Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 1
Conceptualization of the Influence of Strategic Management on the Layered Corporate Business Processes
Oleksandr Olshanskiy, Kharkiv State University of Food Technology and Trade
Oksana Osetrova, Oles Honchar Dnipro National University
Volodymyr Holubka, National Academy of Management
Viktoriia Tretiak, V. N. Karazin Kharkiv National University
Igor Rodchenko, Interregional Academy of Personnel Management
Abstract
The article discusses the conceptual aspects of the relationship between strategic management and corporate business processes. Strategic changes within the corporation when changing the structure of business processes are identified and classified. The model of strategic management of business process reengineering was created and the economic and mathematical substantiation of its prospects of functioning was developed. Methodologically, the development of a strategic management system should be carried out using modern analytical approaches, which will allow at the systemic level to form decisions on the management of business processes taking into account the market features of corporations. Strategic level and business architecture interconnection techniques provide tools to evaluate, streamline business processes to meet corporate performance targets. Development of a comprehensive program of changes in the structure of business processes, which should take into account all areas of activity. The proposed model of strategic management of layered business processes can be used to develop strategic charts of a corporation, to record and control performance indicators of business processes, to assess the degree of achievement of strategic goals and to increase the adequacy of management decisions. The proposed model and analytical technologies allow to increasing the effectiveness of strategic business process management. Based on the proposed model, it seems possible to form and make a reasonable choice of the optimal management decision at the system level, taking into account the structure of the business process and the goals of the corporate strategy.
Keywords
Strategic Management, Business Processes, Management Model, Strategic Charts, Corporation Resources.
JEL Classifications
M21
Introduction
The high level of dynamism of the international business environment significantly influences the business processes (BP) of every corporation in the world. In such conditions it is advisable to create a comprehensive strategic management system, which should be based on the principles of adapting business processes to the environment, which will allow implementing the main business goals of corporations.
Literature Review
A considerable number of works of modern economists is devoted to the study of business processes management of corporations, in particular (Becker et al., 2013; Melao and Pidd, 2010; Seidel et. al. 2012). The issues related to strategic support of business processes flow are discussed in such works as (Fraternali et al., 2011; Harmon, 2007; Lederer, 2016). However, from a scientific point of view, strategic modeling of corporate business process management requires continuous improvement (Drobyazko et al., 2019 a & b; Durmanov et al., 2019).
Methodology
Methodologically, the development of a strategic management system should be carried out using modern analytical approaches, which will allow at the systemic level to form decisions on the management of business processes taking into account the market features of corporations. Strategic level and business architecture interconnection techniques provide tools to evaluate, streamline business processes to meet corporate performance targets.
Findings and Discussions
Business process refers to a sustainable, purposeful set of interconnected activities that, using a certain technology, transforms inputs into outputs that are of value to consumers (Niehaves and Plattfaut, 2011). Development of a comprehensive program of changes in the structure of business processes, which should take into account all areas of activity and anticipate the activities proposed in the Table 1.
| Table 1 Strategic Actions Carried in the Corporation Operations When Changing the Structure of Business Processes | ||
| Sphere of business | Type of strategic action | Measures to be taken |
| Production | Production output | Updating the range of products (and related services) output by the corporation |
| Increasing the production volume | ||
| Quality control | Development and refinement of quality requirements for products manufactured by the corporation and raw materials purchased for production | |
| Production | Logistics | Attraction of investment resources, purchase of the latest equipment and raw materials, expansion of production facilities |
| Organizational management | Technological process | Improving the methods of technological process implementation |
| Staff composition | Expansion of personnel (by specialties), retraining of personnel | |
| Sales of products | Improvement of marketing schemes of sales of products | |
| Economic security | Securing trade secrets, improving the system of protection of material goods of the corporation | |
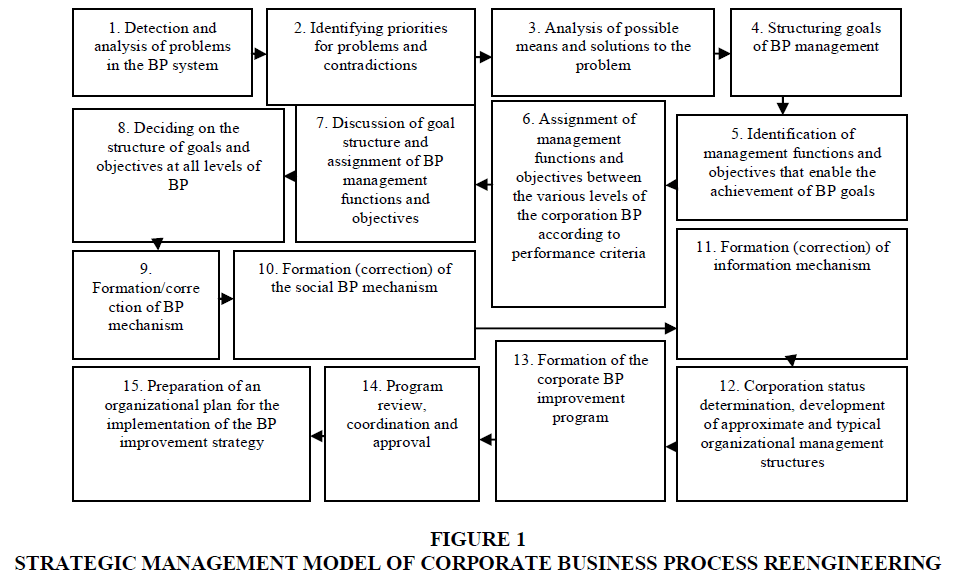
In order to create an effective system of managing the layered business processes of corporations, it is proposed to monitor the characteristics of each stage of the business process, to timely determine the most rational decisions and make the necessary changes (Elo & Kyngäs, 2008; Kuzior, A., & Zozulak, J., 2019). We create a model of strategic management of business processes of a corporation that can be used at different levels of their existence (Figure 1).
We dwell on the characteristics of the main blocks of the proposed model.
1. Block 1: Detection and analysis of problems in the BP system; this block is an integral process and requires the ability to carry out a purposeful analysis of production and economic activity and corporate governance.
2. Block 2: Identifying priorities for problems and contradictions; the priority of solving problems and contradictions is related, first of all, to the role of the management organization and its focus on solving industrial, scientific, technical and economic problems (Leonardi, 2011). An important role in the implementation of the block is played by the availability of resources available to the corporation.
3. Block 3: Analysis of possible means and solutions to the problem; the block is based on the analysis and forecast of available resources at all levels of management.
4. Block 4: Structuring goals of BP management; the construction of a management goal structure should fully reflect the desire to address relevant problems in view of available and predictive tools.
5. Block 5: Identification of management functions and objectives that enable the achievement of BP goals; a set of management objectives is based on the structure of goals and subgoals of the corporation (Janiesch et. al. 2012).
6. Block 6: Assignment of management functions and objectives between the various levels of the corporation BP according to performance criteria.
7. You should also note the complexity of the implementation of blocks 9, 10, 11 related to the formation of social and information management mechanisms.
8. Blocks 12, 13, 14, 15 are fully responsible for the strategic support of BP.
In addition, we can describe, using an economic and mathematical model, a strategic perspective on the existence of a business process within a corporation:
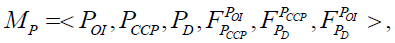 (1)
(1)
Where POI – set of perspectives for business process deployment; PCCP – set of strategic perspectives of the management object (BP); PD – set of strategic perspectives of subsidiary business processes of the corporation; 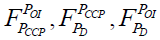 – injective mapping.
– injective mapping.
The distribution of strategic perspectives of the management object (BP) – PCCP between perspectives POI is mapped in such a way F , when any set of perspectives 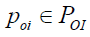 is mapped with a certain set of perspectives for business process deployment
is mapped with a certain set of perspectives for business process deployment 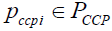 .
.
The strategic perspective model can be presented as follows:
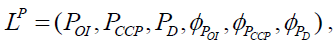 (2)
(2)
Where POI,PCCP,PD – objects of perspective category; 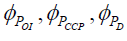 – morphisms of perspective category.
– morphisms of perspective category.
Similarly, we present the category of strategic goals LG and performance indicators LI :
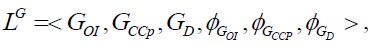 (3)
(3)
Where GOI,GCCP,GD – objects of strategic goal category: GOI – set of all goals of a management object, GCCP – set of goals for the business processes of a corporation, GD – set of goals of the subdivision of a management object; 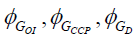 – morphisms of the category of strategic goals for business processes.
– morphisms of the category of strategic goals for business processes.
The model of performance indicators can be presented as follows:
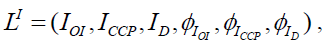 (4)
(4)
Where IOI, ICCP, ID – objects of performance indicator category: IOI – set of all performance indicators of a management object, ICCP – set of all indicators of the strategic chart of a management object, ID – set of function indicators of the business processes of subdivisions of a management object; 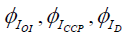 – morphisms of the category of performance indicators. The relationships between these categories are described as follows:
– morphisms of the category of performance indicators. The relationships between these categories are described as follows:
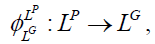 (5)
(5)
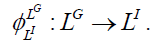 (6)
(6)
Thus, the model of strategic management of business processes of the corporation enables the transition from strategy to performance indicators and evaluation of all its activities in accordance with strategic goals.
Recommendations
The proposed model of strategic management of layered business processes can be used to develop strategic charts of a corporation, to record and control performance indicators of business processes, to assess the degree of achievement of strategic goals and to increase the adequacy of management decisions.
Conclusion
On the basis of conceptual aspects of strategic management practical recommendations on management of business processes of modern corporations have been formed. The proposed model and analytical technologies allow increasing the effectiveness of strategic business process management. Based on the proposed model, it seems possible to form and make a reasonable choice of the optimal management decision at the system level, taking into account the structure of the business process and the goals of the corporate strategy.
References
- Becker, J., Kugeler, M., & Rosemann, M. (2013). Process management: A guide for the design of business processes. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Drobyazko, S., Okulich-Kazarin, V., Rogovyi, A., & Marova, S. (2019a). Factors of influence on the sustainable development in the strategy management of corporations. Academy of Strategic Management Journal.
- Drobyazko, S., Potyshniak, O., Radionova, N., Paranytsia, S., & Nehoda, Y. (2019b). Security of organizational changes via operational integration: Ensuring methodology. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues.
- Durmanov, A., Bartosova, V., Drobyazko, S., Melnyk, O., & Fillipov, V. (2019). Mechanism to ensure sustainable development of enterprises in the information space.
- Elo, S., & Kyngäs, H. (2008). The qualitative content analysis process. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 62(1), 107-115.
- Fraternali, P., Brambilla, M., & Vaca, C. (2011). A model-driven approach to social BPM applications. Social BPM: Work, Planning and Collaboration under the Impact of Social Technology, 95-112.
- Harmon, P., & Trends, B.P. (2010). Business process change: A guide for business managers and BPM and six sigma professionals. Elsevier.
- Janiesch, C., Matzner, M., & Müller, O. (2012). Beyond process monitoring: a proof?of?concept of event?driven business activity management. Business Process Management Journal.
- Kuzior, A., & Zozu?ak, J. (2019). Adaptation of the idea of phronesis in contemporary approach to innovation. Management Systems in Production Engineering.
- Lederer, M. (2016). Business Process Transparency Management. University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Nuremberg.
- Leonardi, P.M. (2011). When flexible routines meet flexible technologies: Affordance, constraint, and the imbrication of human and material agencies. MIS quarterly, 147-167.
- Melão, N., & Pidd, M. (2000). A conceptual framework for understanding business processes and business process modelling. Information Systems Journal, 10(2), 105-129.
- Niehaves, B., & Plattfaut, R. (2011). Collaborative business process management: status quo and quo vadis. Business Process Management Journal.