Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
E-Government Application Management in Riau Province of Indonesia
Karmila Sari, University of Brawijaya Malang Indonesia
Bambang Supriyono, University of Brawijaya Malang Indonesia
Andy Fefta Wijaya, University of Brawijaya Malang Indonesia
Abdullah Said, University of Brawijaya Malang Indonesia
Abstract
This research aims to; explain, describe & analyse e-government management in Riau Province, Indonesia. E-government management requires Maturity to prioritize the stages of online existence, interaction, transactions, fully integrated and changing e-government, and the application of digital democracy. Thus, this collaboration is a necessity for managing maturity e-government. E-Government is currently still at the development stage, not yet at the evaluation/assessment evaluation/assessment stage of e-government itself. This research uses qualitative methods and uses a logistic model with a program, equipped with the calculation of the governance index processed by the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method. The results show that the application of accountability, professionalism, and e-government harms reducing the probability of corruption, while decentralization increases the probability of corruption occurring. Meanwhile, fairness, transparency, and responsiveness have not been able to affect play a role in reducing the level of corruption. Besides, the research provides additional results that the implementation of comprehensive governance can be able to reduce the level of corruption so that efforts to create a Clean and Good Government in the Riau Provincial Government can be realized properly. In properly.
Keyword
E-government, Management, Corruption, Clean & Good Government
Introduction
Governance is the process by which communities make important decisions, determine who is involved, and how they relate to each other. Governance is not only about how a government and social organizations interact with each other, but also how they relate to society (Graham et al., 2003), how far the state can serve citizens and other actors, and how public functions are carried out, how regulators manage public resources, and how the government is run.
Mimicopoulos (2006) identifies three dimensions of governance, namely, efficiency, transparency, and participation. The efficiency is also a question of properly prioritizing government services for the needs of citizens (Afonso et al., 2010). "Who is accountable to whom and for what" is at the heart of all accountability concepts (Scott, 2000). Information and Communication Technology (ICT) can involve more people to achieve deeper penetration (Trucano et al., 2007). Sachdeva (2002) concluded that Information and Communication Technology (ICT) have valuable potential to help fulfill good governance. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has proven to be a powerful means of disseminating information in times of political uncertainty (Kyj, 2006). More importantly, shown in Figure 1.
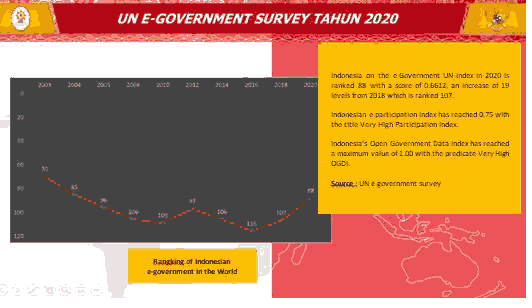
The United Nations (UN) e-Government Survey 2020 has placed Indonesia in the 88th place for the development and implementation of e-government or an electronic-based government system (SPBE). The results for 2020, released in July, show an increase of 19 rankings compared to 2018, which was in 107th place and 116th in 2016.
Overall, Indonesia scored a score of 0.6612 in the High e-Government Development Index (EGDI) group in the 2020 UN e-Government Survey so that it succeeded in placing Indonesia in the top 100 world rankings in position 88 of 193 countries. The United Nations (UN) predicts countries that get more than 0.75 points as Very High EGDI, for points 0.50 to 0.75 as High EGDI, points 0.25 to 0.50 as Middle EGDI, and less than 0.25 as Low EGDI.
Meanwhile, in their own country, Ranking e-government Indonesia (PeGI), from the results of research conducted on e-government travel in Riau Province, according to (Gafar, 2018) that:
"There have been fluctuations of ups and downs in the performance of e-government for more than a decade, but in general the symptoms that can be seen based on facts and data are still beyond expectations due to some obstacles and obstacles, even though some progress has been made."
The Provincial Government of Riau began developing e-government since Rusli Zainal's administration, marked by the launch of the Riau Provincial Government's official website https: //www.riau.go.id/home/ and Electronic Procurement Services. During Arsyad Juliandi Rahman's time as governor after Annas Maamun, a soft launch-government was conducted, which marked the joining of all Regional Apparatus Organizations in one domain, namely, Riau.go.id which was managed by the Riau Province Communication, Informatics and Statistics (DCIS) Office (Gafar, 2018).
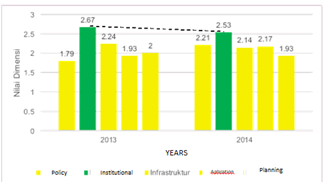
To support the smooth running of e-government, The Riau Provincial Government has issued Regional Regulation Number 6 of 2015 concerning Information Technology-Based Government Systems & Openness and Governor Regulation (Governor regulation) Number 11 of 2018 concerning the Implementation of Electronic Government (e-government) in the Riau Provincial Government Environment. However, in practice, the implementation of e-government in the Riau Provincial Government is not encouraging. This can be seen from several sides, namely, the size of the budget does not reflect the seriousness of the Riau Provincial Government in implementing e-government. The results of interviews with researchers with the Head of the Riau Province Communication, Informatics, and Statistics (DCIS) Office, (Yg *), until now, the amount of the budget earmarked for the implementation of e-government in the Riau Provincial Government are inadequate. So that the database integration conducted by the Riau Province Communication, Informatics and Statistics Office (DCIS) is only in the e-attitude application. However, e-attitude is only specific to CIVIL APPARATUS (State Civil Apparatus) within the Riau Provincial Government. E-attitude is e-government for the type of government to government, which means that it can only be accessed by CIVIL APPARATUS within the Riau Provincial Government. Meanwhile, e-government, whose database is integrated with the type of government access to society, does not yet exist. This means that it is only accessed by State Civil Apparatus within the Riau Provincial Government. Meanwhile, e-government, whose database is integrated with the types of government access to the community, does not yet exist. Meanwhile, which means it can only be accessed by State Civil Apparatus within the Riau Provincial Government. e-government, whose database is integrated with the types of government access to the community, does not yet exist. According to the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Office (DCIS) 2019, evaluating applications of e-government and measurement to see to what extent the success rate of implementing e-government in the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Office (DCIS) has never been conducted. Meanwhile (Gafar, 2018), who researched e-government travel in Riau Province found that when viewed based on the 5 (five) dimensions of PeGI, namely, policies, institutions, infrastructure, applications, and planning. Only the institutional dimension is in the "good" category (green), although there was a slight negative trend or a decline of several points in 2014, it was still in the "good" category, while the rest was still in the "less" category. This means it is urgent to immediately do the treatment (repair) on the other 4 dimensions (Figure 2),
From the beginning, policy implementation e-government Generally, Riau Province has been entrusted to the Department of Communication and Information and Statistics (DCIS) as the leading sector through a roadmap prepared by the Regional Planning and Development Agency (RPDA), where regional planning is under the national e-government objectives, namely 1) improving the quality of public services; (2) efficiency and effectiveness of government organizations; and (3) accelerating bureaucratic reform. In the roadmap or work agenda on much reliable local governance, it can be seen that the direction of e-government development has been indicated systematically where e-government is used as an instrument or tool in conducting activities in the area of governance related to systems, processes, and procedures, clear, effective work,
When aligned with the main duties and functions of the Office of Communication and Information, Statistics (DCIS) as the leading sector, which refers to the Riau Province Mid-Term Development Plan 2014–2019, the vision of the Department of Communication and Informatics Statistics (DCIS) is "Realizing reliable and competitive communication and informatics services." Based on this vision, of course, it is also hoped that the implementation of e-government in the Riau Provincial Government in the future can improve interoperability between work units and can improve e-government clusters not only at the level of publication and interaction but also at the level of transactions through the webpage agencies/Regional Apparatus Organizations, so that the distribution of information to the people of Riau is also expected to progress further to increase participation and public services, exercise social control,
In the process of implementation, e-government involves the government and community where there is a need for smooth communication between the existing Agencies/Services/Institutions and encouraging wider community participation. The rapid flow of public aspirations be responded to quickly and effectively because the public expects public services that are integrated and unblocked by communication boundaries and bureaucratic authority. The Riau Provincial Government is implementing the e-government transformation process by using electronic media-based information technology to improve the quality of public services effectively and efficiently. The establishment of information networks and public service transactions that have a quality of life that can satisfy people in all regions of Riau Province.
That is a form of bureaucratic transformation motivated by demands for a government system that is transparent, clean, and able to respond to demands for change more effectively. With this service system, the public can access information 7 days a week, 24 h a day, without having to wait for an office to open. The efforts and hard work conducted by the Riau Provincial Government have paid off, the Minister of State Apparatus Empowerment and Bureaucratic Reform (Asman Annur during a visit to Riau appreciated the Provincial Government's Information and Communication Technology (ICT) services. Riau, which has set the riau.co.id domain. Ministry of Administrative Reform also recommends that the riau.go.id domain be applied to all districts/cities in Riau so that the service system is no longer complicated, with this ICT, the community can take care of permits, where officers no longer meet leaders, but leaders function as decision-makers and control the running of services. If there is a complaint, the public can use the facilities in the application in the system.
Through Government Service Bus, namely: e-Finance, e-Personnel, e-Monev, e-LPSE, e-ULP, SDDKD, e-Health Profile, e-Simple, and e-Planning. In the public satisfaction index (customer satisfaction) in Riau Province, namely: 1). Regional Regulation Policy Number 6 of 2015 and Governor Regulation Number 11 of 2018 are the legal umbrella for developing e-government. So that e-government activity is not hampered by budget allocations, 2) Leadership The leadership factor is the most important thing in the implementation of e-government. The people of Riau are grateful for having a Governor who is committed to e-government development. Service/agency leaders also have the same enthusiasm as their superiors, so that they want to learn to use information technology and care about its development, 3). Institutions To accelerate e-government development require good institutions that have a vital position in development. So far, the unit related to e-government in the regions has been managed by one agency, namely, DCIS, 4). Infrastructure The availability of infrastructure, both hardware, software, and access, is another main thing in the implementation of e-government. Building roads or buildings is expensive. It is said to be relative, because IT (Information Technology) is not really like building roads or buildings, 5). Human Resources All the sophistication of information technology is also supported by the quality of Human Resources (HR) in government. Don't expect much if the Human Resources (HR) ability cannot keep up with fast-running IT developments.
The basis for the implementation of the preparation of the Development master plan E-government Riau Province is 1). Law No. 14 the Year 2008 dated April 30, 2008, concerning Freedom of Information; 2) Ministry of Home Affairs Number 70 of 2019 concerning SPID (Regional Government Information System); 3). Presidential Instruction No. 3 of 2003, dated June 9, 2003, concerning the National Policy and Strategy for E-Government Development; 4). Regional Regulation Number 6 of 2015 concerning Information Technology-Based Government Systems and Openness; 5). Government Regulation of the Republic of Indonesia Number 82 of 2012 concerning Implementation of Electronic Systems and Transactions; 6) Riau Province Information and Communication Technology Master Plan.
Generally, the purposes and objectives of the preparation plan Parent Riau Province e-government development are to 1). Arrange the implementation system of government administration and development; 2) Streamlining information between institutions; 3). Preparation to face the transformation from the era of industrial society to the era of the information society; 4). The establishment of a government that is clean, transparent, and able to respond to the demands of change effectively; 5). Build a new dimension in the government bureaucracy system; 6) Increasing the quality of public services effectively and efficiently; 7). The establishment of information networks and public service transactions; 8). Establishing interactive relationships with the business world; 9) Establishment of communication mechanisms and channels between institutions; 10) Establishment of a management system and work processes that are transparent and effective.
After the budget was provided in 2018 at the Statistics Communication and Informatics Office (DCIS), the current condition of e-government within the Riau Provincial Government is as follows: 1). Several information systems have been built in several work units/agencies by applying various technologies and operating system platforms, 2). An external information system has been built in the form of a website with a URL http://www.riau.go.id. This site has been developed so that each unit has its subdomain which can be managed independently, 3). Several work units have been held in training for operators and users in general, especially the Riau Province Electronic Data Processing Agency.
However, in practice, the application of e-government in Riau is not satisfying. As far as the author can observe, when opening the e-government page belonging to the Riau Provincial Government, only local news related to the activities of the Riau Provincial Government are easy to obtain. However, find certain data about the government, still tends to be difficult to access, and it is not updated regularly. Meanwhile, the problems still being faced are 1). The absence of an integrated and comprehensive Governance and Development Management Information System across sectors; 2). The operating system platform has not been based on Open Source software to support the IGOS (Indonesia Go Open Source) program planned by the Government of the Republic of Indonesia so that complaints often arise about the lack of performance of information systems; 3). From the empirical facts on the object of research that the author observes, there is still a lack of transparency in government administration due to poor implementation of e-government thus resulting in many acts of corruption. To actualize this idea, the writer developed it into a systematic scientific writing concept, entitled Management of e-government in Riau Province, Indonesia.
Formulas Problem; Management of e-government in Riau Province, Indonesia. Research purposes; Explain, describe and analyze e-government management in Riau Province, Indonesia. Benefits of research; theoretically the benefits. E-government management with a maturity model and a Penta Helix perspective involves stakeholders who work together to prevent corruption. Each of these stakeholders affects each other so that future research is to become five related stakeholders or corruption prevention research using other perspectives. Also, practical benefits; Contributing to the Riau Government in developing a more mature e-government by involving 5 stakeholders (Penta helix) in efforts to prevent corruption so that progress and prosperity in Riau Province are more evenly distributed.
Research Methods
Types of research; The research method is used as a formula for managing e-government. E-government in the perspective of Penta Helix in the Riau Provincial Government qualitatively. The focus of this research is 1). Data system infrastructure, 2). Legal infrastructure, 3). Infrastructure, 4). Institutional, 5). Human infrastructure, 6). Technology infrastructure, 7). Leadership, and 8). Strategic thinking. Location; This research was conducted in the Riau Provincial Government of the Republic of Indonesia Data collection techniques; 1). Interview, 2). Documentation. Sources of Informant Data from the Riau Provincial Government Office; 1). (Kh*) (Head of DCIS), 2). (Nrl*) (DCIS-Field of Application and Informatics), 3). Jdi (DCIS-Infrastructure Network Section), 4). (Fr*) (DCIS-Senior Programmer), 5). (Yg*) (DCIS-Former Head of DCIS (2017–2019)), 6). (USA*) (Bureau of Procurement of Goods and Services, 7). Plot (Bureau of Goods and Services Procurement, Regional Secretariat of Riau Province), 8). (MR*) (Bureau of Goods and Services Procurement - Head of Goods and Services Procurement) Sources of interview data from informants include a) Riau Provincial Government Service, b) Private, c) Community, d) Academics, and e) Media.
Data analysis
Data Validity
According to (Lincoln & Guba, 1985), the data validity test in qualitative research includes credibility (internal validity), transferability (external validity), dependability (reliability), & confirmability (objectivity) tests.
Results & Discussion
Result
The result for this study and discussion has performed by researchers when researching E-Government Management in Corruption Prevention Efforts in the Perspective of Penta Helix. The explanation given is a description of the existing problem formulations.
The database is a collection of information stored in a computer system so that it can be checked using a computer program to obtain information from the database. The software used to manage and call database queries is called a Database Management System (DBMS). Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that;
"Each Regional Apparatus Organization is responsible for updating the information on the riau.go.id website according to the application per Regional Apparatus Organization. For example, The Electronic Procurement Service System application is updated by the staff of the Goods and Services Procurement Bureau. Parties who need LPSE (Electronic Procurement Agency) information are helped by a bundled application on the riau.go.id website. However, the awareness of OPD in updating data is not maximal and there is no consequence for OPD if the data have not been updated. DCIS can only be a reminder. "(Result of the interview on March 20, 2020, in Riau Province at 11.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Furthermore, Mr (Yg*) as the Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that
“The public uses the reporting service on the riau.go.id website for complaints about infrastructure needs, commodity prices in the market, and other things. If they need more complete and detailed data, the officer suggests opening the riau.go.id website or coming directly to the relevant office. Ministry of Administrative and Bureaucratic Reform of the Republic Indonesia takes measurements of Electronic Based Government System to see what integrated services are in the Regional Apparatus Organization. This SPBE is conducted once a year. In 2020, the procurement of bandwidth worth Rp. 4.1 billion and distributed to all Regional Apparatus Organizations and tailored to their respective needs. (Result of the interview on March 20, 2020, in Riau Province at 11.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Based on the results of the interview above, it can be concluded that the application on the website of the Riau Provincial Government and Regional Apparatus Organizations within the Riau Provincial Government has begun to be optimized properly. Some of the problems are that information or data is not frequently updated. The Riau Provincial Government has limited valid and complete information and data for publication.
Legal Infrastructure
There, the policy changes in e-government management as measured by the PeGI (Indonesian e-Government Ranking), which has since changed to SPBE (Electronic Based Government System). PeGI assessment with a high score for the Riau Province Communication, Informatics, & Statistics (DCIS) Office is because it has been supported by Local regulation, Governor regulation, and Circular and has begun integrating applications between OPDs on the riau.go.id website. So that it can be seen here, the amount of concern of the Regional Heads in managing e-government in Riau Province. Even when PeGI changed to SPBE, Riau Province was still in the top 5 rankings.
Mr. (Yg) as Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that
"Within the Riau Provincial Government, there are some people who are not experts in their fields, including in this field of IT, they are still not right in the passion of this State Civil Service employees. Plus other problems besides competence, such as commitment, employee laziness, indecisive law, environment, and so on. (Result of the interview on March 26, 2020, in Riau Province at 12.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Based on the above interview results, it can be concluded that the legal basis within the Riau Provincial Government exists and is complete, both nationally and regionally. The obstacle in the legal infrastructure for implementing e-government is that there is no sanction if the Regional Apparatus Organization does not update data and does not budget consistently and continuously for technology and networks that are qualified in e-government management
Institutional Infrastructure
The rules of the game, ethics, and code of ethics between Regional Apparatus Organizations in integrating into good e-government management will coordinate and work together so that institutional infrastructure will make it easier to achieve the goals of good e-government management. Mr. (YG) as Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that
"The KPK does not agree if the Central, Provincial, and Regency/Municipalities have applications that are held repeatedly for the same thing. It is better if the application is submitted to the Regional Apparatus Organization Province, Regency/City because they have a more work process flows so that there is no waste of funds for the use of the same thing but can be integrated into the Central Government."
(Result of the interview on March 20, 2020, in Riau Province at 11.00 Western Indonesian Time). Furthermore, Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that
"Political Obstacles So, the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) are more dominant in managing e-government. Public relations should have been combined in the Riau Province Communication & Informatics Office (DCIS), but in reality, it is still under the Adpim bureau (Leadership Administration). Meanwhile, in the perception of the Governor, public relations have joined the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) even though Main Duties and Functions Decree is still listed in the admin. So the governor blames the Riau Province DCIS if the main duties and functions are negligent of public relations. "(Result of the interview on March 23, 2020, in Riau Province at 10:00 Western Indonesian Time).
The availability of data and information owned by institutions/government will greatly assist the policy-making process that concerns common interests. Policymaking that is supported by data will have a major effect on the implementation pattern in the field. Based on the results of the interview above, it can be concluded that the institutional infrastructure within the Riau Provincial Government is good enough, but there are technical obstacles such as a lack of good coordination between employees and between Regional Apparatus Organizations so that it has not achieved the goal of integrating e-government management Expected.
Human Infrastructure
The Riau Provincial Government should prepare various means in e-government development such as human resources, information technology facilities, and infrastructure and initiatives and responsibilities of parties directly involved so that the initiation to create good governance and quality service can be realized properly, is not it? The implementation that seems to be demanded by the policy of Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that.
"These parties can check the specifications of the project/item being auctioned when the auction will occur when the end is due to implementation and other related information. DCIS familiarizes Regional Apparatus Organizations to conduct computerized activities and minimize manual activities so that services between Regional Apparatus Organizations can be integrated, recorded, and provide convenience in working anywhere. "(Result of the interview on March 20, 2020, in Riau Province at 11.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Furthermore, Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) explained that "In March 2020, there was a change in the Head of Service at the Riau Discotheque Service. The e-office was not implemented, which means manual rework. If this condition continues, how can DCIS integrate with other OPDs, it is feared that the SPBE assessment will decline? office affects the TPP (Employee Income Allowance). E-office contains attendance and daily agenda, if the employee's daily agenda is not filled in, the TPP will be deducted. There is a waste of paper and the length of administrative processing procedures.
Based on the above interview results, it can be concluded that human infrastructure is the most important means of implementing and managing e-government in the Riau Provincial Government. Each Regional Apparatus Organization has its respective duties, principal, and functions, but there are still obstacles in the coordination and implementation of their respective duties. Even in several activities and application management, few Human Resources (HR) within the Riau Provincial Government have competencies related to the IT field.
Technology Infrastructure
The development of e-government is still limited to publishing information through the website, the interaction between the public and government offices via e-mail, and the user community can make reciprocal transactions with government offices. The Riau Provincial Government has not yet reached the level of integration in all government offices, where the public can make transactions with all government offices that have the use of a database. The lack of improvement in the use of technology and network tools can support the proper management of the operation e-government.
Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Communication and Informatics Statistics (DCIS) Office of Riau Province explained that
“The public uses the REPORT service on the riau.go.id website for complaints about infrastructure needs, commodity prices in the market, and other things. If they need more complete and detailed data, the agency recommends opening the riau.go.id website or coming directly to the relevant agency. Every application that is always updated, be it version 1, version 2, and so on, is evidence that must be prepared in SPBE assessment. Application development is conducted continuously according to the needs of Regional Apparatus Organizations. "(Result of interview on March 20, 2020, in Riau Province at 11.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Furthermore, Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Communication and Informatics Statistics (DCIS) Office of Riau Province explained that
"The financial constraints of the Regional House of Representatives (DPRD) passed the Regional Regulation in 2015 and the Governor Regulation issued in 2018, but in 2017 it has been budgeted in the Regional Revenue and Expenditure Budget (APBD) for the use of e-government through the Head of the Office of Communication and Statistical Information. (DCIS) Riau Province. During the reign of Arsyad juliandi Rachman, known as the slogan Go IT where the government supported the management of e-government, the first launch was attended by the Ministry of Administrative and Bureaucratic Reform as response 3 hamrick governors were arrested by the Corruption Eradication Commission. In Pak Andi's era, approximately 30 billion were budgeted for e-government, thus using the procurement of 250 computer units scattered throughout the Regional Apparatus Organization as support for e-government management. However, unfortunately, the procurement in this amount is an obstacle for the Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) to procure other computerized equipment because the BPKAD (Regional Financial and Asset Management Agency) consider it an expense for one Head of the Office of Communication and Statistical Informatics (DCIS). Riau Province, while in realization computers were spread throughout the Regional Apparatus Organizations. In 2019, only Rp. 1 billion for procuring bandwidth for all Regional Apparatus Organizations. Finally, the Regional Apparatus Organization fulfills the bandwidth needs by procuring internet using indiehome and the Regional Equipment Organization helps connect the indiehome internet to the UPT of the existing Regional Apparatus Organization. So that it is integrated. Meanwhile, for data security over commercial networks, it is not too secure. The chat can be intercepted by hackers or it can be sent to a popup of inappropriate photos. "(Result of interview on March 23, 2020, in Riau Province at 10.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Mr. (Hs*) as an employee of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Office (DCIS) explained that "Following the prevailing Presidential Decree, it requires Regional Equipment Organizations to use FO (Fiber Optic) -based intranets to ensure data transmission security because intranets are closed networks. The biggest budget for information and communication technology infrastructure is in the provision of bandwidth." (Result of the interview on March 22, 2020, in Riau Province at 10:00 Western Indonesian Time).
Based on the results of the interview above, it can be concluded that the community uses REPORT services on the riau.go.id website for complaints about infrastructure needs, commodity prices in the market, and other matters. Every application that is always updated, be it version 1, version 2, and so on, is evidence that must be prepared in the SPBE assessment. Application development is conducted continuously according to the needs of Regional Apparatus Organizations and the community.
Leadership
The background of the leader of the Regional Apparatus Organization DCIS (Office of Communication, informatics, and statistics) in the IT field is inconsistent, so there is no consistency and commitment in implementing SOPs for managing good government on an ongoing basis. Mr. (Yg*) as Head of the Communication Office and Statistical Informatics (DCIS) Riau Province argues that "The Riau Province Communication and Information Service (DCIS) familiarizes Regional Apparatus Organizations to carry out computerized activities and minimize manual activities so that services between Regional Apparatus Organizations can be integrated, recorded, and provide convenience in working anywhere. During his leadership period, Mr. Arsyadjuliandi Rahman (2015–2019) paid great attention to the development of e-government management, especially during the active moments of the Korsupgah KPK (Prevention and Supervision Coordination) to promote transparency through e-government management. Besides, at this time also the launch of e-government in Riau was attended by Minister of State Apparatus Empowerment. Application development is carried out continuously by the needs of the Regional Apparatus Organization. (Result of the interview on March 20, 2020, in Riau Province at 10:20 Western Indonesian Time).
Based on the results of the interview above, it can be concluded that the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) has different habits depending on the leadership and leadership every year in running e-government, as well as Regional Apparatus Organizations within the Provincial Government Riau. The Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) familiarize Regional Apparatus Organizations to conduct computerized activities and minimize manual activities so that services between Regional Apparatus Organizations can be integrated, recorded, and provide convenience in working anywhere.
Strategic Thinking
The disposal of DCIS (Department of Communication, informatics, and statistics) is not the main center for information disclosure and ease of communication with the government of Riau Province. Mr. (Yg*) as the Head of the Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) argues that "In implementing E-governance, the government should be serious and sustained to update the data provided to make it more accurate. Because E-government improves the quality of public services by using information and communication technology in the process of organizing local governments so that clean and transparent governance can be formed and to respond to the demands of change effectively." (Result of interview on March 23, 2020, in Riau Province at 12.00 Western Indonesian Time).
Based on the above interview results, it can be concluded that in implementing E-governance, the government must be serious and sustainable in updating the data provided to make it more accurate. Because e-government aims to improve the quality of public services by using information and communication technology in the process of organizing the Riau Provincial Government so that clean and transparent governance can be formed, and respond to the demands of change effectively.
Discussion
Based on the explanation above, both operators and users of the e-government system, both from the government or other Penta helix actors, will benefit. Also, such a technology system minimizes the potential for data manipulation because it is directly published and assessed by all parties. Corruptors are a group of elites who act as controllers, therefore controlling deviant behavior be endeavored to reduce the potential for this behavior. In terms of the amount of corruption that remains. It took a long time to prove wrong, resulting in a small number of interacts. However, the number of each position has fluctuated and decreased.
Data Analysis and Discussion
Management of e-government in developing countries has found several failures, due to (Heeks, 2001), among others: The strategic challenges of e-readiness (e-readiness): preparing six identified pre-conditions for e-governance, namely
Data System Infrastructure
Ectronic Government is the use of information and telecommunications technology for efficient and effective government administration, as well as providing transparent and satisfying public services to the public. Today's integrated technology and information systems affect institutions public such as local government. The regional government system has now begun to be integrated into a technology that can be controlled by the central government. An example is an implementation of electronic-government (e-Gov) that has begun to be implemented in Indonesia. As an illustration, e-government does not need many state administrators (government apparatus), but few but reliable, fulfilling the principles of effectiveness and efficiency in conducting tasks that can create professionalism. There is one of the challenges of the current and future (local) government. Of course, to deal with these changes, ideally from now on efforts have been made to organize the human resources.
Evaluation of the policy dimension is conducted on policies in the real form of official documents that have legal force. This document contains, among other things, the determination and determination of direction/objectives, work programs, procedures, or arrangements for the development and implementation of e-government within the participating agencies. Documents can be in the form of decrees, regulations, guidelines, or other official documents. The allocation of sufficient financing to conduct the development and implementation of ICT properly is one of the aspects evaluated in policy dimensions.
Information and communication technology can be used to support the operational and managerial systems of various institutional activities that include government activities in the provision of public services to the public. Data are an embodiment or record of a fact. which is the result of observing a variable that can be represented in the form of numbers, words, or pictures/images. Initial data are facts that can produce a conclusion in drawing a decision. A database is a collection of data stored in a computer that is systematically arranged and can be checked/retrieved, processed/manipulated using a computer program to retrieve this information. The three main contributions of e-government (Heeks, 2001) improve government processes (e-administration); connecting citizens (e-citizens and electronic services), and building external interactions (e-society). Electronic governance is a reality today, not just the future, for developing countries. However, in many countries, especially developing countries, e-governance initiatives failed.
The database is a critical aspect because it is a data storage/warehouse that can be processed further. The database-processing system started after some time manual processing and file processing. The manual processing system that uses paper is a basic system that stores all records/data on paper and is stored on bookshelves/archives. If the data are needed, it must be searched one by one on the shelf. A file-processing system, where files are stored on a computer, especially in text form. A database is a collection of various information stored on a computer and arranged systematically so that it can be checked using a computer program to obtain information from the database. Information systems require a database as a data storage medium. In an institution, the presence of a database makes it easy for each performance. The software used to process the database is called a database management system. Another benefit provided by a database for an institution is the process of retrieving fast information and easily so that it can provide good service to the community in Riau Province.
Applications on the website of the Riau Provincial Government and Regional Apparatus Organizations within the Riau Provincial Government can be optimized properly. Some of the obstacles are that there is not much information or data being shared to provide information to the public. The Riau Provincial Government has limited valid and complete information and data for publication. Riau Province also has a media center as center for information and facilitating people's needs for information. Through the Media Center, the people of Riau can communicate and exchange information related to various strategic or local issues of public institutions. The purpose of this Media Center is to support the implementation of the Riau Provincial Government's duties, especially in disseminating information for public needs and vice versa, accommodating development information submitted by the public to be disseminated again. The Media Center affects communicating public policies in a fast, precise, accurate, and relevant manner so that they are easy to understand and increase public participation in the exchange of information. Electronic Government is the use of information and telecommunications technology for efficient and effective government administration, as well as providing transparent and satisfying public services to the public. Today's integrated technology and information systems affect institutions public such as local government. The regional government system has now begun to be integrated into a technology that can be controlled by the central government. An example is an implementation of electronic-government (e-Gov) that has begun to be implemented in Indonesia. As an illustration, e-government does not need many state administrators (government apparatus), but few but reliable, fulfilling the principles of effectiveness and efficiency in conducting tasks that can create professionalism. There is one of the challenges of the current and future (local) government. Of course, to deal with these changes, ideally from now on efforts have been made to organize the human resources. Evaluation of the policy dimension is conducted on policies in the real form of official documents that have legal force. This document contains, among other things, the determination and determination of direction/objectives, work programs, procedures, or arrangements for the development and implementation of e-government within the participating agencies. Documents can be in the form of decrees, regulations, guidelines, or other official documents. The allocation of sufficient financing to conduct the development and implementation of ICT properly is one of the aspects evaluated in policy dimensions. Information and communication technology can be used to support the operational and managerial systems of various institutional activities that include government activities in the provision of public services to the public. Data are an embodiment or record of a fact. Which is the result of observing a variable that can be represented in the form of numbers, words, or pictures/images. Initial data are facts that can produce a conclusion in drawing a decision. A database is a collection of data stored in a computer that is systematically arranged and can be checked/retrieved, processed/manipulated using a computer program to retrieve this information. The three main contributions of e-government (Heeks, 2001) improve government processes (e-administration); connecting citizens (e-citizens and electronic services), and building external interactions (e-society). Electronic governance is a reality today, not just the future, for developing countries. However, in many countries, especially developing countries, e-governance initiatives failed. The database is a critical aspect because it is a data storage/warehouse that can be processed further. The database-processing system started after some time manual processing and file processing. The manual processing system that uses paper is a basic system that stores all records/data on paper and is stored on bookshelves/archives. If the data are needed, it must be searched one by one on the shelf. A file-processing system, where files are stored on a computer, especially in text form. A database is a collection of various information stored on a computer and arranged systematically so that it can be checked using a computer program to obtain information from the database. Information systems require a database as a data storage medium. In an institution, the presence of a database makes it easy for each performance. The software used to process the database is called a database management system. Another benefit provided by a database for an institution is the process of retrieving fast information and easily so that it can provide good service to the community in Riau Province.
Applications on the website of the Riau Provincial Government and Regional Apparatus Organizations within the Riau Provincial Government can be optimized properly. Some of the obstacles are that there is not much information or data being shared to provide information to the public. The Riau Provincial Government has limited valid and complete information and data for publication. Riau Province also has a media center as center for information and facilitating people's needs for information. Through the Media Center, the people of Riau can communicate and exchange information related to various strategic or local issues of public institutions. The purpose of this Media Center is to support the implementation of the Riau Provincial Government's duties, especially in disseminating information for public needs and vice versa, accommodating development information submitted by the public to be disseminated again. The Media Center affects communicating public policies in a fast, precise, accurate, and relevant manner so that they are easy to understand and increase public participation in the exchange of information.
Legal Infrastructure
There has been a policy change in the use of e-government. The high PeGI assessment for the Riau Province Communication, Informatics, and Statistics (DCIS) Office is because it has been supported by Local regulation, Governor regulation, and Circular. So that it can be seen here, the amount of concern of the Regional Heads in managing e-government in Riau Province. Law is a rule in the form of a norm made by power or custom that applies to all people to regulate human behavior, maintaining order, justice, peace, preventing chaos, and imposing sanctions for people who violate the law.
In anticipation of the failure of e-Government applications, it is interesting to remember what was said by (Heeks et al., 2003) that most of the failures of e-Government applications in developing countries are due to a lack of understanding of the “current state” (where we are now) with “what we will achieve with e-government projects” (where the e-government project wants to get us). In other words, what is often the case is the broad response between current realities and existing e-Government designs to change things. These gaps exist in various dimensions, which Heeks summarize as ITPOSMO (Information, Technology, Processes, Objectives and Values, Staffing and skills, Management systems & structures, Other resources: time and money).
E-government is an internet-based information technology application and other digital tools that are managed by the government for delivering information from the government to the public, business partners, employees, business entities, and other institutions online. The legal basis within the Riau Provincial Government exists and is complete, both nationally and regionally. The obstacle in the legal infrastructure for implementing e-government is that law enforcers are less firm in implementing e-government in Riau Province.
Institutional Infrastructure
E-government improves the quality of public services by using information and communication technology in the process of organizing local governments so that clean and transparent governance can be formed and to respond to the demands of change effectively. Apart from that, e-government also supports good governance. The use of technology that makes it easier for the public to access information can reduce corruption by increasing the transparency and accountability of public institutions. E-government can expand public participation in the community possible to be actively involved in decision/policy making by the government.
The institutional dimension is closely related to the existence of an organization that has the authority and responsibility for the development and use of ICT. Evaluation of the Institutional Dimension is conducted on, among others: (1) The existence of a complete structural organization so that it can conduct the functions of ICT governance, development, operation, provision of ICT services and other functions properly, (2) The existence of documents that provides clear formulations regarding duties and functions, (3) There are a complete work unit and its apparatus to support the usage and development of adequate ICT in terms of number, competence, career path, and employment status; (4) There is sufficient authority so that the institution can conduct its duties and functions properly, including the control and supervision functions of the development and implementation of ICT in participating agencies.
The use of technology and information media by local governments will be able to maximize its public services to the community. With this one-door licensing, the positive impact it will cause is the efficiency and effectiveness of the performance of bureaucrats. The advancement of information technology today requires the public to be more advanced and aware. the need for information technology. Information technology can make it easier for the public to access all desired information. The institutional infrastructure within the Riau Provincial Government is good enough, but there are technical obstacles such as a lack of good coordination between employees and between Regional Apparatus Organizations.
Human Infrastructure
One of the promising solutions and alternatives for creating transparency in realizing Good Governance is an electronic government management system or electronic government (e-government). Electronic management of institutions/agencies for both the private sector and government in addition to increasing transparency can also increase efficiency (reduce costs and increase effectiveness/increase yield power).
Human infrastructure is the most important means of implementing and managing e-government in the Riau Provincial Government. Each Regional Apparatus Organization has its respective duties, principal, and functions, but sometimes there are still obstacles in the coordination and implementation of their respective duties. Even in several activities and application management, few Human Resources (HR) within the Riau Provincial Government have competencies related to the IT field.
Technology Infrastructure
There is an increasing drawback in the use of network technologies and devices that can support the proper functioning of e-government management. The development of e-government in the Riau Provincial Government is still in process. This means that e-government development can be said to be successful or otherwise failed in the future. The Riau Provincial Government must prepare various ways in e-government development such as human resources, information technology facilities, and infrastructure as well as the initiatives and responsibilities of the parties directly involved so that the initiation to create good governance and quality services can be realized properly, not a proper implementation. Impressed being demanded by the policy of the Riau Provincial Government.
The public uses "REPORT service" e on the riau.go.id website for complaints about infrastructure needs, commodity prices in the market, and other matters. Every application is always updated, be it version 1, version 2, and so on, is evidence that is prepared in the SPBE assessment. Application development is carried out continuously by the needs of the Regional Apparatus Organization (1).
Leadership
The background of the leader of the Regional Apparatus Organization DCIS (Department of Communication, informatics, & statistics Office) in the IT field is inconsistent, so there is no consistency and commitment in implementing SOPs for managing good government on an ongoing basis. E-government is an internet-based information technology application. Besides, other digital tools are managed by the government for conveying information from the government to the public, business partners, employees, business entities, and other institutions online. E-government improves the quality of public services by using information and communication technology in the process of organizing local governments so that clean and transparent governance can be formed and to respond to the demands of change effectively.
One of the promising solutions and alternatives to create transparency in realizing good governance is an electronic government management system or electronic government (e-government). The demands of the government in providing data information by using technology information currently available, the government have tried to make it happen to create an effective and efficient government. In its use, the government has used several applications in implementing government processes in managing data within agencies and in managing the State Civil Apparatus.
The Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) has different habits depending on leadership and leadership every year in running e-government, as well as the Regional Apparatus Organization within the Riau Provincial Government. The Riau Province Communication and Informatics Agency (DCIS) familiarize Regional Apparatus Organizations to conduct computerized activities and minimize manual activities so that services between Regional Apparatus Organizations can be integrated, recorded, and provide convenience in working anywhere.
Strategic Thinking
The placement of the DCIS (Department of Communication, informatics, & statistics) is not the main center for information disclosure & the ease with which people communicate with the government of Riau Province information is that people who get the opportunity and access to information quickly and precisely will be far more advanced than those who lack information knowledge. The main mission of the information society is to create a society that is aware of the importance of information, science, and technology, the creation of an integrated, coordinated, and documented information service, and the dissemination of information to the wider community in a fast, precise and useful manner.
The information society is characterized by information behavior, which is human behavior as a whole associated with information sources and channels, with specific goals as a result of the need to fulfill certain objectives, information-seeking behavior aimed at someone when interacting with information systems, and information user behavior, namely, behavior. What a person does when combining the information he finds with the basic knowledge he has.
The dynamics of information bring changes to society. Information is an important part of human life. People who get the first opportunity, wider and more timely access will be able to manage and control the world. While community groups are not or less obtaining the opportunity and access to the information needed adequately will be far behind.
In implementing E-governance, the government must be more serious and the government must continue to update the data provided to make it more accurate. Because e-government aims to improve the quality of public services by using information and communication technology in the process of organizing the Riau Provincial Government so that clean and transparent governance can be formed and to respond to the demands of change effectively.
The challenge of eliminating the design-reality gap: adopting best practices in e-government projects to avoid failure to achieve success. It is necessary to look at differences in reality and perceptions and determine gaps in perceptions. The government that has issued regulations regarding e-government has implemented it within the Riau Provincial Government. It was explained that the e-government of the Riau Province Government was grouped into two, namely in terms of regional financial management and e-government for community services. The implementation of E-Government for this Service is one part of the implementation of e-government in local governments. The use of technology and information media by local governments will be able to maximize its public services to the community.
Conclusion
Management e-government In the Riau Provincial Government, the benefits have not been maximized in terms of budget efficiency and ease of service on the website portal riau.go.id although in a survey the administrative ranking of PeGI (Indonesian E-Government Ranking) and SPBE (Electronic-Based Government System) are among the top 5 in Indonesia. With the management of the riau.go.id website to manage e-government by the Department of Communication, Information, and Statistics (DCIS) Riau Province, it provides several services in the form of the REPORT application (for criticism and suggestions from the public), government information both licensing and the Revenue and Expenditure Budget. Regional Revenue and Expenditure Budget, auctions, and others. However, it is tracked for an update and the follow-up response is still in the slow category.
Suggestion
The Department of Communication, Informatics, and Statistics (DCIS) Riau Province has not yet maximized its function as the leading sector in e-government management. Such as providing recommendations to Regional Apparatus Organizations for what equipment and applications are needed by other Regional Apparatus Organizations in improving the performance of Regional Apparatus Organizations (Kanwil), thus making it easier for the Development Planning Agency at the Sub-National Level to budget for these needs so that there is sustainability in e- management. The government in creating GCG (Good Corporate Government) towards a smart city. The Department of Communication, Informatics, and Statistics (DCIS) Riau Province has not yet maximized its function as the leading sector in e-government management. Such as providing recommendations to Regional Apparatus Organizations for what equipment and applications are required by other Regional Apparatus Organizations in improving the performance of the Regional Apparatus Organizations so that it makes it easier for Development planning agency at the sub-national level in budgeting these needs so that sustainability occurs in e-government management. In creating GCG toward a smart city; a). The Riau Province Communication, Informatics, and Statistics (DCIS) Office has not used the opportunity to partner with the private sector, media, society/NGOs, and academics in disseminating information and improving e-government management, b) The need for dominance with a background in IT dominates for state civil apparatus in the Communication Office,
Suggestions for Regional Apparatus Organizations in the Riau Provincial Government
Initiating amendments to Local regulation No. 6 of 2015 on information technology systems based on technology and openness, which is revised: there are sanctions if the Regional Apparatus Organization does not update the latest information or data that should be published and the head of the service does not apply the SOP for e-government management in the form of a written warning or administrative sanction in the form of employee transfer or budget reduction at the said Regional Apparatus Organization or by the prevailing laws and regulations. Because the sanctions are not imposed, the responsibility of employees is much less to conduct SOPs in e-government management.
Advice for Academics
There are opportunities to work with the Government and academia in improving e-government management whether it is in the form of research that produces the service applications needed, or helps evaluate the service applications that are currently available, and other matters.
Collaboration with the private sector is needed in improving e-government management either in the form of funds for research or procurement of IT equipment and networks.
References
- Afonso, A., Schuknecht, L., & Tanzi, V. (2010). Public sector efficiency: Evidence for new {EU} member states & emerging markets. Applied Economics, 42(17), 2147–2164.
- Abbasi, S.G., Shabbir, M.S., Abbas, M., & Tahir, M.S. (2020). HPWS and knowledge sharing behavior: The role of psychological empowerment & organizational identification in public sector banks. Journal of Public Affairs.
- Al-Kumaim, N.H., Hassan, S.H., Shabbir, M.S., Almazroi, A.A., & Abu Al-Rejal, H.M. (2021). Exploring the inescapable suffering among postgraduate researchers: Information overload perceptions and implications for future research. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education, 17(1), 19-41.
- Arshad, M.A., Shabbir, M.S., Mahmood, A., Khan, S., & Sulaiman, M.A. (2020). An exploration of IQ, EQ, Spiritual Quotient (SQ) elements in the Human Reengineering Program (HRP) practices: A study on the drug rehabilitation Centre in Malaysia. Journal of Human Sport & Exercise, Winter Conferences of Sports Science.
- Gafar, T.F. (2018). Diorama of E-government journey in Riau province: Reflections and expectations on several study results. Journal of Government Dynamics, 1(1), 50–73.
- Graham, J., Plumptre, T.W., & Amos, B. (2003). Principles for good governance in the 21st century.
- Heeks, R. (2001). Understanding e-governance for development.
- Heeks, R., Roberts, J., & others. (2003). Making ICTs work for healthcare: The potential for two-way learning between the UK & developing countries. British Journal of Healthcare Computing and Information Management, 20.
- Kyj, M.J. (2006). Internet use in Ukraine{\textquotesingle}s Orange Revolution. Business Horizons, 49(1), 71–80.
- Lincoln, Y.S., & Guba, E.G. (1985). Establishing trustworthiness. Naturalistic Inquiry, 289(331), 289–327.
- Mimicopoulos, M.G. (2006). Department of economic & social affairs. United Nations, Presentation to the United Nations World Tourism Organization Knowledge Management International Seminar on Global Issues in Local Government: Tourism Policy Approaches, Madrid.
- Sachdeva, S. (2002). e-Governance strategy in India. White Paper on E-Governance Strategy in India.
- Scott, C. (2000). Accountability in the regulatory state. Journal of Law and Society, 27(1), 38–60.
- Shabbir, M.S., Siddiqi, A.F., Yapanto, L.M., Tonkov, E.E., Poltarykhin, A.L., Pilyugina, A.V., Petrov, A.M., Foroughi, A., & Valiullina, D.A. (2021). Closed-loop supply chain design and pricing in competitive conditions by considering the variable value of return products using the whale optimization algorithm. Sustainability, 13(12), 6663.
- Shabbir, M.S., Mahmood, A., Setiawan, R., Nasirin, C., Rusdiyanto, R., Gazali, G., Arshad, M.A., Khan, S., & Batool, F. (2021). Closed-loop supply chain network design with sustainability & resiliency criteria. Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
- Shabbir, M.S., Abbas, M., & Tahir, M.S. (2020). HPWS and knowledge sharing behavior: The role of psychological empowerment and organizational identification in public sector banks. Journal of Public Affairs.
- Shabbir, M.S., Bait Ali Sulaiman, M.A., Hasan Al-Kumaim, N., Mahmood, A., & Abbas, M. (2020). Green Marketing Approaches and Their Impact on Consumer Behavior towards the Environment-A Study from the UAE. Sustainability, 12(21), 8977.
- Siddiqi, A.F., Shabbir, M.S., Abbas, M., Mahmood, A., & Salman, R. (2021). Developing and testing student engagement scale for higher educational students. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education, ahead-of-print (ahead-of-print).
- Trucano, M., Farrell, G., & Isaacs, S. (2007). Survey of ICT & Education in Africa: A summary report based on 53 Country Surveys.