Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 2S
Analysis of Amazon: Customer Centric Approach
Rashri Baboolal-Frank, University of Pretoria
Keywords:
Strategic Marketing Management, Customer Centric Approach, Internal, External
Abstract
The study unpacks the different strategies of strategic marketing in organization from internal to external marketing. The hypothesis of this research is that the external approach regarding focusing on the customer’s needs and wants applying it to the organization of Amazon is mutually beneficial and is a successful strategy for the business continuity and escalated profit margins of Amazon. The vision and mission of Amazon, shows that Jeff Bezos focuses on customer satisfaction to improve and expand the business, in an innovative manner, that is an unorthodox co-petition strategy. The research exposes that by applying the SWOT Analysis to the marketing strategy of Amazon illustrates the holistic overview of both the successes and weaknesses of the company, and that overall Amazon is in a stable and lucrative position as an organization by adopting a customer centric positional strategy for success of their organization. Furthermore, the 3P’s illustrates that Amazon employs both internal and external marketing strategies.
Introduction
The report discusses the literature engaging a strategic marketing management. The case study applied to the respective theory is Amazon. Amazon adopts a customer centric strategy that is their tool of success for their organization by harnessing their customer’s needs and wants and providing to that specific demand. The research postulates that effective marketing strategies starts externally, and then moves internally, which means that the customer’s voice frames the marketing strategy of the organization. The research further critically analyses this position and illustrates the shortcomings, and improvement of the strategy.
Research Objectives
To explore the marketing strategies to illustrate the most effective strategy in terms of Amazon’s customer’s needs and wants. To outline the body of literature dealing with best marketing strategies for organizations and in particular for Amazon as the case study.
Research structure
The research structure is positioned to deal with the literature relating to strategic marketing management and then applies those principles to Amazon and evaluates the most effective methods and concludes with the customer centric strategy as the most effective for Amazon.
Literature Review Applying Amazon Case Study
Strategic Marketing Management Theory
Classical Approach vs Present Approach
The purpose of Shiner’s research is to illustrate that the traditional strategic marketing planning is outdated, and that new methods of tactical design are the way forward (Shiner, 1988). A combination of the emergent and deliberate strategy to ensure that the business action’s are being understood to produce a matrix of the maximum profit output for the company translates to various decisions made by the direct supervision of managers in the company (Shiner, 1988). Spekman & Gronhaug have described that there are three levels to strategic planning, namely corporate level strategies, business level strategies and product/market level strategies (Shiner, 1988). Corporate level strategies relate to the environment in the company (Shiner, 1988). Business level strategy relates to questions that are posed in the business to achieve a competitive advantage and produce an improved corporate portfolio of the company (Shiner, 1988). Product/market level strategies focus on the smallest business unit that is pertinent for serving the market of trade (Shiner, 1988). Businesses are under tremendous pressure to develop the most competitive marketing strategies in order to outwit their competitors and ensure the thriving and survival of their business for a continual number of years, and to evolve and develop with the changing business environment (Shiner, 1988). The practical implications are that theories of strategic management planning needs to evolve to ensure the businesses thrive, otherwise, the risk is that the business will not last a number of years. In this way Amazon was dynamic in their strategy to ensure the longevity of their business. They support a co-opetition business model to collaborate with competitors across the international globe rather than to compete with them for mutual interest and profit output (Ritala et al., 2014).
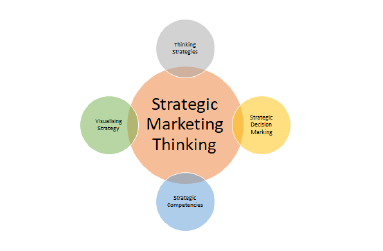
Fodness postulates that there six different aspects to thinking strategies in relation to strategic management planning (Fodness, 2005). The six different aspects to thinking strategies are embrace orthodoxy, challenge orthodoxy, analogize this, break assumptions, cross-fertilize, and attract opposites (Fodness, 2005). Fodness elucidates that too often businesses fail and the question posed is that why, if there are traditional and currently strategic methodology that is adopted. He emphasizes that there are three dimension to ensure a successful strategic strategy namely thinking strategically about marketing and identifying those specific principles and techniques (Fodness, 2005). Thirdly to address the macro skills of the business and fourthly is to ensure the communicating skills with the major business partners and stakeholders of the business to ensure the successful implementation (Fodness, 2005). Fodness proposes that strategic marketing is a method to resolve the challenge to ensure the enhanced functioning of the business. Amazon embraces all aspects of strategic marketing thinking and that what makes them different as an organization, because of the thinking unconventionally to service the needs of the market and to create a market of customers (Ritala et al., 2014) as shows in Figure 1 , Figure 2 and Figure 3.
The author’s purpose of the research is to illustrate that the conventional theory of strategic marketing management is flawed in that there is no consideration for an “illogical” aspect approach in that it does not provide for the human aspect of dealing with the information demand and providing for psychological planning limitations created by the role of the manager’s role (Piercy & Giles, 1990). This hypothesis leads to an array of issues that arise from the role of the executive in managing the strategic marketing planning procedures (Piercy & Giles, 1990). Piercy and Giles propose that a different strategizing plan is to start with the end in mind and work backward, to ensure the final product is executed in the manner envisaged (Piercy & Giles, 1990). A proposed radical approach to apply and consider the human approach of the job roles limitations in relation to strategic management planning, provides for innovative ideologies, taking the organization forward in an unprecedented manner. (Piercy & Giles, 1990). Amazon applies these strategies in an unconventional manner, in providing for the customer’s needs first and adapting that human approach to the data collection of getting into the mind of the customer through different platforms that the organization created (Venkatesan, 2017) as shows in Figure 4.
Piercy & Williams (1990) postulates that there are behavioral problems associated with authority conflict that there are resistances against the situation imposed on them. Fears of uncertainty are anxiety generated by the uncertain future by pro-crastinating the plans. Piercy & Williams (1990) Fear of failure by managers and they distance themselves from the planning. Piercy & Williams (1990) Indecisiveness conflict the anxiety that is associated with future strategies and second guessing and doubting strategies undermines the present Piercy & Williams (1990) “SPOTS” Syndrome stands for the Strategic Plan on the Shelf (Piercy & Williams, 1990) The planning must be a fluid ongoing process to manage the business concerns. (Piercy & Williams, 1900) Amazon aims to be fluid and innovative to keep updated and create the latest technology (aboutamazon.com).
Internal Marketing
The objectives of this paper are to investigate the customer retention practices relating to retaining employees, investors and customers (Ahmad & Buttle, 2002). The traditional marketing strategy constituted of the 4Ps, price, place, promotion and product (Ahmad & Buttle, 2002). The 4Ps were inadequate approach as time passed, as companies required more in respect of marketing to be relevant for their existing customers (Ahmad & Buttle, 2002). The authors propose ongoing research to address the shortcomings of the classical approach method to strategic marketing management (Ahmad & Buttle, 2002). The 4Ps progressed into the 7Ps namely price, place, promotion, product, personnel, procedure management and physical assets (Jain, 2013). Personnel entail providing the advice that is needed to the customer by the employee of the organization, sometimes for reassurance of the product (Jain, 2013). The physical assets is the physical space and setting of the products that creates the space and environment for the customer and the employees (Jain, 2013). Procedure Management are the self-services provided by the organization should the customer have any issues in their shopping, it also categorises the products based on the customers convenience (Jain, 2013). The 7Ps have focused on the mainly on marketing and markets, and the plethora of research has illustrated that this should not be the case, and that marketing should be focused around the customer (Jain, 2013). Amazon has focused their strategy on the customer to ensure that their business needs are changed to the adapting environment of the customer (aboutamazon.com). The 3Ps became a more holistic overview for a customer-centric approach for sustainability, namely “planet, people and profit” (Sheth et al., 2011). The application of the 3Ps strategy is one that Amazon aligns to with their eco-friendly and environmental sustainability initiatives. (aboutamazon.com) Amazon encourages mindful behaviour in caring for nature, self, community to be repetitive, acquisitive and aspirational, with their COVID 19 responsibility to their communities and people and ensuring their carbon footprint is minimal.
External Marketing
The purpose of the research is to present theoretical framework for addressing dissatisfied customers in the service sector (Yanamandram, 2007). The data suggests that customers are more likely to not offer their patronage to companies that offer similar services to other companies so they are likely to shop around for the best deal suited to their needs (Yanamandram, 2007). The companies that offer the best deals to the customers, are the most likely to offer their loyalty and repatronage (Yanamandram, 2007). The studies further expose that if the customer incurs costs to the business relationship, those costs, will ensure the customer’s commitment which is called “cognitive continuance or cognitive instrumental” (Yanamandram, 2007). This means that the “switching costs” translates to a “calculative commitment” by the customer to the company. The strengths of the research is that it is based on theoretical studies. The practical implication is that there is a rational basis for customer dissatisfaction and exposes the basis for loyalty is a complication by various aspects (Yanamandram, 2007). The weakness is that more research needs to be undertaken to support the theoretical framework. Amazon ensures that customers are loyal to the organization by offering a product that the customer cannot source besides Amazon. (aboutamazon.com)
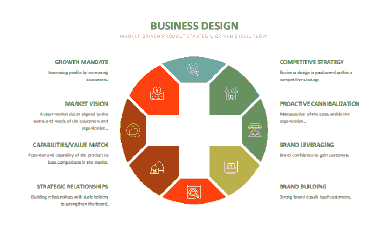
The core leadership value is key to establishing the foundation for a customer orientated organization. Amazon’s leadership a principle is customer obsession meaning to focus on the customers and work from the customers’ needs and wants filtered through to the company. The employees and leaders of Amazon work tirelessly to ensure the customers trusts the organization, and they still pay attention to competitors but their main priority and obsession is with the customers for their successes (aboutamazon.com). The other leading principles of Amazon are passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence and long-term thinking, which complement the top priority of the customer obsession.
It is easier to retain customers than to recruit new customers for business (Coyles & Gokey, 2005). Companies spend money to ensure that customers are retained (Coyles & Gokey, 2005). The majority of customers are categorised into the emotional and budget price driven customers (Coyles & Gokey, 2005). There are various reasons why customers elect to be loyal to particular brands due to their satisfaction of the product (Coyles & Gokey, 2005). Amazon customers are loyal to the brand and organization due to the rewards that they reap in incentives from the organization (Venkatesan, 2017) as shows in Figure 5.
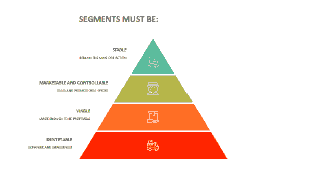
The goal for maintaining customers is to keep them satisfied with the product and make it inconvenient for them to change a service provider (Coyles & Gokey, 2005). The increasing of customer loyalty and to understand the changing needs of customers, assist the companies to cater for those specific needs when they arise (Coyles & Gokey, 2005). Wright proposes that targeting the highest segment does not give an accurate outcome and that is riddled with inaccuracies and errors (Wright, 1996). It is evident that not all brands can be demarcated into specific segments (Wright, 1996). A reconsideration of the segmentation approach must be undertaken as it is not a sustainable methodology approach because of the inaccurate results (Wright, 1996). The Amazon brand is demarcated into different segments that cater for specific needs of its customers (aboutamazon.com).
Jiang postulates mass customization at standardization of cutting costs through mass production (Jiang, 2000) as shows in Figure 6.
Amazon has different segments namely the digitalization, internet services, retail services, mobile devices, Amazon Prime, amongst other aspects of its diversification of the market services that it offers its customers (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 7.
It is important that customers do not want too many options as this can cause anxiety and uncertainty (Jiang, 2000). The companies need to ensure the choices are minimal though caters for all their needs. Amazon has catered for all the options for their online books, the number of books that are available at a click of a button are more convenient for its customers than any physical bookstore, so these numerous options are instead not overwhelming but caters for every need of genre from studies to leisure (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 8.
Amazon target their segments in their organization according to the different customer’s needs and wants, by ensuring the technology is unique, innovative and convenient (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 9.
Businesses must adapt their marketing strategies to the customer’s needs (Simkin, 1999). Data gathered by customers has limitations as the customers that are the study group is those that provide it and the one who elect no to partake are excluded (Cahill, 1997). Amazon has the benefit that all their customers and potential customers’ data they have through the creation of specific programs such as Amazon Dash to collect this data (Venkatesan, 2017) as shows in Figure 10.
Amazon key principle to establishing stability is to focus on their leadership goals (aboutamazon.com). Amazon ensures their quality of the highest standards of their products is produced through innovation and operational excellence (aboutamazon.com). The customer retention is managed through incentives (Venkatesan, 2017) as shows in Figure 11.
The aim of the paper is discussing the challenges and issues with internal marketing (Rafiq, 2003). The customers and employees aim to have their needs satisfied (Ahmed & Rafiq, 2003). Integrated systems that are streamlined are the objective but the most difficult to achieve (Ahmed & Rafiq, 2003). Internal marketing is process orientated driven by the employees of an organization (Ahmed & Rafiq, 2003). Amazon’s key to success of overcoming these challenges is by gaining the data and knowledge about the customer (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 12.
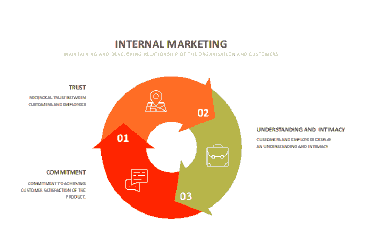
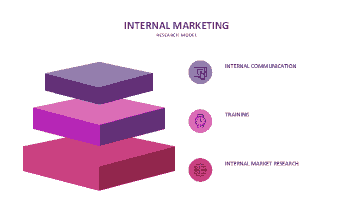
Employees display that they are committed to the customers as partners in the organization, and reciprocally employers guarantee the value of the employees in the organization (Ahmed & Rafiq, 2003). A vital aspect of strategic planning is the core competence of the organization (Green et al., 1994). A genuine plan leads to a competitive advantage and increased profits for the organization (Green et al., 1994). Internal promotion of marketing strategies are essential to the success and continuity of the organization (Green et al., 1994). The internal marketing goals are the same as the external marketing goals and must be satisfied. The goals are namely to support the key decision players for plans; acquiring financial resources, changing the attitudes of the employees in relation to customer relations. Commitment for the marketing plan and addressing problems and managing the culture of the organization to align with the plan. Huang and Rundle-Thiele postulate that the concept of internal marketing has progressed from Berry, et al., (1976). The accepted definition of internal marketing is that is “a cultural framework and an instrument to achieve strategic alignment between employees’ actions and marketing’s brand positioning in the target consumer’s minds (Ahmed & Rafiq, 2003). It was stated that Grönroos (1997); Barkensjo (2005) elucidate that employees that are skilled, trained, educated deal with customers more effectively. Huang & Rundle-Thiele, (2015); Grönroos (1983) proposed an external focused definition to internal marketing through influence rather than external focus by Berry (1981) which was motivating employees. Rafiq & Ahmed (1993) developed a hybrid approach. (Huang & Rundle-Thiele, 2015) The paper focuses on customer satisfaction, and in particular three aspects for internal marketing namely internal communication, training (including cultural change) and market research (for understanding employees). (Huang & Rundle-Thiele, 2015) Internal communication is the focus on the relationship between the employer and employee to understand the needs and wants. (Huang & Rundle-Thiele, 2015) Training is the human resource management function that provides for recruitment, training, incentives, communication and training all employees. (Huang & Rundle-Thiele, 2015) Internal marketing research to analyze and understand customer’s psychological expectations relating to requisite products, and to grasp the employee segments in the organization. (Huang & Rundle-Thiele, 2015) illustrated that there is evidence of a three dimensional model of internal marketing and that there were limitations of the study due to the study group used. (Huang & Rundle-Thiele, 2015) Amazon focuses on the psychological thinking of the customer, through the gathering of data when product purchases are made, so this means they can control the conditions of the customer when shopping online. (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 13.
Wasmer and Bruner propose that is a model of marketing services namely the offer that is the information pertaining to customer expectation. Wasmer, Gordon & Bruner (1991) Secondly, internal communications that represents the information of the employees of the firm and thirdly service specifications pertaining to the service performed. Wasmer, Gordon & Bruner (1991) Service performance is the relationship between a particular customer and employee relating to a performance gap Wasmer, Gordon & Bruner (1991). Fifthly, customer feedback that pertains to the complaints of the customer to the organization. Lastly, employee feedback that is the information from informal reporting mediums such as reports, observations and formal means of research conducted. Wasmer, Gordon & Bruner (1991) Amazon uses the internet to advertise their services, and there are over seven hundred thousand employees at Amazon to streamline the customers communication with the organization relating to products. (aboutamazon.com) The feedback provided by the customer provides the idea platform for improvement of the employees and the organization (aboutamazon.com). The employee feedback is generated through to the management at Amazon for the enhancement of the organization. (aboutamazon.com)as shows in Figure 14.
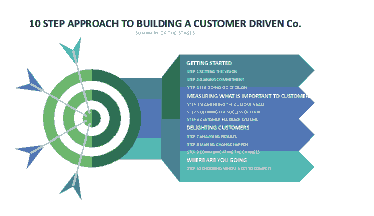
Piercy suggest that’s other factors to consider are internal politics, market simplification, customer fear, corporate culture, market complacency, resources, capability, logistics, cost barriers, perceived market drivers and credibility. Piercy (1995) Amazon strategy of these ten steps are successful because the common focus is the customer, and there is a commitment by the organization to ensure excellence of service and product. (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 15.
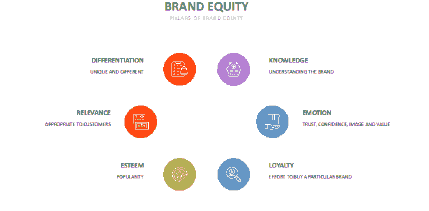
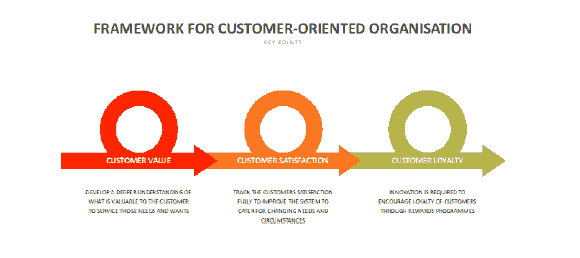
The customer centric approach is supported by Mukerjee’s research. The paper focuses on three aspects namely developing a deeper understanding of what is it that customers really values, secondly what is the motivation of the desired customer value and continuously tracking the customer satisfaction and lastly the rewarding and retaining loyalty because of profitable customers. Mukerjee (2013) Amazon have adopted a deeper understanding of their customers, to provide for their needs and wants. Amazon’s leaders, management and employees are motivated by the desire to track and have their customers satisfied to maintain their lasting loyalty to the retail services of the company as shows in Figure 16.
Dolata illustrates that Amazon is a major player as an internet provider amongst the competitors of Google, Facebook, Apple, Microsoft and Twitter to mention a few. Dolata (2017) The E-commerce market of Amazon is the largest retainer on the internet (Stone, 2013) and by monopolizing the market; they can dictate the conditions of the consumers. (Dolata, 2017) Since Amazon began in 1995, the company has been versatile and adaptable to the environmental circumstances and outlasting competitors. (Dolata, 2017) Amazon has possessed an aggressive expansive strategy with the different diversification of its market. (Dolata, 2017) The research and development of Amazon, is their priority to ensure they are continuously technologically savvy, and have original ideas first, and protecting their coding. (Dolata, 2017) The data of the research has illustrated that the power that Amazon wields due to the demand of its customers and their loyal support to the products of the company. The shortcomings, of the article is that it does not criticize the strategy of aggressive expansive could see Amazon financial trysts if their expansions are not successful such as Amazon’s cellphone, fire tablet expansion, as this environment is highly competitive, and there are always cheaper and expensive devices that have more features like Samsung and Apple to mention a few.
Strategic Plan starting with customer’s needs
Venkatesan exposes Amazon’s customer engagement strategy that guarantees their continuous successes in the global market Venkatesan (2017). Amazon developed Amazon Dash by harnessing the customer engagement, which provides that the device can be paired with the product of the customers and facilitates for the customer to reorder the products with the convenience of pressing a single button only Venkatesan (2017). The objective of Amazon is to achieve the data of the daily routine of the customer, purchase frequency and to ensure the customer retention and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Venkatesan (2017) Amazon also encourages the customers to refer business to them with an incentive of financial reward, as for each referral given for Amazon Prime, five dollars is given to the customer Venkatesan (2017). There is also a crowdsourcing marketplace by Amazon called Amazon Mechanical Turk that provides for feedback from customers regarding products Venkatesan (2017). The marketplace provides for an opportunity for employers to post job opportunities and for employees to fill out those job opportunities and get paid for it Venkatesan (2017). In this way a platform is created for interaction of data of customers and potential customers. Amazon associates is a program that is created that allows customers to earn up to ten percent on referral fees for products, thus creating a platform for the customer to benefit and earn an income from their loyalty and referral to the brand and attracting other customers Venkatesan (2017). It is apparent from this connection to the customers that Amazon creates is that the Customer Engagement Value (CEV) becomes a strategic imperative Venkatesan (2017).
Ritala, et al. (2014) exposes Amazon for adopting a coopetition business model, meaning that the organization collaborates with its competitors for a mutual benefit instead of competing for profit. This business model creates a win-win situation for Amazon when it partnered with Apple to offer the kindle app on the iPad and creates a new market for business for both companies. (Ritala et al., 2014) Amazon focuses on its customers rather than its competitors which Jeff Bezos has attested to this strategy, because Amazon has a customer centric approach. (Ritala et al., 2014)
Amazon has also ensured that they service their client needs in the COVID 19 global crisis, by catering for the needs of the elderly, medical supplies that there are a shortage and the general demand and supply for essential supplies, that they have focused to ensure that their suppliers are in constant supply or can source it within a reasonable turnaround time. (Annual report 2019) Amazon is committed to doing all that it can for its customer, potential customers and the community by providing for customers to donate through Alexa to a number of charities that require assistance amidst the COVID crisis. (Annual report, 2019) Amazon is committed to sustainable development, and has announced a number of ways in which the company has invested to being ecofriendly to the environment and global world. (aboutamazon.com) Amazon has invested in trade-in store, device recycling, refurbished devices and a second chance site that provides packaging of recycled materials. (aboutamazon.com) as shows in Figure 17.
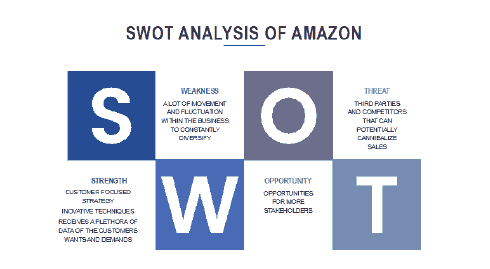
Some of the other threats experienced by Amazon are disruptions of the business which pertains to the loss of management on existing businesses. A further threat experienced by Amazon is that they have experienced the risk and fluctuations of foreign exchange risk that caused loses. (Annual report, 2019) A threat has been that there has been harm data and loss of data due to security breaches. (Annual report, 2019) Another threat that is posed is an inventory risk. Furthermore other threats also include supplier relationship risks, additional tax liability risks, litigation claims, government regulations that are unfavorable to the organization and intellectual property infringements are some of the threats experienced by Amazon. (Annual report, 2019) There have been further weaknesses such as impairment of other relationships within the organization, variability to revenue and difficulty of the integration of strategic alliances under commercial agreements of Amazon. (Annual Report, 2019) A further weakness is that the seasonality of retail business places increased the strain on the operations of Amazon (Annual report, 2019). A strength of Amazon that despite all the weaknesses and threats for the period of 2019 a profit of 11, 588 million dollars was still generated within the company and its respective segments (Annual report, 2019).
The main sections of the plan cover:
• SWOT and competitive analysis-to assess where the business or brand is currently and what competitors are doing. In Amazon the brand is reputable and known as a trustworthy brand. The competitors are collaborating with Amazon where there is a niche market to do so, such as Apple and YouTube.
• Objectives-what the plan needs to achieve. The plan of Amazon is to ensure satisfied customers and to ensure the company thrives in profits, which it is currently achieving its targets and profit margins. (Annual Report 2019)
• The marketing strategy-how the objectives will be achieved. The objectives are achieved by providing the customers with an opportunity to engage with the organization relating to Amazon meeting their current needs and their future needs.
• Sales forecast-by how much sales are likely to increase. At least a 100% increase due to the various volatilities of the share price because of the evolving business model of Amazon. (Annual report 2019)
• Budget-how much the marketing activities will cost and how the plan will be financed. The marketing activities are sourced from investments into Amazon. (Annual report 2019)
• Evaluation-how outcomes will be monitored and measured, they will be measured against the revenue generated by Amazon and the investments that were able to be secured. (Annual report 2019)
Strategic Marketing Planning and Implementation by Dr. Paula Stephens
• Sostac is a planning model, originally developed in the 1990s to help with marketing planning by PR Smith. Sostac model stands for:
• Situation-where are we now? Amazon has monopolized the market through their internet and digital services through the diversification of their broad portfolio of fire tablets, cellphones, Amazon Prime Channel and their respective sales of the products.
• Objectives-where do we want to be? Amazon wants to continue to be a global game changer and collaborate with stakeholders and competitors to ensure that all gaps in the market are fulfilled for their customers.
• Strategy-how do we get there? Through their customer oriented focus and to focus on their innovation and technology for designing to their customers’ needs and wants.
• Tactics-how exactly do we get there? Through the gathering of data from their intel systems to illustrate where the company should diversify and which competitors to partner with to make it a win-win for them.
• Action-what is our plan? The plan is to design, innovate and produce so that the products are distributed to the customers at a click of a button to their convenience.
• Control-did we get there? Employees, customers and Management to stream roll the action plan into implementation.
Conclusion
Applying the principle that the best marketing strategies are outside in, focusing on the customer’s needs and wants of the Amazon case study, illustrated that this statement is true, as this strategy has enabled Amazon to grow from strength to strength. Though will all strategies there is still room for improvement in relation to securing more investment for Amazon, creating stability in relation to the share price, by refining the business model of the company.
Recommendation
The recommendations are:
• Amazon to recruit more stakeholders to invest in the company
• Provide stability with the share price, by avoiding cannibalization of the retail sales through coopetition.
• Amazon should focus on their employees in relation to curbing operating losses
• Strengthen the security protection of Amazon data and privacy information
• Safety mechanisms to protect inventory.
References
- Ahmad, R., & Buttle, F. (2002). "Customer retention management: A reflection of theory and practice". Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 20(3), 149-161.
- Cahill, D.J. (1997). "Target marketing and segmentation: Valid and useful tools for marketing". Management Decision, 35(1), 10-13.
- Cravens, D.W., Piercy. N.F., & Prentice, A. (2000). "Developing market-driven product strategies". Journal of Product & Brand Management, 9(6), 369-388.
- Coyles, S., & Gokey, T.C. (2005). "Customer retention is not enough". Journal of Consumer Marketing, 22(2), 101-105.
- Dolata, U. (2017). “Apple, Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft: Market concentration-competition-innovation strategies” SOI Discussion Paper, No. 2017-01. Institute for Social Sciences, Department of Organizational Sociology and Innovation Studies, University of Stuttgart.
- Donovan, P., & Samler, T. (1994). "Delighting customers", managing service quality. An International Journal, 4(6), 38-43.
- Greene, W.E., Walls, G.D., & Schrest, L.J. (1994). "Internal marketing". Journal of Services Marketing, 8(4), 5-13.
- Fodness, D. (2005). "Rethinking strategic marketing: Achieving breakthrough results". Journal of Business Strategy, 26(3), 20-34.
- Huang, Y., & Rundle-Thiele, S. (2015). "A holistic management tool for measuring internal marketing activities", Journal of Services Marketing, 29(6/7), 571-584.
- Jain, M.K. (2013). “An analysis of marketing mix: 7Ps or more”. Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 1(4), 23-28.
- Jiang, P. (2000). "Segment-based mass customization: An exploration of a new conceptual marketing framework". Internet Research, 10(3), 215-226.
- Pervaiz, K., & Rafiq, A.M. (2003). "Internal marketing issues and challenges". European Journal of Marketing, 37(9), 1177-1186.
- Piercy, N., & Giles, W. (1990). "The logic of being illogical in strategic marketing planning". Journal of Services Marketing, 4(3), 27-37.
- Piercy, N., & Morgan, N. (1990). "Internal marketing: Making marketing happen". Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 8(1), 4-6.
- Mukerjee, K. (2013). "Customer-oriented organizations: A framework for innovation". Journal of Business Strategy, 34(3), 49-56.
- Piercy, N.F. (1995). "Customer satisfaction and the internal market". Journal of Marketing Practice: Applied Marketing Science, 1(1), 22-44.
- Ritala, R., Golnam, A., & Wegmann, A. (2014). “Coopetition-based business models: The case of Amazon.com” Industrial Marketing Management, 43(2), 236-249.
- Sheth, J.N., Sethia, N.K., & Srinivas, S. (2011). “Mindful consumption: A customer-centric approach to sustainability”. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 39, 21-39.
- Shiner, D.V. (1988). "Marketing's role in strategic and tactical planning". European Journal of Marketing, 22(5), 23-31.
- Dibb, S., & Simkin, L. (1991),"Targeting, segments and positioning". International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 19(3).
- Stephens, P. “Strategic Marketing Planning and Implementation” Power point Slides Textbook Chapter 5: Customer Acquisition Strategies and Tactics. Retrieved from https://uk.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-binaries/30433_Clow_05.pdf.
- Wasmer, D.J., Gordon, C., & Bruner, II. (1991). "Using organizational culture to design internal marketing strategies". Journal of Services Marketing, 5(1), 35-46.
- White, L., & Yanamandram, V. (2007). "A model of customer retention of dis-satisfied business services customers". Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 17(3), 298.
- Venkatesan, R. (2017). “Executing on a customer engagement strategy”. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45, 289-293.
- Wright, M. (1996). "The dubious assumptions of segmentation and targeting". Management Decision, 34(1), 18-24.