Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 1
Formation of Strategic Change Management System at an Enterprise
Henryk Dzwigol, Silesian University of Technology, Poland
Serhii Shcherbak, Poltava University of Economics and Trade
Marina Semikina, Central Ukrainian National Technical University
Olena Vinichenko, Ukrainian State University of Chemical Technology
Viktoriia Vasiuta, National University «Yuri Kondratyuk Poltava Polytechnic»
Abstract
The conducted research of leadership potential and its scaling at enterprises proves that leadership is required by every subsystem of strategic management of the enterprise. Correlation-regression analysis of the relationship of elements of leadership potential and components of change potentials demonstrated that the greatest mutual effects are observed between leadership potential, human resources, management, innovation subsystems for managers, and personnel and operational subsystems for experts. The conducted studies prove that the leadership potential for each enterprise has its own individual influences. The peculiarities of staffing and constituents of change potential are very influential. The research of the impact of managers’ leadership potential on change potentials states that the key components are in almost all enterprises: personality psycho type and value orientations. Therefore, it is advisable to conclude that leadership potential cannot ensure a lasting status of change potential. For each stage of the life cycle of the activity, both a certain level of potential for change will be inherent and the level of leadership potential will require managerial decisions and influences.
Keywords
Leadership, Strategic Change Management, Human Potential, Professional Development, Competencies.
JEL Classifications
M5, Q2
Introduction
The contemporary conditions of enterprise management are imposing dramatically new requirements for the management system and achieving effective management. An important factor in improving effectiveness of the activity is the development of human potential, filling it with professionally trained staff, able to get rid of inherited unproductive stereotypes of professional activity in a timely manner and to respond to socially-oriented requirements imposed to specialists in different fields of activity; clearly and qualitatively perform functional duties in the situation of constant changes, inconsistency of regulatory legal support; deeply reflect on their shortcomings and professional values, assessing the effectiveness of their use in the process of management, while paying special attention to continuous professional development. On the other hand, the high dynamics of today's economic space require businesses to develop key competencies such as ability to respond effectively and quickly to change. Formation of the stated competence at the enterprise is possible, if sufficient attention is given to managing changes that involve transformation of the enterprise on the whole, or its individual subsystems from the current to the desired status, which more closely meets the requirements of the environment: the needs of consumers and society on the whole (Rankhumise & Letsoalo, 2019).
At the beginning of the XXI century one of the key factors which influence the success of organizations' activities, is recognized as effective leadership. Today efforts are directed on the development of leadership in many countries, both developed and those seeking to enhance their competitiveness in the international arena. Leadership is developed both in the private and public sectors, and in particular in public services. Leadership is a heart of good democratic governance, modern concept of governance. Leadership is recognized as a powerful factor in improving the managerial capacity and effectiveness of business structures activities at different levels.
Leadership is a response to the modern rhythm of life, constant dynamic changes in all spheres, in particular, increased competition and globalization, international economic integration, market growth in developing countries, greater deregulation and privatization; technological changes (faster and better communication, more information networks uniting more people in the world). Such changes caused both greater risks and more opportunities.
Consequently, change management based on productive leadership as a direction of modern management is the driving force for enterprise development. Development and improvement of effective tools of change management based on the theory of leadership makes it possible not only to increase the adaptability of the enterprise to changes, but also to realize the concept of continuous improvement and development (Kelvin-ILoafu et al., 2019).
The purpose of the paper is to develop theoretical, scientific and methodological and practical bases for the formation of a change management system in industrial enterprises, substantiation of increasing efficiency of change management in the conditions of unstable environment on the basis of optimization of the change management system in the economic activity.
Review of Previous Studies
The current conditions of enterprise management make radically new requirements for the system of change management in terms of ensuring its effectiveness.
It should be kept in mind that none of the studied models of change management is the best and able to adapt to a particular enterprise, because they all take into account the conditions of business organization, explore the external and internal environment and pay little attention to the effectiveness of the social component in management, behavioral features an employee, etc. (Drobyazko et al., 2019 a, b &c).
Currently, enterprises are not paying enough attention to change management, which is constantly occur management syste ring within the economic entities contributing to the need to create an appropriate change m in an industrial enterprise (Jiménez et al., 2017).
The enterprise change management system is mainly associated with the identification of fluctuations in the economic situation of the consumer market due to its positive or negative dynamics, change in consumer needs and preferences, influence of the state on trade processes, and development of effective measures to adapt business entities to existing conditions to prevent stagnation and reduce business activity (Lord et al., 2017).
We do not deny the relevance of these factors during the process of designing change management model. But it should be noted that the changes apply to all aspects of enterprise activity.
Considering the above, the development changes which can occur in industrial enterprises can be roughly divided into partial, local and radical changes (Hilorme et al., 2019; Sokolova et al., 2019).
Partial changes imply individual changes in any area of activity of industrial enterprises (modernization of technological base of production process, improvement of assortment structure, optimization of personnel structure, diversification of financial resources, etc.); (Parker et al., 2017).
Due to the complexity and volatility of the business environment, the number of changes which enterprises need to make is increasing (Mumford et al., 2017). The requirements for the quality changes are also increasing - they need to be implemented faster, more efficiently, have greater reach and depth.
Methodology
The theoretical and methodological basis of the paper was the scientific papers of scientists on the subject. The methodological basis of the research is a system of general scientific and special methods, which allowed us to explore the process of change management on the basis of leadership theory. The study was based on the use of: method of comparison, generalization - to clarify and streamline the conceptual and categorical apparatus of the theory of change management and theories of leadership, analysis of the business structures activity; methods of classification and typology, abstract and logical methods; induction and deduction methods - to build the theoretical foundations for managing change in enterprises in the context of productive leadership; graph analytical method - to give clarity of the material and schematic representation of a number of theoretical and practical provisions of the study.
Results and Discussions
Actualization of leadership as a new management paradigm, the essence of which corresponds to contemporary realities, is determined by the existing social trends, transformation of values and organizational structures and the crisis of the dominant administrative-managerial model of governance.
The current conditions of enterprise management impose radically new requirements for the system of change management in terms of ensuring its effectiveness. Today, it no longer requires the axiom to prove that a key element in the effectiveness of any business is staff.
Staff is a key element of change. Conducted studies of the enterprises changes potential and leadership potential in the framework of the consulting company «3S» activity make it possible to state that the tool of personnel and their management assessment in the era of changes is a leadership potential. As a scientific problem, it is necessary to highlight the need to find out what to understand under the leadership potential and to find out methodological approaches to the assessment integration of the leadership potential to the overall potential of the enterprise.
Testing of methodological developments is carried out on the materials of the partners of the consulting agency “3S” and the enterprises selected as objects of research. It is worth noting that the study of the structure of leadership potential and the study of peculiarities of its formation in the individual enabled to structure it by the main constituent elements integrated into the overall assessment of the potential then. Thus, testing the management staff and specialists of each enterprise made it possible to identify the main three blocks of leadership potential: personality psycho type by 16 classic psycho types; values of orientation (natural level of leadership potential (PLP), result orientation (P), development and improvement (B), independence (C), initiative (I), attachment to traditions (T); potentials of individuals (responsibility (Bi), autonomy (A), will (B), focus on problems solving (EE), ability to cooperate with others (EO).
Grouping and statistical processing of the survey results enabled to obtain generalized values of indicators for enterprises on the whole.
Analyzing the values of a complex leadership potential indicator also requires establishing a range of levels of the integral indicator of the leadership potential. The following ranges were established on the basis of the statistical studies Table 1.
| Table 1 Range of Values of the Integral Indicator of the Level of Leadership Potential | |
| Range of values | Evaluation characteristics of |
| 0.00 - 0.20 | critically low level of leadership potential |
| 0.21-0.36 | critically low level of leadership potential |
| 0.37-0.62 | satisfactory level of leadership potential |
| 0.63-0.79 | strategic level of leadership potential |
| 0.80-1.00 | critically high level of leadership potential |
According to the research and calculations results, the leadership potential varies between low level and strategic one among the research objects (Table 2).
| Table 2 Evaluation Results of Leadership Potential and Potential of the Enterprise | |||
| Enterprise | Categories of staff | Level of leadership potential by staff category | The level of the potential for the enterprise change |
| E1 | Managers | 0.62 | 0.75 |
| Specialists | 0.38 | ||
| E2 | Managers | 0.38 | 0.67 |
| Specialists | 0.28 | ||
| E3 | Managers | 0.45 | 0.56 |
| Specialists | 0.32 | ||
| E4 | Managers | 0.72 | 0.68 |
| Specialists | 0.42 | ||
| E5 | Managers | 0.72 | 0.38 |
| Specialists | 0.52 | ||
An important step in the study of the level of the leadership potential is to establish closeness and direction of the relationship between the indicators of the level of change potential and components of the leadership potential.
At this stage, the scientific interest is the closeness and direction of the relationship between the indicators of the level of enterprise potential and the components of leadership potential implemented through the construction of a multifactor correlation model (method of correlation Pleiades). In order to gain a greater understanding of leadership potential, it is necessary to analyze more detailed the intrinsic characteristics of all components and the degree of interaction within each group.
The purpose of the study is to determine the significance of individual parameters both in the subsystem of the leadership potential research, and in the subsystem of changes potential of the enterprise. Studying the modeling experience, it was decided to use models of longitudinal (panel) data. The research results are presented in the form of multidimensional correlation matrices and graphs - correlation Pleiades based on longitudinal data using the Statgraphics Centurion statistical package (SPSS 22). The value of the correlation coefficient and closeness of relationship are traditionally determined by the “Cheddock Scale”. The correlation coefficient has the following values: 1.00 (functional link); 0.90-0.99 (very strong); 0.70 to 0.89 (strong); 0.50-0.69 (significant); 0.30-0.49 (moderate); 0.10-0.29 (weak); 0.00 (no connection).
Since the study of leadership potential was conducted under the condition of staff division into two categories: staff and specialists, the calculations results are presented in two categories. The following factors are distinguished for evaluating the value orientations of management personnel: the natural level of leadership potential, result-oriented, development and improvement, independence, initiative, and attachment to traditions. The results of descriptive statistics and closeness, direction, significance of correlations are presented in Table 3.
| Table 3 Descriptive Statistics of Managers' Value Orientations | |||
| Name of the factor | Average value of the factor | Limits of factors fluctuations | |
| Lower | Upper | ||
| Natural level of leadership potential | 0.6713 | 0.41041 | 0.93219 |
| Result-oriented | 0.6338 | 0.42276 | 0.84484 |
| Development and improvement | 0.6700 | 0.493 | 0.847 |
| Independence | 0.4425 | 0.2222 | 0.6628 |
| Initiative | 0.5875 | 0.3951 | 0.7799 |
| Attachment to traditions | 0.8375 | 0.41041 | 0.93219 |
The highest average value of the factors of managers' value orientations is “Attachment to traditions”, i.e. this factor is dominant, as its value approaches to 1. A number of factors also have significant impact on value orientations: “Natural level of the leadership potential”, “Development and Improvement” and “Result-oriented”, as the averages of these factors are above the median.
In the next stage, it is advisable to pay attention to the closeness, direction and significance of value orientations and the interaction of factors within the group (Table 4).
| Table 4 Closeness, Direction and Significance of Correlation of Managers' Value Orientations | ||||
| Correlation of factors | Correlation coefficient | p-value | Direction of relationship | Closeness of relationship on the Cheddock scale |
| R → ID | 0.589 | 0.0001 | straight | significant |
| R → I | 0.573 | 0.0001 | straight | significant |
| R → T | -0.547 | 0.0001 | inverse | significant |
| R → IM | -0.329 | 0.0500 | inverse | moderate |
| NLP → R | 0.570 | 0.0001 | straight | significant |
| NLP → ID | 0.381 | 0.0150 | straight | moderate |
| NLP → E | -0.390 | 0.0130 | inverse | moderate |
| ID → I | 0.727 | 0.0001 | straight | strong |
| ID → T | -0.664 | 0.0001 | inverse | significant |
| ID → IM | -0.471 | 0.0040 | inverse | moderate |
| I → T | -0.705 | 0.0001 | inverse | strong |
| I → IM | -0.730 | 0.0001 | inverse | strong |
| T → IM | 0.720 | 0.0001 | straight | strong |
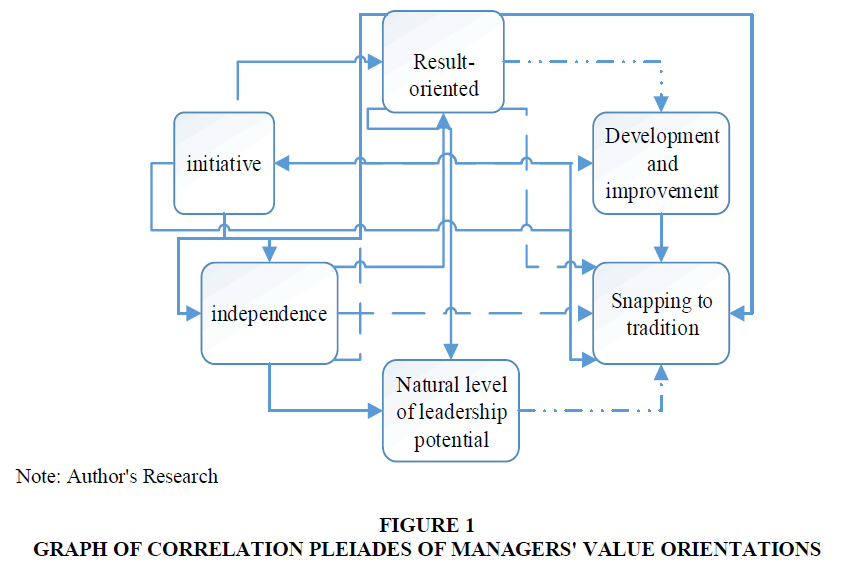
Correlations for management personnel revealed the following features: there are 14 significant, statistically significant relationships between factors; seven relationships have the inverse direction (“Initiative” and “Development and Improvement”; “Result-oriented” and “Attachment to Traditions”; “Development and Improvement” and “Independence”; “Initiative” and “Attachment to traditions”; “Initiative” and “Independence”; “Attachment to traditions” and “Independence”; “Attachment to traditions” and “Natural level of leadership potential”), six factors have a direct dependency; ten pairs of factors have a high and significant closeness of relationships by the Cheddock scale (Figure 1).
Summarizing results we can conclude that the individual elements of the potential interact with each other, forming essential links. Some elements of the enterprise's potential (innovative, environmental and energy potentials) have the low level. However, many of these elements are intangible in nature, so given their strategic nature for the enterprise; it is advisable to consider them as assets.
Recommendations
The study of managerial experience and practice of business activity proves that the level of activity effectiveness depends on the efficiency of the use of managers' professional and personal competencies. Accordingly, activity of the enterprise will be effective when the managers' leadership qualities of different division’s levels are used effectively in management practice.
Therefore, search and research of personal factors are of particular importance. They determine the effectiveness of the activities and features of the managers functioning in the context of changes in the external and internal environment.
Conclusions
In order to ensure the long-term existence and development of an industrial enterprise, it is important to understand the need to compare the trends of change and level of the change potential of an industrial enterprise. The concept of strategic management is based on combination of systemic, integrated and process approaches. It is determined that change management is a continuous process of the enterprise management aimed at maintaining the viability of the company and enhancing its competitive advantages by adapting the enterprise to external changes and maintaining an appropriate level of change potential.
The research results proved that the leadership potential is the effective dominant of the changes effectiveness in the enterprise. Based on the conducted research, the main purpose of assessing the leadership potential of the company is to find, select, form and provide competitive levers which will ensure the use of an effective system of change and vitality of the business structure.
Structuring of the leadership potential of the enterprise was conducted by three subsystems of the leadership potential: personality psycho type by 16 classic psycho types; values of orientation (natural level of leadership potential (NLP), result orientation (R), development and improvement (IM), independence (ID), initiative (I), attachment to traditions (T); potential possibilities of individuals (responsibility (Bi), autonomy (A), will (W), focus on problems solving (PS), ability to cooperate with others (CO).
An important step in the study of the level of the leadership potential is to establish closeness and direction of the relationship between the indicators of the level of change potential and components of the leadership potential. The highest average value of the factors of managers' value orientations is “Attachment to traditions”, i.e. this factor is dominant, as its value approaches to 1. A number of factors also have significant impact on value orientations: “Natural level of the leadership potential”, “Development and Improvement” and “Result-oriented”. The highest average value of the factors of specialists' value orientations is “Development and improvement”, this factor is dominant. Also, Initiative is of average importance. This arrangement of factors fully corresponds to the qualitative characteristics typical for the study group of staff of the lower management personnel.
References
- Drobyazko, S., Bondarevska, O., Klymenko, D., Pletenetska, S., & Pylypenko, O. (2019a). Model for forming of optimal credit portfolio of commercial bank. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 22(4), 501-506.
- Drobyazko, S., Makedon, V., Zhuravlov, D., Buglak, Y., & Stetsenko, V. (2019b). Ethical, technological and patent aspects of technology blockchain distribution. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues.
- Drobyazko, S., Potyshniak, O., Radionova, N., Paranytsia, S., & Nehoda, Y. (2019c). Security of organizational changes via operational integration: ensuring methodology. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues.
- Hilorme, T., Sokolova, L., Portna, O., Lysiak, L., & Boretskaya, N. (2019a). Smart grid concept as a perspective for the development of Ukrainian energy platform.
- Jiménez, P., Winkler, B., & Dunkl, A. (2017). Creating a healthy working environment with leadership: The concept of health-promoting leadership. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28(17), 2430-2448.
- Kelvin-ILoafu, L.E., Adeleke, B.S., Adekitan, R.A., Nwonye, A.J.C., & Ngwu, M.C. (2019). Does emotional intelligence affect attainment of strategic goals of small scale enterprises (sces) in developing economies?. International Journal of Entrepreneurship.
- Lord, R.G., Day, D.V., Zaccaro, S.J., Avolio, B.J., & Eagly, A.H. (2017). Leadership in applied psychology: Three waves of theory and research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(3), 434.
- Mumford, M.D., Todd, E.M., Higgs, C., & McIntosh, T. (2017). Cognitive skills and leadership performance: The nine critical skills. The Leadership Quarterly, 28(1), 24-39.
- Parker, C.F., Karlsson, C., & Hjerpe, M. (2017). Assessing the European Union’s global climate change leadership: From Copenhagen to the Paris agreement. Journal of European Integration, 39(2), 239-252.
- Rankhumise, E.M., & Letsoalo, M.E. (2019). Owners perspective of factors associated with performance of small, medium and micro enterprises. International Journal of Entrepreneurship.
- Sokolova, L.V., Guillermo, T.V., Portna, O.V., Lisyak, L.V., & Boretska, N.P. (2019). The model of the evaluation of renewable energy resources development under conditions of efficient energy consumption.