Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 6S
Customers' Perception of Service Quality in Syrian Restaurants Operating in Jordan: The Mediating Effect of Customer Satisfaction
Jamal M. M. Joudeh, Applied Science Private University
Ahmad Khraiwish, Applied Science Private University
Jassim Ahmad Al-Gasawneh, Applied Science Private University
Nabil A. Abu-Loghod, Arab Open University
Nawras M. Nusairat, Applied Science Private University
Nafez Nimer Ali, Al-Zaytoonah University of Jordan
Abstract
Last decade, Jordan has witnessed an increase in the Syrian investment in Jordan by indifferent fields. The reason behind that is the inflow of Syrian people to Jordan as a result of civil war. The most of Syrian investment were concentrated in the field of restaurants which spread throughout the large cities and offered a wide menu of Levantine kitchen to Jordanian customer. Therefore, the objective of this study is to explore the impact of service quality in Syrian restaurants operating in Jordan according to Jordanian customers' perception. This study is depended on the primary data collected through a developed questionnaire. The questionnaire has been distributed on a (421) customers on the basis of convenient sample. Multiple Regression Analysis and Path Analysis were applied to test 3 hypotheses. The results indicated that service quality has a significantly positive impact on customer satisfaction that is attributed to environment. In addition, service quality has a significantly impact on loyalty of customers that is attributed to food quality. Moreover, it found that the customer loyalty has positively influenced by service quality and customer satisfaction. The study recommended that organizations operating in the field of restaurant industry must adopt the service quality strategy as a basis for competition to improve the services provided.
Keywords
Food Industry, Service Quality, Customer Loyalty, Entrepreneurship, Refugees
Introduction
After ten years of the crisis in Syria, around 1.4 million of Syrian nationals are living in Jordan as refugees. At the beginning, Syrian refugees put a heavy pressure on the Jordanian society and economy, including pressures on the infrastructure, unemployment and increase in the prices of some goods and services (Alshoubaki & Harris, 2018). On the other hand, despite of what is reported of the existence of negative impact for the Syrian refugees on Jordan which might be partially true, the existence of Syrian refugees has a positive impact in enhancing the country’s economy and market situation through increasing their investments in Jordan which creates more employment opportunities and enhances the public revenues (Jordan Independent Economic Watch, 2017).
For mutual benefit and coexistence between Syrians and the Jordanians, the Ministry of Labor (MOL) has issued about 182 thousands work permits for Syrian refugees between 2016 and 2020. Furthermore, (MOL) has provided work permits for Syrians free of charge, facilities for establishing Home Based Businesses (HBBs), and Small-Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and provided many facilities to those who transferred their businesses from Syria to Jordan (MOPIC, 2020). The idea behind those decisions is maintaining social and political stability, creating more employment opportunities and increasing economic growth rate. According to the Companies Control Department, the number of Syrian companies registered at the amounted to 4062, which were active in different fields, including textile, foodstuffs, trade and real estate with total investment of 373 million US dollars. Regarding the catering sector such as restaurants and sweet shops, the total Syrian investment is worth more than 100 million US dollars and that 16.6% out of 18,000 restaurants registered in 2016 in Jordan are Syrians (Baladi, 2019).
From that point, with the continued flow of Syrian refugees to Jordan and their settlement - to a certain extent - in the Kingdom, with the grow in the number of Syrian restaurants in Jordan have appeared some differences between the natures of services that are presented by Jordanian restaurants in comparison to Syrian restaurants. It is worth mentioning that the presence of Syrian restaurants in Jordan has increased the competition with Jordanians restaurants in the market were Syrian capital was strongly concentrated in. This has resulted in the widespread presence of restaurants throughout the large cities and become very popular mostly to the customers who prefer Syrian food.
Here, we raise the dilemma of service and service quality, especially that the main sector under investigation is food, which means that service is highly expected in such sector. Moreover, digging in depth in the Jordanian food market, Syrian restaurants are growing bigger in number especially after the civil war in Syria which led many refugees and investors to move to safer and more secure countries including Jordan.
The current study is related to the perception of customers towards the food industry. To clarify, restaurants and customers have mutual interest in this situation, where customers are mainly concerned about getting high service quality. Meanwhile, restaurants aim at providing their customers with a high service quality to make them feel satisfied. Hence, this study is conducted to provide answers to the following three questions:
1. Is the food service quality provided by Syrian restaurants considered adequate and able to fulfill their customers' needs?
2. What is the impact of the food service quality provided by Syrian restaurants upon customers’ satisfaction?
3. What is the impact of food service quality provided by Syrian restaurants upon customers’ loyalty?
Therefore, the objective of this study is to investigate the opinion of Jordanian customers towards Syrian restaurants that operate in Jordan. Moreover, to our knowledge, no previous study has analyzed the influence of food service quality on the customers in the field of restaurants that owned by refugees. Therefore, this study offers a new contribution to the body of literature in the field of service quality through studying a unique sample that has not been explored before.
Literature Review
The concept of quality and its improvement first appeared in Japan, at the beginning of 20th century and then expanded to America and to the countries of Europe until it became the topic of the times (Keshavarz et al., 2016). According to Tsai, et al., (2020) there is no standard definition of quality of service, but there is a tendency among many writers in the field of marketing to view service quality as a comparison between what customers expect and their perception of actual performance. Furthermore, Mahin & Adeinat (2020) added that the concept of expectations here refers to the desires of customers, which were reflected the customer's previous experience. While, Lisnawati & Astawa (2020) said that the notion of service quality was defined as evaluating and measuring the extent of compatibility between the service that is provided, and the expectations of the customer who receives the service, that is, the service provider measures the extent of customers’ satisfaction with the service provided in order to clarify the difference and introduce the required modifications, developments and improvements later. Measuring customer behavior is a challenging task because purchasing intention of customer is affected by several factors (Al-Gasawneh et al., 2020), therefore, Zeitham, et al., (1996) emphasized that understanding exactly what customers expect is the most crucial step in defining and delivering high-quality service.
Customer Satisfaction
The expression of customers’ satisfaction has become a commonly used expression in theoretical and empirical studies conducted in the field of marketing; that has resulted from the increasing attention given to consumers who have become the focus of many companies and an indicator to measure of managers’ success (Joudeh, 2017a). According to marketing literatures, customer satisfaction is considered as an important factor that can affect the profitability, market share and competition of the organisation. Therefore, customer satisfaction is defined as measuring the degree of customer satisfaction with a specific experience, and how the customer deals with this experience (Kim & Shim, 2019; Tama, 2015). Satisfied customers are likely to become loyal customers and they are more likely to spread a positive opinion about the relevant companies’ products or services (Gibson, 2005). At the same time, customers having a bad experience or receiving a poor service is an early indication that customers may be lost (which is a critical factor in business growth), as no organization can sustain a steady growth rate if it face the problem of satisfying their customers (Fitria & Yuliati, 2020). Moreover, organisations should pay more attention to early indications of customer loss by measuring the satisfaction level of their customers and take proper actions to improve it constantly. Therefore, customer satisfaction is considered to be of great importance given that the food sector has both the service and the product that a customer can be satisfied about (Kiatkawsin & Sutherland, 2020).
Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty is crucial to the success of an organization, as loyal customers facilitate the growth of businesses faster than sales and marketing. Customer loyalty is among the factors that increase the competitive advantage of stores and raise its market share among the other stores (Joudeh, 2017b). Therefore, Bowen & Chen (2001) defined customer loyalty as customers desire to buy from a brand or organization over and over again, which results from a good customer experience, and satisfaction that customers get from the transaction. In addition, Shin & Yu (2020) referred to customer loyalty as a result of customer satisfaction and positive customer experiences with the organization. According to Jin, et al., (2015) customer loyalty is the most effective way to protect the organization against competition, as loyal customers adhere to their relationships with the organization, which reduces the percentage of losing customers. Özdemir-Güzel & BA? (2020) indicated that customer loyalty is a guarantee of creating competition between small, medium and large organizations, all through caring for customers and communicating with them and enhance the percentage of their loyalty to the organization. Therefore, Shin & Yu (2020) said that customer loyalty is the customer's tendency to repeat business with a particular organization as a result of customer satisfaction.
Model And Hypotheses Development
Study Conceptual Model
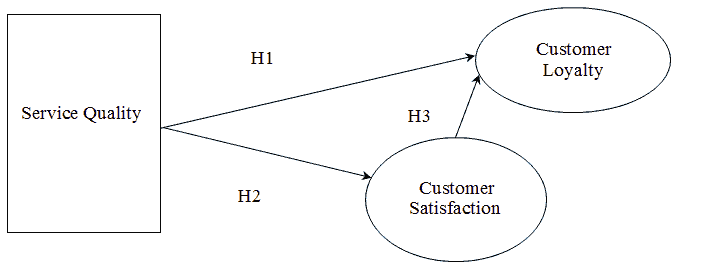
Based on the aforementioned aim of study, we were able to build the following model that highlighted the nature of relationship between dependent and independent variables:
Development of Hypotheses
Based on the literature in this study and Figure 1, we were able to extract the following three main hypotheses:
Development of H1
Inkumsah (2011) found that service quality along with its variable of staff quality appeared to be the most influential on customer satisfaction, followed by price and food quality. According to the study of Andaleeb & Conway (2006), responsiveness is the most influential factor that increases customers’ satisfaction and followed by price, food and environment. Rahman, et al., (2012) indicated that customers may develop negative impressions regarding a restaurant just if the price is not fair, or the environment was not welcoming. Morano, et al., (2018) revealed that "attendance and healthiness" were influential, while cleanliness influenced healthiness which played a role in determining the perception of customers towards food quality. Chia-Hsin (2020) in his study to examine the influence of restaurants' environment on the satisfaction of people with disabilities towards restaurants in Taiwan. He found that people are not satisfied with service quality and some environmental issues within restaurants including space, restroom and slipperiness of floors. Based on that, hypothesis 1 will appear as the following:
H1: Service Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1a: Food Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1b: Employee has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1c: Price has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1d: Environment has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Development of H2
Bichler, et al., (2020) mentioned that quality of service proved a positive relationship with intention to revisit. It meant that there is a vivid relationship between service presented by employees attentiveness and reliability in giving a more comfortable atmosphere along with the mediating role of food quality which opens the gate for chances to revisit the place again by customers. Rafdinal & Suhartanto (2020) stated that aspects such as quality and environment can affect customers' loyalty. While service had an indirect effect on customer loyalty through price and emotional values. Njelita & Anyasor (2020) showed that there is positive relationship between price, food, personnel, image and trust with customers' loyalty and patronage to a certain fast food chain. According to Dhanasekaran & Anandkumar (2020) food quality, menu, ambience and price were the most influential aspects that drive customers towards being loyal to a certain restaurant compared to others. Based on that, hypothesis 2 will appear as the following:
H2: Service Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H2a: Food Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H2b: Employee has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H2c: Price has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H2d: Environment has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
Development of H3
Zhong & Moon (2020) indicated that variables such as perceived price, food, service, and environment are playing an important role in changing customer's behavior towards restaurants in terms of satisfaction and loyalty. Furthermore, both happiness and satisfaction can lead to customer loyalty. Uddin (2019) pointed that food quality, price and service quality were influential on the relationship between satisfaction and loyalty; and there is a positive relationship between satisfaction and loyalty where the increase on one of them may increase the level of the other. Thielemann, et al., (2018) stated that service quality is one of the aspects that have the ability to influence customer satisfaction and this can come from the perceived value that customers gain from high quality service which in turn is able to increase the level of their satisfaction and loyalty. Carranza, et al., (2018) mentioned that food quality can influence customer satisfaction and trust which in its turn can build up more loyal customers. Tripathi (2018) indicated that service quality has the ability to influence the loyalty of customers and it may increase their satisfaction and willingness to spread a positive WoM among others. Based on that, hypothesis 3 will appear as the following:
H3: Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction have a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
Research Methodology
Data Collection
In order to be able to answer study questions; a questionnaire was developed in order to gather the primary data and all needed data. The questionnaire was developed based on the previous literature review as well as the other research surveys and built on likert 5 scale with confidence level at P ≤ 0.05. The questionnaire was divided into two sections. The first section took into consideration the demographics of the study sample including (gender, age, education, occupation and income), while the second section took into consideration adopted variables of service quality (food quality, employees, prices and environment) in addition to dependent and mediating variables of (customer satisfaction and customer loyalty). The population of study consisted of all customers who are accustomed to attending Syrian restaurants. Therefore, a sample of 500 customers was chosen based on a convenient sample. After the application process 425 customers responded to it with responding rate of 87.5%. Multiple Regression Analysis and Path Analysis were used in order to screen and analyzed gathered data.
Demographic Analysis
According to demographic variables of the study as appeared in Table 1, as for the individuals’ gender, 50.8% of them were females and the others are males with 49.2%. As for individuals’ ages, 36.2% of them were between 31-40 years old and followed by the age of 30 years and less with 31.3% and 41-50 years with 24.9% of them. Regarding the education, 40.9% of them hold a bachelor degree and followed by the high school and less with 30.4% and diploma with 21.2%. Furthermore, individuals who were employed within the private sector forming 25.2%, and followed by the unemployed with 22.1% and self-employed with 21.9%. In addition, individuals who had an income of JD 500 and less formed 37.6%, followed by the income of JD 501-1000 with 28.2% and JD 1001-1500 with 14.6%.
| Table 1 Demographics Sample |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| F | % | ||
| Age | 30 and less | 133 | 31.3 |
| 31-40 | 154 | 36.2 | |
| 41-50 | 106 | 24.9 | |
| 51-60 | 29 | 6.8 | |
| Gender | Male | 209 | 49.2 |
| Female | 216 | 50.8 | |
| Education | High School and less | 129 | 30.4 |
| Diploma | 90 | 21.2 | |
| BA | 174 | 40.9 | |
| Occupation | Postgraduate | 32 | 7.5 |
| Private | 107 | 25.2 | |
| Civil Servant | 73 | 17.2 | |
| Self-Employed | 93 | 21.9 | |
| Retired | 58 | 13.6 | |
| Unemployed | 94 | 22.1 | |
| Income (1 USD=0.71 JD) | JD 500 and less | 160 | 37.6 |
| JD 501-1000 | 120 | 28.2 | |
| JD 1001- 1500 | 62 | 14.6 | |
| JD 1501-2000 | 50 | 11.8 | |
| JD +2000 | 33 | 7.8 | |
Questionnaire Analysis
In the Table 2, appeared mean and standard deviation of responses towards statements of study. As it appeared from that Table 2, individuals had positive attitudes towards statements given that all means scored higher than mean of scale 3.00 which was a positive indication. It can be seen through analysis that the statement articulated "location is convenience" scored a mean of (4.08/5.00), on the other hand, the least positively answered statement was articulated "I would consider this restaurant as my first choice" which scored a mean of (3.21/5.00).
| Table 2 Descriptive Statistics Of Questionnaire |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | S.D | Alpha | Tolerance | VIF | ||
| Food Quality | The restaurant provides a High quality food | 3.77 | 0.964 | 0.739 | 0.45 | 2.223 |
| The restaurant provides Healthy and nutritional food | 3.77 | 0.916 | ||||
| The restaurant offers fresh products | 3.85 | 0.85 | ||||
| The restaurant serves Superior taste and favorable food | 3.61 | 1.01 | ||||
| The restaurant offers fresh food | 3.55 | 1.01 | ||||
| The restaurant offers a wide menu | 3.25 | 1.1 | ||||
| The restaurant uses a natural materials | 3.78 | 0.898 | ||||
| Employees | Employees know how to do their Job | 3.34 | 1.09 | 0.773 | 0.419 | 2.384 |
| Employees provide a quick service | 4 | 0.867 | ||||
| Employees are always ready to help | 3.72 | 0.967 | ||||
| Employees have an extensive communication skills | 3.65 | 0.977 | ||||
| Employees understand my needs | 3.26 | 1.14 | ||||
| Employees ready to solve my complaints | 3.51 | 1 | ||||
| Price | Prices are reasonable and affordable | 3.59 | 0.956 | 0.775 | 0.417 | 2.397 |
| The price meets the given quality. | 3.8 | 1.03 | ||||
| It provides a various prices offers | 3.91 | 0.967 | ||||
| Prices are competitive | 4.03 | 0.918 | ||||
| Environment | Location is Convenience | 4.08 | 0.903 | 0.85 | 0.532 | 1.881 |
| It is easy to reach the restaurant | 3.88 | 0.977 | ||||
| The environment is visually appealing | 3.78 | 1.07 | ||||
| The spaces are wide and comfortable. | 3.69 | 0.95 | ||||
| Satisfaction | I am contented with the restaurant | 3.79 | 0.934 | 0.886 | ||
| I am satisfied with the restaurant | 3.66 | 1.01 | ||||
| I am happy to be a customer of this restaurant | 3.55 | 0.97 | ||||
| this restaurant always meets my expectation | 3.48 | 1.01 | ||||
| Loyalty | I am very loyal to this restaurant | 3.54 | 1.02 | 0.882 | ||
| This restaurant will be my first choice | 3.21 | 1.1 | ||||
| I plan to dine from this restaurant | 3.4 | 1.08 | ||||
| I will encourage others to purchase from this restaurant | 3.42 | 1.08 | ||||
Going on the same track, Table 2 presented means of all variables employed in study; it appeared that all variables scored a mean higher than mean of scale 3.00 and this showed that individuals had positive attitudes towards variables as the highest mean was scored for the variable of "environment" scoring a mean of (3.85/5.00) while the lowest mean was for the benefit of "loyalty" scoring a mean of (3.39/5.00).
Internal Consistency
Cronbach alpha was used to test the reliability of the scale as it appeared in the Table 3 which indicated alpha values were reflected a reliable scale since they were greater than accepted value>0.70 (Hair et al., 2010). Also, Table 4 showed that VIF values are less than 10 whereas Tolerance values are greater than 0.10 that means there are no multicolleniarity (Gujarati & Porter, 2009).
| Table 3 Values Of Goodness Of Fit Model |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | AGFI | χ2/df | GFI | RMSEA | CFI | NFI |
| Value of Recommended | > 0.8 | < 5 | > 0.90 | = 0.10 | > 0.9 | > 0.9 |
| References | (Miles & Shevlin, 1998). | (Tabachnick & Fidell, 2007) | (Miles & Shevlin, 1998). | (MacCallum et al., 1996) | (Hu & Bentler, 1999). | (Hu & Bentler, 1999). |
| Value of Model | 0.83 | 4.27 | 0.917 | 0.097 | 0.905 | 0.901 |
| Table 4 Testing H1 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Std. Error | |||
| 0.777a | 0.604 | 0.6 | 0.51618 | |||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | ||
| Regression | 170.842 | 4 | 42.711 | 160.302 | 0 | |
| Residual | 111.904 | 420 | 0.266 | |||
| Total | 282.746 | 424 | ||||
| Coefficient | ||||||
| B | Std. Error | ?eta | T | Sig. | ||
| Food | 0.357 | 0.046 | 0.326 | 7.737 | 0 | |
| Employees | 0.337 | 0.056 | 0.274 | 5.997 | 0 | |
| Prices | -0.084 | 0.052 | -0.077 | -1.616 | 0.107 | |
| Environment | 0.404 | 0.051 | 0.373 | 7.848 | 0 | |
Validation of Model
Before testing of hypotheses, the proposed study model must be validated by a set of indicators to check the suitability of the model of this study. The results of the fit model in Table 3 showed that the value of chi-square/degree of freedom (χ2/df)=4.27 which is less than the recommended value <5. The Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index (AGFI)=0.83 which is more than recommended value >0.8. Also, root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA)=0.097 which is less than the recommended value ≤ 0.10. Moreover, normed fit index (NFI)=0.901, comparative fit index (CFI)=0.905 and Goodness of Fit Index (GFI)=0.917 all met the standards that all must be greater than 0.9. Thus, Table 3 showed that the all indicators have passed the values recommended by the relevant references and proved satisfactory for the study.
Results
H1: Service Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction
To test hypothesis H1, a multiple regression analysis was used. As shown in Table 4, (F) value scored 160.302 with Sig.=0.000 which is less than the confidence level of the study P ≤ 0.05. This means that customer satisfaction has positively influenced by the service quality. Also it was found that (R)=0.777 reflected a high level of correlation as well as the regression analysis reveals that (R2)=0.46, which means that 46% of the overall of customer satisfaction was attributed to service quality and the remaining 54% can be attributed to other factors which weren’t examined, because they are not included in this study. As we see in the coefficient Table 4, the value for each variable (food quality, employees and environment) was significant at P ≤ 0.05, but only price has no impact on customer satisfaction where Sig.=0.107>0.05. Thus, hypothesis (1) is accepted.
H 1a: Food Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1b: Employee has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1c: Price has no Significant Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H 1d: Environment has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
H2: Service Quality has a Significant Impact on the Customer Loyalty
To test hypothesis H2, a multiple regression analysis was used. As shown in Table 5, (F) value scored 108.452 with Sig.=0.000, it means that service quality has a significantly positive impact on customer loyalty. Also, it was found that (R)=0.713 reflected a high level of correlation as well as the regression analysis reveals that (R2)=0.508, which means that 50.8% of the overall of customer satisfaction was attributed to service quality and the remaining 49.2% can be attributed to other factors which weren’t examined, because they are not included in this study. As we see in the coefficient Table 5, the value for each variable (food quality, employees, prices and environment) was significant at P ≤ 0.05. Thus, hypothesis (2) is accepted.
| Table 5 Testing H2 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Std. Error | ||
| 0.713a | 0.508 | 0.503 | 0.64221 | ||
| ANOVA | |||||
| Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Regression | 178.916 | 4 | 44.729 | 108.452 | 0 |
| Residual | 173.221 | 420 | 0.412 | ||
| Total | 352.138 | 424 | |||
| Coefficient | |||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | T | Sig. | |
| Food | 0.449 | 0.057 | 0.367 | 7.815 | 0 |
| Employees | 0.369 | 0.07 | 0.269 | 5.278 | 0 |
| Prices | -0.132 | 0.065 | -0.108 | -2.049 | 0.001 |
| Environment | 0.337 | 0.064 | 0.279 | 5.26 | 0 |
H 2a: Food Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H 2b: Employee has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H 2c: Price has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H 2d: Environment has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
H3: Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction have a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
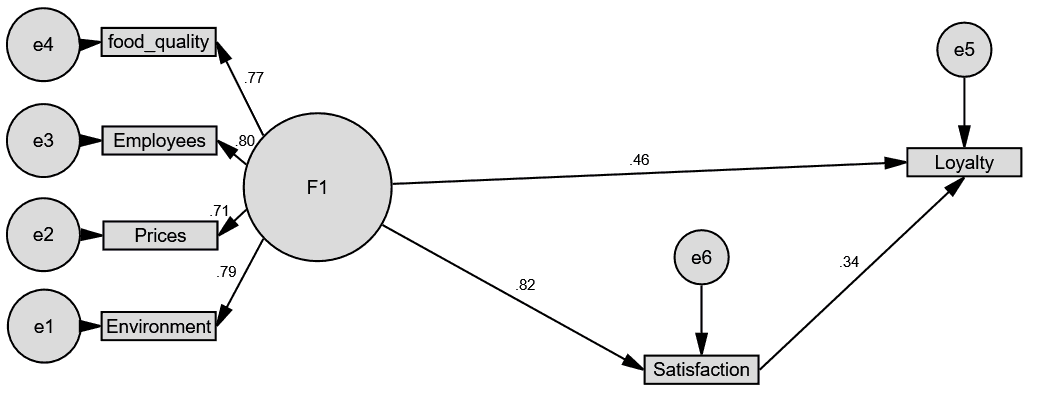
Table 6 summarizes the direct and indirect effects among latent variables. Through the data presented, there are indirect effects which are all significant at P ≤ 0.05. Therefore, this hypothesis is accepted (C.R.=6.23; P<0.05). This means that customer loyalty has positively influenced by service quality and customer satisfaction.
According to previous literature and the proposed hypotheses, we can determine the path diagrams of the model and their standardized path coefficients. As evident from Table 6 and Figure 2, service quality has a direct impact on the perception of Jordanian customer satisfaction where β=0.82 and P=0.000; customer satisfaction has a direct impact on the customer loyalty where β=0.34 and P=0.000; service quality has a direct impact on the customer loyalty where β=0.46 and P=0.000 and service quality and mediation of customer satisfaction have indirectly on customer loyalty where β=0.275 and P=0.000. In other words, the three major proposed hypotheses were strongly supported by our model.
| Table 6 Direct And Indirect Testing Results |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct impact | Indirect impact | C.R. | P | Result | |
| Satisfaction <---Service Quality | 0.817 | 17.8 | *** | Accept | |
| Loyalty <--- Satisfaction | 0.336 | 5.03 | *** | Accept | |
| Loyalty <--- Service Quality | 0.458 | 0.275 | 6.23 | *** | Accept |
Discussion
This study aimed to evaluate customers' perception of service quality in Syrian restaurants operating in Jordan. Through adopting the quantitative approach, a questionnaire was distributed to (425) Jordanian customers who are used to attending restaurants of different origins and backgrounds. Results of the study indicated that there is a positive impact of service quality on satisfaction and loyalty of customers within Syrian restaurants. Such impact was attributed to service quality dimensions.
Also, results of study presented the following findings:
• Service quality has a significantly positive impact on customer satisfaction
• Service quality has a significantly positive impact on customer loyalty
• With (C.R.=6.23; P ≤ 0.05) findings revealed that service quality and customer satisfaction have a significantly positive impact on customer loyalty.
• Through analysis, it was seen that in the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction it appeared that environment scored the highest value of influential on customer satisfaction.
• From another side and in the relationship between service quality and customer loyalty, it appeared that food quality scored the highest value of influential on customer loyalty.
Based on that, it can be said that all hypotheses were accepted and there is a relationship between customer satisfaction and service quality which would eventually lead to better customer loyalty. Study revealed that service quality is like the magnet that attracts customers, their satisfaction and their loyalty towards the restaurant in order to increase the connection and develop the positive emptions they hold towards the place.
H1: Service Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Through the results of the study, the above theory was proven and the idea that service quality has a positive impact on customer satisfaction, as the hypothesis acceptance rate in the analysis reached 60.4%, which is a good indication that the hypothesis is generalizable and that there is actually an effect of service quality on customer satisfaction. This result was in agreement with all of Chia-Hsin (2020); Morano et al (2018); Rahman et al (2012); Inkumsah (2011); Andaleeb & Conway (2006) when they indicated that the quality of service and the interest in providing a service at a high level of quality has a great impact in generating a feeling of satisfaction on the consumer, especially about the perceived service (which the customer receives) and thus increases his sense of satisfaction about the option which he has done.
H2: Service Quality has a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
The above hypothesis, which linked service quality and customer loyalty, was also met with positive results during the analysis, as it was previously explained, where the acceptance rate of the second hypothesis was 50.8%, indicating the presence of insistence on the high level of service and the increased level of customer loyalty to the organization providing this service. This result was consistent with the studies of each of Bichler, et al., (2020); Rafdinal & Suhartanto (2020); Anyasor & Njelita (2020); Dhanasekarana & Anandkumar (2020) when they confirmed in their studies that the high level of service quality directly affects the perceived value of this service, which would end the state of anxiety and suspicion that the client has and thus increase the chance of it repeating the service request from the same source given that the previous experiences of dealing were satisfactory to him, and there is no objection to the client from repeating the deal again, and this is evidence of the high level of customer loyalty towards the organization.
H3: Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction have a Significantly Positive Impact on Customer Loyalty.
The above hypothesis dealt with the idea that the quality of service and the ability to satisfy the customer through it directly affect his loyalty, meaning that the organization can reach the customer’s loyalty by working to raise the level of satisfaction with the service provided. Here, the two variables of customer satisfaction and customer loyalty were combined and that the first affects the second through the correlation of service quality with a positive impact on customer satisfaction. And through the results that were previously reviewed, the study proved that - in fact - the organization can target customer satisfaction through service quality in order to reach a higher level of loyalty, and this is consistent with each of Zhong & Moon (2020); Uddin (2019); Thielemann, et al., (2018); Carranza, et al., (2018); Tripathi (2017).
The study proved that high-quality services meet or exceed the client's expectations, while remaining economically competitive. Evidence drawn from the current study indicates that improving the quality of services would increase customer satisfaction, which would be reflected in the firm's profitability and competitiveness. In the case of Syrian restaurants, logic requires that there be some measure of the level of customer satisfaction - given that going to these restaurants is optional and not compulsory - and therefore improving the service in them, identifying problems and solving them, and commitment to providing reliable and capable service measurement is the only option in order to achieve customer loyalty and satisfaction.
As previously indicated, attending Syrian restaurants in Jordan by Jordanian consumers is by nature an optional matter related to the consumer's taste and desire to try something new, and it is not a compulsory thing that the individual does due to the difference in public taste and the idea that the Jordanian consumer has local options (Jordanian) what is enough, except that dining at Syrian restaurants is related to the desire to experience different customs, flavours and presentation methods from the Jordanian society.
From here, it can be said that the link between service quality and consumer satisfaction is inevitable, especially in light of the multitude of options available to the consumer. The idea of consumer satisfaction and loyalty may not be associated only with (non-Jordanian) restaurants, but the Jordanian consumer expects from it the best and the highest in terms of service and quality since these restaurants try, with their best potential, to win the largest share of the Jordanian market by influencing consumer feelings such as satisfaction, desire, loyalty and taste.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Syrian restaurants spread in Jordan side by side with Jordanian restaurants to create a great atmosphere of competition and push their owners to move forward in the development and renewal process. Syrian restaurants are spread all over the country and have received an unrivaled turnout in light of a variety of options between Jordanian and Syrian restaurants and fast food restaurants with their multiple branches. Levantine dishes are popular with Syrian citizens and refugees, along with Jordanian food, and in addition to restaurants in cities and the capital, there are many small Syrian restaurants that are spread in the villages of the province and run by Syrian women. The turnout of Syrian restaurants has led Jordanian restaurants to offer Syrian food to compete and diversify in what they offer of Jordanian food.
The influence of the Levantine restaurants created a state of competition between the Syrian and Jordanian restaurants in providing the finest, which was positively reflected on the quality of service and quantity of food.
Study recommended the following:
• Ethnic and foreign food investments should put extra efforts in managing customers and gain their satisfaction in order to attract more customers and preserve current ones.
• In general, establishments operating in the field of food and drink must adopt the service quality strategy as a basis for competition to improve the services provided.
• The quality of service is a continuous development issue and it is one of the important principles that many organizations continue to try to reach, for that, the study recommends the necessity of developing new plans and policies within the establishments operating in the field of food and drink in order to be consistent with the idea of quality, thus ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty.
References
- Al-Gasawneh, J.A., Al-Wadi, M.H., Al Wadi, B.M., Alown, B.E., & Nuseirat, N.M. (2020). The interaction effect of comprehensiveness between social media and online purchasing intention in Jordanian pharmacies. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 14(15), 208-221.
- Alshoubaki, W.E., & Harris, M. (2018). The impact of Syrian refugees on Jordan: A framework for analysis. Journal of International Studies, 11(2), 154-179.
- Andaleeb, S.S., & Conway, C. (2006). Customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry: An examination of the transaction?specific model. Journal of Services Marketing, 20(1), 3-11.
- Bichler, B.F., Pikkemaat, B., & Peters, M. (2020). Exploring the role of service quality, atmosphere and food for revisits in restaurants by using an E-Mystery quest approach. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.
- Bowen, J.T., & Chen, S.L. (2001). The relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 13(5), 213-217.
- Carranza, R., Díaz, E., & Martín-Consuegra, D. (2018). The influence of quality on satisfaction and customer loyalty with an importance-performance map analysis: Exploring the mediating role of trust. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 9(3), 380-396.
- Chia-Hsin, C. (2020). The satisfaction study of people with disabilities regarding the restaurant with barrier-free environment in Taiwan tourism area. International Business Research, 13(4), 1-13.
- Dhanasekaran, R., & Anandkumar, R. (2020). Customers revisiting select restaurants in Coimbatore city: An interaction effect. The International Journal of Analytical and Experimental Modal Analysis, 8(1), 2447- 2454.
- Enab, B. (2019). Localization of foreign investments in jordan, syrians are about to become naturalized, Economic Reports. Retrieved from https://english.enabbaladi.net/archives/2019/01/localization-of-foreign-investments-injordan-syrians-are-about-to-become-naturalized/#ixzz6kP4cqd40.
- Fitria, N.A., & Yuliati, E. (2020). Analysis of the effect of employee service on customer satisfaction and WoM intention at casual dining restaurants in Jakarta. The Journal for Technology and Science, 31(1), 91-100.
- Gibson, H. (2005). Towards an understanding of why sport tourists do what they do, sport in society. Sport Tourism: Concepts and Theories, 8(2), 198-217.
- Gujarati, D.N., & Porter, D.C. (2009). Basic econometrics, (5th Edition). McGraw Hill Inc., NY.
- Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E., & Tatham, R.L. (2010). Multivariate data analysis. Prentice Hall, NJ.
- Hu, L.T., & Bentler, P.M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives, structural equation modelling. A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1-55.
- Inkumsah, W.A. (2011). Measuring customer satisfaction in the local Ghanaian restaurant industry. European Journal of Business and Management, 3(2), 153-166.
- Jin, N., Line, N.D., & Merkebu, J. (2016). The impact of brand prestige on trust, perceived risk, satisfaction and loyalty in upscale restaurants. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 25(5), 523-546.
- Jordan Independent Economic Watch (2017). The Syrian refugees in Jordan: Turning challenges into opportunities. Retrieved from
- http:/www.identitycenter.org/sites/default/files/The%20Syrian%20Refugees%20in%20Jordan%20Turning%20Challenges%20into%20 Opportunities.
- Joudeh, J.M.M. (2017a). The impact of service quality dimensions upon customers' satisfaction: An empirical study applied in the Jordanian mobile telecommunication sector. International Review of Management and Business Research, 6(1), 206-220.
- Joudeh, J.M.M. (2017b). The influence of the store internal dimensions on the customer loyalty: A comparative study between sameh mall and Khalid mall. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 9(1), 139-149.
- Keshavarz, Y., Jamshidi, D., & Bakhtazma, F. (2016). The influence of service quality on restaurants' customer loyalty. Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review (Oman Chapter), 6(4), 1-16.
- Kiatkawsin, K., & Sutherland, I. (2020). Examining luxury restaurant dining experience towards sustainable reputation of the Michelin restaurant guide. Sustainability, 12(5), 21-34.
- Kim, H.S., & Shim, J.H. (2019). The effects of quality factors on customer satisfaction, trust and behavioral intention in chicken restaurants. International Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business, 10(4), 43-56.
- Lisnawati, L., & Astawa, I.P. (2020). Service quality analysis of Chinese restaurant at the mulia, mulia resort and mulia villas. Journal of Applied Sciences in Travel and Hospitality, 3(1), 22-29.
- MacCallum, R.C., Browne, M.W., & Sugawara, H.M. (1996). Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structure modelling. Psychological Methods, 1(2), 130-149.
- Mahin, M.A., & Adeinat, I.M. (2020). Factors driving customer satisfaction at shopping mall food courts. International Business Research, 13(3), 1-27.
- Miles, J., & Shevlin, M. (1998). Effects of sample size, model specification and factor loadings on the GFI in confirmatory factor analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 25(1), 85-90.
- MOPIC, (2020). Jordan Response Plan for the Syria Crisis 2020-2022. Amman, Jordan, the Ministry of Planning and International Cooperation. Retrieved from http://www.jrp.gov.jo/Files/JRP%202020-2022%20web.pdf.
- Morano, R.S., Barrichello, A., Jacomossi, R.R., & D’Acosta-Rivera, J.R. (2018). Street food: Factors influencing perception of product quality. RAUSP Management Journal, 53(4), 535-554.
- Njelita, C.I., & Anyasor, O.M. (2020). Customer loyalty and patronage of quick service restaurant in Nigeria. British Journal of Marketing Studies, 8(2), 54-76.
- Özdemir-Güzel, S., & BA?, Y.N. (2020). Understanding the relationship between physical environment, price perception, customer satisfaction and loyalty in restaurants. Journal of Tourism and Gastronomy Studies, 8(2), 762-776.
- Rafdinal, W., & Suhartanto, D. (2020). Loyalty model for ethnic restaurants: The role of quality and value. International Journal of Applied Business Research, 2(2), 123-138.
- Rahman, M.A., Kalam, A., Rahman, M.M., & Abdullah, M. (2012). The influence of service quality and price on customer satisfaction: An empirical study on restaurant services in khulna division. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting, 3(4), 8-15.
- Shin, Y.H., & Yu, L. (2020). The influence of quality of physical environment, food and service on customer trust, customer satisfaction, loyalty and moderating effect of gender: An empirical study on foreigners in South Korean restaurant. International Journal of Advanced Culture Technology, 8(3), 172-185.
- Tabachnick, B.G., & Fidell, L.S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics, (5th Edition). New York: Allyn and Bacon.
- Tama, B.A. (2015). Data mining for predicting customer satisfaction in fast-food restaurant. Journal of Theoretical & Applied Information Technology, 75(1), 18-24.
- Thielemann, V.M., Ottenbacher, M.C., & Harrington, R.J. (2018). Antecedents and consequences of perceived customer value in the restaurant industry: A preliminary test of a holistic model. International Hospitality Review, 32(1), 26-45.
- Tripathi, G. (2017). Customer satisfaction and word of mouth intentions: Testing the mediating effect of customer loyalty. Journal of Services Research, 17(2), 1-16.
- Tsai, S.C., Chen, Y.J., & Wang, J.H. (2020). The moderating effect of over-service on customer value: The case of the restaurant industry in Taiwan. Journal of Economics, Business and Management, 8(3), 230-234.
- Uddin, M.B. (2019). Customer loyalty in the fast food restaurants of Bangladesh. British Food Journal, 121(11), 2791-2808.
- Zeithaml, V.A., Berry, L.L., & Parasuraman, A. (1996). The behavioral consequences of service quality. Journal of Marketing, 60(2), 31-46.
- Zhong, Y., & Moon, H.C. (2020). What drives customer satisfaction, loyalty, and happiness in fast-food restaurants in China? Perceived price, service quality, food quality, physical environment quality and the moderating role of gender. Foods, 9(4), 460.