessities, unarticulated wants, or current market needs. Innovation is influenced by the number of factors among the organizations. Among all other factors, ideas generation is one of the most important factors which has significant influence on sustainable process innovation. In the logistic companies, the role of idea implementation has major effect on the sustainable process innovation. To increase the sustainable process innovation, the idea generation as well as idea implementation should be improved among the logistic firms. In most of the companies, idea generating is lacking by the companies. Low idea generation decreases the innovation among the firms. Therefore, idea generation must be enhanced to increase the sustainable process innovation. Furthermore, idea generation is not sufficient to increase sustainable process innovation, it also requires proper idea implementation. Therefore, idea generation as well as idea implementation has most important role in organizations. As the idea generation and innovation has significant relationship with each other (Chan, Lim & Uy, 2020; Liang, Shu & Farh, 2019).
H4- Idea implementation has positive effect on sustainable process innovation.
Sustainable Process Innovation and Logistic Firm Competency
Sustainabilityemphases on meeting the requirements of the current without compromising the capability of future generations to meet their requirements. The idea ofsustainabilityis composed of three pillars: economic aspect, environmental aspect, as well as social aspect—also known informally as profits, planet, and people. However, the current study is dealing with the sustainability of innovation. The introduction of innovation in the organization is significant. The innovation process should be continued in the organization or the innovations should be upgraded with the passage of time. This study is dealing the sustainability in the process innovation. The sustainable process innovation has positive role in logistic firm competency. Competency of the firm can be increased with the sustainable process innovation. Various companies bring innovation in the process; however, these companies cannot get maximum benefits form this process innovation because these companies cannot sustain process innovation for longer period of time. Therefore, companies should bring process innovation to increase the logistic firm competency, however companies must sustain the process innovation for the longer period of time to enhance the competency. Innovation in the process can decrease the overall cost and increase the effectiveness in the whole process. Therefore, sustainable process innovation is most important which is required for logistic companies. As the process innovation has the relationship with logistic companies (de Paula, de Campos, Pagani, Guarnieri & Kaviani, 2019; Jaehrling, 2018). Thus, the above discussion shows that sustainable process innovation has positive effect on logistic firm competency.
H5- Sustainable process innovation has positive effect on logistic firm competency.
Mediation Effect of Sustainable Process Innovation
The current study also examined the mediation effect of sustainable process innovation. This mediation effect was examined by following the instructions of Baron & Kenny (1986) which suggested that all the three paths must be significant to take mediation effect of a specific variables. This study examined two mediation effect. The first mediation effect of sustainable process innovation was examined between technological innovation and logistic firm competency. The second mediation effect of sustainable process innovation was examined between idea implementation and logistic firm competency. The above discussion shows that technological innovation has positive role in sustainable process innovation. Idea implementation also has positive effect on sustainable process innovation. Furthermore, sustainable process innovation has significant relationship with logistic firm competency. Technological innovation and idea implementation have significant effect on logistic firm competency. Hence, all the relationships are significant to consider sustainable process innovation as mediating variable. Hence, the following mediation hypotheses are proposed.
H6- Sustainable process innovation mediates the relationship between technological innovation and logistic firm competency.
H7- Sustainable process innovation mediates the relationship between idea implementation and logistic firm competency.
Research Methodology
The relationship examined in the current study is measured with the help of quantitative research approach. The relationship between variables is measured by using a questionnaire. Therefore, this study examined the relationship between technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency which is measured by using a questionnaire. A survey questionnaire is the most vital part of research study of current nature (Zhang, Kuchinke, Woud, Velten & Margraf, 2017). Hence, to examine the effect of technological innovation and ideas implementation on process innovation and logistic firm competency, this study collected the data with the help of questionnaire by using quantitative approach.
Hence, a questionnaire was designed with the help of already available studies in the literature. Development of survey questionnaire is not the part of this study, as this study did not develop the scale items for any variables. Hence, all the measures are adapted from other studies and used for the questionnaire development. In the questionnaire, five variables, namely; technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency was measured. After the development of questionnaire, these questionnaires were distributed among the logistic firms in the Indonesia. Only these companies were selected which were purely based on the logistic services. Employee of these companies were selected for data collection. In the first section of questionnaire, the general information was collected related to the respondents. The second section of the questionnaire was comprised of scale items related to the key variables, namely; technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency. The five-point Likert scale was used in this study for data collection. Questionnaires were distributed with the help of cluster sampling which is most suitable in this situation (Altaf, Hameed, Nadeem & Arfan, 2019; Ul-Hameed, Mohammad & Shahar, 2018). Finally, 500 questionnaires were distributed among the employee of logistic firms in Indonesia. From total questionnaires, 260 were returned for data analysis.
Findings
Number of previous studies suggested that the data should be clean before to perform the analysis. As the clean data provide the accurate results. On the other hand, errors in the data has the significant potential to decrease the originality of the results. As the errors like missing value has negative role in the analysis and influence on the results (Aydin & ŞENOĞLU, 2018). Furthermore, along with the missing value, outlier in the data also has negative effect on the results. Hence, this study cleans the data from missing value and outlier as given in Table 1. Furthermore, normality of the data is also given in Table 1. However, normality of the data has no role in the current study because this study used Partial Least Square (PLS) which is suitable in non-normal data (Hameed et al., 2018).
| Table 1 Data Statistics |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Missing | Mean | Median | Min | Max | SD | Kurtosis | Skewness | |
| TM1 | 1 | 0 | 3.421 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.394 | -0.201 | -0.378 |
| TM2 | 2 | 0 | 3.409 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.942 | -1.03 | -1.418 |
| TM3 | 3 | 0 | 2.99 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.191 | -0.43 | -0.62 |
| TM4 | 4 | 0 | 3.44 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.232 | -1.64 | -0.524 |
| TM5 | 5 | 0 | 3.415 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.235 | -0.877 | -0.389 |
| TM6 | 6 | 0 | 3.478 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.933 | -1.575 | -1.569 |
| TM7 | 7 | 0 | 2.997 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.11 | -0.221 | -0.578 |
| II1 | 8 | 0 | 3.673 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.119 | -0.772 | -0.468 |
| II2 | 9 | 0 | 3.692 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.264 | -0.533 | -0.722 |
| II3 | 10 | 0 | 3.717 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.122 | -0.44 | -1.635 |
| SPI1 | 11 | 0 | 3.579 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1.173 | -0.473 | -0.474 |
| SPI2 | 12 | 0 | 3.541 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1.153 | -0.594 | -0.448 |
| SPI3 | 13 | 0 | 3.629 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.944 | -0.766 | -0.694 |
| SPI4 | 14 | 0 | 3.535 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.359 | -1.955 | -0.537 |
| SPI5 | 15 | 0 | 3.623 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.222 | -0.54 | -0.622 |
| SPI6 | 16 | 0 | 3.623 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.222 | -0.54 | -1.622 |
| SPI7 | 17 | 0 | 3.516 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.165 | -0.249 | -0.689 |
| LFC1 | 18 | 0 | 3.509 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.207 | -0.515 | -0.585 |
| LFC2 | 19 | 0 | 3.421 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.22 | -1.801 | -0.413 |
| LFC3 | 20 | 0 | 3.535 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.131 | -0.281 | -0.586 |
| LFC4 | 21 | 0 | 3.692 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.121 | -0.768 | -0.475 |
| LFC5 | 22 | 0 | 3.686 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.26 | -0.523 | -0.721 |
| LFC6 | 23 | 0 | 3.704 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1.13 | -0.372 | -1.663 |
| LFC7 | 24 | 0 | 3.585 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1.167 | -0.425 | -0.507 |
| LFC8 | 25 | 0 | 3.553 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1.125 | -0.42 | -0.496 |
| Note: TM=Technological Management; II=Idea Implementation; SPI=Sustainable Process Innovation; LFC=Logistic Firm Competency | |||||||||
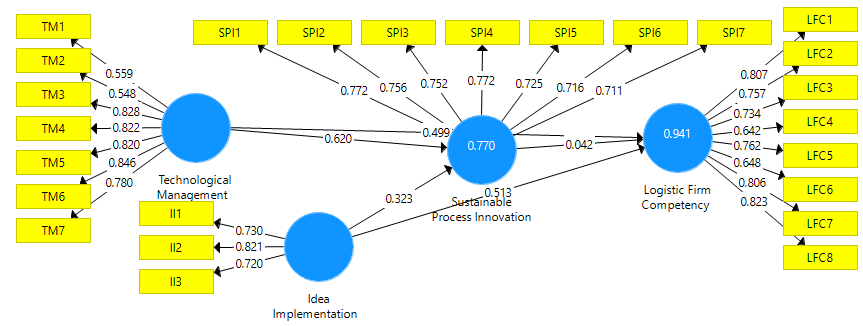
Different number of items were used to measure each variable. For instance, as shown in Figure 3 that technological innovation is measured by using seven items. Idea implementation is measured by using three items. Sustainable process innovation is measured by using seven items and finally, logistic firm competency is measured by using eight scale items. However, few scale items were removed due to low factor loadings from 0.5. Results of the analysis shows that all the variables; technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency have factor loadings above 0.5. The factor loadings was examined with the help of Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) as shown in Figure 3 Hair Jr, Sarstedt, Hopkins & Kuppelwieser, 2014; Hair, Ringle & Sarstedt, 2013; Hair, Sarstedt, Pieper & Ringle, 2012; Hair Jr, Hult, Ringle & Sarstedt, 2016). Factor loadings obtained from CFA is also given in Table 2.
| Table 2Factor Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idea Implementation | Logistic Firm Competency | Sustainable Process Innovation | Technological Management | |
| II1 | 0.73 | |||
| II2 | 0.821 | |||
| II3 | 0.72 | |||
| LFC1 | 0.807 | |||
| LFC2 | 0.757 | |||
| LFC3 | 0.734 | |||
| LFC4 | 0.642 | |||
| LFC5 | 0.762 | |||
| LFC6 | 0.648 | |||
| LFC7 | 0.806 | |||
| LFC8 | 0.823 | |||
| SPI1 | 0.772 | |||
| SPI2 | 0.756 | |||
| SPI3 | 0.752 | |||
| SPI4 | 0.772 | |||
| SPI5 | 0.725 | |||
| SPI6 | 0.716 | |||
| SPI7 | 0.711 | |||
| TM1 | 0.559 | |||
| TM2 | 0.548 | |||
| TM3 | 0.828 | |||
| TM4 | 0.822 | |||
| TM5 | 0.82 | |||
| TM6 | 0.846 | |||
| TM7 | 0.78 | |||
| Note: TM=Technological Management; II=Idea Implementation; SPI=Sustainable Process Innovation; LFC=Logistic Firm Competency | ||||
After the factor loadings, Composite Reliability (CR) and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) was examined through CFA. According to J. Hair, Hollingsworth, Randolph, and Chong (2017), CR must be above 0.7 and AVE must be above 0.5. According to the results, CR and AVE for technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency is above 0.7 and 0.5 respectively. Discriminant validity is shown in Table 3, 4 (Fornell & Larcker, 1981)
| Table 3Reliability and Convergent Validity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | rho_A | CR | AVE | |
| Idea Implementation | 0.728 | 0.738 | 0.801 | 0.575 |
| Logistic Firm Competency | 0.887 | 0.891 | 0.911 | 0.563 |
| Sustainable Process Innovation | 0.872 | 0.88 | 0.897 | 0.553 |
| Technological Management | 0.867 | 0.882 | 0.899 | 0.567 |
| Note: TM=Technological Management; II=Idea Implementation; SPI=Sustainable Process Innovation; LFC=Logistic Firm Competency | ||||
| Table 4Cross-Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idea Implementation | Logistic Firm Competency | Sustainable Process Innovation | Technological Management | |
| II1 | 0.73 | 0.635 | 0.561 | 0.482 |
| II2 | 0.821 | 0.749 | 0.641 | 0.602 |
| II3 | 0.72 | 0.645 | 0.515 | 0.505 |
| LFC1 | 0.609 | 0.807 | 0.668 | 0.79 |
| LFC2 | 0.571 | 0.757 | 0.595 | 0.521 |
| LFC3 | 0.51 | 0.734 | 0.617 | 0.676 |
| LFC4 | 0.734 | 0.842 | 0.568 | 0.476 |
| LFC5 | 0.81 | 0.862 | 0.635 | 0.625 |
| LFC6 | 0.706 | 0.648 | 0.508 | 0.508 |
| LFC7 | 0.715 | 0.806 | 0.769 | 0.65 |
| LFC8 | 0.716 | 0.823 | 0.736 | 0.69 |
| SPI1 | 0.702 | 0.791 | 0.799 | 0.643 |
| SPI2 | 0.74 | 0.822 | 0.856 | 0.687 |
| SPI3 | 0.407 | 0.451 | 0.752 | 0.554 |
| SPI4 | 0.49 | 0.505 | 0.772 | 0.54 |
| SPI5 | 0.403 | 0.415 | 0.725 | 0.522 |
| SPI6 | 0.392 | 0.412 | 0.716 | 0.518 |
| SPI7 | 0.604 | 0.766 | 0.711 | 0.604 |
| TM1 | 0.382 | 0.402 | 0.633 | 0.859 |
| TM2 | 0.385 | 0.395 | 0.633 | 0.848 |
| TM3 | 0.606 | 0.759 | 0.701 | 0.828 |
| TM4 | 0.622 | 0.82 | 0.684 | 0.822 |
| TM5 | 0.566 | 0.754 | 0.586 | 0.82 |
| TM6 | 0.569 | 0.734 | 0.634 | 0.846 |
| TM7 | 0.512 | 0.732 | 0.616 | 0.78 |
| Note: TM=Technological Management; II=Idea Implementation; SPI=Sustainable Process Innovation; LFC=Logistic Firm Competency | ||||
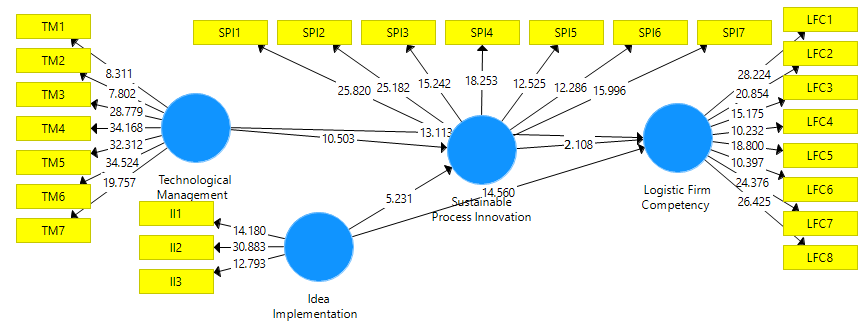
Furthermore, this study examined the direct effect of technological management and idea implementation on sustainable process innovation and logistic firm competency. These results were examined with the help of PLS structural model (Henseler & Chin, 2010; Henseler, Ringle & Sarstedt, 2015; Henseler, Ringle & Sinkovics, 2009). Results of the study shows that technological management and idea implementation has positive effect on sustainable process innovation and logistic firm competency. These results are given in Table 5 and Figure 4 shows the process.
| Table 5 Direct Effect Results |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (O) | (M) | SD | T Statistics | P Values | |
| Idea Implementation -> Logistic Firm Competency | 0.513 | 0.512 | 0.035 | 14.56 | 0 |
| Idea Implementation -> Sustainable Process Innovation | 0.323 | 0.325 | 0.062 | 5.231 | 0 |
| Sustainable Process Innovation -> Logistic Firm Competency | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.02 | 2.108 | 0.043 |
| Technological Management -> Logistic Firm Competency | 0.499 | 0.5 | 0.038 | 13.113 | 0 |
| Technological Management -> Sustainable Process Innovation | 0.62 | 0.619 | 0.059 | 10.503 | 0 |
| Note: TM=Technological Management; II=Idea Implementation; SPI=Sustainable Process Innovation; LFC=Logistic Firm Competency | |||||
Finally, this study examined that sustainable process innovation is a mediating variable between technological innovation and logistic firm competency with t-value 2.329. The mediation effect of sustainable process innovation between idea implementation and logistic firm competency with t-value 4.665. These results are given in Table 6.
| Table 6 Indirect Effect Results |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (O) | (M) | SD | T Statistics | P Values | |
| Idea Implementation -> Sustainable Process Innovation -> Logistic Firm Competency | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 4.665 | 0 |
| Technological Management -> Sustainable Process Innovation -> Logistic Firm Competency | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.011 | 2.329 | 0.031 |
| Note: TM=Technological Management; II=Idea Implementation; SPI=Sustainable Process Innovation; LFC=Logistic Firm Competency | |||||
Conclusion
This study examined the relationship between technological management, idea implementation, process innovation and logistic firm competency. This study was an attempt to highlight the role of technological management and idea implementation in logistic firm competency. The current study considered the logistic firms of Indonesian; consequently, data were collected from the Indonesian logistic firms and employees of logistic firms were selected for data collection. After the data analysis, results of the study revealed that logistic firm competency has major role which is influenced by the number of factors. Among all other factors, it is revealed that technological management has major role in logistic firm competency. Technological management has positive effect on logistic firm competency which indicates that increase in technological management increases the logistic firm competency. The other factor, idea implementation also has positive effect on logistic firm competency. Increase in idea implementation among the logistic companies increases the logistic firm competency. Therefore, both technological management and idea implementation have positive role to promote logistic firm competency. Along with these two factors, sustainable process innovation has vital role to enhance logistic firm competency. Sustainable process innovation has direct effect on logistic firm competency. Increase in innovation increase the logistic firm competency. Sustainable process innovation has significant role to transfer the positive effect of technological management and idea implementation on logistic firm competency.
Acknowledgement
Komson Sommanawat, an Assistant Professor and the Vice President of Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand is the corresponding author. His email address is komson.so@ssru.ac.th.
References
- Altaf, M., Hameed, W., Nadeem, S., & Arfan, S. (2019). Successful entrepreneurial process as contributor towards business performance in banking: moderating role of passion for inventing. South Asian Journal of Management Sciences, 13(1).
- Aydin, D., & Şenoğlu, B. (2018). Estimating the missing value in one-way anova under long-tailed symmetric error distributions. Sigma: Journal of Engineering & Natural Sciences, 36(2).
- Baron, R.M., & Kenny, D.A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of personality and social psychology, 51(6), 1173-1182.
- Basit, S.A., Kuhn, T., & Ahmed, M. (2018). The effect of government subsidy on non-technological innovation and firm performance in the service sector: Evidence from Germany. Business Systems Research: International Journal of the Society for Advancing Innovation and Research in Economy, 9(1), 118-137.
- Brykman, K., & Raver, J.L. (2018). From words to actions: The effects of voice quality on idea implementation. Paper presented at the academy of management proceedings.
- Butschan, J., Heidenreich, S., Weber, B., & Kraemer, T. (2019). Tackling hurdles to digital transformation—The role of competencies for successful Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) implementation. International Journal of Innovation Management, 23(04), 1950036.
- Chada, W., Leethongdee, S., Pengpid, S., & Chualinfa, S. (2020). Competency-based assessment of public health professionals in the Northeastern Region, Thailand: An exploratory factors analysis. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development, 11(1), 1735-1740.
- Chan, K.Y., Lim, K.H., & Uy, M.A. (2020). Entrepreneurship-professionalism-leadership: A framework for nurturing and managing the R&D workforce for a national innovation ecosystem Entrepreneurship–Professionalism–Leadership 177-207: Springer.
- De Guimarães, J.C.F., Severo, E.A., Dorion, E.C.H., Coallier, F., & Olea, P.M. (2016). The use of organizational resources for product innovation and organisational performance: A survey of the Brazilian furniture industry. International Journal of Production Economics, 180, 135-147.
- De Paula, I.C., De Campos, E.A.R., Pagani, R.N., Guarnieri, P., & Kaviani, M.A. (2019). Are collaboration and trust sources for innovation in the reverse logistics? Insights from a systematic literature review. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal.
- Erna, E., Surachman, S., Sunaryo, S., & Djajuli, A. (2019). Integration between radical innovation and incremental innovation to expedite supply chain performance through collaboration and open-innovation: A case study of Indonesian logistic companies. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 7(2), 191-202.
- Fornell, C., & Larcker, D.F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Journal of marketing research, 382-388.
- Hair, J., Hollingsworth, C.L., Randolph, A.B., & Chong, A.Y.L. (2017). An updated and expanded assessment of PLS-SEM in information systems research. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 117(3), 442-458.
- Hair, J.F., Ringle, C.M., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance.
- Hair Jr, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Hopkins, L., & G. Kuppelwieser, V. (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) An emerging tool in business research. European Business Review, 26(2), 106-121.
- Hair, J.F., Sarstedt, M., Pieper, T.M., & Ringle, C.M. (2012). The use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in strategic management research: A review of past practices and recommendations for future applications. Long range planning, 45(5-6), 320-340.
- Hair Jr, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM): Sage Publications.
- Hameed, W.U., Basheer, M.F., Iqbal, J., Anwar, A., & Ahmad, H.K. (2018). Determinants of firm’s open innovation performance and the role of R & D department: an empirical evidence from Malaysian SME’s. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 8(1), 29.
- He, W., Han, Y., Hu, X., Liu, W., Yang, B., & Chen, H. (2019). From idea endorsement to idea implementation: A multilevel social network approach toward managerial voice implementation. Human relations.
- Henseler, J., & Chin, W.W. (2010). A comparison of approaches for the analysis of interaction effects between latent variables using partial least squares path modeling. Structural Equation Modeling, 17(1), 82-109.
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 43(1), 115-135.
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M., & Sinkovics, R.R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing new challenges to international marketing. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 277-319.
- Jaehrling, K. (2018). –The digitization of warehousing work. Innovations, employment and job quality in French, German and Dutch retail logistics companies. Virtuous circles between innovations, job quality and employment in Europe? Case study evidence from the manufacturing sector, private and public service sector, 280.
- Jermsittiparsert, K., & Wajeetongratana, P. (2019). The role of organizational culture and it competency in determining the supply chain agility in the small and medium-size enterprises. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 5(2), 416-431.
- Kusdarjito, C. (2019). China’s belt and road initiatives and indonesia’s maritime fulcrum: Building scenarios for economic multipolarity in South East Asia. Paper presented at the International Conference on Banking, Accounting, Management, and Economics (ICOBAME 2018).
- Latan, H., Jabbour, C.J.C., De Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L., De Camargo Fiorini, P., & Foropon, C. (2020). Innovative efforts of ISO 9001-certified manufacturing firms: Evidence of links between determinants of innovation, continuous innovation and firm performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 223, 107526.
- Liang, J., Shu, R., & Farh, C.I. (2019). Differential implications of team member promotive and prohibitive voice on innovation performance in research and development project teams: A dialectic perspective. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 40(1), 91-104.
- Michaelis, T.L., & Markham, S.K. (2017). Innovation training: Making innovation a core competency a study of large companies shows that, although managers see human capital as central to innovation success, most aren’t providing innovation training. Research-Technology Management, 60(2), 36-42.
- Moh’d Abu Bakir, S. (2019). Human resources development strategy and its role in promoting employees strategic thinking competencies: A study at jordanian information technology companies. European Scientific Journal, ESJ, 15(4), 238-262.
- Najafi-Tavani, S., Najafi-Tavani, Z., Naudé, P., Oghazi, P., & Zeynaloo, E. (2018). How collaborative innovation networks affect new product performance: Product innovation capability, process innovation capability, and absorptive capacity. Industrial Marketing Management, 73, 193-205.
- Sabuhari, R., Sudiro, A., Irawanto, D., & Rahayu, M. (2020). The effects of human resource flexibility, employee competency, organizational culture adaptation and job satisfaction on employee performance. Management Science Letters, 10(8), 1775-1786.
- Sjödin, D.R., Parida, V., Leksell, M., & Petrovic, A. (2018). Smart factory implementation and process innovation: A preliminary maturity model for leveraging digitalization in manufacturing moving to smart factories presents specific challenges that can be addressed through a structured approach focused on people, processes, and technologies. Research-Technology Management, 61(5), 22-31.
- Sriyakul, T., Umam, R., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2019). Total quality management and logistic performance: Moderating role of reserve supply chain in pharmaceutical industry of Indonesia. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 5(2), 228-248.
- Sumantri, Y., & Lau, S.K. (2011). The current status of logistics performance drivers in Indonesia: An emphasis on potential contributions of Logistics Service Providers (LSPs). Journal of Asia Pacific Business Innovation & Technology Management, 1, 34-50.
- Ul-Hameed, W., Mohammad, H., & Shahar, H. (2018). Microfinance institute’s non-financial services and women-empowerment: The role of vulnerability. Management Science Letters, 8(10), 1103-1116.
- Van Esch, E., Wei, L.Q., & Chiang, F.F. (2018). High-performance human resource practices and firm performance: The mediating role of employees’ competencies and the moderating role of climate for creativity. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(10), 1683-1708.
- Zhang, X., Kuchinke, L., Woud, M.L., Velten, J., & Margraf, J. (2017). Survey method matters: Online/offline questionnaires and face-to-face or telephone interviews differ. Computers in human behavior, 71, 172-180.