Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
The Strategic Lens and its Impact on the Entrepreneurial Orientation of Business Organizations
Ahmed Hashem Alsaqal, AL-Iraqia University
Hameed Ali Ahmed, AL-Iraqia University
Sudfa Muwafaq Aljubory, AL-Iraqia University
Abstract
This study aims to analyze the impact of the strategic lens on the entrepreneurial orientation of organizations on a sample of managers in private commercial banks in the city of Baghdad. The importance of the study lies in the scarcity of research that dealt with strategic lenses and their role in the entrepreneurial trend in banks. Where this study dealt with the problem of the complexity of the internal and external environments of the organizations that contributed to creating problems and obstacles in the implementation of the strategy, with the lack of understanding or understanding of this issue by managers in private banks (study community). The field study tool was the questionnaire to collect information by (156) individual, which represented the number of retrieved questionnaires out of (160) questionnaires distributed to the managers working in the research sample banks, as the results of the study confirmed the existence of an impact of the strategic lens on the pioneering orientation of the banks investigated. This indicates that the approach of the strategic lens has a fundamental role in achieving the entrepreneurial orientation in the surveyed banks, and the study recommended several recommendations, the most important of which is that the managers of organizations should be motivated by change and try to look at the strategy through a set of lenses to accurately assess situations, and that organizations should Those who want to be successful in entrepreneurship should have an entrepreneurial orientation.
Keywords
Strategic Lens, Entrepreneurial Orientation
Introduction
In light of a highly volatile and complex environment, business organizations seek to implement their strategies with as few problems and obstacles as possible that they may face, as the increased intensity of competition between them made them look for modern scientific frameworks to implement their strategies and affect the pioneering trend to achieve competitive advantage in front of their peers.
Therefore, the approach to the strategic lens, which was put forward by business administration researchers in the last two decades, was concerned with forming multiple perceptions and visions related to the future of implementing the strategy and ways to confront the problems of its implementation in the present to avoid their occurrence in the future, as well as seeking to anticipate the activities of competitors and try to evaluate them in order to lead them and quickly present ( Good / service) of the organization to the customer and persuading him, where researchers saw in the strategic lens that it is the attempt of managers of organizations to provide different visions on issues related to strategy and the possibility of obtaining a more complete picture to give different visions from multiple points of view and these different ideas can lead to thinking about Different options or solutions to strategic problems.
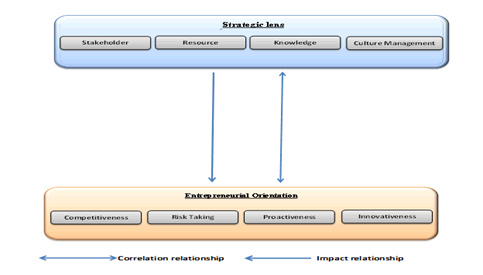
Therefore, the current study was concerned with choosing the subject of the strategic lens as an independent variable and to identify its relationship to one of the most important variables that distinguished organizations are interested in, which is the pioneering orientation of business organizations. In light of facing intense internal competition and trying to deliver its services to its customers inside and outside Iraq, the main measurement tool was adopted by designing a questionnaire and distributing it to a sample of managers in those banks to reach the desired results through the use of the statistical package (SPSS.V.25) with the aim of Determining the relationship between the two variables of the study, the strategic lens with its dimensions (stakeholder participation, resource mobilization, knowledge development, culture management) and the entrepreneurial orientation with its dimensions (competitiveness, risk tolerance, proactivity, creativity).
First: Review the Literature
Concept of the Strategic Lens and its Importance in Business Organizations:
Study's (Padurean, 2010) on the strategic lens stated that it focuses on the roles, policies, and formal procedures in the areas of strategy, and indicates the importance of the organizational design and structure, and is concerned with understanding behavior and identifying the players who lead processes and change, and defining goals, tasks and motives for implementing the strategy. While (Al-Khafaji, 2015) considered it a set of different ways of looking at the issues of developing the strategy of the organization, and provides insight into the different points of view on the strategy that arose and emerged from the research and studies in the field of strategy. While (Al-Janabi, 2019) argued that it is the process of looking at strategic issues differently by analyzing strategic situations, diagnosing weaknesses and strengths in the situation, and guiding the organization towards making sound decisions. To tackle one problem with multiple solutions. Hussain & Atiyah (2019) concluded that the strategic lens means the ability of organizations to focus in a way that allows them to see the signs that move clearly from all angles around the organization to allow them to achieve their goals.
A comprehensive definition of the strategic lens can be drawn as multiple visions of various methods aimed at developing the implementation of what has been formulated from the strategy of the business organization, through which the flow of tasks and information and how to accomplish things are examined, and the lens reveals many dimensions, practices and activities in the organization. Using all of these areas as a lens, managers look to improve workflow to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization.
Researchers have argued about the problems of strategies and obstacles to their implementation in business organizations, where studies gather that the implementation of the strategy is no less important than its formulation, and even if the formulation is good and the implementation is weak, there will be problems and obstacles, and it is difficult to master the formulation of the strategy if not impossible to evaluate in the absence of Good implementation (Abu Al-Nasr, 2009). Formulation is the strategy development process (where are we now? and where do we want to be?), it includes internal and external analyzes of the organization, and the ability of companies to formulate strategies is more sophisticated than their ability to implement the strategy (Engert & et al., 2016). With the importance of strategy formulation, attention must also be paid to implementing the formulated strategies, otherwise the entire formulation phase becomes worthless, and despite the difficulty of formulating the strategy, its implementation throughout the organization is more difficult than that (Tomac & Danijel, 2010).
In order to be effective, the implementation of the strategy must be a multifaceted and variable process in which managers and employees carry out a number of decisions and tasks, which are affected by different organizational and environmental factors to achieve strategic goals (Alharthy, 2017). In this direction the lens calls for conceptual and practical value in a multi-modal approach to strategy since there are limitations and potential risks of one method over another (Johnson & et al., 2008). Thus, the lens is considered one of the most important tools that give organizations the ability and power to work with effective strategies and policies that enable them to compete, excel, and achieve strategic transparency (Hussain & Atiyah, 2019).
Dimensions of the Strategic Lens
Most of the challenges that organizations face require action in four common strategic areas: stakeholder engagement, resource mobilization, knowledge development, and culture management. These four central themes - we call them strategic lenses - highlight a series of common strategic questions (Dawans & Alter, 2009).
Participation of Stakeholders
They are “individuals and groups who have an interest in the organization, which includes the interest of employees (both managers and non-managers), shareholders, and executives in senior management, suppliers, creditors, official employees, or what they are sometimes called inspectors of organizations and bodies. Integrity in government bodies and managers in competing organizations, charitable organizations, and public sector organizations, and to them were added stakeholders who affect its survival and continuity, and who represent the main nerve of its life and sustainability.
This means that managers should pay attention to external groups, in order to obtain their support, and here they categorized stakeholders as strategic beneficiaries (Al-Anzi, 2007). The dimension of stakeholder participation stems from the idea that strategy is the organization’s tool for the purpose of a balanced response to all the interests of the influential parties inside and outside it, including shareholders, competitors, suppliers and customers. 14).
Resource Mobilization
It is assumed that the environment contains rare and valuable resources necessary for the survival of the organization, and for organizations to be successful, they adjust their structure and behavior patterns to better secure the required external resources, as the organization gains overall strength by owning the resources that others need and reducing its dependence on others to obtain At the same time, organizations are supposed to create internal and external alliances, where alliances arise from social exchanges formed to influence and control behavior, and organizations are supposed to work to achieve two related goals in their environment: (1) control of resources that reduce their dependence on other organizations and (ii) control the resources that increase the dependence of other organizations on them (Arik & et al., 2016). The organizational studies focused on the resources as (materials, human resources and skills), which are the dimensions of the distinct resources for new projects, and the process of “dealing with the resources at hand” represents the common denominators of each dimension in order to determine the extent of the activity of those projects (Desa, 2012).
Knowledge Development
Is one of the most important processes that help organizations identify, select, arrange, deliver and transfer important information and specialized knowledge, as knowledge development is a business strategy that is driven by the vision of transformations based on products and processes? As it is the main factor in the performance of business organizations and their achievement of competitive advantage (Hussain & Atiyah, 2019). From a strategic point of view, knowledge development is described as knowledge derived from the data of strategic analysis, which is concerned with providing information on the strengths and weaknesses of the organization, as well as with regard to the opportunities and threats it faces as well as one of the fruits of the organization’s achievements in the field of knowledge management through its creation, development, dissemination and adoption to achieve its goals (Al-Janabi, 2019).
Managing Organizational Culture
Many academics and practitioners alike are interested in learning the various dimensions of organizational culture in order to understand the intangible qualities that affect the effectiveness of different work environments, as managing culture generates interest for different organizational levels to influence organizational activities administrative mprocesses and results.
Where organizations work to develop unique cultures that affect business, and work to develop an understanding of the characteristics of organizational culture and effectiveness that are produced through strategic management (Al-Abadi & Al-Dhabawi, 2017). The characteristics of strategic organizations are characterized by cultural frameworks and the interpretation of organizational phenomena that actually occur within organizations through an effective culture that fits with many organizational components and issues related to the organizations’ strategic culture (Hussain & Atiyah, 2019).
Entrepreneurial Orientation and its Importance in Business Organizations
The study of (Putniņš & Sauka, 2019) considered that the entrepreneurial trend reflects the tendencies of the main players within the organization to adopt calculated risks, creativity and follow-up proactive behaviors. While the study of (Al-Atwi & Al-Kaabi, 2019) found that the entrepreneurial orientation refers to the policies and practices that provide a basis for making pioneering decisions and the appropriate procedures for them, which include the development of a strategy and operations aimed at developing opportunities for the organization's projects. As for the study (Majed & Ali, 2020), it saw in the pioneering approach the strategic situation adopted by organizations of all kinds, which expresses their tendencies to adopt new ideas and transform them into new products, services, processes or procedures, and a willingness to bear the risks associated with them, as well as creativity in their products. Whereas (Mahmoud, 2020) defined it as the extent of the organization’s desire to identify, acquire and seize successful opportunities to launch new projects by entering new markets or establishing markets by providing new products.
From the foregoing, it can be concluded that the entrepreneurial approach is the practices and activities through which the organization’s management expresses methods to seize the available opportunities in the market and bear its risks to provide proactive products or services that were not available, risk them, and generate distinct creative ideas that achieve a competitive advantage.
Therefore, researchers agree that the orientation towards entrepreneurial has become an important topic in the field of management, which has been developed as a strategic direction for the organization, which helps it to overcome the problems that it may face and improve its current performance, as well as its contribution to accelerating economic development through the generation of new ideas and transforming them into Profitable risks (Al-Azzawi & Mohsen, 2017). In the current era, the economic environment is changing rapidly and markets are characterized by excessive uncertainty, and therefore entrepreneurial organizations must be willing to take risks. Without risk, the prospects for business growth will diminish (Naldi et al., 2007).
The researchers discussed the importance of the entrepreneurial approach in organizations, as it helps in the renewal and restructuring of economic projects. It is also a means of change, development, and strategic renewal (Abd Ali & Mahdi, 2016). On the economic level, its importance lies in finding many projects that are important for the development of the economy and development, as well as creating job opportunities of long-term importance in order to achieve economic growth (Al-Atwi & Al-Kaabi, 2019). Entrepreneurial orientation is also an important factor for social growth because it provides millions of jobs through opportunities, and provides a variety of goods and services, which leads to increased national prosperity (Lee & Peterson, 2000).
Dimensions of Entrepreneurial Orientation
Most of the literature portrays the entrepreneurial orientation as a complex structure consisting of four dimensions: (competitiveness, risk, proactiveness & creativity), but many studies indicate that the entrepreneurial orientation is nothing but management strategies in the areas of competitiveness, proactiveness, risk-taking and creativity (Herlinawati et al., 2019).
The dimensions of the entrepreneurial orientation can be identified in detail through the research and studies as follows:
Competitiveness
Competitiveness is seen as the ability to perform well that is capable of generating and sustaining competitive advantages for the organization towards competitors, provided that it focuses on the factors that lead to competition; Thus, it contributes to the growth of the organization's productivity, achieving successful long-term results against competitors, securing and growing its market share and increasing profits (Caseiro & Coelho, 2018).
While the competitive entrepreneurial orientation refers to the direct challenge of competitors to achieve a significant entry into the market, or to improve the competitive position in it through hostility in competition and in the form of confronting equal parties, and the goal of confrontation is to achieve a competitive advantage for the organization, and the competitive entrepreneurial orientation is characterized by speed in new entry to the market, by accelerating the product development cycle (Al-Nuaimi et al., 2016).
Take Risks
It indicates that the organization has a great conviction in the face of competitors and that this requires it to adopt risk in the various projects it enters and the activities and operations it undertakes at the internal and external levels, as the organization cannot withstand the currents of strong competition without having a high ability to withstand those The risk is the level that the managers of organizations have a sufficient perception that risk is a key part in achieving sustainability for the success of their organizations’ business (Al-Fatlawi et al., 2020).
Between "risk" and "uncertainty" or "ambiguity", "risk" refers to a situation in which the probabilities of outcomes are known or can be estimated from past data, while "uncertainty" or "ambiguity" is a situation in which the probabilities of the outcomes are the same. Unconfirmed or unknown as when embarking on an unprecedented venture endeavour (Putniņš & Sauka, 2019).
The interpretation of the entrepreneurial approach to risk taking depends on the content in which it is applied, there is the risk in the individual content, the risk in the organizational content, the risk in the financial content, and the risk in the technological content (Al-Naimi et al., 2016).
Proactive
It indicates the extent of the organization's response to new changes and its willingness to be the one affecting the market and not the other way around (Majid & Ali, 2020). That is, proactiveness gives organizations the ability to provide new products or services that gives them a competitive advantage as well, and those organizations are likely to be leaders in their products, services or processes in entering the foreign market (Oladimeji et al., 2019).
Proactive organizations, through the effects of learning and experience gained over time, tend to be more attuned to changes and trends in the market, giving the organization opportunities to reach needs ahead of competitors. (Hughes & Morgan, 2007).
Creativity
Creativity refers to organizations producing new products, new materials, new processes, new services, and new organizational forms to gain a competitive advantage (Guo et al., 2020).
The creative orientation is a pre-creative culture, as it provides the necessary facilities for organizations to develop their ability to innovate and explore new technologies (Al-Sayer, 2017). Rather, it stimulates the organization towards differentiation and to come up with what is different from other direct competitors and others, as it creates a market segment through a unique response to its needs through creativity (Al-Atwi & Al-Kaabi, 2019). The literature confirms that the common denominator among all organizations that can be described as entrepreneurship is the presence of creativity (Karimi & Walter, 2018).
Second: Research Methodology
Research Problem
The researchers sought to convey the idea of the strategic lens to the managers of organizations, considering that those departments are the responsible party for implementing the strategy in them.
The main problem at the level of applying the strategic lens approach in those organizations was its lack of clarity with managers.
This is what was shown in the initial interviews when designing the paragraphs of the research questionnaire included in the applied study of the current research, which is a group of branches of private banks located in Baghdad exclusively, and from this problem other problems were formulated through the following questions:
A- Do the executive directors of private banks follow the modern administrative approaches in which researchers are making strenuous efforts, including the entrance to the strategic lens?
B - Do the managers of private banks realize the importance of searching for solutions to address the problems of implementing the strategy, or is the matter up to them?
C- What is the amount of awareness surrounding the importance of the strategic lens entrance in the banks surveyed?
D- Is there a real awareness of the effectiveness of the dimensions of the strategic lens and its impact on the entrepreneurial trend in the banks surveyed?
Research Objectives
The main objective of the research is to reach the relationship between the strategic lens and the entrepreneurial orientation. Other goals can also be identified as follows:
A - A conceptual and cognitive framing based on previous cognitive efforts for the research variables represented in (strategic lens and entrepreneurial orientation.
B- To draw the attention of the organizations in general and those surveyed in particular to the importance of the research variables and their relationship to each other, and to try to spread the adoption of the strategic lens approach to solve the problems of implementing the strategy.
C- Urging the organizations in general and the banks surveyed in particular on the importance of the strategic lens approach as a modern approach that contributes to strengthening the entrepreneurial orientation in the organizations.
D- Determining the nature of the relationship and influence between the strategic lens and the pioneering orientation of the banks investigated.
Research Hypotheses
In light of the importance of the current research and to achieve its objectives, its hypotheses were formulated as follows:
Study Population and Sample
Eight private banks operating in the city of Baghdad were selected exclusively and the managers working in them considered the research community to apply and test its hypotheses, which are (Al-Mansour Islamic Bank, the Iraqi Islamic Bank for Investment and Development, the National Bank of Iraq, the Spectrum Islamic Bank, Babel Bank, the Gulf Commercial Bank, the Economy Bank for Investment and Finance Sumer Bank)
As for the research sample, a group of managers was selected using the intentional sampling method in selecting the research sample, which amounted to 156 individuals.
Third: Discussing the Results
First: Test the Search Measurement Tool
The primary data was collected to address the analytical aspects of the research topic, through a questionnaire as a research tool, designed specifically for this purpose and distributed to a sample of individuals in different units and departments, and then unloaded and analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences "SPSS" program. In order to calculate the ratios and use the appropriate statistical tests in order to reach valuable indications and indicators that supports the subject of the study. This questionnaire consists of two parts as follows:
The First Section
Represents the personal information of the individual: age, gender, educational qualification, years of service, and job title.
The Second Section
It is about the fields of the questionnaire and it consists of (40) paragraphs and is divided into two axes:
The First Axis
It is a set of questions centered around the (strategic lens) and includes paragraphs (participation of stakeholders, resource mobilization, knowledge development, management of organizational culture).
The Second Axis
A set of questions about (entrepreneurial orientation) and includes paragraphs (competitiveness, accepting risks, proactiveness, creativity).
The Likert Scale, which includes five levels of levels, was adopted to determine the degree of approval of the research sample or not on each of the research paragraphs and converted into quantitative data with relative weights that can be analyzed using statistical tools and means.
It was necessary to conduct the following tests to ensure the accuracy and validity of the data obtained through the use of the questionnaire that relates to the field of validity and reliability, as follows:
The results of the Internal Consistency Test
The results of the stability or internal consistency are tested through the correlation coefficient (Cronbach Alpha) shown in Table (1), with which the internal consistency of the paragraphs of the scale was confirmed at the level of all dimensions after the values of the correlation coefficients (Cronbach Alpha) exceeded the acceptable minimum It has (0.70), which confirms the internal consistency of the scale and thus its stability required in the event of repeated testing.
| Table 1 Results of the Internal Consistency Test of the Scale |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variables and dimensions | Cronbach's alpha dimensional coefficient | honesty |
| Strategic lens | 0.779 | 0.883 |
| Participation of stakeholders | 0.855 | 0.925 |
| Resource mobilization | 0.834 | 0.913 |
| Knowledge development | 0.791 | 0.889 |
| Managing organizational culture | 0.747 | 0.864 |
| Entrepreneurial Orientation | 0.755 | 0.869 |
| Competitiveness | 0.748 | 0.865 |
| Take risks | 0.785 | 0.886 |
| Proactive | 0.763 | 0.873 |
| Creativity | .775 0 | 0.88 |
| For all items of the questionnaire | 0.87 | |
The Reliability of the Questionnaire
To measure the reliability, the split-half method is used, which is summarized by finding the correlation coefficient between the scores of the individual questions and the scores of the even questions in the questionnaire. The correlation coefficient is corrected by the (Spearman – Brown) equation. According to the equation, it is sufficient for the research that depends on the questionnaire as a tool for it, and when applying this method, it was found that the correlation coefficient of the questionnaire was (0.72), which means that with its different scales it has good stability and can be adopted at different times and for the same individuals and gives the same results.
Second: Description and Analysis Of The Study Variables
Strategic Lens Variant
Table (2) shows the arithmetic mean, standard deviation, coefficient of variation, order of dimensions importance in general, the direction of the answer to the opinions of the researched sample. In order to rank the importance of the dimensions of the independent variable, the strategic lens, the coefficient of variation was used to measure the dispersion of the paragraphs depending on the arithmetic mean and the standard deviation, as shown in Table (2), as it is clear that the dimension (development of knowledge) came in the first order in terms of the dispersion of answers about the dimensions of the strategic lens As most of the sample answers were in agreement about that compared to the other dimensions.
| Table 2 Ranking of Importance According to the Coefficient of Variation for the Dimensions of the Strategic Lens |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S NO. | Dimensions of Strategic lens | Arithmetic mean | Standard deviation | Coefficient of variation, | order of dimensions importance |
| 1 | Participation of stakeholders | 3.539 | 1.118 | 31.585 | 4 |
| 2 | Resource mobilization | 3.313 | 0.986 | 29.761 | 3 |
| 3 | Knowledge development | 3.133 | 0.463 | 14.778 | 1 |
| 4 | Managing organizational culture | 3.377 | 0.922 | 27.302 | 2 |
Entrepreneurial Orientation Variant
To order the importance of the dimensions of the dependent variable the entrepreneurial orientation, the coefficient of variation was used, depending on the arithmetic mean and the standard deviation, as shown in Table (3), as it is clear that the dimension (take risk) came in the first order in terms of the dispersion of answers about the dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation, as most of the answers were The sample is in agreement about that compared to the other dimensions.
| Table 3 Ranking of Importance According to the Coefficient of Variation for the Dimensions of the Strategic Lens |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions of Entrepreneurial Orientation | Arithmetic mean | Standard deviation | Coefficient of variation, | Order of dimensions importance | |
| 1 | Competitiveness | 3.31 | 1.044 | 31.54 | 1 |
| 2 | Take risks | 3.489 | 0.441 | 12.639 | 2 |
| 3 | Proactive | 3.554 | 0.577 | 16,235 | 3 |
| 4 | Creativity | 3.277 | 0.572 | 17.454 | 4 |
Third: Analyzing The Correlation Between The Research Variables
Testing the first main hypothesis (there is a significant correlation between the strategic lens and the entrepreneurial orientation of business organizations.
The correlation coefficient between the strategic lens and the entrepreneurial orientation was (0.211**) at the significance level (0.004) which is less than the significance level (0.05), as the calculated (t) value reached (2.945), which is greater than the tabular (t) value of (1.984), This means accepting the hypothesis, which indicates that the dimensions of the strategic lens have an active and clear role in developing the entrepreneurial orientation of the banks surveyed. As the entrance to the strategic lens, which will be adopted by the bank, will have a role in the nature of the level of entrepreneurial orientation.
Fourth: Testing And Analyzing The Effect Between The Study Variables
To test the impact hypothesis, it will be relied on the regression analysis equation to estimate the parameters of the model, as the regression analysis is a statistical tool that builds a statistical model to estimate the relationship between two variables (independent variable) and (dependent variable) so that it produces a statistical equation that shows the causal or interrelationship between the variables. And when the relationship in the statistical model is between a dependent variable and one independent variable, then this model is a simple liner regression.
The influence relationship identified by the research is tested for the purpose of determining the possibility of judging it with acceptance or rejection. As the second effect hypothesis (there is a statistically significant impact relationship for the strategic lens in the entrepreneurial orientation of business organizations), it will be investigated according to the simple linear regression equation as follows:
Y = α+β1X1
(α) Constant represents the amount of the constant, β1 the Marginal propensity, and this relationship means that the entrepreneurial trend (Y) is a function of the real value of the strategic lens variable. As for the estimates of these values and their statistical indicators, they were calculated at the level of the research sample amounting to (156) in the surveyed banks and it will be Analyze the levels of influence between the variables as follows:
The Second Hypothesis Test
To test the hypothesis that states the following (there is a statistically significant impact relationship for the strategic lens practices in the entrepreneurial orientation of business organizations), the analysis will be done according to a simple linear regression model, as follows:
Y= α + β (X)
Y= 2.472+ 0.266 (X)
(A) The value of (F) calculated for the strategic lens in the entrepreneurial trend was (8.673). And it is greater than the tabular value (F) of (3.89) at the level of significance (0.05), and accordingly we accept the hypothesis which states (there is a statistically significant effect of the strategic lens on the entrepreneurial trend) at the level of significance (5%), i.e. with a degree of confidence (95%). This indicates that the entrance of the strategic lens has an essential role in achieving the entrepreneurial orientation.
B) Through the value of the coefficient of determination (²R) of (0.044), it is clear that the strategic lens explains (44%) of the variables that occur in the entrepreneurial trend, while the remaining (56%) is due to other variables that are not included in the research model.
(C) It is clear from the value of the marginal slope coefficient (β) of (0.663) that increasing the strategic lens by one unit will lead to an increase in the entrepreneurial trend by (66%).
(D) The value of the constant (α) in equation (2.472).
Conclusion and Discussion
The main idea behind the concept of a strategic lens is that it provides different visions on issues related to strategy and the possibility of obtaining a more complete picture from multiple perspectives, and these different ideas can lead to thinking of different options or solutions to strategic problems. As the strategic lens aims mainly at developing the implementation of what has been formulated from the strategy of the business organization, through which the flow of tasks and information and how to accomplish things are examined. While the strategic lens focuses on practices and activities in the field of strategy implementation, the entrepreneurial orientation focuses on the processes and decision-making activities that lead to identifying opportunities for the business organization, and deals with the exploitation of internal strengths (strategic management) that result from continuous efforts to explore opportunities (entrepreneurship).
The results proved that there is a significant correlation between the strategic lens and the entrepreneurial orientation in the banks studied. This indicates the existence of an active role in the strategic lens dimension in the entrepreneurial direction.
The results also indicated that there is a significant effect relationship of the strategic lens in the entrepreneurial orientation. This indicates that the dimensions of the strategic lens have an essential role in achieving the entrepreneurial orientation.
The study recommended that the managers of organizations, in order to understand the concept of strategic lenses, should be motivated by change and according to the strategic directions of their organizations, and try to look at the strategy through a set of lenses to accurately assess situations.
Organization managers must also put multiple points of view, that is, look in different ways in the strategic development issues of the organization in order to look at the problems that occur in the organization in different ways and overcome the strategic problems.
Organizations have to take risks in the various projects they enter and the activities and operations they carry out at the internal and external levels. In order to aspire to competitiveness, it must depend on analyzing the interrelationship between business units and diversifying their core values to develop products with consumer satisfaction. As for its proactive approach, the organization must continuously search for new land with a quick response to changing environmental trends and practice activities that affect the environment.
References
- Ali, A., Dayikh, N., & Abeer, Md. (2016). The impact of resistance to change on the organization’s entrepreneurial orientation (An analytical study of the views of a sample of workers in the health department of the Holy Karbala Governorate). Journal of Administration and Economics, 5(19).
- Abu Al-Nasr, M. (2009). The elements of outstanding strategic planning and thinking. The Arab Group for Training and Publishing.
- Al-Abadi, H.F., Al-Dhabawi, S., & Karim, A. (2017). The strategic lens and its role in centralizing organizations at the strategic summit - An applied study in Al-Bashir shopping center in Najaf Governorate. Al-Ghari Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 14(3).
- Al-Anazi, S. (2007). A serious attempt to frame the theory of stakeholders in business administration studies. Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 18(48).
- Al-Atwi, H. (2012). Managing the forces of contradiction to ensure sustainable organizational performance within the framework of the dynamic equilibrium model of organization. PhD thesis in Business Administration Sciences - University of Baghdad - College of Management and Economics.
- Al-Azzawi, A., & Mohsen, Z.H. (2017). Entrepreneurial orientation and its impact on organizational excellence. Anbar University Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 9(18).
- Al-Fatlawi, M. (2020). The impact of the entrepreneurial approach in sustaining the success of competitive strategies - An analytical research of the opinions of the managers of Ur Public Company in Dhi Qar Governorate. The Iraqi Journal of Administrative Sciences, 16(66).
- Alharthy & Abdullah H. (2017). Identification of strategy implementation influencing factors and their effects on the performance. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 8(1).
- Al-Janabi, H. (2019). Employing the relationship between the lens and strategic agility and its role in enhancing cognitive competence. Master's thesis - College of Administration and Economics - Tikrit University.
- Al-Khafaji, N. (2015). Strategic lenses. Al-Yazuri Publishing and Distribution House.
- Al-Nuaimi, A. (2016). The impact of the relationship between the gradual and radical entrepreneurial orientation on the organizational effectiveness of Jordanian private universities in Amman. Journal of Baghdad College of Economic Sciences University, 48.
- Al-Sayer, Y. Md. (2017). The relationship between entrepreneurial orientation and market orientation and their impact on competitive advantage. A study of a sample of workers in private banks in the city of Dohuk. Journal of Baghdad College of Economic Sciences University, 51.
- Arik, M. (2016). Strategic responses of non-profit organizations to the economic crisis: Examining through the lenses of resource dependency and resourced-based view theories. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 15(1).
- Hussain, A.N., & Abbas, G.A. (2019). Strategic lens practices and their role in achieving strategic transparency. Analytical study of the views of a sample of the managers of the / Kufa & Muthanna Cement Plant. Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical and Control Systems, 11(1).
- Nuno, C., & Arnaldo, C. (2018), Business intelligence and competitiveness: The mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation, competitiveness review: An international business journal, business intelligence and competitiveness: The mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation, February.
- Vincent, D., & Kim, A. (2009). The four lenses strategic framework toward an integrated social enterprise methodology. Virtue Ventures LLC. A Building the Field Initiative, Version 1.2 - May,licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 License.
- Desa, G. (2012). Resource mobilization in International social entrepreneurship: Bricolage as a mechanism of Institutional transformation -Entrepreneurship theory and practice. Resource Mobilization in International Social Entrepreneurship: Bricolage as a Mechanism of Institutional Transformation.
- Engert, S. (2016). Exploring the integration of corporate sustainability into strategic management: A literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112.
- Guo, Y. (2020). Green entrepreneurial orientation and green innovation: The mediating effect of supply chain learning, journals .sagepub.
- Herlinawati , E. (2019). The effect of entrepreneurial, orientation on SMES business performance in Indonesia. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(5).
- Hughes, M., & Robert, M.E. (2007). Deconstructing the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation and business performance at the embryonic stage of firm growth. Industrial Marketing Management, 36.
- Johnson, G., & Kevan, S., & Richard, W. (2008). Exploring Corporate Strategy, (8th edition). Published,Pearson Education Limited,Printed and bound by Rotolito Lombarda, Italy.
- Jahangir, K., & Walter, Z. (2016). Corporate entrepreneurship, disruptive business model innovation adoption, and its performance: The case of the newspaper industry. Long Range Planning 49.
- Lee-Sang M., & Suzanne, J. (2000). Culture, entrepreneurial orientation, and global competitiveness. Journal of World Business , 35(4).
- Munib, Md. (2020). The role of the pioneering orientation in comprehensive productive maintenance an exploratory study of the opinions of a sample of managers in the obstetric clothing factory in Mosul. Tikrit Journal of Administrative and Economic Sciences, 61(94) - 6.
- Majed, H.H., & Ali, Md., (2020). The possibility of adopting authentic entrepreneurial orientation behaviors to achieve entrepreneurial orientation - Field research in the Ministry of Housing, Construction, municipalities and public works. Tikrit Journal of Administrative and Economic Sciences, 61(25)-5.
- Lucia, N. (2007). Entrepreneurial orientation, risk taking, and performance in family firms. Family Business Review, 20(1).
- Oladimeji, M.S. (2019). Corporate entrepreneurship and service firms’ performance in Nigeria. Economic Review – Journal of Economics and Business, 17(1).
- Loredana, P. (2010). Looking at destination governance through three lenses. University of Lugano, Center for Action.
- Putniņš, T.J., & Sauka, A. (2019). Why does entrepreneurial orientation affect company performance? Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , 19 .
- Cater, T., & Danijel, P. (2010). Factors of effective strategy implementation: Empirical evidence from Slovenian business practice. Journal for East European Management Studies, Rainer Hampp Verlag, Mering, 15(3).