Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
Crisis Leader: Lessons from Covid-19 of Thai Business Sector
Bangorn Benjathikul, Bangkok Thonburi University
Abstract
The objectives of the research on Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector are 1) to study the corporate management of the Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector and 2) to study the approaches in the development of Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector. It is the qualitative research by collecting the data from 20 key informants who had passed the purposive selection with the good knowledge and relevance to the studied subject including the government executives involving in government policy, private business owners, Industry Association of Thailand, Thai Chamber of Commerce, Thai Restaurant Association, Thai Hotel Association, and Thai Tourism Association. The instruments used for data collection were structured interviews. The research result reveal that the Management Leaders and employees must work together to help brainstorm solutions to problems by setting up a working team to take responsibility during a crisis. Human resource management leaders should set up a monitoring and care center to build morale, take care of employees’ health and safety. The guidelines and measures must be established to prevent transmission in the organization. The work style should be adjusted. In the management and the leadership, the leaders should have high leadership, dare to think, make decisions, have broad vision, be strong and resolute. It is the center of the minds of people in the organization. Decision-making leaders need to make timely decisions based on the information available at that time, knowing the goals of the decisions and understanding the situation well first. For technology and innovation, the leaders should apply technology and innovation to transform and improve processes into a technology organization.
Keywords
Leaders, Crisis, COVID-19, Business Sector, Thailand
Introduction
The global society is encountering with an unexpected crisis, especially with the coronavirus crisis known as COVID-19 (Razzaq, Sharif, Aziz, Irfan & Jermsittiparsert, 2020). The epidemic is rapidly emerging and goes beyond human control today. One of the key players in managing the crisis in encountering the COVID-19 outbreak of Thailand is the organization leader at different levels. Leaders are critical to managing the organization amidst the COVIC-19 epidemic. That the leaders will be able to manage the organization well must rely on important factors such as understanding, sympathy, and effective communication. These are the key factors in building confidence to everyone. It is also extremely important to manage in this crisis while the situation in the epidemic of COVID-19 still spread more widely around the world. The trend is still severe with the number of infections increasing in every country and the end of the outbreak is unknown. Many countries face administrative crises which inevitably affect the economy. Thailand is also in this situation. In this critical time, the organizational leaders should be able to deal with this serious problem. It is a challenge for the leaders of the Thai business sector to face the volatile and highly uncertain situations impacting the businesses. They need to mobilize their energy, knowledge, capability and experience to come up with a method to implement and use to lead the organization through this crisis.
Starting from the end of March 2020, last year, Thailand had the lockdown measure to solve the COVID-19 epidemic. In the first wave, the death rate was very low, only 1.8% of the total number of cases compared to other countries. If only the number of people infected from the country was considered, it will be found that the number was very small. The number of deaths accumulating at 58 cases as of July 1, 2020 (Coronavirus Disease Situation Management Center, 2019) indicated the good management with cooperation from all sectors including the government, private sector and the public sector. However, the effect of lockdowns during the first wave of the outbreak also yield significant economic costs. For example, the government spent approximately 600 billion baht in remedies for those affected by the lockdown during the lockdown period. When the time passed and the situation improved, it was time to unlock. The government prepared a budget of 400 billion baht in order to restore the economy and help the business sector. This would be helped quickly or slowly probably depended on how the money was spent and in which part (Thongaram, 2020). For the business sector, it might not be possible to wait for the government to come to help. If the business did not have a good management that was enough to plan the business or take it against the situation and only the income was lost for just one month, it could cause problems and even shut down to such business. Therefore, it is imperative that the business operator has to assess the situation and plan to deal properly.
The leadership and vision of leaders in trying to solve problems for the organization are essential. What is no less important than solving problems is that the leaders should have maturity and possess good leadership quality. A strong leader can build morale go lead the employees and the organization through the crisis altogether intelligently and efficiently. The duty of the leader is to be able to salvage damage or things that affect life, property, business operations on the organization, and family to return to normal as quickly as possible and to have a minimal impact (Back to business or Back to normal). The key to the leader is to build morale and encouragement. They must be reliable for being trusted by people in the society. The importance of leadership is to be trusted. “Without Trust, Nothing Can Happen.” If they cannot be trusted, then anything will be difficult to happen” (Chanchai, 2020). From the spread in both waves in Thailand which took the long periods of more than one year, Thai business sector was affected a lot. Some small businesses had to close down the operation as they were unable to sustain the business. Meanwhile, the medium business and the large scale had to adapt greatly in terms of business operations and employee retention. Making the organization survive is not easy in this difficult situation.
Research Objective
1. To study the corporate management of the Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector.
2. To study the approaches in the development of Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector.
Research Methodology
Key Informants: The key informants were selected with the purposive selection from 20 persons who have good knowledge and relevance to the studied topic including the government administrators in the policy level, private business owners, Industry Association of Thailand, Thai Chamber of Commerce, Thai Restaurant Association, Thai Hotel Association, and Thai Tourism Association.
Data Collection
It was divided into 2 types; in-depth interview and Non-participant Observation. The researcher collected and recorded the data from the phenomena that occurred and use the observation method. In taking note of the details of the things that need to be observed and related information, the researcher checked the data every time for the accuracy and clarity of the information as well as creating a mutual understanding between the researcher and the key informants.
Research Instrument
The researcher studied information related to the organization management of crisis leaders, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), and lessons learned from COVID 19 of Thai businesses by reviewing relevant literature, concepts and theories to develop the instrument used in this research which was the structured interview.
Data analysis: The group of data obtained from interview and non-participant observation was created to present the results of the analysis based on three principles; data reduction and filtering, displaying and describing information, finding conclusion and examining research results. It is the process of finding conclusions and interpretation of the results or findings in the future.
Research Results
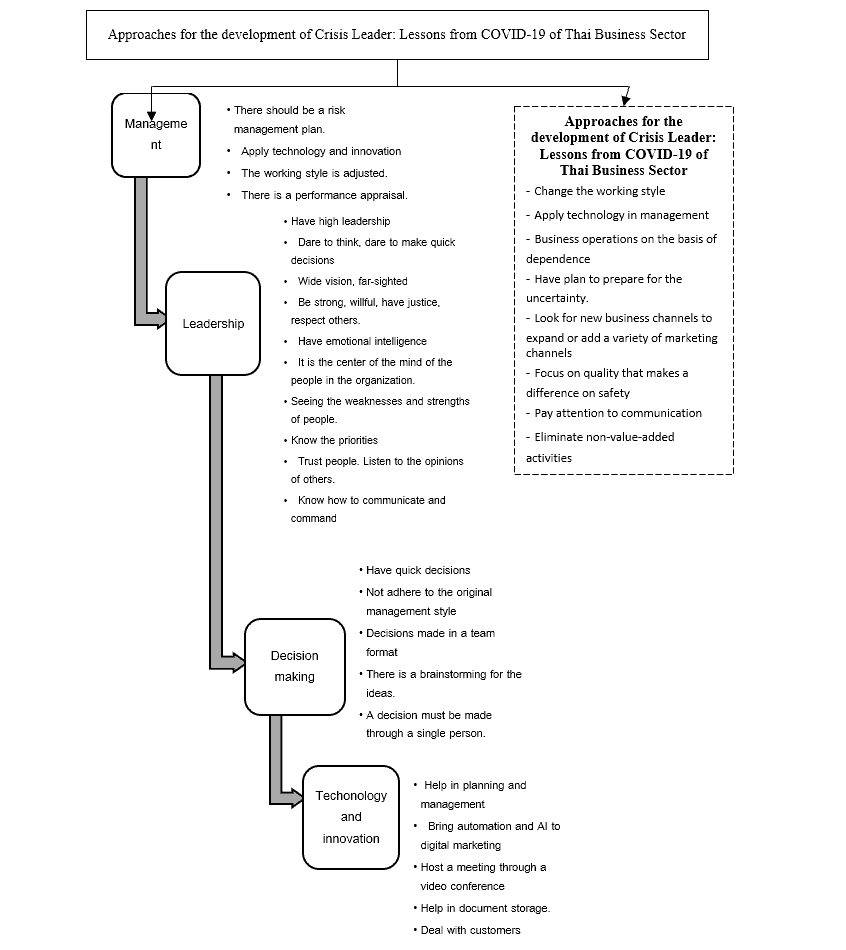
Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector in the management: Leaders and employees must work altogether to help brainstorm solutions to problems and create opportunities. The organization has to set up a working team to have duties and responsibilities to work during this crisis such as problem solving team, risk management team, team prepared for future work. This is consistent with the key informants stating; “...Organizational leaders must adhere the spirit of employees and various stakeholders to work altogether to overcome this COVID-19 crisis. The trust, bond and unity must be built to bring success altogether...” (8th Interviewee) “... Organization leaders in this situation must also be able to pass or empower their subordinates. They must not discourage the subordinates. It is very important. Of course, leaders have to empower themselves first by not being panic, reviewing what they have learned, and applying it during this critical time...” (16th Interviewee).
Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector in the human resource management: The leaders should set up an agency to act as a monitoring center and supervise employees to build morale, take care of health and safety, establish guidelines and measures to prevent the spread in the organization. The style of work should be changed to Work From Home using this opportunity to develop knowledge, skills and competencies of employees. These will be beneficial to operations and the organization. The rules for working should be established in a new way of working. This is consistent with the key informants stating; “...Employees must be safe and protected well. We try to reduce the risk with the measures such as adjusting the working style, time-lapse for employees at all levels, bringing digital technology into work to facilitate employees, and developing the capabilities of employees...” (8th Interviewee).“...The first step is to stop recruiting new employees. The second step is to reduce overtime, or some benefits such as travel expenses because now the employees mostly work from home. The next measure is to reduce working hours and increase productivity...” (7th Interviewee).
Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector in the leadership: Leaders should have high leadership, bold thinking, making decisions, having broad vision. strong and resolute, emotional intelligence to be the center of the mind of the people in the organization, build trust, confidence and unity among employees, honor others, see people’s weaknesses and strengths and be able to draw on their potential, know how to prioritize, be agile, trust people who listen to the opinions of others, know how to communicate and command. This is consistent with the key informants stating; “...Organizational leaders must adhere the spirit of employees and various stakeholders to work altogether to overcome this COVID-19 crisis. The trust, bond and unity must be built to bring success altogether...” (8th Interviewee)“... Organization leaders in this situation must also be able to pass or empower their subordinates. They must not discourage the subordinates. It is very important. Of course, leaders have to empower themselves first by not being panic, reviewing what they have learned, and applying it during this critical time...” (16th Interviewee).
Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector in the decision making: Leaders must make timely decisions based on comprehensive information at that time. They must know the goals of decisions and understand the situation well first. They must not adhere to the decision-making style in the chain of command. Decisions must be made in a team format with a brainstorming for a variety of options and choose the best option to deal with the situation. Transferring decisions into action through a single person can prevent and avoid confusion. This is consistent with the key informants stating; “... Decisions must be made on how to transform the organization in order to survive and grow sustainably in the midst of the COVID-19 epidemic with changing consumer behavior and organizational behavior to embrace the changes that are taking place...” (13th Interviewee). “.... For decisions made during this COVID-19 situation, decisions must be made by the organization leader or the management of any organization or source solely in order to prevent confusion of information and miscommunication possibly occurring...” (18th Interviewee).
Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID -19 of Thai Business Sector in the technology and innovation: Leaders should use this opportunity to transform the organization into a technology and innovation organization bringing technology to help in planning, management, helping to reduce costs, making it easier and faster to reach customers, such as automation and AI to digital marketing, used in video conferences, and helping to store documents. The customers can be communicated to maintain customer base through various online channels such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LINE, applications. There should be the development in the products, services and solutions to meet customer needs, such as increasing online sales channels, using the means of public relations, and the channel to take care of customer service after sales, etc. This is consistent with the key informants stating; “... The organization must recognize the importance of technology that plays a role in our lifestyles such as AI that plays an important role in digital marketing in various fields. This helps entrepreneurs plan their business in the right direction to make consumers access the service easily and quickly...” (1st Interviewee). “.... It is an opportunity to adopt digital platforms to reduce costs and increase the convenience of working from home, such as organizing a meeting via Video Conference as a long-distance communication channel or using tools to assist in managing work with the team...” (20th Interviewee).
Approaches in the development of Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector: Leaders have to change the organization management by bringing technology to develop products and services. For performance, the focus must be on business operations on a dependency to create alliances both with various organizations and stakeholders. It is planned to prepare for current and future uncertainties. Common goals and directions are established within the organization to guide the operation, change the working style, and focus on connecting parties to work altogether. Decisions need to be swift and flexible with adaptive adjustments to the situation. The new business channels should be searched to expand channels, diversify marketing, enhance service levels, focus on quality, make difference, and emphasize safety and communication with all stakeholders. Any subsequent misunderstandings must be avoided to eliminate non-value-added activities and reduce unnecessary expenses. This is consistent with the key informants stating; “... Decision making must be fast but flexible and ready to change. Learning from the lessons to adjust the continuous operation and optimize the business operations with technology as well as cooperation from employees is very important. It will help driving businesses to seize new opportunities...” (10th Interviewee). “.... For the strategies that both organizations must adhere to the action to drive the organization through this crisis, it is possible that the management is placed on the principle of 3F, Fit, Fast and Flexible to allow organizations adapt to the new normal...” (19th Interviewee).
Discussion
Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector
In the management: Leaders should have a risk management plan with Scenario Planning to prepare a response plan and business continuity management. The work process should be adjusted to suit the current situation. There are guidelines for applying technology and innovation to drive the organization and develop competitiveness. Leaders and employees work together to brainstorm solutions to problems and create opportunities. The organization’s work style should be adjusted to keep employees safe. This opportunity can be taken advantage to develop skills and competencies of employees, bringing in various equipment, technology, information systems and innovations to help facilitating the work. The performance can be evaluated all the time in order to adjust them to be timely. Similarly, (Stoner, 1982) stated that management is Process, Planning, Organization, Leading, and Controlling the attempt of the members in the organization to use the resources for achieving the objectives set by the organization. Gulick, Luther & Urwick (1939) classified 7 steps of management into 1) Planning to schedule in advance what to do and the executives must know how to plan because planning is the main fundamental principle of the management process, 2) Organizing to manage the organization or agency by dividing the works of the organization or agency into sub-agency along with setting the objectives, duties, and responsibilities of each work, 3) Staffing to manage personnel which is the recruitment process of qualified persons to work, 4) Directing is the important step affecting the organizational behaviors which possibly follow the set plan or not, 5) Coordinating to collaborate both inside and outside the organization, 6) Reporting the operational performance of the organization, 7) Budgeting to manage the budgets in advance for the procurement or for spending as the expenses. This agrees with the study of (Ariyaprasert, 2020) studying the development of organizational management models for Thai industrial businesses in the economic era using a combination of qualitative and quantitative research. The research results revealed that the organization management model for Thai industrial businesses in the economic era contain four main components and organizational characteristics with 5 sub-elements; 1) direction and vision, 2) organizational strategy, 3) structure and culture, 4) innovation, and 5) networking of work process with a precise working system. In human resource management, there are 2 sub-components including 1) human resource management and development and 2) talent creation. In organizational leadership, there are 4 sub-components including 1) transformational leadership, 2) collaborative leadership, 3) bold and creative leadership, and 4) flexible and swift leadership.
In the leadership: The leaders should have high leadership, dare to make decisions, have broad vision, foresight, strength and determination with honor to others. They must be dependent on the employees to have emotional intelligence. This is the center of the mind of the people in the organization to build trust, confidence and unity among employees. People’s weaknesses and strengths can be drawn on their potential to their advantage. They must know the priorities, be agile, trust people, listen to the opinions of others. They must also know how to communicate and command. Similarly, (Koontz & Weihrich, 1988) stated that the leadership is a matter of the art of influencing or the process of exerting influence on other people to give the willingness and enthusiasm to perform the work until reaching the goals of the group. According to the Democratic Leadership model, University of Iowa’s (Lewin, 1939) has studied and found that the leaders like this use group decisions or involve followers in decision-making. Listening to opinions as a whole, working as a team and having two-way communication can lead to the productivity and work satisfaction. It agrees with the study of (Chunlaaid, 2014) studied the crisis management leadership and modern tourism strategy for creative competition in the region of the Thai tourism industry. The results of the research can be concluded that the tourism industry of Thailand will be successful in implementing a creative strategy. In order to have a victory in the regional competition with its original reputation, “The most outstanding wealth builder of the nation” is the leadership of the tourism administration in the future both from the public and private sectors to have a keen vision of the future. They must strengthen the development of caring and pastoral governance, which is a national character and a symbol of Thai style in the industry. Tourism Authority of Thailand will drive the action to have serious results while maintaining an international standard.
In the decision making: Leaders should make timely decisions based on the information that is available at that time. They must know the goals of decisions and understand the situation well first. They must not adhere to the decision-making style in the chain of command. Decisions must be made in a team format with a brainstorming for a variety of options and choose the best option to deal with the situation. Transferring decisions into action through a single person can prevent and avoid confusion. This agrees with the definition of decision of (Simon, 1960) stating the process of finding opportunities to make decisions. Finding possible alternatives and choice from various jobs available and decisions are based on the situation. It relates to what is planned or predicted, does not comply with a predetermined activity or program, and the other is a planned decision. A pre-planned decision relates to a list of tasks assigned to the discretionary classification. The study of (Campbell et al., 1983) is consistent with the study of (Trisirinthichote, 2016) on the Efficiency of Decision Support Systems Affecting Processes Project Management in the Organization. The research results revealed that the decision support system performance in accuracy, rapidness, ease of use, and employee acceptance affect the process of project management in the management of the organization in all aspects including planning, decision-making, controlling, monitoring, and communication with the statistical significance at level 0.05.
In the technology and innovation: Leaders should use this opportunity to transform the organization into a technology and innovation organization bringing technology to help in planning, management, helping to reduce costs, making it easier and faster to reach customers, such as automation and AI to digital marketing, used in video conferences, and helping to store documents. The customers can be communicated to maintain customer base through various online channels. Dale (1969) stated that technology consists of the sum of experiments, tools and processes. All of these things come from learning, trial, and improvement. Toffler (1980) defined innovation as a combination of tools and techniques that have 3 characteristics in combination; 1) creative and feasible idea, 2) Practical Application, and 3) Distribution. This agrees with the study of (Sukanek, 2018) on the management strategy of private commercial banks towards being a high-performance organization. It was found that 1) the management of underserved commercial banks was under pressure from economic globalization and in the context of private commercial banks which was the center of investment savings giving importance to customers and stakeholders by developing service quality through innovation and digital technology together with the environment. The organization that is the strong commercial bank has potential of vision, management, and competent employees ready for development in all dimensions. Matching opportunities from the government policy in the development of electronic payment infrastructure to a cashless society in the investment market has been expanded to ASEAN countries and through a dialogue with policymakers to assess the quality of private commercial banks’ management strategies to become a high-performance organization in 5 main strategies. The 1st strategy is to create and develop the technological innovation to provide service with the financial system of Smart Banking to a Cashless Society with the customer as the center. The 2nd strategy is to operate the business by adhering to the principles of good corporate governance. The 3rd strategy is to change the organizational culture to ensure supporting the 21st century society. The 4th strategy is to develop transformational leaders. The 5th strategy is to promote commercial banks to be organization of learning throughout the organization. Formulation of strategies to be a model of management strategy for private commercial banks is the Banking Strategy Model.
Approaches in the Development of Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector
For the approaches in the development of Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector, the leaders should adjust their work style, set common goals and direction in the organization. They should bring technology to be used in management. There is a business that is dependent on each other to build alliances with organizations and stakeholders. It is planned to prepare for uncertainty in the present and in the future making quick and flexible decisions ready to adjust according to the situation. The new business channels should be searched to expand channels, diversify marketing, enhance service levels, focus on quality, make a difference, emphasize safety, focus on communication with all stakeholders, eliminate non-value-added activities and reduce unnecessary costs. This is in correspondence with the need to develop ways to survive the long-term coronavirus outbreak since the beginning of 2020 and the outbreak has continued to be widespread almost all over Thailand. On 5th January, 2021, the number of new cases was 527. The number of confirmed cases accumulated 8,966. The death toll accumulated at 65. Thus, the crisis leaders should learn the lessons from the COVID 19 situation. Knowledge or innovation in organizational management according to new approaches are suitable for the current situation to enable entrepreneurs in the Thai business sector to use them as an opportunity to change organizational management to create opportunities for businesses to be able to continue as an important concept between entrepreneurship and innovation. Drucker (1994); Kanungo (1999); Zhao (2001) have been mentioned and studied for a long time. Schumpeter (1934) pointed out the importance of innovation in entrepreneurship and the importance of entrepreneurs for the innovation development. Innovation will only contribute to economic growth if entrepreneurs have created innovations to look for economic benefits.
Research on the Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector brings benefits and new knowledge to guide the approaches for the development of Crisis Leader: Lessons from COVID-19 of Thai Business Sector. These can be summarized as a following Figure 1:
References
- Thongaram, T. (2020). Business preparation to new normal. Searched from www.tmbbank.com/newsroom/news/pr/view/Analytic-YE-New-Normal.html.
- Ariyaprasert, T. (2020). Development of organizational management models for Thai industrial businesses in the recession economy era. Journal of King Mongkut's University of North Bangkok, 30(2), 314-323.
- Trisirinthichote, P. (2016). Efficiency of decision support systems affecting project administrators process management in organization. Independent study of the Master of Business Administration. Bangkok University.
- Chunlaaid, P. (2014). Roles of management executives in crisis situations and tourism strategies in the new era. Academic Journal of the Graduate School of Suan Dusit, 10(2), 211-219.
- Center for the Outbreak of Coronavirus Disease Management 2019. (2021). COVID-19 situation in Thailand, data as of 5 January 2021. Searched from www.moicovid.com/05/01/2021/uncategorized/2359/.
- Sukanek, A. (2018). Strategies for the management of private commercial banks to become an organization of high performance. Doctoral program thesis. Management Program Type 2.1 Doctor of Philosophy Graduate school Silpakorn University.
- Toffler, A. (1980). The third wave. New York: William Marrow.
- Aycan, Z., Kanungo, R.N., & Sinha, J.B.P. (1999). Organizational culture and human resource management practices: The model of culture fit. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 30(4), 501–526.
- Dale, E. (1969). Audio-visual methods in teaching (3rd edition, 108). New York: Dryden Press.
- Drucker, P. (1994). The age of social transformation. Atlantic Monthly, 274, 53-80.
- Luther, G., & Urwick, L. (1939). Paper on the science of administration. New York, 2.
- Stoner, J.A.F. (1982). Management, (2nd edition). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
- Koontz, H., & Weihrich, H. (1988). Management. New York : McGraw –Hill.
- Kanungo, R.N. (1999). Entrepreneurship and innovation: Models for Development. London : Sage Publications.
- Lippitt, L.K.R., & White, K.R. (1939). Pattterns of aggressive behavior in experimentally greated social climate. Journal of Social Psychology.
- Razzaq, A., Sharif, A., Aziz, N., Irfan, M., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2020). Asymmetric link between environmental pollution and covid-19 in the top ten affected states of US: A Novel Estimations from Quantile-On-Quantile Approach. Environmental Research, 191, 110189.
- Schumpeter, J. (1934). The theory of economic development. (reproduced, New York: 1961). Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Simon, H.A. (1960). The new science of management decision. New York: Harper & Row.
- Tesser, A., Campbell, J., & Mickler, S. (1983). The role of social pressure, attention to the stimulus, and self-doubt in conformity. European Journal of Social Psychology, 13(3), 217–233
- Zhao, F. (2001). Managing innovation and quality of collaborative R&D. International & 8th National Research Conference. Melbourne.